Korean J Lab Med.
2009 Apr;29(2):97-103. 10.3343/kjlm.2009.29.2.97.
A Case of a Korean Adult Affected by Type B Niemann-Pick Disease: Secondary Sea-blue Histiocytosis and Molecular Characterization
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Eulji University School of Medicine, Eulji General Hospital, Seoul, Korea. jdchae@eulji.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Eulji University School of Medicine, Eulji General Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiology, Eulji University School of Medicine, Eulji General Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Eulji University School of Medicine, Eulji General Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Laboratory Medicine, University of Ulsan, College of Medicine and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Department of Medical Genetics Clinic & Laboratory, University of Ulsan, College of Medicine and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 7Department of Pediatrics, University of Ulsan, College of Medicine and Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 854963
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/kjlm.2009.29.2.97
Abstract
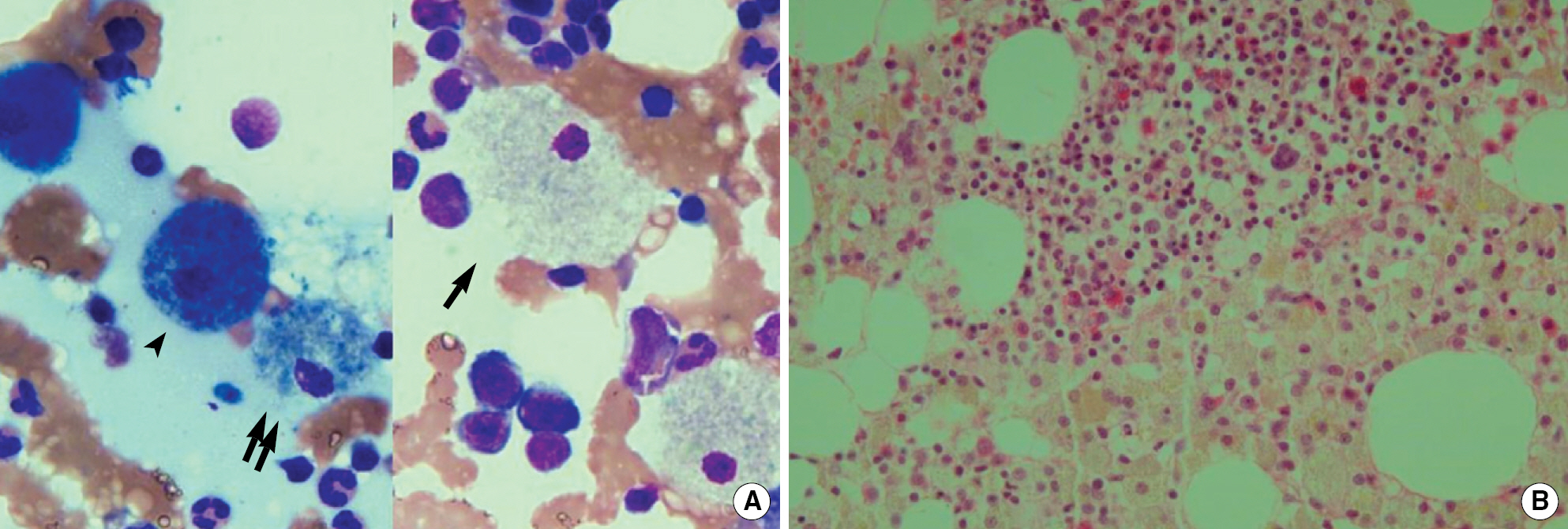
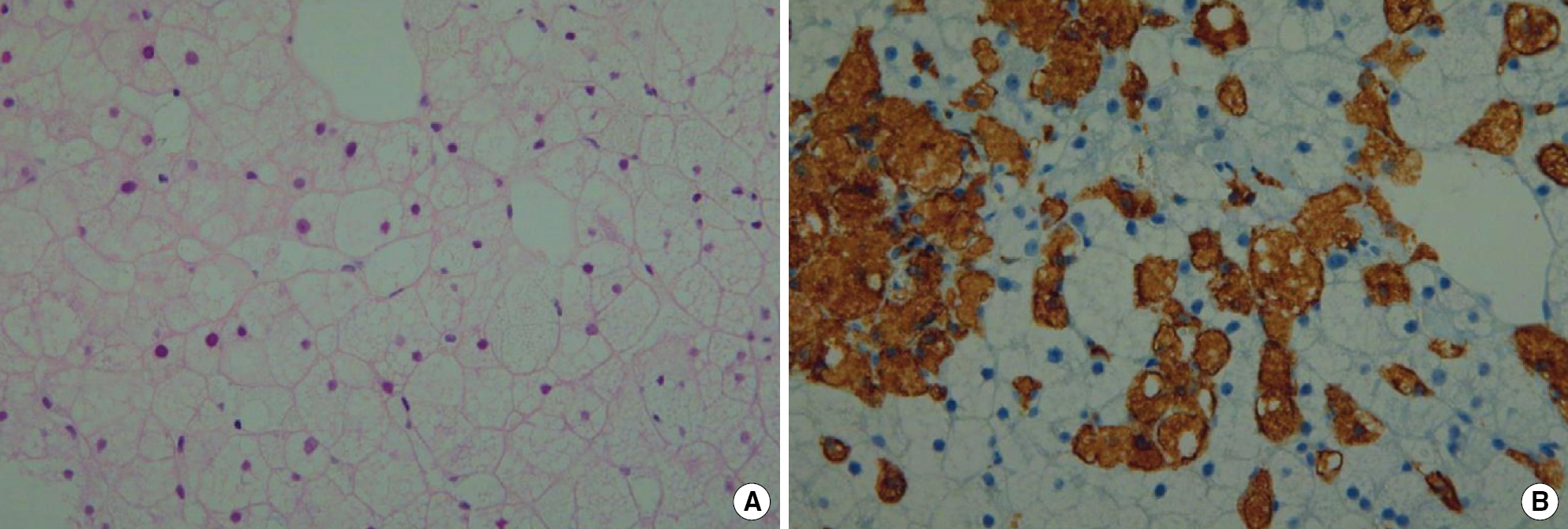
- Niemann-Pick disease (NPD) is an inherited metabolic disorder caused by a deficiency of the enzyme acid sphingomyelinase coded by SMPD1 gene. In contrast with type A NPD, a severe neurodegenerative disease of infancy, type B NPD patients have little or no neurodegeneration, and frequently