Korean J Radiol.
2011 Feb;12(1):107-112. 10.3348/kjr.2011.12.1.107.
The Efficacy of the Coaxial Technique Using a 6-Fr Introducer Sheath in Stent Placement for Treating the Obstructions Proximal to the Descending Colon
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Konkuk University Hospital, Seoul 143-729, Korea. psw0224@kuh.ac.kr
- 2Department of Surgery, Konkuk University Hospital, Seoul 143-729, Korea.
- 3Department of Family Medicine, Konkuk University Hospital, Seoul 143-729, Korea.
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Konkuk University Hospital, Seoul 143-729, Korea.
- KMID: 991688
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2011.12.1.107
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
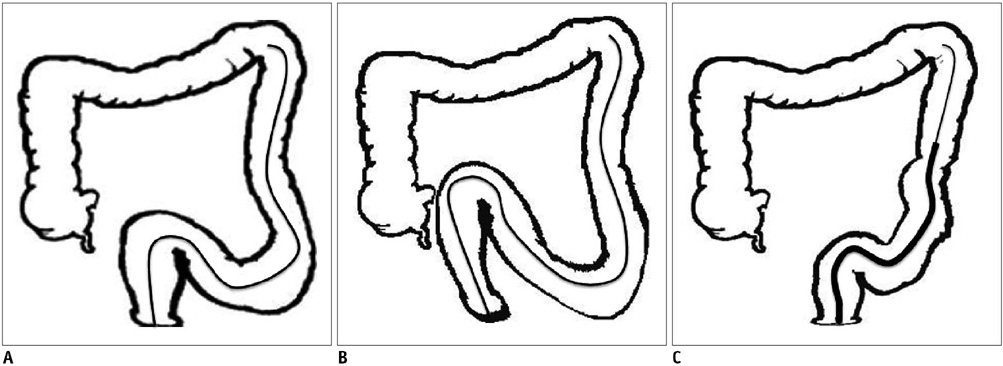
We wanted to evaluate the efficacy of stent placement using the coaxial technique with a stiff, long introducer sheath in patients with technical failure using an angiographic catheter for the obstructions proximal to the descending colon.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
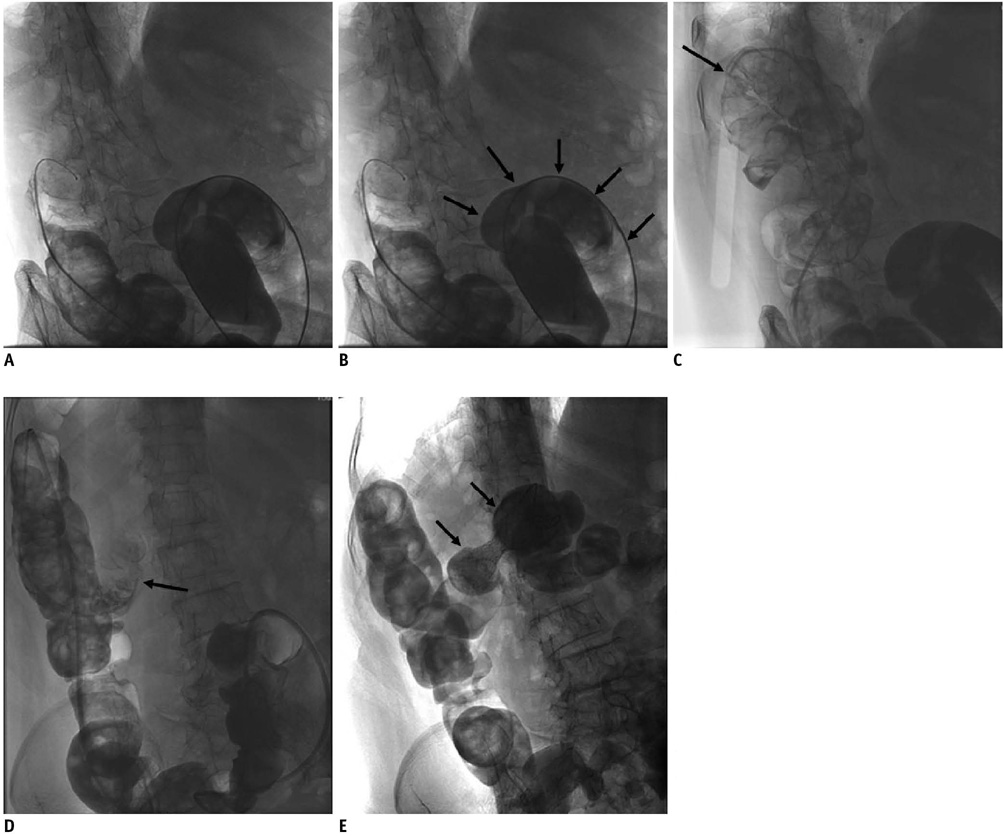
Self-expandable metallic stent placement was attempted under fluoroscopy-guidance in 77 consecutive patients who had malignant colorectal obstruction. Stent placement was performed using an angiographic catheter and a guide wire. If the angiographic catheter could not be advanced over the guide wire into the obstructive lesions proximal to the descending colon, then a 6-Fr introducer sheath was used. The technical success rate, the clinical success rate and the complications were analyzed.
