Yonsei Med J.
2007 Jun;48(3):546-548. 10.3349/ymj.2007.48.3.546.
Hepatic Artery Pseudoaneurysm Associated with Plastic Biliary Stent
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gastroenterology, Institute of Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, 250 Seongsanno, Seodaemoon-gu, Seoul 120-752, Korea. jbchung@yumc.yonsei.ac.kr
- KMID: 724114
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2007.48.3.546
Abstract
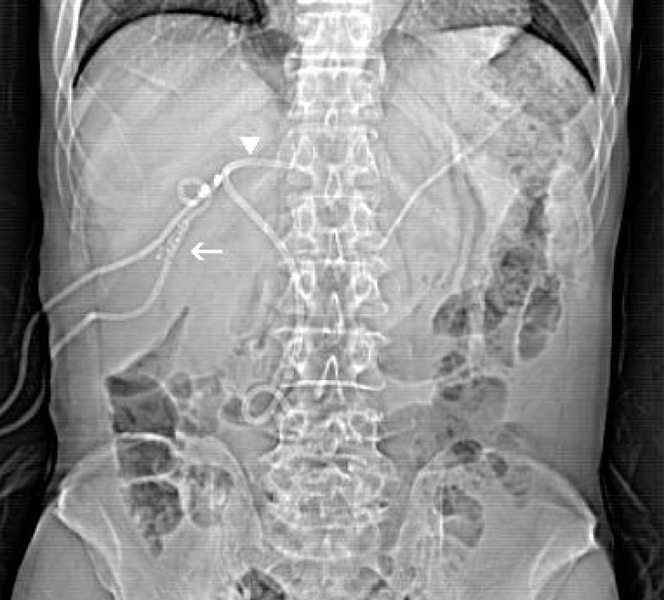
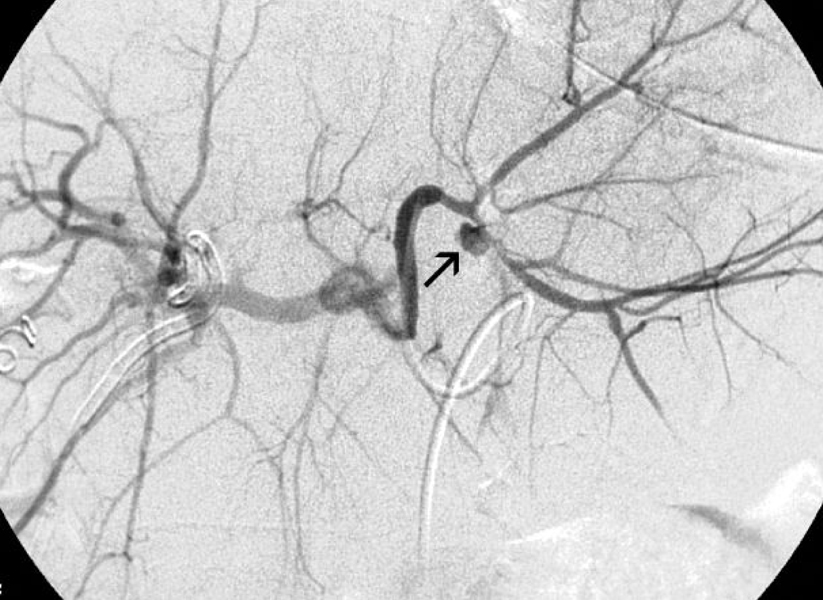
- The increased use of interventional procedures and laparoscopic cholecystectomy in the management of hepatobiliary disorders is associated with an increased incidence of hemobilia and hepatic artery aneurysm. Here we report a case of hepatic artery pseudoaneurysm associated with a plastic biliary stent. Multiple factors were involved in the formation of the hepatic artery aneurysm (HAA) and it was successfully treated by embolization.
