Investig Magn Reson Imaging.
2019 Dec;23(4):341-350. 10.13104/imri.2019.23.4.341.
Parameters Affecting India Ink Artifacts on Opposed-Phase MR Images
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Dong-A University Medical Center, Busan, Korea. hdhdoc@dau.ac.kr
- KMID: 2468051
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2019.23.4.341
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To determine the MR parameters affecting India ink artifacts on opposed-phase chemical shift magnetic resonance (MR) imaging.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
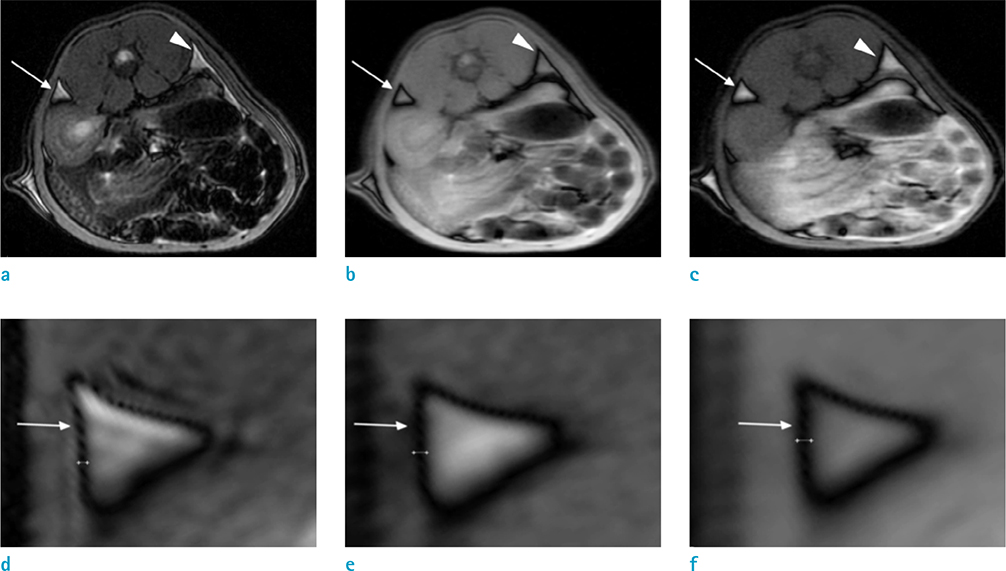
