Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2008 Jun;1(2):80-85. 10.3342/ceo.2008.1.2.80.
Apoptotic Pattern of Cochlear Outer Hair Cells and Frequency-specific Hearing Threshold Shift in Noise-exposed BALB/c Mice
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otolaryngology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jwchung@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 1486058
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3342/ceo.2008.1.2.80
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
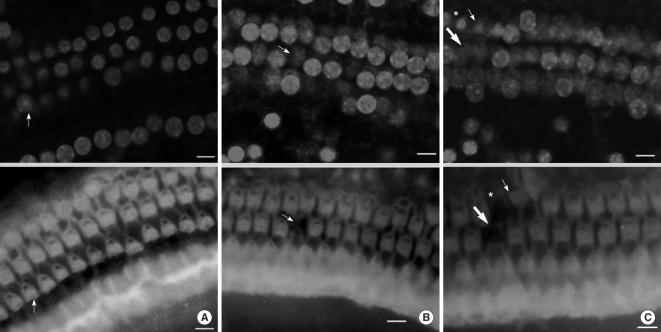
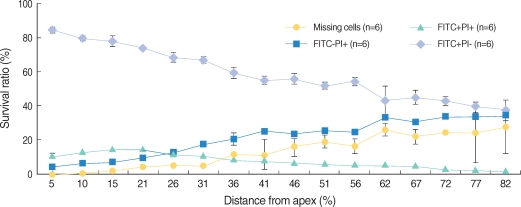
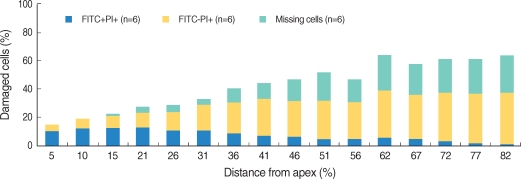
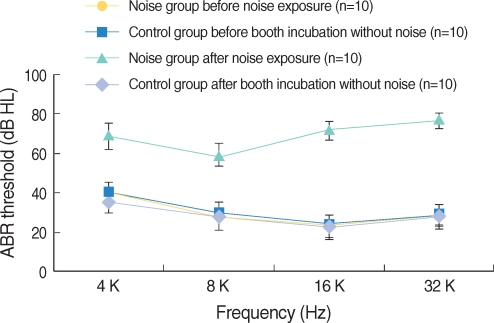
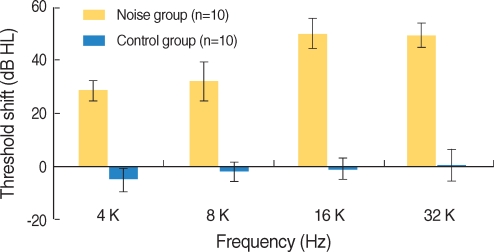
Apoptosis of outer hair cell (OHC) can be identified through nuclear staining by specific nuclear changes. The change of filamentous actin (F-actin) is also involved in early cell death process. The study was designed to investigate OHC death along the whole length of the organ of Corti. METHODS: BALB/c hybrid mice were used in this study. The noise group was exposed to white noise of 120 dB SPL for 3 hr per day for 3 consecutive days. The tone burst auditory brainstem response (ABR) test was conducted and cochleas from each group were obtained for the immunostaining of FITC phalloidin for F-actin and propidium iodide (PI) for nuclei. RESULTS: ABR threshold of the noise group significantly increased after noise exposure (P<0.001). No threshold shift was found in the control group. Threshold shift of the noise group constantly increased from 4 to 16 kHz, but threshold shifts at 16 kHz and 32 kHz were similar. Patterns of OHC staining were subclassified as FITC+PI- cells, FITC+ PI+ cells, FITC-PI+ cells and missing cells. Proportion of normal live OHCs (FITC+PI-) rapidly decreased from the apex to the base. In the basal turn, FITC-PI+ cells and vacancy OHC (missing cells) were observed easily. Apoptotic and missing cells were most abundant at 60% of the whole length of the Corti organ. CONCLUSION: We could subclassify morphologic changes in OHC death after noise exposure. Quantitative changes in OHCs along the whole Corti organ showed a plateau pattern similar to that of a frequency-specific threshold shift.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Expression of Insulin-like Growth Factors in a Mouse Model of Salicylate Ototoxicity
Gi Jung Im, June Choi, Ji Won Chang, Seo Jin Kim, Hye In Kim, Hak Hyun Jung
Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2010;3(3):115-121. doi: 10.3342/ceo.2010.3.3.115.
