Clin Orthop Surg.
2011 Mar;3(1):77-80. 10.4055/cios.2011.3.1.77.
Navigation-Assisted Total Knee Arthroplasty for the Knee Retaining Femoral Intramedullary Nail, and Distal Femoral Plate and Screws
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Konyang University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea. oskkk7@yahoo.co.kr
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- 3Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 999464
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2011.3.1.77
Abstract
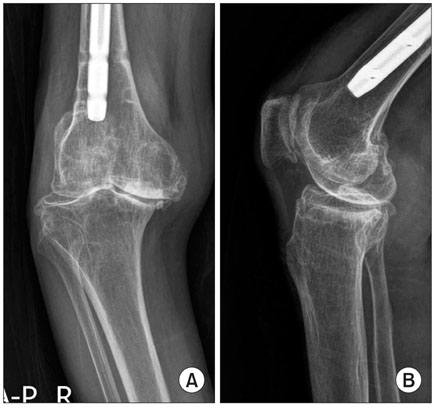
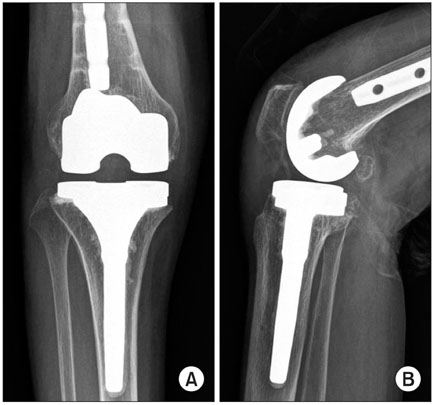
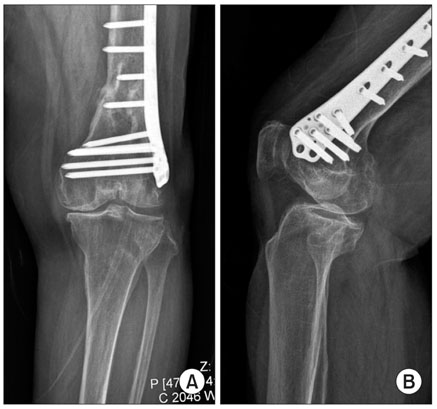
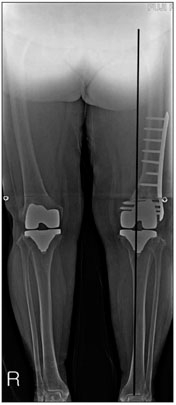
- Proper ligament balancing, restoration of the mechanical axis and component alignment are essential for the success and longevity of a prosthesis. In conventional total knee arthroplasty (TKA), an intramedullary guide is used to improve the alignment. An extramedullary guide can be used in cases of severe femoral bowing or intramedullary nailing but its use is more subjective and relies on the surgeon's experience. This paper reports two successful cases of navigation-assisted TKA for severe right knee osteoarthritis retaining a femoral intrameullary nail, and left knee osteoarthritis retaining a distal femoral plate.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Computer-Assisted Navigation in Total Knee Arthroplasty
Hwa-Jae Jeong, Yong-Beom Park, Han-Jun Lee
J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2018;53(6):478-489. doi: 10.4055/jkoa.2018.53.6.478.
Reference
-
1. Berend ME, Ritter MA, Meding JB, et al. Tibial component failure mechanisms in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004. (428):26–34.2. Jeffery RS, Morris RW, Denham RA. Coronal alignment after total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991. 73(5):709–714.
Article3. Rand JA, Coventry MB. Ten-year evaluation of geometric total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988. (232):168–173.
Article4. Bolognesi M, Hofmann A. Computer navigation versus standard instrumentation for TKA: a single-surgeon experience. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005. 440:162–169.5. Chou WY, Ko JY, Wang CJ, Wang FS, Wu RW, Wong T. Navigation-assisted total knee arthroplasty for a knee with malunion of the distal femur. J Arthroplasty. 2008. 23(8):1239.e13. 1239.e19.
Article6. Haaker RG, Stockheim M, Kamp M, Proff G, Breitenfelder J, Ottersbach A. Computer-assisted navigation increases precision of component placement in total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005. (433):152–159.
Article7. Brooks DB, Burstein AH, Frankel VH. The biomechanics of torsional fractures: the stress concentration effect of a drill hole. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1970. 52(3):507–514.8. Johnson BA, Fallat LM. The effect of screw holes on bone strength. J Foot Ankle Surg. 1997. 36(6):446–451.
Article9. Bonutti P, Dethmers D, Stiehl JB. Case report: femoral shaft fracture resulting from femoral tracker placement in navigated TKA. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2008. 466(6):1499–1502.
Article10. Li CH, Chen TH, Su YP, Shao PC, Lee KS, Chen WM. Periprosthetic femoral supracondylar fracture after total knee arthroplasty with navigation system. J Arthroplasty. 2008. 23(2):304–307.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Supracondylar Intramedullary Nail for Femoral Supracondylar Fracture following TKA: 3 Cases Report
- Treatment of Distal Femoral Fractures with a Retrograde Supracondylar Intramedullary Nail assisted with Arthroscopy
- Arthrodesis of the Knee Using a Retrograde Femoral Intramedullary Nail: Technical Report
- Effects of Femoral Lateral Bowing on Coronal Alignment and Component Position after Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Comparison of Conventional and Navigation-Assisted Surgery
- Comparison of an Accelerometer-Based Portable Navigation System, Patient-Specific Instrumentation, and Conventional Instrumentation for Femoral Alignment in Total Knee Arthroplasty