Korean J Lab Med.
2010 Oct;30(5):451-459. 10.3343/kjlm.2010.30.5.451.
Immature Platelet Fraction: Establishment of a Reference Interval and Diagnostic Measure for Thrombocytopenia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine & Genetics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. heejinkim@skku.edu
- KMID: 1022034
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/kjlm.2010.30.5.451
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
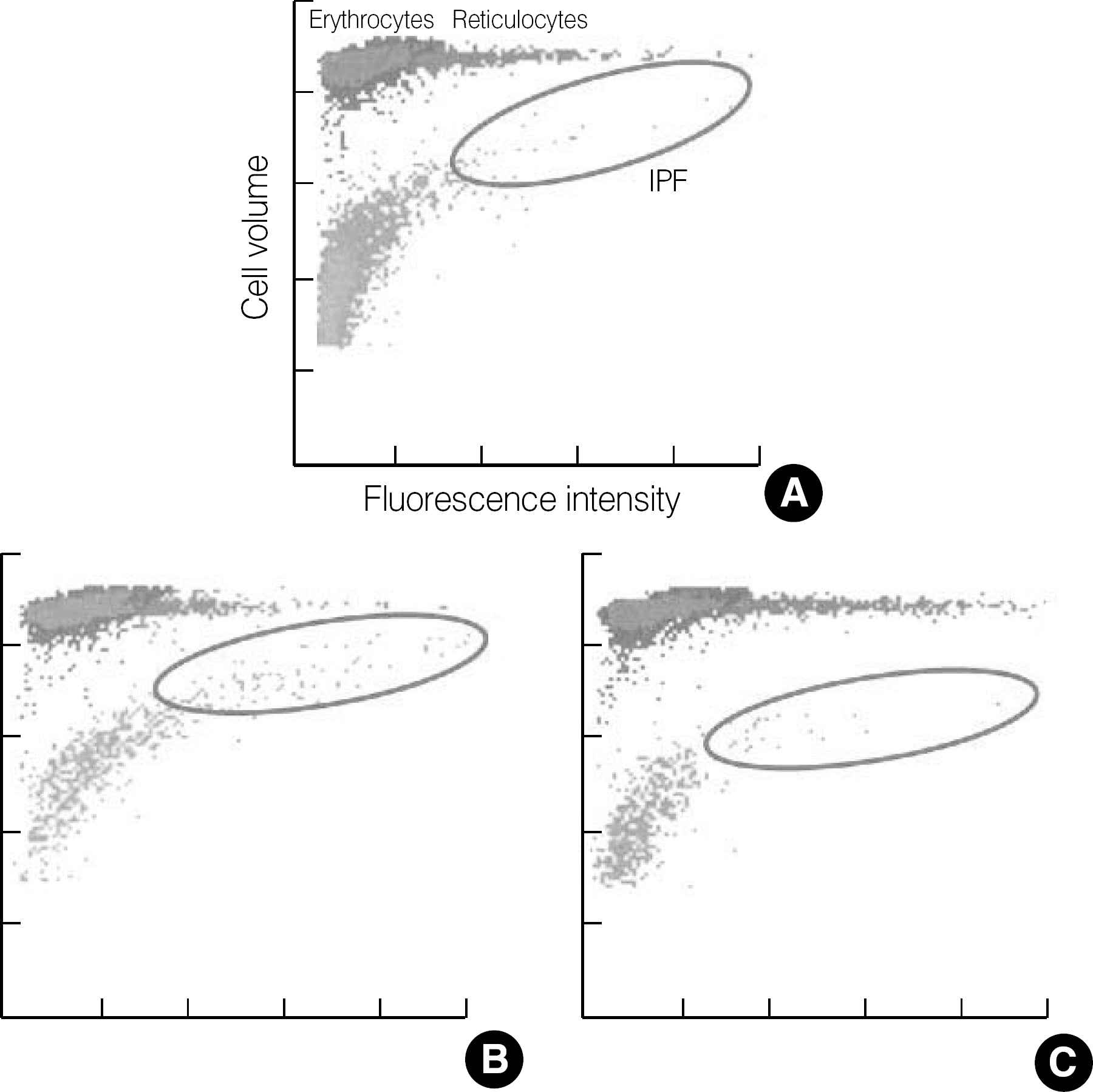
Immature platelet fraction (IPF, %) is a measure of reticulated platelets (RPs), which represents the state of thrombopoiesis. The IPF is obtained from an automated hematology analyzer as one of the platelet parameters. This study was performed to establish reference intervals of IPF and its cut-off values for the differential diagnosis of thrombocytopenia.