survive into adulthood. Although over 100 mutations have been found within the SMPD1 gene causing NPD, there was only one report about SMPD1 mutation status of a Korean NPD patient. We report a case of a 32-yr-old female, who presented with thrombocytopenia without any neurologic involvement. Hepatosplenomegaly was detected by both physical examination and imaging studies, and a thoracic radiograph examination showed a pattern of interstitial lung disease. Biochemical tests revealed increased liver enzymes, cholesterol, triglyceride, and LDL-cholesterol, and decreased HDL-cholesterol. Sea-blue or foamy vacuolated histiocytes occurred in bone marrow and liver. Sequencing analysis of SMPD1 using genomic DNA from peripheral leukocytes identified a compound heterozygote of two mutations at exon 2: p.E246K and p.A357V. The former is a known mutation in an Italian patient, and the latter has not been reported yet. She has received oral rosuvastatin to treat hyperlipidemia at a dose of 10 mg per day for 4 months. This is the second report in which the mutation of SMPD1 gene was detected in a Korean NPD patient. The active genetic analysis of SMPD1 gene in patients with typical findings of type B NPD would enable us to facilitate diagnosis as well as to accumulate data on molecular characteristics of Korean NPD patients.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1.Schuchman EH. The pathogenesis and treatment of acid sphingomyelinase-deficient Niemann-Pick disease. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2007. 30:654–63.
