Korean J Radiol.
2003 Mar;4(1):19-26. 10.3348/kjr.2003.4.1.19.
Radiofrequency Ablation of the Gastrointestinal Tract with a Stent-Like Electrode: Experimental Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Chosun University College of Medicine, Gwangju, Korea. gangsg@mail.chosun.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Chosun University College of Medicine, Gwangju, Korea.
- 3Department of Occupational and Environmental Medicine, Chosun University College of Medicine, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 754038
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2003.4.1.19
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
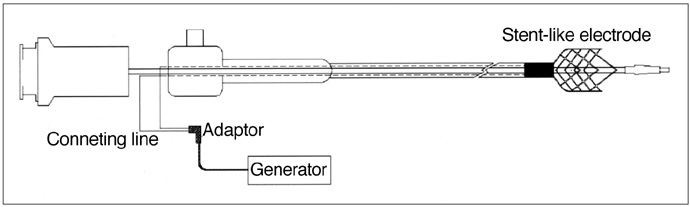
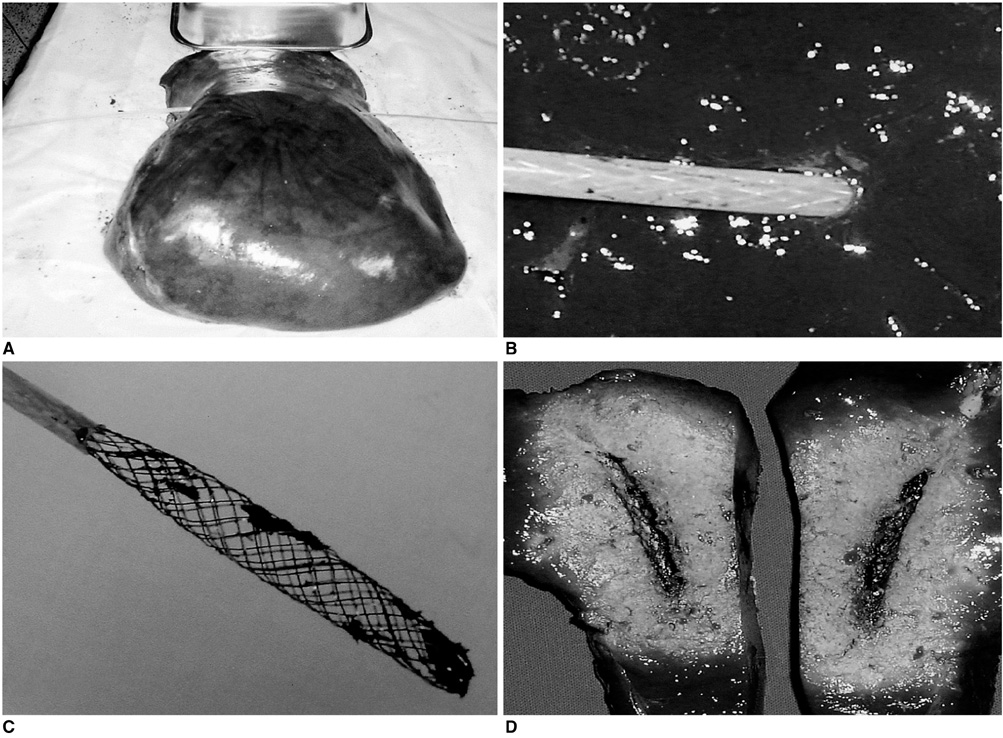
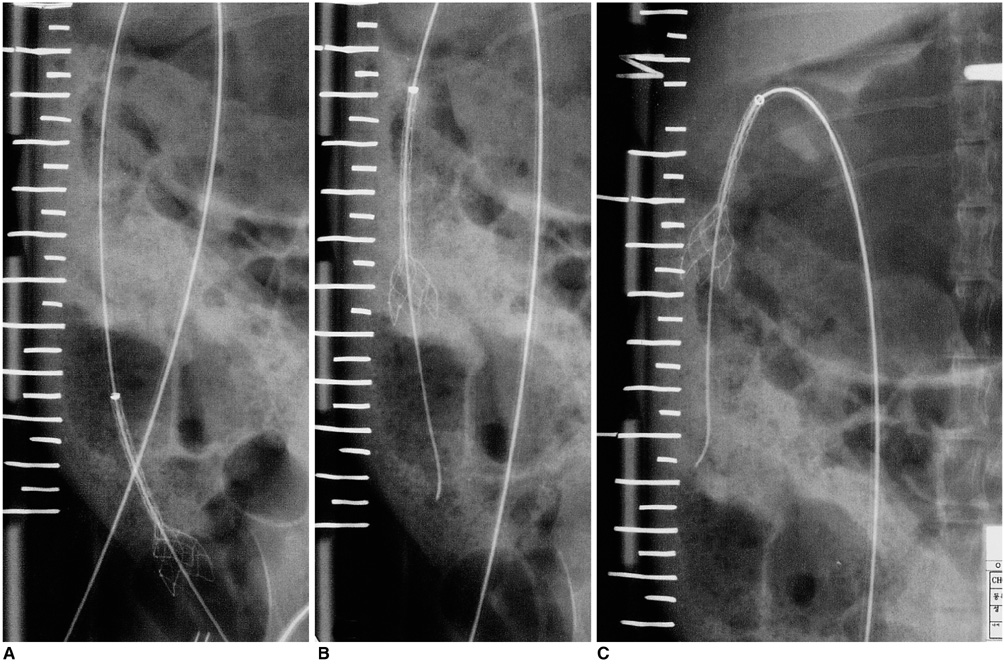
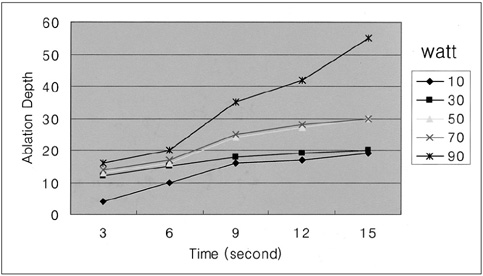
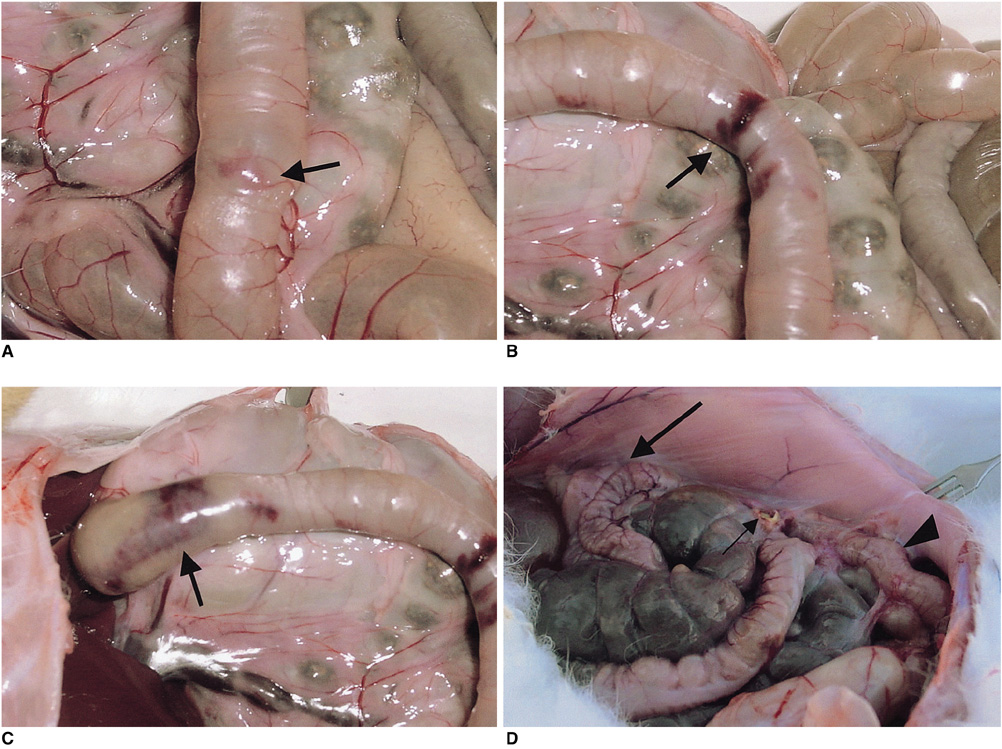
To assess the technical feasibility of a newly designed stent-like electrode in rabbits. MATERIALS AND METHODS: A stent-like electrode was knitted from a single thread of nitinol wire and interconnected to a generator using similar wire. In order to gauge the extent of radiofrequency ablation (RFA), we measured the depth of the ablated area in cow liver using a combination of 180-sec time intervals and 20-watt power increments. For data processing, Cox regression analysis was used. RFA was also applied to the small intestine of rabbits using this stent-like electrode under six different sets of conditions: 10 watts for 1 min, 10 watts for 2 mins, 20 watts for 1 min, 20 watts for 2 mins, 30 watts for 1 min, and 30 watts for 2 mins. To determine the gross and microscopic findings, six animals were sacrificed immediately after the procedure and the results obtained under the different sets of conditions were correlated. Eight rabbits were monitored for 4 weeks prior to sacrifice. RESULTS: For both ex-vivo and in-vivo ablations, the depth of the thermal lesion showed linear correlation with both the duration of RFA and the power applied. RFA of the duodenum was technically successful in all 14 rabbits. The acute changes occurring in the rabbits' small intestine included color change, cytoplasmic denaturation, fibrin deposition and hemorrhage, among which hemorrhage of the mucosal layer was the earliest finding. RF ablation for 2 mins at 30 watts caused serosal hemorrhage. The gross and histologic changes occurring showed close correlation under all six sets of conditions. CONCLUSION: Use of the stent-like electrode proves technically feasible but to determine the nature of the chronic change occurring in the gastrointestinal tract after RF ablation, further investigation and long-term follow-up in animals are required.