METHODS
Blood samples from 2,039 healthy individuals (1,161 males, 878 females) were obtained to establish reference intervals. The patient group included patients with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) (N=150) and aplastic anemia (AA) (N=51) with platelet counts of less than 100x10(9)/L. We evaluated the reliability of the IPF measurements, the reference intervals, and cut-off value for the diagnosis of ITP.
RESULTS
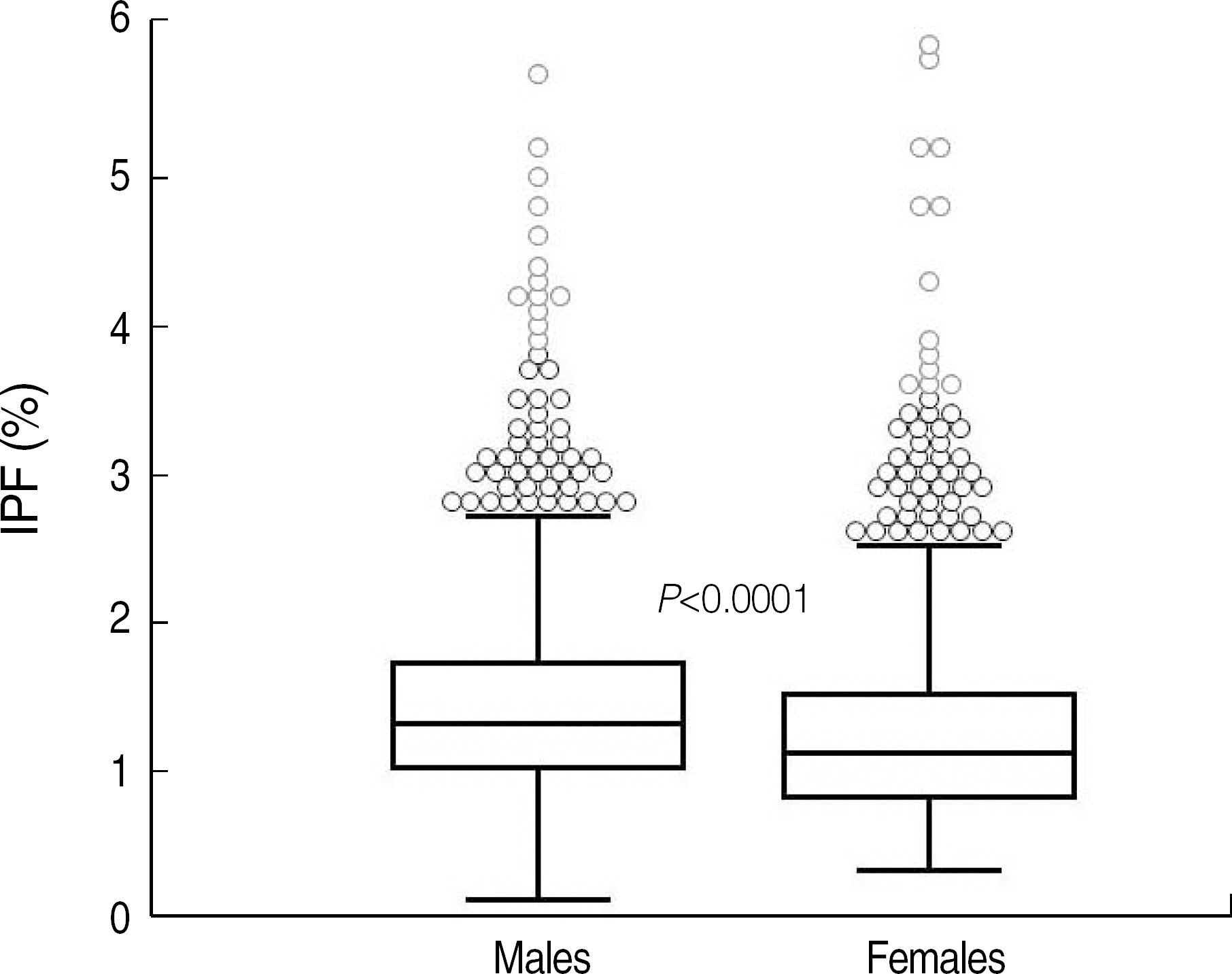
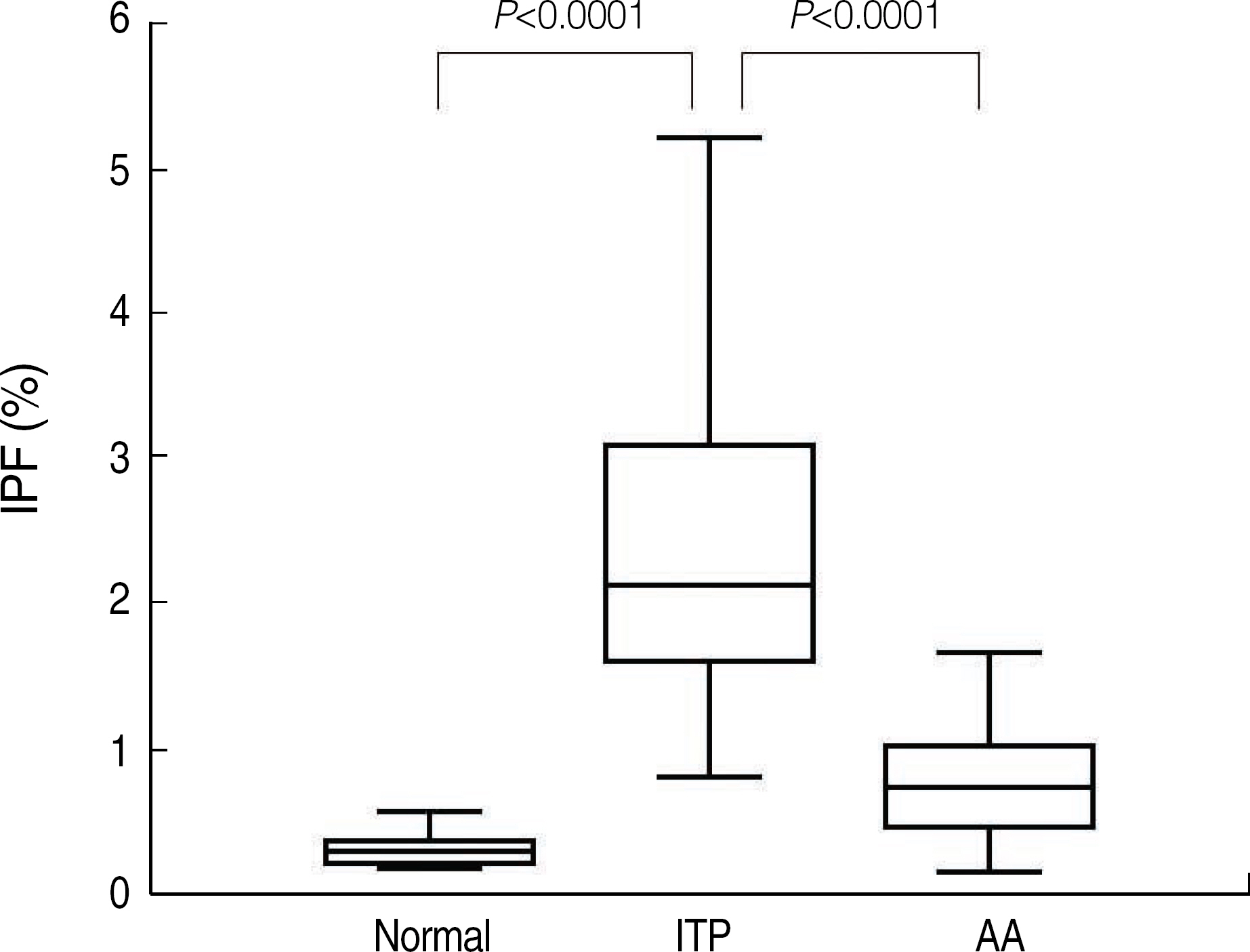
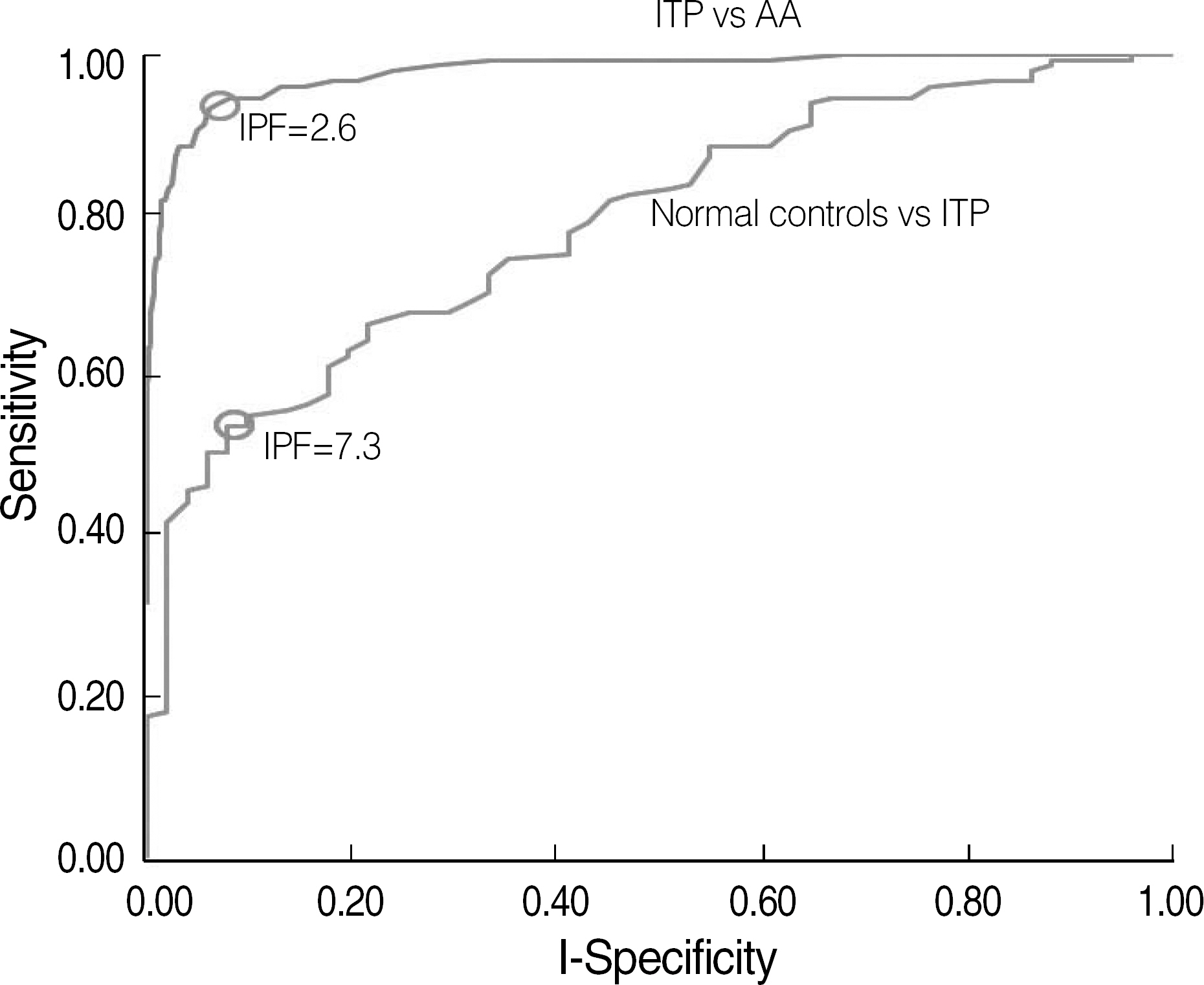
The reference intervals of IPF were 0.5-3.2% in males and 0.4-3.0% in females (95% confidence interval). The median IPF% of ITP and AA were 7.7% (range, 1.0-33.8%) and 3.5% (range, 0.6-12.9%), respectively. Statistical analysis revealed a significant difference between the IPF% of ITP and AA (P<0.0001). The cut-off value of IPF for differentiating ITP from AA was 7.3% with a sensitivity and specificity of 54.0% and 92.2%, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS
