J Korean Orthop Assoc.
2007 Apr;42(2):147-152. 10.4055/jkoa.2007.42.2.147.
Treatment of Periprosthetic Femoral Fractureaccording to the Vancouver Classification
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, College of Medicine, Hanyang University, Seoul, Korea. kimyh1@hanyang.ac.kr
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, College of Medicine, Ewha Womans University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 854581
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/jkoa.2007.42.2.147
Abstract
- PURPOSE: To determine the treatment results according to the guideline of the Vancouver classification in periprosthetic femoral fractures. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Thirty-five periprosthetic femoral fractures treated between May 1981 and February 2003 were assessed. The mean age of the patients was 56 years (30-83 years). The outcomes were estimated according to the Beals and Tower's criteria. RESULTS: The overall incidence of postoperative periprosthetic femoral fracture was 0.91%. The frequency of the fracture types in decreasing order was B1, B2, B3, C, AG and AL. The treatment outcomes according to the Vancouver guidelines were excellent in 27 hips, good in 5 hips and poor in 3 hips. Suspicious risk factors of periprosthetic fractures were found in 6 hips (osteoporosis in 4 hips, osteolysis in 1 hip and loosening of femoral stem in 1 hip). Complications related to the treatment included a bony defect in 1 hip and an infection with non-union in 1 hip. The complications related to treatment for an implant were loosening in 2 hips and subsidence of stem in 1 hip. CONCLUSION: In order to obtain favorable results, in addition to following the Vancouver treatment guideline, consideration should be made to the basic principles such as the stability of the fractures, the stability of the implant and restoration of the bone stock.
MeSH Terms
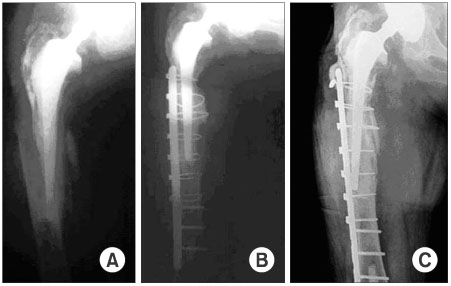
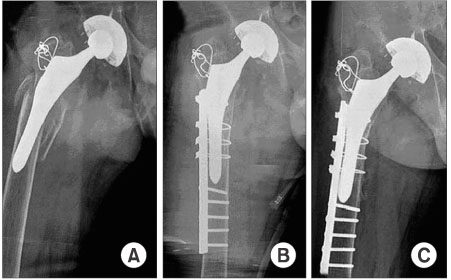
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ahn HS, Lee KW, Kim CH, Lee JH, Jeon JS. Treatment of periprosthetic femoral fractures with cable plate. J Korean Fract Soc. 2006. 19:78–82.
Article2. Beals RK, Tower SS. Periprosthetic fractures of the femur. An analysis of 93 fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1996. 327:238–246.3. Bethea JS 3rd, DeAndrade JR, Fleming LL, Lindenbaum SD, Welch RB. Proximal femoral fractures following total hip arthroplasty. Cin Orthop Relat Res. 1982. 170:95–106.
Article4. Brady OH, Garbuz DS, Marsri BA, Duncan CP. Classification of the hip. Orthop Clin North Am. 1999. 30:215–220.
Article5. Brady OH, Garbuz DS, Marsri BA, Duncan CP. The reliability and validity of the Vancouver classification of femoral fractures after hip replacement. J Arthroplasty. 2000. 15:59–62.6. Campbell P, McWilliams TG. Periprosthetic femoral fractures. Curr Orthop. 2002. 16:126–132.
Article7. Chandler HP, Tigges RG. The role of allografts in the treatment of periprosthetic femoral fractures. Instr Course Lect. 1998. 47:257–264.8. Cooke PH, Newman JH. Fractures of the femur in relation to cemented hip prostheses. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1988. 70:386–389.
Article9. Duncan CP, Masri BA. Fractures of the femur after hip replacement. Inst Course Lect. 1995. 44:293–304.10. Garbuz DS, Masri BA, Duncan CP. Periprosthetic fractures of the femur: principles of prevention and management. Inst Course Lect. 1998. 47:237–242.11. Fitzgerald RH Jr, Brindley GW, Kavanagh BF. The uncemented total hip arthroplasty. Intraoperative femoral fractures. Clin Orthop Realt Res. 1998. 235:61–66.12. Garcia-Cimbrelo E, Munuera L, Gil-Garay E. Femoral shaft fractures after cemented total hip arthroplasty. Int Orthop. 1992. 16:97–100.