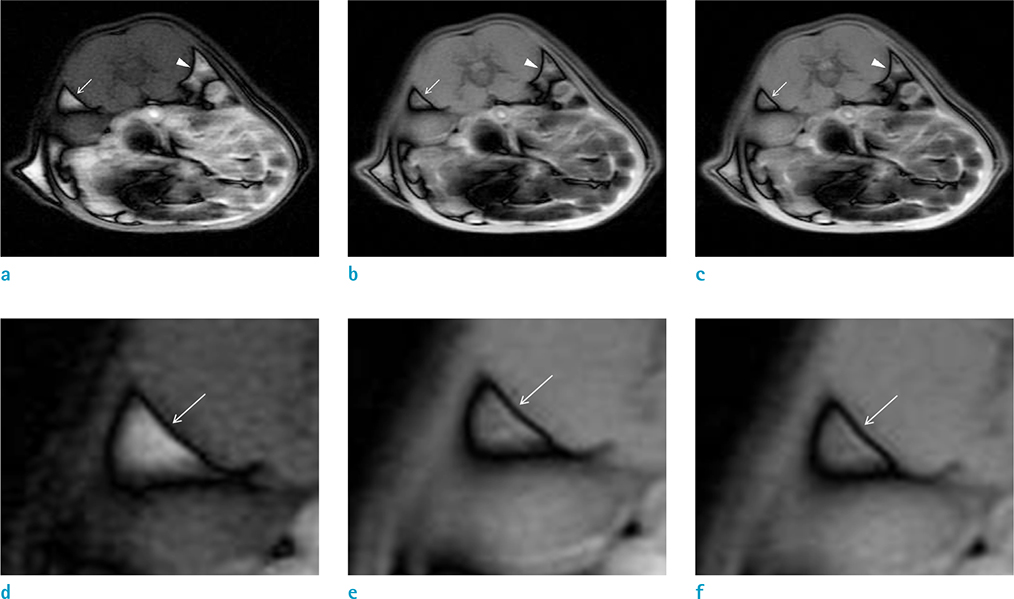
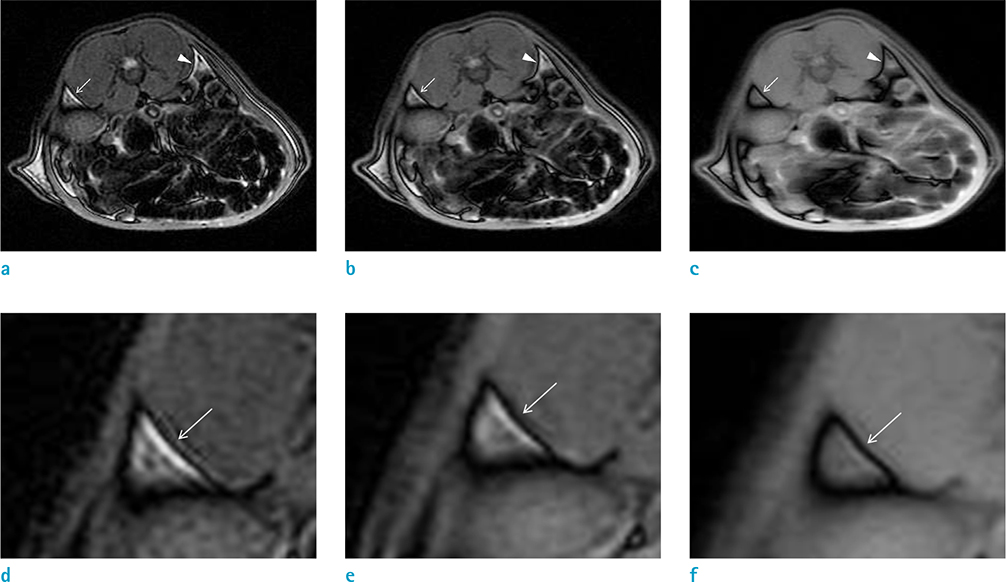
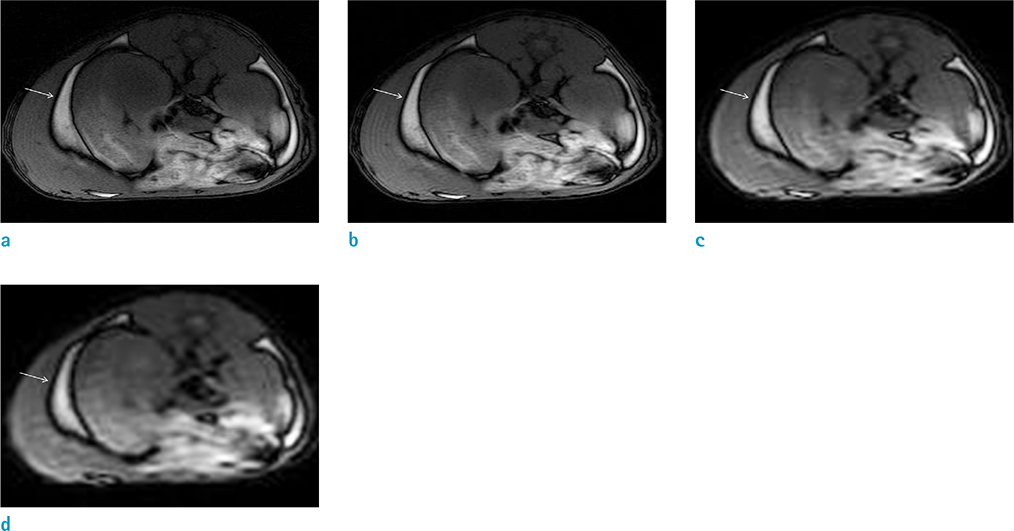
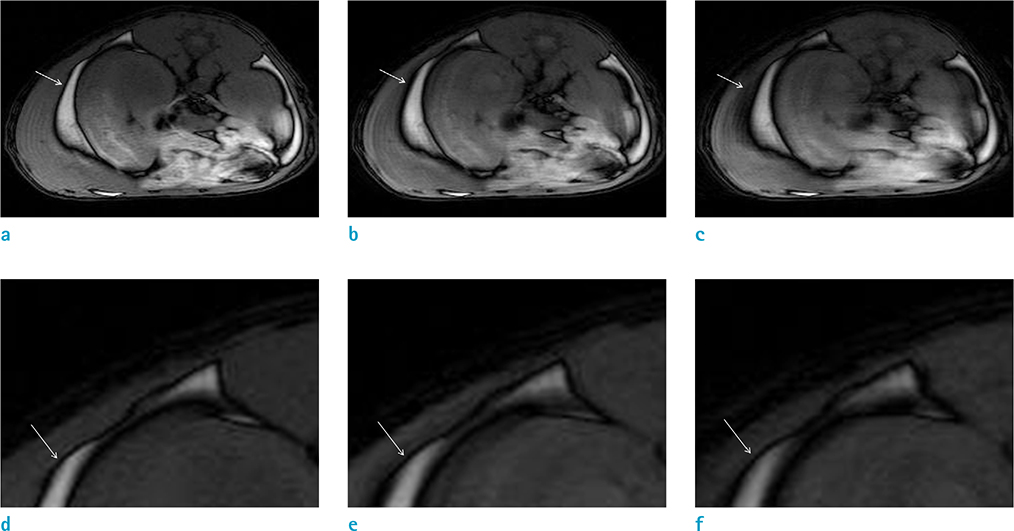
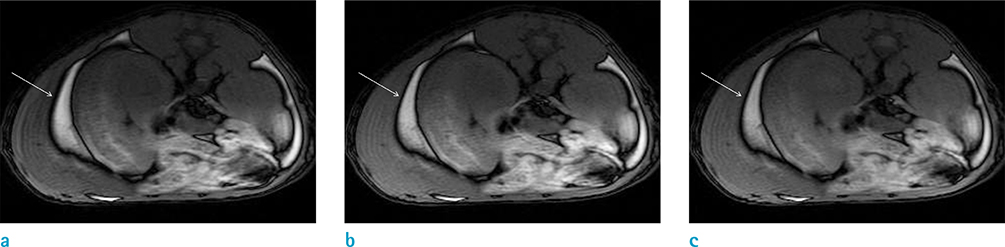
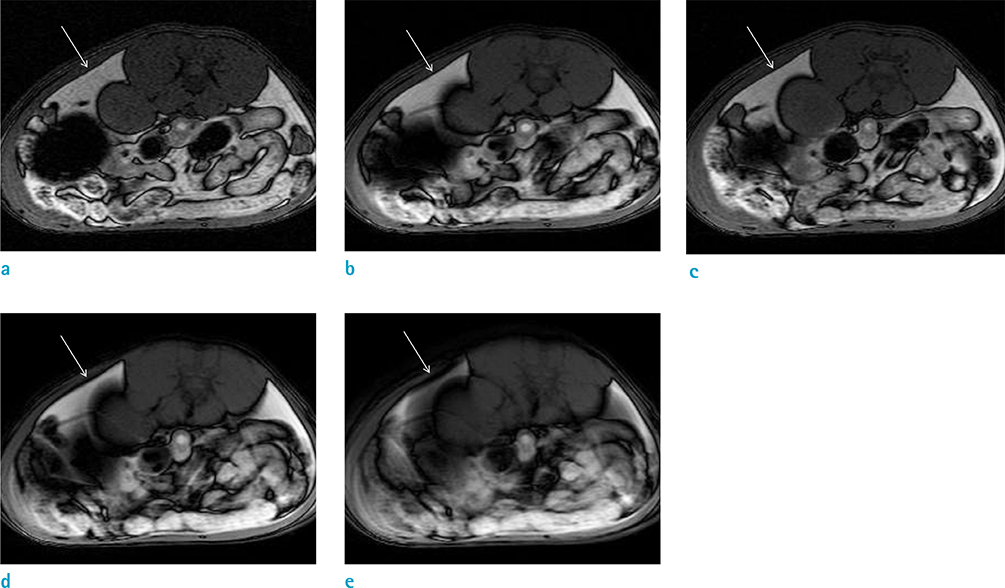
The use of a female Sprague-Dawley rat was approved by our Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee. Using an iterative decomposition of water and fat with echo asymmetry and least-squares estimation (IDEAL) images, which is a modified Dixon method, axial opposed-phase images of the abdominal cavity were obtained with different MR parameters: series 1, different repetition times (TRs; 400, 2000, and 4000 ms); series 2, different echo times (TEs; 10, 50, and 100 ms); series 3, different field of views (FOVs; 6, 8, 16, and 24 cm); series 4, different echo train lengths (ETLs; 2, 4, and 8); series 5, different bandwidths (25, 50, and 85); and series 6, different slice thicknesses (1, 2, 4, 8, and 16 mm). Artifacts on opposed images obtained with different parameters were compared subjectively by two radiologists. For objective analysis, the thickness of the artifact was measured. Spearman's correlation between altered MR parameters and thicknesses of India ink artifact was obtained via objective analysis.