A rapid and inexpensive automated measurement of IPF can be integrated as a standard parameter to evaluate the thrombopoietic state of the bone marrow. This study determined the reference intervals of IPF from a large population of healthy individuals, including children. Further studies are needed to establish the clinical utility of IPF.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Erratum : Figure Correction
Hee-Jin Kim
Ann Lab Med. 2012;32(2):169-169. doi: 10.3343/alm.2012.32.2.169.Immature Platelet Fraction in Septic Patients: Clinical Relevance of Immature Platelet Fraction is Limited to the Sensitive and Accurate Discrimination of Septic Patients From Non-Septic Patients, Not to the Discrimination of Sepsis Severity
Sang Hyuk Park, Sang Ook Ha, Young-Uk Cho, Chan-Jeoung Park, Seongsoo Jang, Sang-Bum Hong
Ann Lab Med. 2016;36(1):1-8. doi: 10.3343/alm.2016.36.1.1.
Reference
-
1.Abe Y., Wada H., Tomatsu H., Sakaguchi A., Nishioka J., Yabu Y, et al. A simple technique to determine thrombopoiesis level using immature platelet fraction (IPF). Thromb Res. 2006. 118:463–9.
Article2.Cooper N., Bussel J. The pathogenesis of immune thrombocytopaenic purpura. Br J Haematol. 2006. 133:364–74.
