J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2013 Feb;53(2):72-76. 10.3340/jkns.2013.53.2.72.
Dysregulated Expression Profiles of MicroRNAs of Experimentally Induced Cerebral Aneurysms in Rats
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Daejeon St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Daejeon, Korea. yangjiho1963@gmail.com
- 2Clinical Research Institute, Daejeon St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Daejeon, Korea.
- KMID: 2190681
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2013.53.2.72
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
Cerebral aneurysm (CA) is an important acquired cerebrovascular disease that can cause catastrophic results. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small non-coding RNAs, playing essential roles in modulating basic physiologic and pathological processes. Currently, evidences have been established about biologic relationship between miRNAs and abdominal aortic aneurysms. However, biologic roles of miRNAs in CA formation have not been explained yet. We employed microarray analysis to detect and compare miRNA expression profiles in late stage of CA in rat model.
METHODS
Twenty-six, 7-week-old male Sprague-Dawley rats underwent a CA induction procedure. The control animals (n=11) were fed a normal diet, and the experimental animals (n=26) were fed a normal diet with 1% normal saline for 3 months. Then, the rats were sacrificed, their cerebral arteries were dissected, and the five regions of aneurysmal dilation on the left posterior communicating artery were cut for miRNA microarrays analysis. Six miRNAs (miRNA-1, miRNA-223, miRNA-24-1-5p, miRNA-551b, miRNA-433, and miRNA-489) were randomly chosen for validation using real-time quantitative PCR.
RESULTS
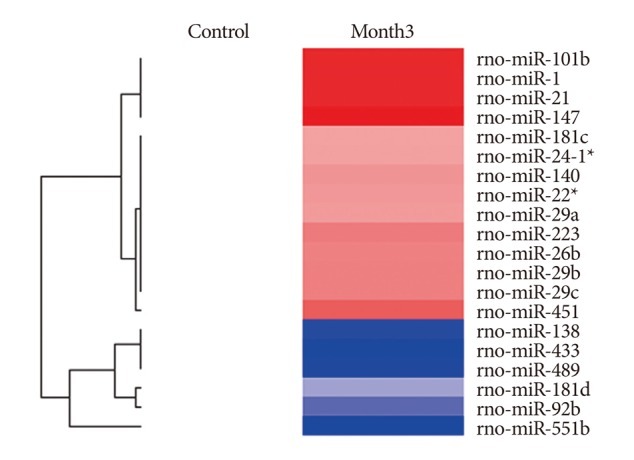
Among a set of differentially expressed miRNAs, 14 miRNAs were over-expressed more than 200% and 6 miRNAs were down-expressed lower than 50% in the CA tissues.
CONCLUSION
The results show that miRNAs might take part in CA formation probably by affecting multiple target genes and signaling pathways. Further investigations to identify the exact roles of these miRNAs in CA formation are required.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Identification of MicroRNAs with Altered Expression Profiles in a Rat Model of Experimentally Induced Early Cerebral Aneurysms
Seung-Hwa Jeong, Hyung-Jin Lee, Jin-Seok Yi, Hong-Jae Lee, Il-Woo Lee, Ki-Cheol Park, Ji-Ho Yang
Korean J Neurotrauma. 2013;9(2):41-46. doi: 10.13004/kjnt.2013.9.2.41.
Reference
-
1. Aoki T, Kataoka H, Moriwaki T, Nozaki K, Hashimoto N. Role of TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 in the progression of cerebral aneurysms. Stroke. 2007; 38:2337–2345. PMID: 17569872.
Article2. Aoki T, Moriwaki T, Takagi Y, Kataoka H, Yang J, Nozaki K, et al. The efficacy of apolipoprotein E deficiency in cerebral aneurysm formation. Int J Mol Med. 2008; 21:453–459. PMID: 18360691.