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Goldberg SN, Gazelle GS, Mueller PR. Thermal ablation therapy for focal malignancy: a unified approach to underlying principles, techniques, and diagnostic imaging guidance. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000. 174:323–331.2. Rossi S, Buscarini E, Garbagnati F, et al. Percutaneous treatment of small hepatic tumors by an expandable RF needle electrode. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1998. 170:1015–1022.3. Livraghi T, Goldberg SN, Meloni F, Solbiati L, Gazelle GS. Hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison of efficacy between percutaneous ethanol instillation and radiofrequency. Radiology. 1999. 210:655–663.4. Seki T, Wakabayashi M, Nakagawa T, et al. Ultrasonically guided microwave coagulation therapy for small hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 1994. 74:817–825.5. Anzai Y, Lufkin R, Desalles A, Hamilton DR, Rarahani K, Black KL. Preliminary experience with MR-guided thermal ablation of brain tumors. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1995. 16:39–48.6. Zlotta AR, Wildschutz T, Raviv G, et al. Radiofrequency interstitial tumor ablation (RITA) is a possible new modality for treatment of renal cancer : in-vivo and in-vivo experience. J Endourol. 1997. 11:251–258.7. Lewin JS, Connell CF, Duerk JL, et al. Interactive MRI-guided radiofrequency interstitial thermal ablation of abdominal tumors: clinical trial for evaluation of safety and feasibility. J Magn Reson Imaging. 1998. 8:40–47.8. Rosenthal DI, Hornicek FJ, Wolfe MW, Jennings LC, Gephart MC, Mankin JH. Percutaneous radiofrequency coagulation of osteoid osteoma compared with operative treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1998. 80-A:815–821.9. Dupuy DE, Goldberg SN. Image-guided radiofrequency tumor ablation: challenges and opportunities, part II. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2001. 12(10):1135–1148.10. Choi DI, Lim HK, Park JM, et al. An experimental study on hepatic ablation using an expandable radio-frequency needle electrode. J Korean Radiol Soc. 1999. 