Korean J Lab Med.
2008 Apr;28(2):160-168. 10.3343/kjlm.2008.28.2.160.
Meta-Analysis for the Pooled Sensitivity and Specificity of Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Rapid Tests
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 2Medical Research Institute, Pusan National University, Busan, Korea.
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, Asan Medical Center and University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hboh@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 854857
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/kjlm.2008.28.2.160
Abstract
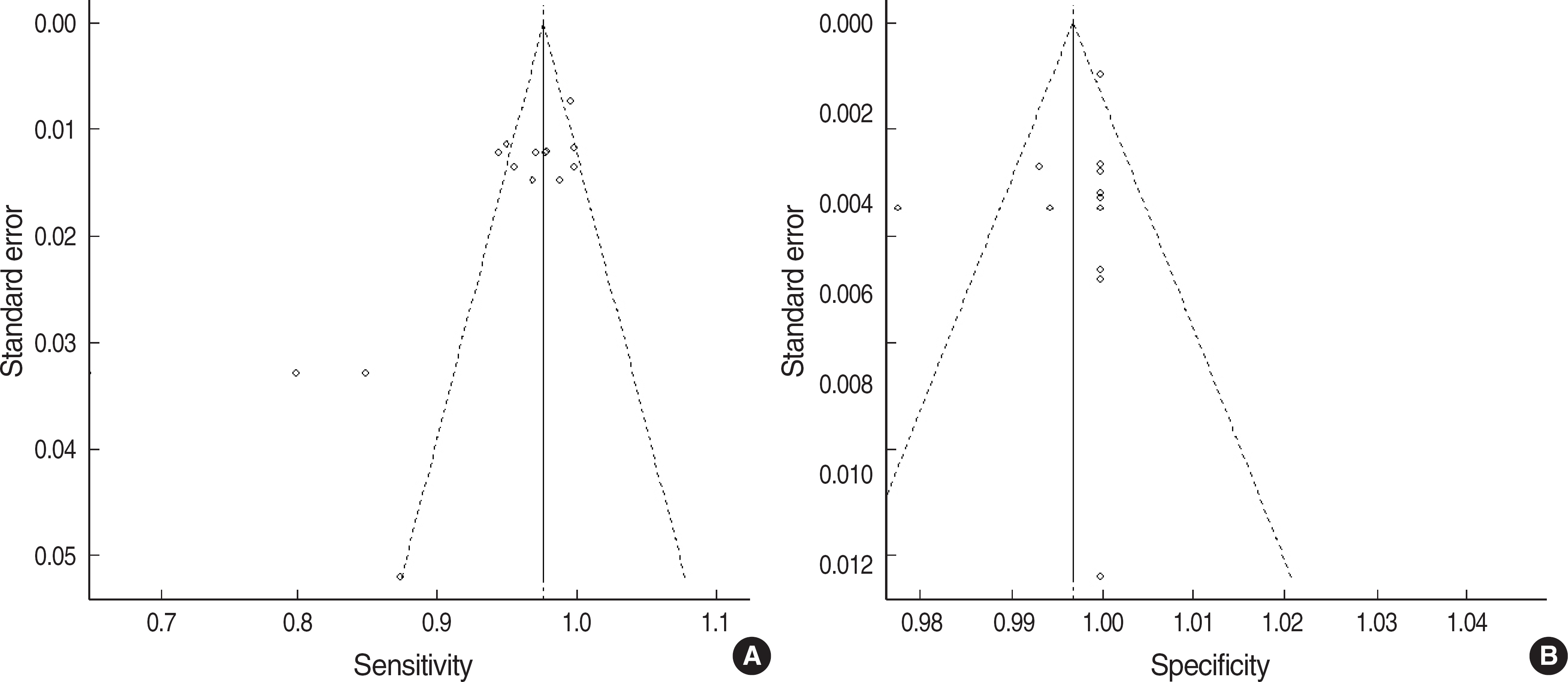
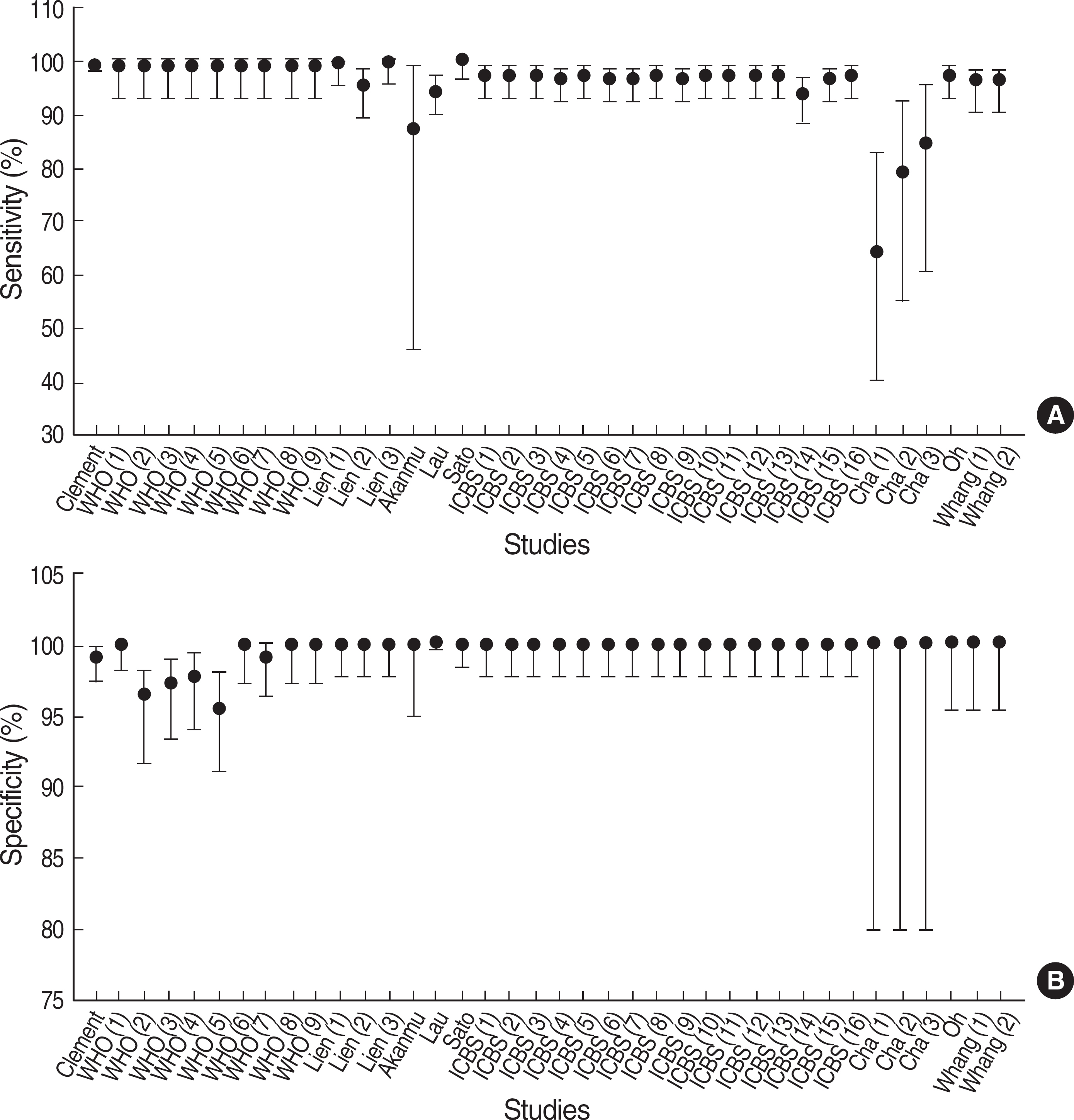
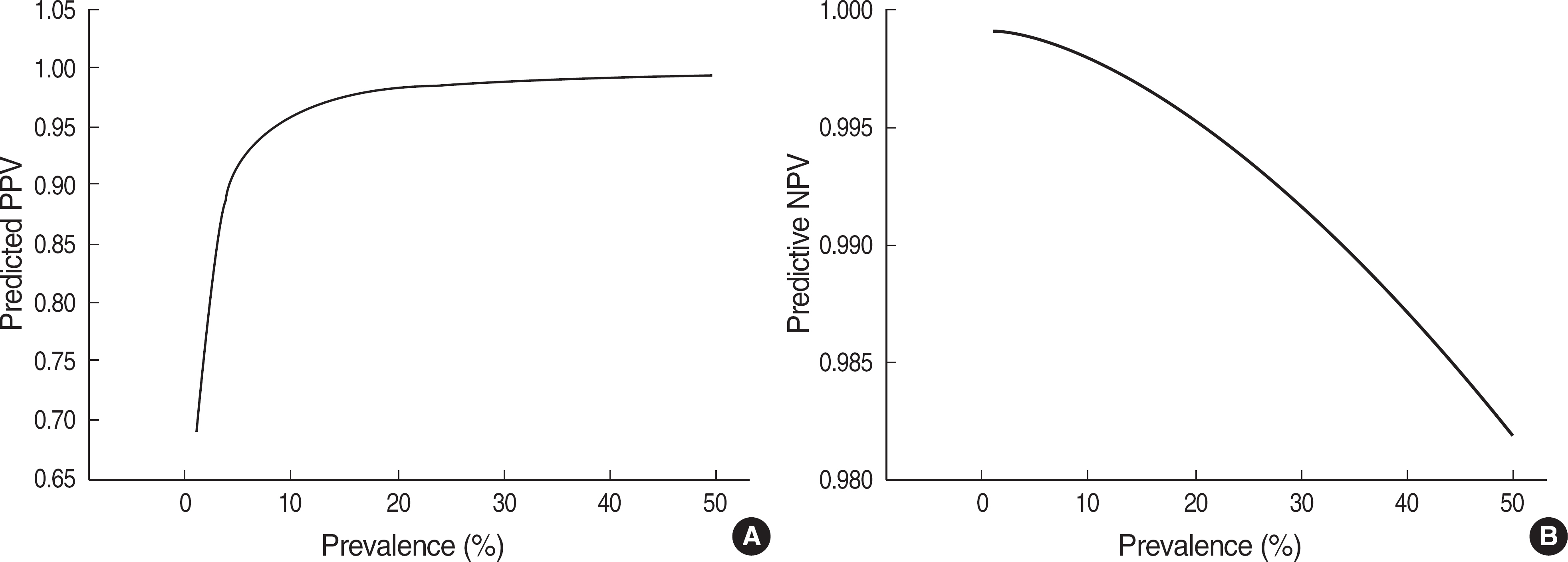
- BACKGROUND: Although hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) rapid test based on immunochromatographic assay (ICA) is now widely used, the test has