Article3. Bartel DP. MicroRNAs : genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004; 116:281–297. PMID: 14744438.4. Chan MC, Hilyard AC, Wu C, Davis BN, Hill NS, Lal A, et al. Molecular basis for antagonism between PDGF and the TGFbeta family of signalling pathways by control of miR-24 expression. EMBO J. 2010; 29:559–573. PMID: 20019669.
Article5. Cheung TH, Quach NL, Charville GW, Liu L, Park L, Edalati A, et al. Maintenance of muscle stem-cell quiescence by microRNA-489. Nature. 2012; 482:524–528. PMID: 22358842.
Article6. Choi YM, Yi JS, Lee HJ, Yang JH, Lee IW. Apolipoprotein E expression in experimentally induced intracranial aneurysms of rats. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2006; 39:46–51.7. Garzon R, Heaphy CE, Havelange V, Fabbri M, Volinia S, Tsao T, et al. MicroRNA 29b functions in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2009; 114:5331–5341. PMID: 19850741.
Article8. Guo F, Li Z, Song L, Han T, Feng Q, Guo Y, et al. Increased apoptosis and cysteinyl aspartate specific protease-3 gene expression in human intracranial aneurysm. J Clin Neurosci. 2007; 14:550–555. PMID: 17430778.
Article9. Gurha P, Abreu-Goodger C, Wang T, Ramirez MO, Drumond AL, van Dongen S, et al. Targeted deletion of microRNA-22 promotes stress-induced cardiac dilation and contractile dysfunction. Circulation. 2012; 125:2751–2761. PMID: 22570371.
Article10. Johnnidis JB, Harris MH, Wheeler RT, Stehling-Sun S, Lam MH, Kirak O, et al. Regulation of progenitor cell proliferation and granulocyte function by microRNA-223. Nature. 2008; 451:1125–1129. PMID: 18278031.
Article11. Kanematsu Y, Kanematsu M, Kurihara C, Tada Y, Tsou TL, van Rooijen N, et al. Critical roles of macrophages in the formation of intracranial aneurysm. Stroke. 2011; 42:173–178. PMID: 21106959.
Article12. Liu G, Huang Y, Lu X, Lu M, Huang X, Li W, et al. Identification and characteristics of microRNAs with altered expression patterns in a rat model of abdominal aortic aneurysms. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2010; 222:187–193. PMID: 21030819.
Article13. Maegdefessel L, Azuma J, Toh R, Deng A, Merk DR, Raiesdana A, et al. MicroRNA-21 blocks abdominal aortic aneurysm development and nicotine-augmented expansion. Sci Transl Med. 2012; 4:122ra22.
Article14. Mishra PK, Metreveli N, Tyagi SC. MMP-9 gene ablation and TIMP-4 mitigate PAR-1-mediated cardiomyocyte dysfunction : a plausible role of dicer and miRNA. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2010; 57:67–76. PMID: 20422465.
Article15. Park SH, Yim MB, Lee CY, Kim E, Son EI. Intracranial fusiform aneurysms : it's pathogenesis, clinical characteristics and managements. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2008; 44:116–123. PMID: 19096660.
Article16. Wang XF, Shi ZM, Wang XR, Cao L, Wang YY, Zhang JX, et al. MiR-181d acts as a tumor suppressor in glioma by targeting K-ras and Bcl-2. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2012; 138:573–584. PMID: 22207524.
Article17. Zhuang G, Meng C, Guo X, Cheruku PS, Shi L, Xu H, et al. A novel regulator of macrophage activation : miR-223 in obesity-associated adipose tissue inflammation. Circulation. 2012; 125:2892–2903. PMID: 22580331.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Identification of MicroRNAs with Altered Expression Profiles in a Rat Model of Experimentally Induced Early Cerebral Aneurysms
- Apolipoprotein E Expression in Experimentally Induced Intracranial Aneurysms of RatsIntroduction
- Dysregulated MicroRNA Expression in Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- Regulation of Colonic Mucosal MicroRNA Expression via Multiple Targets in Visceral Hypersensitivity Rats by Tongxieyaofang
- Superior Temporal Gyrus Approach to Middle Cerebral Artery Aneurysms