Ann Clin Microbiol.
2025 Mar;28(1):5. 10.5145/ACM.2025.28.1.5.
A survey on laboratory capacity, testing practices, and management during COVID-19 pandemic response in Korea: a cross-sectional survey study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Gangneung Asan Hospital, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Gangneung, Korea
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Gil Medical Center, Gachon University College of Medicine, Incheon, Korea
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, Gyeongsang National University Hospital, Gyeongsang National University College of Medicine, Jinju, Korea
- 4Department of Laboratory Medicine, Inje University Ilsan Paik Hospital, Goyang, Korea
- 5Department of Laboratory Medicine, Eunpyeong St. Mary’s Hospital, Catholic University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 6Department of Laboratory Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2566601
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5145/ACM.2025.28.1.5
Abstract
- Background
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has significantly impacted global infrastructure. We surveyed laboratories to analyze the changes in testing methods and procedures to improve future pandemic preparedness.
Methods
This study surveyed laboratory physicians and technologists in South Korea and analyzed responses from 126 of 323 institutions. The survey was conducted in May 2023 using the proficiency test of the Korean Association of External Quality Assessment Service and examined the diagnostic procedures, personnel, equipment, and quality control. The survey comprised 15 questions covering respondent demographics, public-private proficiency projects, COVID-19 testing procedures, and laboratory status.
Results
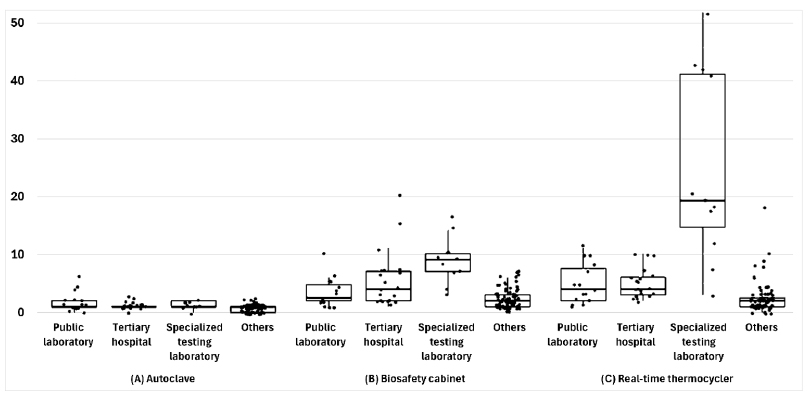
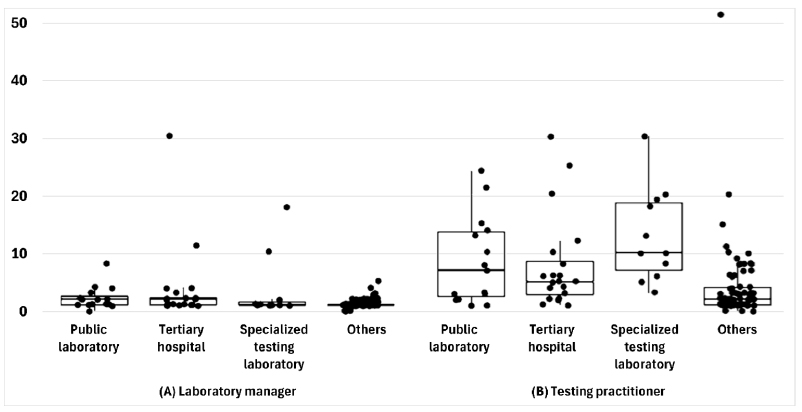
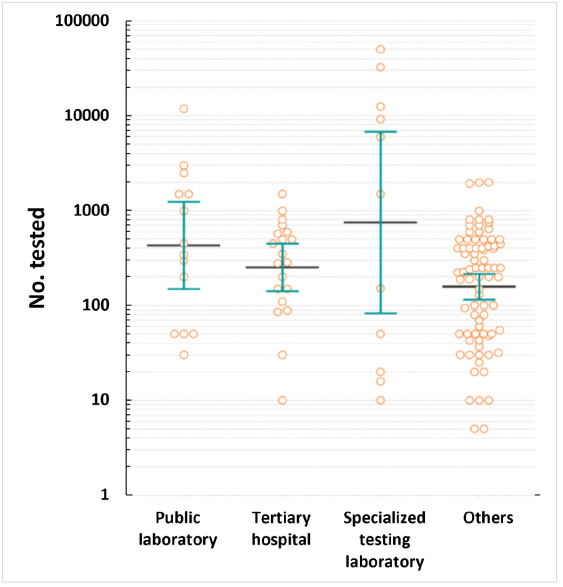
Of the 126 laboratories, 66.7% performed bacterial smear and culture, 65.9% had biosafety level 2 facilities, and 39.7% had separate nucleic acid extraction areas. Furthermore, 98.4% of the laboratories had biological safety cabinets, the median number of PCR machines was four units, and 77.8% had autoclaves. The median numbers of personnel managing and conducting tests were one and three, respectively. Additionally, 88.1% of the laboratories found the COVID-19 proficiency test helpful, with key benefits in terms of accuracy and skill improvement. COVID-19 tests were primarily used for symptomatic or contact person testing, pre-admission screening, and periodic proactive testing. Specialized testing laboratories conducted up to 50,000 tests daily, and tertiary hospitals conducted up to 1,500 tests. Emergency, pooled, and rapid antigen tests were widely used. Most respondents wanted future tests for respiratory viruses, bacteria, and viral diarrhea, indicating a willingness to participate.
