Korean J Radiol.
2007 Feb;8(1):57-63. 10.3348/kjr.2007.8.1.57.
Interventional Management of Malignant Colorectal Obstruction: Use of Covered and Uncovered Stents
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University, School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. swchoo@smc.samsung.co.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, Dongsan Medical Center, Keimyung University, School of Medicine, Taegu, Korea.
- KMID: 753866
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2007.8.1.57
Abstract
Objective
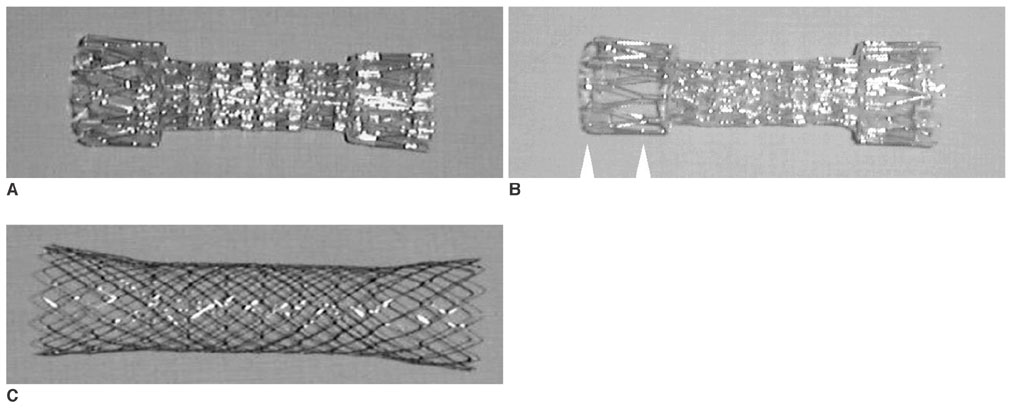
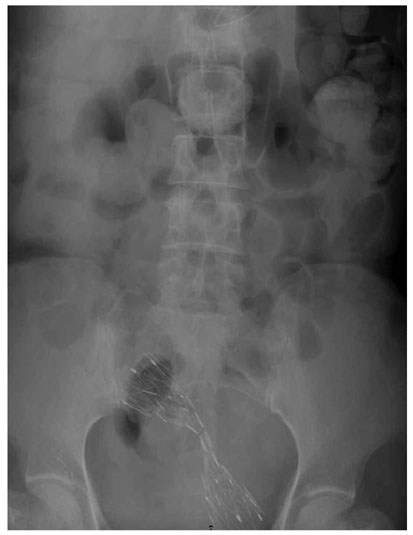
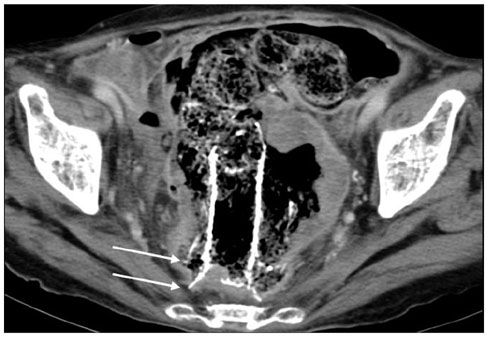
We wanted to evaluate usefulness of uncovered stent in comparison with covered stent for the palliative treatment of malignant colorectal obstruction. Materials and Methods: Covered (n = 52, type 1 and type 2) and uncovered (n = 22, type 3) stents were placed in 74 patients with malignant colorectal obstruction. Stent insertion was performed for palliative treatment in 37 patients (covered stent: n = 23 and uncovered stent: n = 14). In the palliative group, the data on the success of the procedure, the stent patency and the complications between the two groups (covered versus uncovered stents) were compared. Results: The technical success rate was 89% (33/37). Symptomatic improvement was achieved in 86% (18/21) of the covered stent group and in 92% (11/12) of the uncovered stent group patients. The period of follow-up ranged from three to 319 days (mean period: 116+/-85 days). The mean period of stent patency was 157+/-33 days in the covered stent group and 165+/-25 days in the uncovered stent group. In the covered stent group, stent migration (n = 11), stent fracture (n = 2) and poor expansion of the stent (n = 2) were noted. In the uncovered stent group, tumor ingrowth into the stents (n = 3) was noted. Conclusion: Self-expanding metallic stents are effective for relieving malignant colorectal obstruction. The rate of complications is lower in the uncovered stent group than in the covered stent group.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Evidence-Based Recommendations on Colorectal Stenting: A Report from the Stent Study Group of the Korean Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy
Kwang Jae Lee, Sang Woo Kim, Tae Il Kim, Jong-Hoon Lee, Bo-In Lee, Bora Keum, Dae Young Cheung, Chang Heon Yang,
Clin Endosc. 2013;46(4):355-367. doi: 10.5946/ce.2013.46.4.355.