Article3.Diagnosis and treatment of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. American Society of Hematology ITP Practice Guideline Panel. Am Fam Physician. 1996. 54:2437–47. 51-2.4.Jubelirer SJ., Harpold R. The role of the bone marrow examination in the diagnosis of immune thrombocytopenic purpura: case series and literature review. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2002. 8:73–6.
Article5.Ancliff PJ., Machin SJ. Trigger factors for prophylactic platelet transfusion. Blood Rev. 1998. 12:234–8.
Article6.Norfolk DR., Ancliffe PJ., Contreras M., Hunt BJ., Machin SJ., Murphy WG, et al. Consensus Conference on Platelet Transfusion, Royal College of Physicians of Edinburgh, 27-28 November 1997. Synopsis of background papers. Br J Haematol. 1998. 101:609–17.
Article7.Buttarello M., Plebani M. Automated blood cell counts: state of the art. Am J Clin Pathol. 2008. 130:104–16.8.Ingram M., Coopersmith A. Reticulated platelets following acute blood loss. Br J Haematol. 1969. 17:225–9.
Article9.Briggs C., Kunka S., Hart D., Oguni S., Machin SJ. Assessment of an immature platelet fraction (IPF) in peripheral thrombocytopenia. Br J Haematol. 2004. 126:93–9.
Article10.Takubo T., Yamane T., Hino M., Tsuda I., Tatsumi N. Usefulness of determining reticulated and large platelets in idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Acta Haematol. 1998. 99:109–10.
Article11.Kienast J., Schmitz G. Flow cytometric analysis of thiazole orange uptake by platelets: a diagnostic aid in the evaluation of thrombocytopenic disorders. Blood. 1990. 75:116–21.
Article12.Robinson MS., Mackie IJ., Khair K., Liesner R., Goodall AH., Savidge GF, et al. Flow cytometric analysis of reticulated platelets: evidence for a large proportion of non-specific labelling of dense granules by fluorescent dyes. Br J Haematol. 1998. 100:351–7.
Article13.Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. How to define and determine reference intervals in the clinical laboratory: approved guideline. CLSI document C28-A2. 2nd ed.Wayne, PA: CLSI;2008.14.de Vries RA., de Bruin M., Marx JJ., Van de Wiel A. Radioisotopic labels for blood cell survival studies: a review. Nucl Med Biol. 1993. 20:809–17.