Conclusion
Aggressive testing and collaboration between health agencies and laboratories are crucial for managing emerging diseases. Systematic preparations are essential to maintain and strengthen laboratory capabilities for future infectious disease outbreaks.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Chen J, Vullikanti A, Santos J, Venkatramanan S, Hoops S, Mortveit H, et al. Epidemiological and economic impact of COVID-19 in the US. Sci Rep 2021;11:20451.2. Lee C, Apio C, Park T. Estimation of undetected asymptomatic COVID-19 cases in South Korea using a probabilistic model. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2021;18:4946.3. Yimer SA, Booij BB, Tobert G, Hebbeler A, Oloo P, Brangel P, et al. Rapid diagnostic test: a critical need for outbreak preparedness and response for high priority pathogens. BMJ Glob Health 2024;9:e014386.4. Sung H, Yoo CK, Han MG, Lee SW, Lee H, Chun S, et al. Preparedness and rapid implementation of external quality assessment helped quickly increase COVID-19 testing capacity in the Republic of Korea. Clin Chem 2020;66:979–81.5. Kim YJ, Sung H, Ki CS, Hur M. COVID-19 testing in South Korea: current status and the need for faster diagnostics. Ann Lab Med 2020;40:349–50.6. Olalekan A, Iwalokun B, Akinloye OM, Popoola O, Samuel TA, Akinloye O. COVID-19 rapid diagnostic test could contain transmission in low- and middle-income countries. Afr J Lab Med 2020;9:1255.7. Huh HJ, Hong KH, Kim TS, Song SH, Roh KH, Lee H, et al. Surveillance of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) testing in clinical laboratories in Korea. Ann Lab Med 2021;41:225–9.8. Zayed RA, Omran D, Zayed AA. COVID-19 clinical and laboratory diagnosis overview. J Egypt Public Health Assoc 2021;96:25.9. Reidy N, Coetzee H, Roche C, Brazil E, O'Sullivan L, Brady D, et al. SARS-CoV-2 testing and patient waiting times in the emergency department. Ir Med J 2022;115:633.10. Jarrett M, Garrick R, Gaeta A, Lombardi D, Mayo R, McNulty P, et al. Pandemic preparedness: COVID-19 lessons learned in New York's hospitals. Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf 2022;48:475–91.11. Kaufer AM, Theis T, Lau KA, Gray JL, Rawlinson WD. Laboratory biosafety measures involving SARS-CoV-2 and the classification as a Risk Group 3 biological agent. Pathology 2020;52:790–5.12. Naeem W, Zeb H, Rashid MI. Laboratory biosafety measures of SARS-CoV-2 at containment level 2 with particular reference to its more infective variants. Biosaf Health 2022;4:11–4.13. Lee K. Laboratory diagnosis of COVID-19 in Korea. Ewha Med J 2021;44:1–10.14. Hong KH, Kim GJ, Roh KH, Sung H, Lee J, Kim SY, et al. Update of guidelines for laboratory diagnosis of COVID-19 in Korea. Ann Lab Med 2022;42:391–7.15. Dinnes J, Deeks JJ, Berhane S, Taylor M, Adriano A, Davenport C, et al. Rapid, point-of-care antigen and molecular-based tests for diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2020;8:CD013705.16. Kim SY, Lee J, Sung H, Lee H, Han MG, Yoo CK, et al. Pooling upper respiratory specimens for rapid mass screening of COVID-19 by real-time RT-PCR. Emerg Infect Dis 2020;26:246972.17. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Interim guidance for use of pooling procedures in SARS-CoV-2 diagnostic, screening, and surveillance testing. https://stacks.cdc.gov/view/ cdc/90937 [Online] (last visited on 28 February 2025).18. European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). Methodology for estimating point prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 infection by pooled RT-PCR testing. https://www.ecdc. europa.eu/en/publications-data/methodology-estimating-point-prevalence-sars-cov-2infection-pooled-rt-pcr [Online] (last visited on 28 May 2020).19. Scohy A, Anantharajah A, Bodéus M, Kabamba-Mukadi B, Verroken A, Rodriguez-Villalobos H. Low performance of rapid antigen detection test as frontline testing for COVID-19 diagnosis. J Clin Virol 2020;129:104455.20. Lee J, Kim SY, Huh HJ, Kim N, Sung H, Lee H, et al. Clinical performance of the Standard Q COVID-19 rapid antigen test and simulation of its real-world application in Korea. Ann Lab Med 2021;41:588–92.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Survey on Blood Donation Recognition and Korean Red Cross’ Response during COVID-19 Pandemic
- Attitudes and Practices toward Droplet and Airborne Universal Precaution among Nurses during the COVID-19 Outbreak in Indonesia
- Clinical Gastroenterology and Gastrointestinal Endoscopy Practices during the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic in Indonesia: An Online Nationwide Survey
- Difference in the practice of COVID-19 prevention according to the reliability of COVID-19 response among high school students in Korea
- Influence of COVID-19–Induced Anxiety on Job Turnover Intention among Emergency Room Nurses during the COVID-19 Pandemic, the Mediating Effect of Needs Satisfaction: A Cross-Sectional Study