41:1127–1132.11. Lee JD, Lee JM, Kim SW, Kim CS, Mun WS. MR imaging-histopathologic correlation of radiofrequency thermal ablation lesion in a rabbit liver model: observation during acute and chronic stage. Korean J Radiol. 2002. 2(3):151–158.12. Lim HK. Radiofrequency thermal ablation of heptocellular carcinomas. Korean J Radiol. 2000. 1(4):175–184.13. Park HS, Do YS, Suh SW, et al. Upper gastrointestinal tract malignant obstruction: initial results of palliation with a flexible covered stent. Radiology. 1999. 210:865–870.14. Park GH, Cho SG, Kang SG, et al. Intraluminal brachytherapy after metallic stent placement in primary bile duct carcinoma. Korean J Radiol. 2001. 44:675–682.15. Kim IH, Lee DH, Yoo JG, et al. The efficacy of intraluminal radiotherapy after metallic stent insertion in malignant biliary tract obstruction. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 2000. 20:449–455.16. Solbiati L, Goldberg SN, Lerace T, Livraghi T, Sironi S, Gazelle GS. Hepatic metastases: percutaneous radiofrequency ablation with cooled-tip electrodes. Radiology. 1997. 205:367–374.17. Siperstein AE, Gitomirski A. History and technological aspect of radiofrequency thermoablation. Cancer J. 2000. 6:supp.4. s293–s303.18. Goldberg SN, Gazelle GS, Solbiati L, Rittman WJ, Mueller PR. Radiofrequency tissue ablation : increased lesion diameter with a perfusion electrode. Acad Radiol. 1996. 3:636–644.19. Yeh MM, Trembly BS, Douple EB, et al. Theoretical and experimental analysis of air cooling for intracavitary microwave hyperthermia application. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 1994. 41:874–882.20. Lu DS, Raman SS, Vodopich DJ, Wang M, Sayre J, Lassman C. Effect of vessel size on creation of hepatic radiofrequency lesions in pigs: assessment of the "heat-sink" effect. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002. 178(1):47–51.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Endovenous Radiofrequency Ablation using Stent-type Electrode for Varicose Veins: an Experimental Study in Goats
- Radiofrequency Thermal Ablation of Hepatocellular Carcinomas
- New Radiofrequency Device to Reduce Bleeding after Core Needle Biopsy: Experimental Study in a Porcine Liver Model
- Radiofrequency Tissue Ablation with Cooled-Tip Electrodes:An Experimental Study in a Bovine Liver Model on Variables Influencing Lesion Size
- Intraductal Radiofrequency Ablation as a Palliative Treatment for Advanced Malignant Hilar Biliary Obstruction