Reference
-
1. Hamernik RP, Turrentine G, Roberto M, Salvi R, Henderson D. Anatomical correlates of impulse noise-induced mechanical damage in the cochlea. Hear Res. 1984; 3. 13(3):229–247. PMID: 6735931.
Article2. Wyllie AH, Kerr JF, Currie AR. Cell death: the significance of apoptosis. Int Rev Cytol. 1980; 68:251–306. PMID: 7014501.
Article3. Saunders JC, Dear SP, Schneider ME. The anatomical consequences of acoustic injury: a review and tutorial. J Acoust Soc Am. 1985; 9. 78(3):833–860. PMID: 4040933.
Article4. Henderson D, Spongr V, Subramaniam M, Campo P. Anatomical effects of impact noise. Hear Res. 1994; 6. 01. 76(1-2):101–117. PMID: 7928703.
Article5. Hu BH, Guo W, Wang PY, Henderson D, Jiang SC. Intense noise-induced apoptosis in hair cells of guinea pig cochleae. Acta Otolaryngol. 2000; 1. 120(1):19–24. PMID: 10779180.
Article6. Hu BH, Henderson D, Nicotera TM. Involvement of apoptosis in progression of cochlear lesion following exposure to intense noise. Hear Res. 2002; 4. 166(1-2):62–71. PMID: 12062759.
Article7. Robertson JD, Orrenius S, Zhivotovsky B. Review: nuclear events in apoptosis. J Struct Biol. 2000; 4. 129(2-3):346–358. PMID: 10806085.
Article8. Atencia R, Asumendi A, García-Sanz M. Role of cytoskeleton in apoptosis. Vitam Horm. 2000; 58:267–297. PMID: 10668402.
Article9. Asumendi A, Andollo N, Boyano MD, Hilario E, Perez-Yarza G, Atencia R, et al. The role of cleavage of cell structures during apoptosis. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2000; 2. 46(1):1–11. PMID: 10726967.10. Rao JY, Jin YS, Zheng Q, Cheng J, Tai J, Hemstreet GP 3rd. Alterations of the actin polymerization status as an apoptotic morphological effector in HL-60 cells. J Cell Biochem. 1999; 12. 15. 75(4):686–697. PMID: 10572251.
Article11. Hu BH, Henderson D, Nicotera TM. F-actin cleavage in apoptotic outer hair cells in chinchilla cochleas exposed to intense noise. Hear Res. 2002; 10. 172(1-2):1–9. PMID: 12361861.
Article12. Yang WP, Henderson D, Hu BH, Nicotera TM. Quantitative analysis of apoptotic and necrotic outer hair cells after exposure to different levels of continuous noise. Hear Res. 2004; 10. 196(1-2):69–76. PMID: 15464303.13. Ding D, McFadden SL, Salvi RJ. Willott JF, editor. Cochlear hair cell densities and inner-ear staining techniqiues. Handbook of mouse auditory research: from behavior to molecular biology. 2001. 1st ed. Florida: CRC press;p. 189–204.14. Mashima T, Naito M, Tsuruo T. Caspase-mediated cleavage of cytoskeletal actin plays a positive role in the process of morphological apoptosis. Oncogene. 1999; 4. 15. 18(15):2423–2430. PMID: 10229193.
Article15. Maruyama W, Irie S, Sato TA. Morphological changes in the nucleus and actin cytoskeleton in the process of Fas-induced apoptosis in Jurkat T cells. Histochem J. 2000; 8. 32(8):495–503. PMID: 11095075.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Changes of Cochlear Nerve Terminals after Temporary Noise-Induced Hearing Loss
- Histopathologic Changes of Cochlea and Hearing Threshold Changes according to Duration of Noise-Exposure in the Rat
- Expression of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor in the Inner Ear of Noise-Exposed Mouse
- Morphological Change of Mouse Inner Ear Hair Cells after Noise Exposure
- The Effect of Pretreatment of CoCl2 on the Prevention of Noise-Induced Hearing Loss