RESULTS
Successful stent placement was achieved in 75 of 77 patients (97%). The angiographic catheter failed to advance into the obstructive lesions of 11 patients (M:F = 7:4; mean age, 65.5 years) whose lesions were at the level of the splenic flexure or transverse colon. Therefore, the coaxial technique was implemented in all these 11 patients using a 6-Fr stiff introducer sheath and then the stent placement was successful. There were no complications related to the use of a stiff introducer sheath. Clinical success, which was defined as relief of clinical obstructive bowel symptoms, was obtained within 24 hours in all of patients.
CONCLUSION
The coaxial technique using a stiff introducer sheath can increase the technical success of fluoroscopy-guided, self-expandable metallic stent placement in patients with colonic obstruction proximal to the descending colon.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Comparison of Clinical Outcomes between Endoscopic and Radiologic Placement of Self-expandable Metal Stent in Patients with Malignant Colorectal Obstruction
Ji Won Kim, Ji Bong Jeong, Kook Lae Lee, Byeong Gwan Kim, Yong Jin Jung, Won Kim, Hwi Young Kim, Dong Won Ahn, Seong-Joon Koh, Jae Kyung Lee
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2013;61(1):22-29. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2013.61.1.22.
Reference
-
1. Repici A, Adler DG, Gibbs CM, Malesci A, Preatoni P, Baron TH. Stenting of the proximal colon in patients with malignant large bowel obstruction: techniques and outcomes. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007. 66:940–944.2. Meisner S, Hensler M, Knop FK, West F, Wille-Jørgensen P. Self-expanding metal stents for colonic obstruction: experiences from 104 procedures in a single center. Dis Colon Rectum. 2004. 47:444–450.3. Suzuki N, Saunders BP, Thomas-Gibson S, Akle C, Marshall M, Halligan S. Colorectal stenting for malignant and benign disease: outcomes in colorectal stenting. Dis Colon Rectum. 2004. 47:1201–1207.4. Law WL, Chu KW, Ho JW, Tung HM, Law SY, Chu KM. Self-expanding metallic stent in the treatment of colonic obstruction caused by advanced malignancies. Dis Colon Rectum. 2000. 43:1522–1527.5. Fan YB, Cheng YS, Chen NW, Xu HM, Yang Z, Wang Y, et al. Clinical application of self-expanding metallic stent in the management of acute left-sided colorectal malignant obstruction. World J Gastroenterol. 2006. 12:755–759.6. Baron TH, Dean PA, Yates MR 3rd, Canon C, Koehler RE. Expandable metal stents for the treatment of colonic obstruction: techniques and outcomes. Gastrointest Endosc. 1998. 47:277–286.7. Mainar A, De Gregorio Ariza MA, Tejero E, Tobío R, Alfonso E, Pinto I, et al. Acute colorectal obstruction: treatment with self-expandable metallic stents before scheduled surgery-results of a multicenter study. Radiology. 1999. 210:65–69.8. Kim TH, Song HY, Shin JH, Park IK, Kim JH, Lim JO, et al. Usefulness of multifunctional gastrointestinal coil catheter for colorectal stent placement. Eur Radiol. 2008. 18:2530–2534.9. Sebastian S, Johnston S, Geoghegan T, Torreggiani W, Buckley M. Pooled analysis of the efficacy and safety of self-expanding metal stenting in malignant colorectal obstruction. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004. 99:2051–2057.10. Baraza W, Lee F, Brown S, Hurlstone DP. Combination endo-radiological colorectal stenting: a prospective 5-year clinical evaluation. Colorectal Dis. 2008. 10:901–906.11. de Gregorio MA, Mainar A, Tejero E, Tobio R, Alfonso E, Pinto I, et al. Acute colorectal obstruction: stent placement for palliative treatment--results of a multicenter study. Radiology. 1998. 209:117–120.12. Kim H, Kim SH, Choi SY, Lee KH, Won JY, Lee do Y, et al. Fluoroscopically guided placement of self-expandable metallic stents and stent-grafts in the treatment of acute malignant colorectal obstruction. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2008. 19:1709–1716.13. Harris GJ, Senagore AJ, Lavery IC, Fazio VW. The management of neoplastic colorectal obstruction with colonic endoluminal stenting devices. Am J Surg. 2001. 181:499–506.14. Sebastian S, Johnston S, Geoghegan T, Torreggiani W, Buckley M. Pooled analysis of the efficacy and safety of self-expanding metal stenting in malignant colorectal obstruction. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004. 99:2051–2057.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Malignant Duodenal Obstructions: Palliative Treatment with Covered Expandable Nitinol Stent
- Usefulness of a Self-expandable Nitinol Stent Through an Endoscope for the Treatment of a Malignant Colorectal Obstruction
- Clinical Outcome of Self-Expandable Metal Stent Placement in the Management of Malignant Proximal Colon Obstruction
- Usefulness of a Guiding Sheath for Fluoroscopic Colorectal Stent Placement
- A Case of Inserting Two Self-expandable Metal Stents in Dual Malignant Colonic Obstructions