Article15.Steinberg MH., Kelton JG., Coller BS. Plasma glycocalicin. An aid in the classification of thrombocytopenic disorders. N Engl J Med. 1987. 317:1037–42.16.Porcelijn L., Folman CC., Bossers B., Huiskes E., Overbeeke MA., v d Schoot CE, et al. The diagnostic value of thrombopoietin level measurements in thrombocytopenia. Thromb Haemost. 1998. 79:1101–5.
Article17.Danpure HJ., Osman S., Brady F. The labelling of blood cells in plasma with 111In-tropolonate. Br J Radiol. 1982. 55:247–9.18.Hayashi S., Oshida M., Kiyoi T., Tadokoro S., Kashiwagi H., Honda S, et al. Comparison of reticulated platelet count with plasma glycocalicin concentration as a marker of platelet turnover in patients with thrombocytopenic disorders. Rinsho Ketsueki. 2000. 41:705–11.19.Steffan A., Pradella P., Cordiano I., Girolami A., De Marco L., Fabris F. Glycocalicin in the diagnosis and management of immune thrombocytopenia. Eur J Haematol. 1998. 61:77–83.
Article20.Harrison P. Reticulated platelet taskforce report. Lab Hematol. 2003. 9:91.21.Rinder HM., Munz UJ., Ault KA., Bonan JL., Smith BR. Reticulated platelets in the evaluation of thrombopoietic disorders. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1993. 117:606–10.22.Albanyan A., Murphy MF., Wilcock M., Harrison P. Changes in the immature platelet fraction within ageing platelet concentrates. J Thromb Haemost. 2008. 6:2213–5.
Article23.Briggs C., Hart D., Kunka S., Oguni S., Machin SJ. Immature platelet fraction measurement: a future guide to platelet transfusion requirement after haematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Transfus Med. 2006. 16:101–9.
Article24.Cesari F., Marcucci R., Caporale R., Paniccia R., Romano E., Gensini GF, et al. Relationship between high platelet turnover and platelet function in high-risk patients with coronary artery disease on dual antiplatelet therapy. Thromb Haemost. 2008. 99:930–5.
Article25.Zucker ML., Murphy CA., Rachel JM., Martinez GA., Abhyankar S., McGuirk JP, et al. Immature platelet fraction as a predictor of platelet recovery following hematopoietic progenitor cell transplantation. Lab Hematol. 2006. 12:125–30.
Article26.Sugimori N., Kondo Y., Shibayama M., Omote M., Takami A., Sugimori C, et al. Aberrant increase in the immature platelet fraction in patients with myelodysplastic syndrome: a marker of karyotypic abnormalities associated with poor prognosis. Eur J Haematol. 2009. 82:54–60.
Article27.Takami A., Shibayama M., Orito M., Omote M., Okumura H., Yamashita T, et al. Immature platelet fraction for prediction of platelet engraftment after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2007. 39:501–7.
Article28.Kim HR., Park BR., Lee MK., Park AJ., Ahn JY. Comparison of an immature platelet fraction and reticulated platelet in liver cirrhosis. Korean J Lab Med. 2007. 27:7–12.
Article29.Cho YG., Lee JH., Kim DS., Lee HS., Choi SI. Clinical usefulness of the simple technique to diagnose thrombocytopenia using immature platelet fraction. Korean J Lab Med. 2007. 27:1–6.
Article30.Saigo K., Sakota Y., Masuda Y., Matsunaga K., Takenokuchi M., Nishimura K, et al. Automatic detection of immature platelets for decision making regarding platelet transfusion indications for pediatric patients. Transfus Apher Sci. 2008. 38:127–32.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Usefulness of the Simple Technique to Diagnose Thrombocytopenia Using Immature Platelet Fraction
- Immature platelet fraction based diagnostic predictive scoring model for immune thrombocytopenia
- Neonatal Thrombocytopenia: Diagnostic Approach and Platelet Transfusion Guideline
- Comparison of an Immature Platelet Fraction and Reticulated Platelet in Liver Cirrhosis
- Diagnostic workup of inherited platelet disorders