Int J Thyroidol.
2024 Nov;17(2):304-308. 10.11106/ijt.2024.17.2.304.
Diagnosing Dysphagia Due to Thyroid Nodules by Thyroid Ultrasound, a Case Series
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Medicine, Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, IN, USA
- KMID: 2561612
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.11106/ijt.2024.17.2.304
Abstract
- Background and Objectives
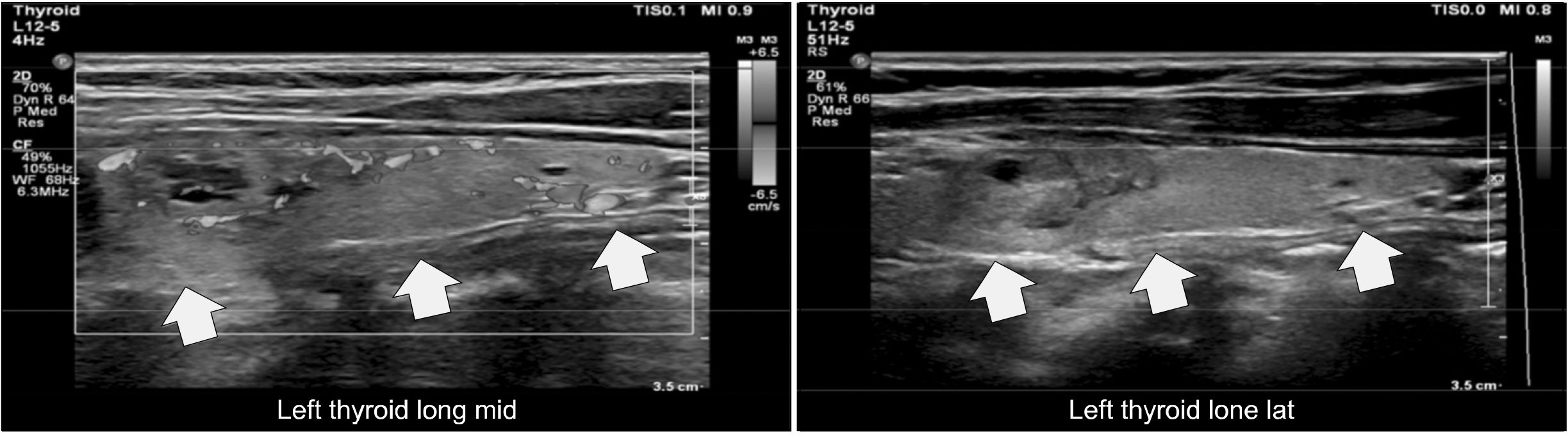
Thyroid nodules can cause dysphagia by direct esophageal compression. Diagnosis of esophageal compression during thyroid ultrasound (US) has not been described.
Materials and Methods
We present a case series of four patients who presented with dysphagia due to compressive thyroid nodules. Thyroid US demonstrated esophageal compression due to the culprit nodules, which were subsequently treated with radiofrequency ablation (RFA). Two benign biopsies were confirmed for each before ablation. Symptom scoring was used to assess the severity of dysphagia before and one month after the procedure.
Results
All patients reported improvement in their dysphagia and a decline in symptom scores a month after the procedure. Thyroid US also demonstrated improvement in esophageal compression at that time.
Conclusion
Thyroid US can be a valuable tool in diagnosing dysphagia due to esophageal compression caused by thyroid nodules.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Chaudhary V, Bano S. 2013; Thyroid ultrasound. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 17(2):219–27. DOI: 10.4103/2230-8210.109667. PMID: 23776892. PMCID: PMC3683194.2. Kim JH, Choi YS, Kim BK, Lee JS, Park Y-H, Hur B. Zenker's diverticulum suspected to be a thyroid nodule diagnosed on fine needle aspiration: a case report. J Med Cases. 2012; 3(4):261–3. DOI: 10.4021/jmc635e.3. Sierra M, Sebag F, De Micco C, Loudot C, Misso C, Calzolari F, et al. 2006; Abrikossoff tumor of the proximal esophagus misdiagnosed as a thyroid nodule. Ann Chir. 131(3):219–21. DOI: 10.1016/j.anchir.2005.09.007. PMID: 16242662.4. Abundiz-Bibiano KE, Rivera-Villanueva R, Roldan-Valadez E, Santiago-Herrera R. 2018; Normal esophagus misdiagnosed as a thyroid nodule by non-radiologist reading thyroid US: case report. Clin Radiol Imaging J. 2(2):000123. DOI: 10.23880/CRIJ-16000123.5. Hamidi O, Callstrom MR, Lee RA, Dean D, Castro MR, Morris JC, et al. 2018; Outcomes of radiofrequency ablation therapy for large benign thyroid nodules: a Mayo Clinic case series. Mayo Clin Proc. 93(8):1018–25. DOI: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2017.12.011. PMID: 29572016.6. Ugurlu MU, Uprak K, Akpinar IN, Attaallah W, Yegen C, Gulluoglu BM. 2015; Radiofrequency ablation of benign symptomatic thyroid nodules: prospective safety and efficacy study. World J Surg. 39(4):961–8. DOI: 10.1007/s00268-014-2896-1. PMID: 25446486.7. Haugen BR. 2017; 2015 American Thyroid Association management guidelines for adult patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer: what is new and what has changed? Cancer. 123(3):372–81. DOI: 10.1002/cncr.30360. PMID: 27741354.8. Verloop H, Louwerens M, Schoones JW, Kievit J, Smit JW, Dekkers OM. 2012; Risk of hypothyroidism following hemithyroidectomy: systematic review and meta-analysis of prognostic studies. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 97(7):2243–55. DOI: 10.1210/jc.2012-1063. PMID: 22511795.9. Christou N, Mathonnet M. 2013; Complications after total thyroidectomy. J Visc Surg. 150(4):249–56. DOI: 10.1016/j.jviscsurg.2013.04.003. PMID: 23746996.10. Bernardi S, Dobrinja C, Carere A, Giudici F, Calabro V, Zanconati F, et al. 2018; Patient satisfaction after thyroid RFA versus surgery for benign thyroid nodules: a telephone survey. Int J Hyperthermia. 35(1):150–8. DOI: 10.1080/02656736.2018.1487590. PMID: 30107758.11. Fuller CW, Nguyen SA, Lohia S, Gillespie MB. 2014; Radiofrequency ablation for treatment of benign thyroid nodules: systematic review. Laryngoscope. 124(1):346–53. DOI: 10.1002/lary.24406. PMID: 24122763.12. Ebert E. 2021. Ultrasound for the confirmation of nasogastric tube placement in the emergency department. Ultrasound;Available from: https://brownemblog.com/blogposts/2021/4/5/ultrasound-for-the-confirmation-of-nasogastric-tube-placement-in-the-emergency-department. cited Aug 20, 2024.13. Ahn JH, Sohn Y. 2020; Application of point-of-care ultrasound for different types of esophageal foreign bodies: three case reports: a CARE-compliant article. Medicine (Baltimore). 99(4):e18893. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000018893. PMID: 31977900. PMCID: PMC7004603.14. Stan MN, Papaleontiou M, Schmitz JJ, Castro MR. 2022; Nonsurgical management of thyroid nodules: the role of ablative therapies. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 107(5):1417–30. DOI: 10.1210/clinem/dgab917. PMID: 34953163. PMCID: PMC9016471.15. Cervelli R, Mazzeo S, De Napoli L, Boccuzzi A, Pontillo-Contillo B, Materazzi G, et al. 2017; Radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of benign thyroid nodules: an efficient and safe alternative to surgery. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 28(10):1400–8. DOI: 10.1016/j.jvir.2017.07.009. PMID: 28844832.16. Che Y, Jin S, Shi C, Wang L, Zhang X, Li Y, et al. 2015; Treatment of benign thyroid nodules: comparison of surgery with radiofrequency ablation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 36(7):1321–5. DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A4276. PMID: 25814656. PMCID: PMC7965284.17. Bernardi S, Giudici F, Cesareo R, Antonelli G, Cavallaro M, Deandrea M, et al. 2020; Five-year results of radiofrequency and laser ablation of benign thyroid nodules: a multicenter study from the italian minimally invasive treatments of the thyroid group. Thyroid. 30(12):1759–70. DOI: 10.1089/thy.2020.0202. PMID: 32578498.18. Ha EJ, Baek JH, Che Y, Chou YH, Fukunari N, Kim JH, et al. 2021; Radiofrequency ablation of benign thyroid nodules: recommendations from the asian conference on tumor ablation task force - secondary publication. J Med Ultrasound. 29(2):77–83. DOI: 10.4103/JMU.JMU_178_20. PMID: 34377636. PMCID: PMC8330684.19. Kim JH, Baek JH, Lim HK, Ahn HS, Baek SM, Choi YJ, et al. 2018; 2017 thyroid radiofrequency ablation guideline: Korean Society of Thyroid Radiology. Korean J Radiol. 19(4):632–55. DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2018.19.4.632. PMID: 29962870. PMCID: PMC6005940.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Elastography of the Thyroid Glands
- Sonographic Evaluation of Thyroid Nodules
- Diagnosis of Parathyroid Adenoma Detected during Thyroid Ultrasound: The Role of Parathormone Measurement in Fine-Needle Aspiration Washout
- Ultrasound (US)-Guided Ablation of Thyroid Nodules
- Indications for Fine Needle Aspiration in Thyroid Nodules