Article2.Rodon P., Ramain JP., Bruandet P., Piedon A., Akli J., Penot J. Type B Niemann-Pick disease and sea-blue histiocytes syndrome. Rev Med Interne. 1991. 12:299–302.3.Strigaris K., Kokkinis K., Liberopoulos K., Kavvadias S., Tsouroulas M., Nikolacopoulou Z. Liver lesion on computed tomography and ultrasonography in adult Niemann Pick disease related to sea blue histiocyte syndrome–a case report. Hepatogastroenterology. 1993. 40:240–3.4.Candoni A., Grimaz S., Doretto P., Fanin R., Falcomer F., Bembi B. Sea-blue histiocytosis secondary to Niemann-Pick disease type B: a case report. Ann Hematol. 2001. 80:620–2.5.Gonzalez-Reimers E., Sanchez-Perez MJ., Bonilla-Arjona A., Rodriguez-Gaspar M., Carrasco-Juan JL., Alvarez-Arguelles H, et al. Case report. Pulmonary involvement in an adult male affected by type B Niemann-Pick disease. Br J Radiol. 2003. 76:838–40.6.Falco F., Bembi B., Cavazza A., Pittis MG., Zucchi L. Pulmonary involvement in an adult female affected by type B Niemann Pick disease. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2005. 22:229–33.7.Suzuki O., Abe M. Secondary sea-blue histiocytosis derived from Niemann-Pick disease. J Clin Exp Hematopathol. 2007. 47:19–21.
Article8.Kim YS., Lim SH., Seo JK., Ahn HS., Moon HR. A case of Niemann-Pick disease with sea-blue histiocytes in the bone marrow. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1985. 28:72–8. (김영선, 임수흠, 서정기, 안효섭, 문형로. 골수에서 Sea Blue Histiocytes가출현된 Niemann Pick씨병 1예. 소아과 1985;28: 72-8.).9.Cho HN., Lee HJ., Song JW., Choi JH., Moon HR., Ji JG, et al. A case of type A Niemann Pick disease. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1987. 30:1461–7. (조효남, 이홍진, 송재원, 최중환, 문형로, 지제근 등. A형(유아형) Niemann Pick씨병 1예. 소아과 1987;30: 1461-7.).10.Levran O., Desnick RJ., Schuchman EH. Niemann-Pick type B disease. Identification of a single codon deletion in the acid sphingomyelinase gene and genotype/phenotype correlations in type A and B patients. J Clin Invest. 1991. 88:806–10.
Article11.Takahashi T., Suchi M., Desnick RJ., Takada G., Schuchman EH. Identification and expression of five mutations in the human acid sphingomyelinase gene causing type A and B Niemann-Pick disease, Molecular evidence for genetic heterogeneity in the neuronopathic and non-neuronopathic forms. J Biol Chem. 1992. 267:12552–8.12.Simonaro CM., Desnick RJ., McGovern MM., Wasserstein MP., Schuchman EH. The demographics and distribution of type B Niemann-Pick disease: novel mutations lead to new genotype/phenotype correlations. Am J Hum Genet. 2002. 71:1413–9.
Article13.Ricci V., Stroppiano M., Corsolini F., Di Rocco M., Parenti G., Regis S, et al. Screening of 25 Italian patients with Niemann-Pick A reveals fourteen new mutations, one common and thirteen private, in SMPD1. Hum Mutat. 2004. 24:105.14.Pittis MG., Ricci V., Guerci VI., Marcais C., Ciana G., Dardis A, et al. Acid sphingomyelinase: identification of nine novel mutations among Italian Niemann Pick type B patients and characterization of in vivo functional in-frame start codon. Hum Mutat. 2004. 24:186–7.15.Dardis A., Zampieri S., Filocamo M., Burlina A., Bembi B., Pittis MG. Functional in vitro characterization of 14 SMPD1 mutations identified in Italian patients affected by Niemann Pick Type B disease. Hum Mutat. 2005. 26:164.16.Levran O., Desnick RJ., Schuchman EH. Niemann-Pick disease: a frequent missense mutation in the acid sphingomyelinase gene of Ashkenazi Jewish type A and B patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1991. 88:3748–52.