not been evaluated sufficiently enough to validate its performance. Thus, it is important to summarize the clinical performance of the test kits. In this study, we performed meta-analysis for the performance of the HBsAg rapid tests. METHODS: PubMed database was searched using keywords about the accuracy of diagnostic tests for hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. Two investigators assessed methodological quality utilizing standards for reporting of diagnostic accuracy studies (STARD) checklist. After performing a heterogeneity test, we obtained pooled sensitivity and specificity. Positive and negative predictive values (PPV and NPV) were simulated according to HBV prevalence. RESULTS: A total of 38 studies was selected from 10 papers. The quality scores ranged from 3 to 13 (median, 8). Kappa value was good (0.85). The performance of the 38 studies was heterogeneous. When 33 studies with better quality from 7 papers were re-selected, the pooled sensitivity and specificity were 98.07% (95% confidence interval, CI: 97.67-98.47%) and 99.56% (95% CI: 99.21-99.91%), respectively. With an HBV prevalence of 5%, PPV and NPV were predicted to be 92.14% and 99.90%, respectively. CONCLUSIONS: In view of high HBV prevalence in Korea, it is thought that the HBsAg rapid test can be used for HBV screening in small-sized laboratories or for epidemiologic studies. This study should be helpful in establishing a guideline for the proper performance evaluation of the HBsAg rapid tests.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Meta-Analysis for the Pooled Sensitivity and Specificity of anti-Human Immunodeficiency Virus Ab Rapid Tests
Soo Jin Yoo, Yong-Hak Sohn, Sung-Eun Choi, Heung-Bum Oh
Korean J Lab Med. 2009;29(4):345-352. doi: 10.3343/kjlm.2009.29.4.345.