Reference
-
1. Nugent KP, Daniels P, Stewart B, Patankar R, Johnson CD. Quality of life in stoma patients. Dis Colon Rectum. 1999. 42:1569–1574.2. Stone JM, Bloom RJ. Transendoscopic balloon dilatation of complete colonic obstruction. An adjunct in the treatment of colorectal cancer: report of three cases. Dis Colon Rectum. 1989. 32:429–431.3. Spinelli P, Mancini A, Dal Fante M. Endoscopic treatment of gastrointestinal tumors: indications and results of laser photocoagulation and photodynamic therapy. Semin Surg Oncol. 1995. 11:307–318.4. Hoekstra HJ, Verschueren RC, Oldhoff J, van der Ploeg E. Palliative and curative electrocoagulation for rectal cancer. Cancer. 1985. 55:210–213.5. Davids PH, Groen AK, Rauws EA, Tytgat GN, Huibregtse K. Randomised trial of self-expanding metal stents versus polyethylene stents for distal malignant biliary obstruction. Lancet. 1992. 340:1488–1492.6. Bethge N, Sommer A, Vakil N. Palliation of malignant esophageal obstruction due to intrinsic and extrinsic lesions with expandable metal stents. Am J Gastroenterol. 1998. 93:1829–1832.7. Adam A, Morgan R, Ellul J, Mason RC. A new design of the esophageal Wallstent endoprosthesis resistant to distal migration. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1998. 170:1477–1481.8. Dohmoto M. New method: endoscopic implantation of rectal stent in palliative treatment of malignant stenosis. Endoscopia Digestiva. 1991. 3:1507–1512.9. Khot UP, Lang AW, Murali K, Parker MC. Systematic review of the efficacy and safety of colorectal stents. Br J Surg. 2002. 89:1096–1102.10. Keymling M. Colorectal stenting. Endoscopy. 2003. 35:234–238.11. De Gregorio MA, Mainar A, Tejero E, Tobio R, Alfonso E, Pinto I, et al. Acute colorectal obstruction: stent placement for palliative treatment-results of a multicenter study. Radiology. 1998. 209:117–120.12. Camunez F, Echenagusia A, Simo G, Turegano F, Vazquez J, Barreiro-Meiro I. Malignant colorectal obstruction treated by means of self-expanding metallic stents: effectiveness before surgery and in palliation. Radiology. 2000. 216:492–497.13. Repici A, Reggio D, De Angelis C, Barletti C, Marchesa P, Musso A, et al. Covered metal stents for management of inoperable malignant colorectal strictures. Gastrointest Endosc. 2000. 52:735–740.14. Rey JF, Romanczyk T, Greff M. Metal stents for palliation of rectal carcinoma: a preliminary report on 12 patients. Endoscopy. 1995. 27:501–504.15. Kang SG, Jung GS, Cho SG, Kim JG, Oh JH, Song HY, et al. The efficacy of metallic stent placement in the treatment of colorectal obstruction. Korean J Radiol. 2002. 3:79–86.16. Hunerbein M, Krause M, Moesta KT, Rau B, Schlag PM. Palliation of malignant rectal obstruction with self-expanding metal stents. Surgery. 2005. 137:42–47.17. Miyayama S, Matsui O, Kifune K, Yamashiro M, Yamamoto T, Kitagawa K, et al. Malignant colonic obstruction due to extrinsic tumor: palliative treatment with a self-expanding nitinol stent. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000. 175:1631–1637.18. Spinelli P, Mancini A. Use of self-expanding metal stents for palliation of rectosigmoid cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2001. 53:203–206.19. Law WL, Chu KW, Ho JW, Tung HM, Law SY, Chu KM. Self-expanding metallic stent in the treatment of colonic obstruction caused by advanced malignancies. Dis Colon Rectum. 2000. 43:1522–1527.20. Saida Y, Sumiyama Y, Nagao J, Takase M. Stent endoprosthesis for obstruction colorectal cancers. Dis Colon Rectum. 1996. 39:552–555.21. Choo IW, Do YS, Suh SW, Chun HK, Choo SW, Park HS, et al. Malignant colorectal obstruction: treatment with a flexible covered stent. Radiology. 1998. 206:415–421.22. Longo WE, Ballantyne GH, Bilchick AJ, Modlin IM. Advanced rectal cancer. What is the best palliation? Dis Colon Rectum. 1988. 31:842–847.23. Moran MR, Rothenberger DA, Lahr CJ, Buls JG, Goldberg SM. Palliation for rectal cancer. Resection? Anastomosis? Arch Surg. 1987. 122:640–643.24. Mainar A, De Gregorio Ariza MA, Tejero E, Tobio R, Alfonso E, Pinto I, et al. Acute colorectal obstruction: treatment with self-expandable metallic stents before scheduled surgery-results of a multicenter study. Radiology. 1999. 210:65–69.25. Baron TH, Dean PA, Yates MR 3rd, Canon C, Koehler RE. Expandable metal stents for the treatment of colonic obstruction: techniques and outcomes. Gastrointest Endosc. 1998. 47:277–286.26. Liberman H, Adams DR, Blatchford GJ, Ternent CA, Christensen MA, Thorson AG. Clinical use of the self-expanding metallic stent in the management of colorectal cancer. Am J Surg. 2000. 180:407–412.27. Canon Cl, Baron TH, Morgan DE, Dean PA, Koehler RE. Treatment of colonic obstruction with expandable metal stents: radiologic features. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1997. 168:199–205.28. Dauphine CE, Tan P, Beart RW Jr, Vukasin P, Cohen H, Corman ML. Placement of self-expanding metal stents for acute malignant large-bowel obstruction: a collective review. Ann Surg Oncol. 2002. 9:574–579.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Preoperative Colonoscopy for Detection of Synchronous Neoplasms after Insertion of Self-Expandable Metal Stents in Occlusive Colorectal Cancer: Comparison of Covered and Uncovered Stents
- Management of Occluded Biliary Uncovered Metal Stents: Covered Self Expandable Metallic Stent vs. Uncovered Self Expandable Metallic Stent
- Stepwise Algorithmic Approach to Endoscopic Removal of Biliary Partially Covered and Uncovered Self-Expanding Metal Stents (with Videos)
- A Comparison of Covered Expandable Metal Stent and Uncovered Expandable Metal Stent for the Management of Distal Malignant Biliary Obstruction
- Malignant Colorectal obstruction: Treatment with Flexible Covered Stent