Article17.Levran O., Desnick RJ., Schuchman EH. Identification and expression of a common missense mutation (L302P) in the acid sphingomyelinase gene of Ashkenazi Jewish type A Niemann-Pick disease patients. Blood. 1992. 80:2081–7.
Article18.Levran O., Desnick RJ., Schuchman EH. Type A Niemann-Pick disease: a frameshift mutation in the acid sphingomyelinase gene (fs-P330) occurs in Ashkenazi Jewish patients. Hum Mutat. 1993. 2:317–9.
Article19.Vanier MT., Ferlinz K., Rousson R., Duthel S., Louisot P., Sandhoff K, et al. Deletion of arginine (608) in acid sphingomyelinase is the prevalent mutation among Niemann-Pick disease type B patients form northern Africa. Hum Genet. 1993. 92:325–30.20.Kim SH., Choi YJ., Kim IH., Kim SW. A case of Niemann Pick disease. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1983. 26:1039–43. (김성환, 최영주, 김인호, 김상우. Niemann Pick병 1예. 소아과 1983;26: 1039-43.).21.Moon YB., Im YB., Lee DH., Lee SJ., Kim IS., Kwon TJ, et al. A case of type A Niemann-Pick disease. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1989. 32:402–11. (문영봉, 임양빈, 이동환, 이상주, 김인숙, 권태정등. A형 Niemann-Pick 병 1예. 소아과 1989;32: 402-11.).22.Jeon EY., Choi KA., Koo CH., Lee WM., Jeon YS., Lee CH, et al. A case of type A Niemann-Pick disease. J Korean Pediatr Soc. 1998. 41:275–80. ((전은영, 최경아, 구철회, 이화모, 전영석, 이창훈등. A형 Niemann-Pick병 1예. 소아과 1998;41: 275-80.).23.Lee CW., Goo HW. Three-year follow-up of Niemann-Pick disease with pulmonary involvement: a case report. J Korean Radiol Soc. 2005. 52:37–40. (이충욱및구현우. 폐침윤을동반한 Niemann-Pick Disease의 3년간추적검사: 증례보고. 대한영상의학회지 2005;52: 37-40.).
Article24.Yu HY., Oh JE., Park JS., Kim MH., Kim SD., Jung KS. A case of Niemann-Pick disease type A. Korean J Pediatr. 2006. 49:1358–62. (유호연, 오지은, 박재선, 김미향, 김신동, 정경순. A형 Niemann-Pick 병 1예. 대한소아과학회지 2006;49: 1358-62.).
Article25.Lee JH., Jung WS., Lee HY., Kim AR., Yoon HS., Go YK. An anesthetic experience in a patient with Niemann-Pick disease -a case report-. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2008. 54:109–12. (이준화, 정우석, 이호영, 김아름, 윤희석, 고영권. Niemann-Pick 병환자의전신마취경험 -증례보고-. 대한마취과학회지 2008;54: 109-12.).26.Choi JH., Shin YL., Kim GH., Hong SJ., Yoo HW. Treatment of hyperlipidemia associated with Niemann-Pick disease type B by fenofibrate. Eur J Pediatr. 2006. 165:138–9.
Article27.McGovern MM., Wasserstein MP., Giugliani R., Bembi B., Vanier MT., Mengel E, et al. A prospective, cross-sectional survey study of the natural history of Niemann-Pick disease type B. Pediatrics. 2008. 122:e341–9.
Article28.Foucar K, editor. Bone marrow pathology. 2nd ed.Chicago: ASCP Press;2001. p. 528–31.