J Korean Acad Nurs.
2013 Jun;43(3):361-369. 10.4040/jkan.2013.43.3.361.
Effect of Anorexia and Neuropathic Pain Induced by Cisplatin on Hindlimb Muscles of Rat
- Affiliations
-
- 1School of Nursing, University of Maryland, Baltimore, MD, U.S.A. gsyang@umaryland.edu
- 2College of Nursing, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 1707126
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2013.43.3.361
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to examine the effect of anorexia and neuropathic pain induced by cisplatin on hindlimb muscles of rats.
METHODS
Adult male Sprague-Dawley rats were divided into two groups, a cisplatin-treated group (n=10) and a control group (n=10). In the cisplatin-treated group, cisplatin at a dose of 2 mg/kg was injected intraperitoneally two times a week up to a cumulative dose of 20 mg/kg over 5 weeks, and in the control group saline (0.9% NaCl) was injected intraperitoneally at the same dose and duration as the cisplatin-treated group. At 34 days all rats were anesthetized, after which the soleus and plantaris muscles were dissected. Withdrawal threshold, body weight, food intake, activity, muscle weight, Type I and II fiber cross-sectional areas and myofibrillar protein content of the dissected muscles were determined.
RESULTS
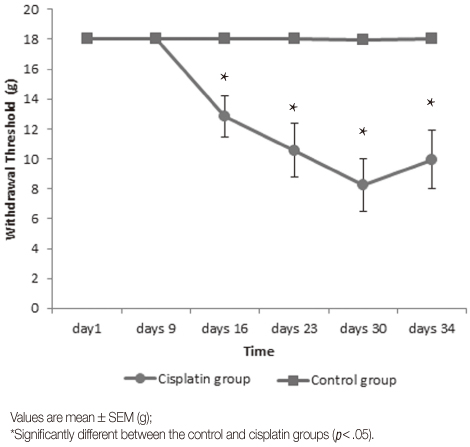
Compared with the control group, the cisplatin-treated group showed significant decreases (p<.05) in withdrawal threshold, activity, food intake, body weight, Type I and II fiber cross-sectional areas, myofibrillar protein content and weight of the soleus and plantaris muscles.
CONCLUSION
Muscular atrophy in hindlimb occurs due to anorexia and neuropathic pain induced by the cisplatin treatment.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
*Anorexia
Body Weight
Cisplatin/*toxicity
Eating
Hindlimb
Injections, Intraperitoneal
Male
Motor Activity
Muscle Fibers, Skeletal/metabolism/pathology
Muscle Proteins/metabolism
Muscle, Skeletal/*drug effects/physiology
Neuralgia/*chemically induced/pathology
Rats
Rats, Sprague-Dawley
Cisplatin
Muscle Proteins
Figure
Reference
-
1. Adachi J, Kudo R, Asano M, Ueno Y, Hunter R, Rajendram R, et al. Skeletal muscle and liver oxysterols during fasting and alcohol exposure. Metabolism. 2006; 55(1):119–127. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2005.08.003.2. Ahn DW, Kim SR, Ha DH, Kim SH. Mechanism of amelioration of cisplatin nephrotoxicity by procaine treatment in mice. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2007; 52(3):318–327. http://dx.doi.org/10.4097/kjae.2007.52.3.318.3. Almurshed K, Grunewald K. The effects of dietary energy restriction on overloaded skeletal muscle in rats. Br J Nutr. 2000; 84(5):697–704.4. Authier N, Gillet JP, Fialip J, Eschalier A, Coudore F. An animal model of nociceptive peripheral neuropathy following repeated cisplatin injections. Exp Neurol. 2003; 182(1):12–20. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0014-4886(03)00003-7.5. Carrieri-Kohlman V, Lindsey AM, West CM, editors. Pathophysiological phenomena in nursing: Human response to illness. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders;2003.6. Choe MA, An GJ. Effects of nitric oxide synthase inhibitor on hindlimb muscles in rats with neuropathic pain induced by unilateral peripheral nerve injury. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2011; 41(4):520–527. http://dx.doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2011.41.4.520.7. Choe MA, Ji JK, Kim EH. Effect of intermittent low-intensity, short duration exercise on Type II muscle of suspended rats. J Nurs Acad Soc. 1995; 25(2):193–209.8. Choe MA, Kim KH, An GJ, Lee KS, Choi JA. Hindlimb muscle atrophy of rat induced by neuropathic pain. J Korean Biol Nurs Sci. 2008; 10(1):88–95.9. Demark-Wahnefried W, Peterson BL, Winer EP, Marks L, Aziz N, Marcom PK, et al. Changes in weight, body composition, and factors influencing energy balance among premenopausal breast cancer patients receiving adjuvant chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2001; 19(9):2381–2389.10. Gandara DR, Perez EA, Phillips WA, Lawrence HJ, DeGregorio M. Evaluation of cisplatin dose intensity: Current status and future prospects. Anticancer Res. 1989; 9(4):1121–1128.11. Holecek M. Effect of starvation on branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase activity in rat heart and skeletal muscle. Physiol Res. 2001; 50(1):19–24.12. Houston ME. Biochemistry primer for exercise science. 