Reference
-
1.Lee WM. Hepatitis B virus infection. N Engl J Med. 1997. 337:1733–45.
Article2.Lee DH., Kim JH., Nam JJ., Kim HR., Shin HR. Epidemiological findings of hepatitis B infection based on 1998 National Health and Nutrition Survey in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2002. 17:457–62.
Article3.Cha YJ., Kum DG., Kim SW., Kim TY., Kim JR., Kim HS, et al. Annual report on external quality assessment in immunoserology in Korea (2002). J Lab Med & Quality Assurance. 2003. 25:51–72. (차영주, 금동길, 김성원, 김신규, 김재룡, 김현숙등. 면역혈청검사신빙도조사결과보고(2002). 임상검사와정도관리 2003;25: 51-72.).4.Cha YJ., Kwon SY., Kim TY., Kim JR., Kim HS., Park MH, et al. Annual report on external quality assessment in immunoserology in Korea (2006). J Lab Med Qual Assur. 2007. 29:45–64. (차영주, 권소영, 김신규, 김재룡, 김현숙, 박명희등. 면역혈청검사신빙도조사결과보고(2006). 임상검사와정도관리 2007;29: 45-64.).5.Oh J., Kim TY., Yoon HJ., Min HS., Lee HR., Choi TY. Evaluation of Genedia® HBsAg Rapid and Genedia® anti-HBs Rapid for the screening of HBsAg and Anti-HBs. Korean J Clin Pathol. 1999. 19:114-7. (오지하, 김신규, 윤현정, 민형식, 이혜림, 최태열. B형간염표면항원및항체검사를위한 Genedia Rapid법의비교평가. 대한임상병리학회지 1999;19:. 114–7. ).6.Whang DH., Um T. Comparison of immunochromatography assays and quantitative immunoassays for detecting HBsAg and anti-HBs. Korean J Lab Med. 2005. 25:186–91. (황동희 및 엄태현. B형간염항원및항체검사를위한신속검사법과정량적효소면역법의비교. 대한진단검사의학회지 2005;25: 186-91.).7.Cha YJ., Yang JS., Chae SL. Evaluation of indigenously manufactured immunochromatographic assay systems for rapid detection of hepatitis B surface antigen and antibody. Korean J Lab Med. 2006. 26:52–7. (차영주, 양주석, 채석래. 국내에서생산되는면역크로마토그래피법을이용한B형간염표면항원및항체검사제품의평가. 대한진단검사의학회지 2006;26: 52-7.).
Article8.Reid MC., Lachs MS., Feinstein AR. Use of methodological standards in diagnostic test research. Getting better but still not good. JAMA. 1995. 274:645–51.
Article9.Lumbreras-Lacarra B., Ramos-Rincon JM., Hernandez-Aguado I. Methodology in diagnostic laboratory test research in clinical chemistry and clinical chemistry and laboratory medicine. Clin Chem. 2004. 50:530–6.
Article10.Bossuyt PM., Reitsma JB., Bruns DE., Gatsonis CA., Glasziou PP., Irwig LM, et al. Towards complete and accurate reporting of studies of diagnostic accuracy: the STARD Initiative. Ann Intern Med. 2003. 138:40–4.
Article11.Kim S., Oh HB., Cha CH., Choi SE., An HY., Lee KJ. Quality evaluation of the performance study of diagnostic tests using STARD checklist and meta-analysis for the pooled sensitivity and specificity of third generation anti-HCV EIA tests. Korean J Lab Med. 2006. 26:307–15. (김솔잎, 오흥범, 차충환, 최성은, 안홍엽, 이관제. STARD를이용한진단검사법성능평가연구의질평가와메타분석을통한3세대HCV 효소면역항체검사의통합민감도와특이도분석. 대한진단검사의학회지 2006;26: 307-15.).12.World Health Organization. Hepatitis B surface antigen assays: operational characteristics (phase I). http://www.who.int/diagnostics_laboratory/evaluations/en/hep_B_rep1.pdf. (Updated on July 19. 2007.13.International Consortium for Blood Safety. Evaluation results of some commercially available HBsAg assays using ICBS HBV clinical panel and ICBS negative panel. http://www.icbs-web.org/HB290107P.pdf. (Updated on July 19. 2007.14.Egger M., Davey Smith G., Schneider M., Minder C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. 1997. 315:629–34.