MeSH Terms
-
Aneurysm, False/etiology/*therapy
Biliary Tract Surgical Procedures/adverse effects
Embolization, Therapeutic/methods
Female
Hemobilia/etiology/therapy
Hepatic Artery/*pathology/radiography
Humans
Middle Aged
*Stents
Abdominal Injuries/complications
Abdominal Wall/pathology/*surgery
Female
Hernia, Abdominal/etiology/radiography/*surgery
Humans
Middle Aged
Tomography, X-Ray Computed
Treatment Outcome
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Delayed Severe Hemobilia after Endoscopic Biliary Plastic Stent Insertion
Sung Hak Lee, Seung Goun Hong, Kyoung yong Lee, Pyung Kang Park, Sung Du Kim, Mahn Lee, Dong Wook Yu, Man Yong Hong
Clin Endosc. 2016;49(3):303-307. doi: 10.5946/ce.2015.081.
Reference
-
1. Green MH, Duell RM, Johnson CD, Jamieson NV. Hemobilia. Br J Surg. 2001. 88:773–786.2. O'Driscoll D, Olliff SP, Olliff JF. Hepatic artery aneurysm. Br J Radiol. 1999. 72:1018–1025.3. Rai R, Rose J, Manas D. An unusual case of hemobilia. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2003. 15:1357–1359.4. Harlaftis NN, Akin JT. Hemobilia from ruptured hepatic artery aneurysm. Report of a case and review of the literature. Am J Surg. 1977. 133:229–232.5. Vanangunas A, Ehrenpreis E. Endoscopic evacuation of hematobilia induced by large bore self-expanding biliary mesh stent. Gastrointest Endosc. 1991. 37:101–103.
Article6. Lammer J, Neumayer K. Biliary drainage endoprosthesis: experience with 201 placements. Radiology. 1986. 159:625–629.
Article7. Mueller PR, Ferrucci JT Jr, Teplick SK, vanSonnenberg E, Haskin PH, Butch RJ, et al. Biliary stent endoprosthesis: analysis of complications in 113 patients. Radiology. 1985. 156:637–639.
Article8. Monroe PS, Deeter WT, Rizk P. Delayed hemobilia secondary to expandable metal stent. Gastrointest Endosc. 1993. 39:190–191.
Article9. Rai R, Rose J, Manas D. Potentially fatal haemobilia due to inappropriate use of an expanding biliary stent. World J Gastroenterol. 2003. 9:2377–2378.
Article10. Conio M, Caroli-Bosc FX, Buckley M, Chiaramondia M, D'Addazio G, Munizzi F. Massive hematobilia after extraction of plastic biliary endoprosthesis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1997. 25:706.
Article11. Strickland SK, Khoury MB, Kiproff PM, Raves JJ. Cystic artery pseudoaneurysm: a rare cause of hemobilia. Cardiocasc Intervent Radiol. 1991. 14:183–184.
Article12. Fagan EA, Allison DJ, Chadwick VS, Hodgson HJ. Treatment of haemobilia by selective arterial embolization. Gut. 1980. 21:541–544.
Article13. Siersema PD, Hop WC, Dees J, Tilanus HW, van Blankenstein M. Coated self-expanding metal stents versus latex prostheses for esophagogastric cancer with special reference to prior radiation and chemotherapy: a controlled, prospective study. Gastrointest Endosc. 1998. 47:113–120.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pancreaticoduodenal artery pseudoaneurysm-induced hemobilia caused by a plastic biliary stent
- Jejunal Migration of the Stent-Graft Used for Common Hepatic Artery Pseudoaneurysm
- A Case of Hemobilia Developed in a Hepatic Artery Aneurysm after Biliary Stenting
- Endovascular Exclusion of Hepatic Artery Pseudoaneurysm after Living-Donor Liver Transplantation with a Stent-Graft Using Conical Remodeling: A Case Report
- Iatrogenic Pseudoaneurysm of Splanchnic Artery after Hepato-Biliary-Pancreatic Surgery