2nd ed. Champaign, IL: Human Kinetics;2001.13. Kang YH, editor. Encyclopedia of life science. Seoul: Academybook;2008.14. Kim JY. Effects of short-term undernutrition on type I and II muscles in rat. Seoul: Seoul National University;2005. Unpublished master's thesis.15. Kim TK, Kim YS, Yoon JR, Han IS, Kim JS, Lee CW. The effect of an intraperitoneal injection of ketamine and ketorolac on mechanical allodynia in rats with spinal nerve ligation. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2004; 46(6):719–723.16. Kim YB, Choe MA. Effect of decreased locomotor activity on hindlimb muscles in a rat model of Parkinson's disease. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2010; 40(4):580–588. http://dx.doi.org/10.4040/jkan.2010.40.4.580.17. Kohn DF, Wixson SK, White WJ, Benson GJ. Anesthesia and analgesia in laboratory animals. San Diego, CA: Academic Press;1997.18. Krarup-Hansen A, Helweg-Larsen S, Schmalbruch H, Røth M, Krarup C. Neuronal involvement in cisplatin neuropathy: Prospective clinical and neurophysiological studies. Brain. 2007; 130(Pt 4):1076–1088. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/brain/awl356.19. Lee DH. The clinical neurology II. Seoul: Korea University Press;2003.20. Lieu FK, Powers SK, Herb RA, Criswell D, Martin D, Wood C, et al. Exercise and glucocorticoid-induced diaphragmatic myopathy. J Appl Physiol. 1993; 75(2):763–771.21. McLoughlin DM, Wassif WS, Morton J, Spargo E, Peters TJ, Russell GF. Metabolic abnormalities associated with skeletal myopathy in severe anorexia nervosa. Nutrition. 2000; 16(3):192–196.22. Nicolao P, Giometto B. Neurological toxicity of ifosfamide. Oncology. 2003; 65:Suppl 2. 11–16. http://dx.doi.org/73352.23. Park Y, Kim YH. Chemotherapy related oral and gastrointestinalmucositis. J Korean Med Assoc. 2009; 52(9):897–906. http://dx.doi.org/10.5124/jkma.2009.52.9.897.24. Prado CM, Baracos VE, McCargar LJ, Mourtzakis M, Mulder KE, Reiman T, et al. Body composition as an independent determinant of 5-fluorouracil-based chemotherapy toxicity. Clin Cancer Res. 2007; 13(11):3264–3268. http://dx.doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-06-3067.25. Prado CM, Lieffers JR, McCargar LJ, Reiman T, Sawyer MB, Martin L, et al. Prevalence and clinical implications of sarcopenic obesity in patients with solid tumours of the respiratory and gastrointestinaltracts: A population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2008; 9(7):629–635. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(08)70153-0.26. Sweeney CW. Understanding peripheral neuropathy in patients with cancer: Background and patient assessment. Clin J Oncol Nurs. 2002; 6(3):163–166. http://dx.doi.org/10.1188/02.cjon.163-166.27. Taillandier D, Aurousseau E, Meynial-Denis D, Bechet D, Ferrara M, Cottin P, et al. Coordinate activation of lysosomal, Ca 2±activated and ATP-ubiquitin-dependent proteinases in the unweighted rat soleus muscle. Biochem J. 1996; 316(Pt 1):65–72.28. Vera G, Castillo M, Cabezos PA, Chiarlone A, Martín MI, Gori A, et al. Enteric neuropathy evoked by repeated cisplatin in the rat. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2011; 23(4):370–378. e162–e163. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2982.2011.01674.x.29. Vera G, Chiarlone A, Martn MI, Abalo R. Altered feeding behaviour induced by long-term cisplatin in rats. Auton Neurosci. 2006; 126-127:81–92. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.autneu.2006.02.011.30. Windebank AJ, Grisold W. Chemotherapy-induced neuropathy. J Peripher Nerv Syst. 2008; 13(1):27–46. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1529-8027.2008.00156.x.31. Yakabi K, Sadakane C, Noguchi M, Ohno S, Ro S, Chinen K, et al. Reduced ghrelin secretion in the hypothalamus of rats due to cisplatin-induced anorexia. Endocrinology. 2010; 151(8):3773–3782. http://dx.doi.org/10.1210/en.2010-0061.32. Yang YH. Anorexia, nausea and vomiting, and food intake patterns in patients on chemotherapy. J Korean Acad Fundam Nurs. 2004; 11(2):177–185.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A New Rat Model of Cisplatin-induced Neuropathic Pain
- Effects of Antioxidant on Reduction of Hindlimb Muscle Atrophy Induced by Cisplatin in Rats
- Effects of Exercise on Affected and Unaffected Hindlimb Muscles in Rats with Neuropathic Pain Induced by Unilateral Peripheral Nerve Injury
- Effect of Dehydroepiandrosterone on Affected and Unaffected Hindlimb Muscles in Rats with Neuropathic Pain Induced by Unilateral Peripheral Nerve Injury
- Effects of Nitric Oxide Synthase Inhibitor on Hindlimb Muscles in Rats with Neuropathic Pain Induced by Unilateral Peripheral Nerve Injury