Article13. Haddad FS, Duncan CP, Berry DJ, Lewallen DG, Gross AE, Chandler HP. Periprosthetic femoral fractures around well-fixed implants; use of cortical onlay allografts with or without a plate. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002. 84:945–950.14. Harrington IJ, Tountas AA, Cameron HU. Femoral fractures associated with Moore's prosthesis. Injury. 1979. 11:23–32.
Article15. Jensen JS, Barfod G, Hansen D, et al. Femoral shaft fracture after hip arthroplasty. Acta Orthop Scand. 1988. 59:9–13.
Article16. Kavanagh BF. Femoral fractures associated with total hip arthroplasty. Orthop Clin North Am. 1992. 23:249–257.
Article17. Larsen E, Menck H, Rosenklint A. Fractures after hemialloplastic hip replacement. J Trauma. 1987. 27:72–74.
Article18. Lee SR, Bostrom MP. Periprosthetic fractures of the femur after total hip arthroplasty. Instr Course Lect. 2004. 53:111–118.19. Lewallen DG, Berry DJ. Periprosthetic fractures of the femur: principles of prevention and management. Instr Course Lect. 1998. 47:243–249.20. Macdonald SJ, Paprosky WG, Jablonsky WS, Magnus RG. Periprosthetic femoral fractures treated with long-stem cementless component. J Arthroplsty. 2001. 16:379–383.21. Maury AC, Pressman A, Cayen B, Zalzal P, Backstein D, Gross A. Proximal femoral allograft treatment of vancouver type-B3 periprosthetic femoral fractures after total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006. 88:953–958.
Article22. McLauchlan GJ, Robinson CM, Singer BR, Christie J. Results of an operative policy in the treatment of periprosthetic femoral fracture. J Orthop Trauma. 1997. 11:170–179.
Article23. Mulay S, Hassan T, Birtwistle S, Power R. Mangement of types B2 and B3 femoral periprosthetic fractures by a tapered, fluted, and distally fixed stem. J Arthroplasty. 2005. 20:751–756.24. Ogden WS, Rendall J. Fractures beneath hip prostheses: a special indication for Parham bands and plating. Orthop Trans. 1978. 2:70.25. O'Shea K, Quinlan JF, Kutty S, Mulcahy D, Brady OH. The use of uncemented extensively porous-coated femoral components in the management of Vancouver B2 and B3 periprosthetic femoral fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005. 87:1617–1621.26. Roffman M, Mendes DG. Fracture of the femur after total hip arthroplasty. Orthopedics. 1989. 12:1067–1070.
Article27. Ruedi TP, Luscher JN. Results after internal fixation of comminuted fractures of the femor al shaft with DC plates. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1979. 138:74–76.28. Schmidt AH, Kyle RF. Periprosthetic fractures of the femur. Orthop Clin North Am. 2002. 33:143–152.
Article29. Scott RD, Turner RH, Leitzes SM, Aufranc OE. Femoral fractures on conjunction with total hip replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1975. 57:494–501.30. Serocki JH, Chandler RW, Dorr LD. Treatment of fractures about hip prostheses with compression plating. J Arthroplasty. 1992. 7:129–135.
Article31. Wilson D, Marsri BA, Duncan CP. Periprosthetic fractures: an operative algorithm. Orthopedics. 2001. 24:869–870.
Article32. Yoo MC, Kim YY, Lee MH, Kim KT. Fracture of the ipsilateral femur in patients with the total hip arthroplasty. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 1991. 26:1058–1066.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Periprosthetic Femoral Fractures after Hip Arthroplasty
- Treatment of Periprosthetic Femoral Fractures after Hip Arthroplasty
- Recurrent Treatment Failure in Vancouver Classification Type C Periprosthetic Fractures around a Well Fixed Short Femoral Stem
- Treatment of Periprosthetic Femoral Fractures in Hip Arthroplasty
- Decision-Making and Principle of Management in Periprosthetic Femoral Fracture after Total Hip Arthroplasty