Article15.Macaskill P., Walter SD., Irwig L. A comparison of methods to detect publication bias in meta-analysis. Stat Med. 2001. 20:641–54.
Article16.Clement F., Dewint P., Leroux-Roels G. Evaluation of a new rapid test for the combined detection of hepatitis B virus surface antigen and hepatitis B virus e antigen. J Clin Microbiol. 2002. 40:4603–6.
Article17.Lien TX., Tien NT., Chanpong GF., Cuc CT., Yen VT., Soderquist R, et al. Evaluation of rapid diagnostic tests for the detection of human immunodeficiency virus types 1 and 2, hepatitis B surface antigen, and syphilis in Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2000. 62:301–9.
Article18.Akanmu AS., Esan OA., Adewuyi JO., Davies AO., Okany CC., Olatunji RO, et al. Evaluation of a rapid test kit for detection of HBsAg/eAg in whole blood: a possible method for pre-donation testing. Afr J Med Med Sci. 2006. 35:5–8.19.Lau DT., Ma H., Lemon SM., Doo E., Ghany MG., Miskovsky E, et al. A rapid immunochromatographic assay for hepatitis B virus screening. J Viral Hepat. 2003. 10:331–4.
Article20.Sato K., Ichiyama S., Iinuma Y., Nada T., Shimokata K., Nakashima N. Evaluation of immunochromatographic assay systems for rapid detection of hepatitis B surface antigen and antibody, Dainascreen HBsAg and Dainascreen Ausab. J Clin Microbiol. 1996. 34:1420–2.
Article21.Hennig H., Puchta I., Luhm J., Schlenke P., Goerg S., Kirchner H. Frequency and load of hepatitis B virus DNA in first-time blood donors with antibodies to hepatitis B core antigen. Blood. 2002. 100:2637–41.
Article22.Hwang SH., Oh HB., Kim HS., Lee EY. Evaluation of HBs Ag, HCV and HIV Ag-Ab assays using Bio-Rad Elite microplate analyzer. Korean J Lab Med. 2006. 26:436–41. (황상현, 오흥범, 김현숙, 이은엽. Bio-Rad Elite Microplate 장비를이용한HBs 항원, HCV, HIV 항원-항체검사시약평가. 대한진단검사의학회지 2006;26: 436-41.).
Article23.Weber B. Diagnostic impact of the genetic variability of the hepatitis B virus surface antigen gene. J Med Virol. 2006. 78(S1):S59–65.
Article24.Weber B., Dengler T., Berger A., Doerr HW., Rabenau H. Evaluation of two new automated assays for hepatitis B virus surface antigen (HBsAg) detection: IMMULITE HBsAg and IMMULITE 2000 HBsAg. J Clin Microbiol. 2003. 41:135–43.
Article25.Saito T., Shinzawa H., Uchida T., Kawamata O., Honma S., Watanabe H, et al. Quantitative DNA analysis of low-level hepatitis B viremia in two patients with serologically negative chronic hepatitis B. J Med Virol. 1999. 58:325–31.
Article26.Deville WL., Buntinx F., Bouter LM., Montori VM., de Vet HC., van der Windt DA, et al. Conducting systematic reviews of diagnostic studies: didactic guidelines. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2002. 2:9.
Article27.Normand SL. Meta-analysis: formulating, evaluating, combining, and reporting. Stat Med. 1999. 18:321–59.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Eligibility Study of Anesthesia and Surgery for HBs Antigen Positive Patients
- Meta-Analysis for the Pooled Sensitivity and Specificity of anti-Human Immunodeficiency Virus Ab Rapid Tests
- Evaluation of Various Rapid Immunochromatographic Assays Performed on Aircrews
- The Evaluation of Immunochromatographic Assay kit for Rapid Detection of Hepatitis B Surface Antigen
- Prevalence of hepatitis B surface antigen in pediatric in patients