RESULTS
India ink artifact was increasingly apparent using shorter TE, larger FOV and ETL, and thicker slices upon subjective analysis. The objective analysis revealed a strong negative correlation between the thickness of the artifact and TE (r = -0.870, P < 0.01); however, strong positive correlations were found between FOV (r = 0.854, P < 0.01) and slice thickness (r = 0.971, P < 0.01).
CONCLUSION
India ink artifact was thicker with shorter TE, larger FOV, and larger slice thickness.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Delfaut EM, Beltran J, Johnson G, Rousseau J, Marchandise X, Cotten A. Fat suppression in MR imaging: techniques and pitfalls. Radiographics. 1999; 19:373–382.2. Pokharel SS, Macura KJ, Kamel IR, Zaheer A. Current MR imaging lipid detection techniques for diagnosis of lesions in the abdomen and pelvis. Radiographics. 2013; 33:681–702.3. Adam SZ, Nikolaidis P, Horowitz JM, et al. Chemical shift MR imaging of the adrenal gland: principles, pitfalls, and applications. Radiographics. 2016; 36:414–432.4. Brandao S, Seixas D, Ayres-Basto M, et al. Comparing T1-weighted and T2-weighted three-point Dixon technique with conventional T1-weighted fat-saturation and shorttau inversion recovery (STIR) techniques for the study of the lumbar spine in a short-bore MRI machine. Clin Radiol. 2013; 68:e617–e623.5. Low RN, Ma J, Panchal N. Fast spin-echo triple-echo Dixon: initial clinical experience with a novel pulse sequence for fat-suppressed T2-weighted abdominal MR imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2009; 30:569–577.6. Le-Petross H, Kundra V, Szklaruk J, Wei W, Hortobagyi GN, Ma J. Fast three-dimensional dual echo dixon technique improves fat suppression in breast MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2010; 31:889–894.7. Gerdes CM, Kijowski R, Reeder SB. IDEAL imaging of the musculoskeletal system: robust water fat separation for uniform fat suppression, marrow evaluation, and cartilage imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007; 189:W284–W291.8. Babcock EE, Brateman L, Weinreb JC, Horner SD, Nunnally RL. Edge artifacts in MR images: chemical shift effect. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1985; 9:252–257.9. Hood MN, Ho VB, Smirniotopoulos JG, Szumowski J. Chemical shift: the artifact and clinical tool revisited. Radiographics. 1999; 19:357–371.10. Bolster F, Lawler L, Geoghegan T. Loss of renal India ink artifact-a useful radiological sign for obstructive hydronephrosis in pregnancy. Clin Imaging. 2015; 39:717–719.11. Israel GM, Hindman N, Hecht E, Krinsky G. The use of opposed-phase chemical shift MRI in the diagnosis of renal angiomyolipomas. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2005; 184:1868–1872.12. Kemmling A, Noelte I, Gerigk L, Singer S, Groden C, Scharf J. A diagnostic pitfall for intracranial aneurysms in time-offlight MR angiography: small intracranial lipomas. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008; 190:W62–W67.13. Aquaro GD, Todiere G, Strata E, Barison A, Di Bella G, Lombardi M. Usefulness of India ink artifact in steadystate free precession pulse sequences for detection and quantification of intramyocardial fat. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2014; 40:126–132.14. Park EH, Lee KB. Usefulness of black boundary artifact on opposed-phase imaging from turbo spin-echo twopoint mDixon MRI for delineation of an arthroscopically confirmed small fracture of the lateral talar dome: a case report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017; 96:e949.15. Gokalp G, Topal U, Bolca N, Ercan I. Chemical shift MRI: is there any contribution to morphologic evaluation of solid breast masses? Acad Radiol. 2009; 16:1263–1271.16. Schieda N, Al Dandan O, Kielar AZ, Flood TA, McInnes MD, Siegelman ES. Pitfalls of adrenal imaging with chemical shift MRI. Clin Radiol. 2014; 69:1186–1197.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Focal Sparing in Fatty Liver: Mimicking Hypervascular Tumor on Gadolinium-Enhanced Opposed-Phase Gradient-Echo Images
- Artifacts in MR Angiography of the Intracranial Vessels Using the 3D TOF and 3D PC Techniques
- MR imaging of metallic artifacts
- Artifacts in MR imaging caused by air and fat: an experimental study
- Hepatic Enhancement on Gd-BOPTA-enhanced MR Imaging: Comparison between Cirrhotic and Normal Livers