Ann Lab Med.
2024 Nov;44(6):553-561. 10.3343/alm.2023.0405.
Evaluation of Droplet Digital PCR for the Detection of BRAF V600E in Fine-Needle Aspiration Specimens of Thyroid Nodules
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Severance Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Biomedical Laboratory Science, Dankook University, Chungnam, Korea
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, Kyung Hee University College of Medicine, Kyung Hee University Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- 4Department of Laboratory Medicine and Genetics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2560802
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2023.0405
Abstract
- Background
Droplet digital (dd)PCR is a new-generation PCR technique with high precision and sensitivity; however, the positive and negative droplets are not always effectively separated because of the “rain” phenomenon. We aimed to develop a practical optimization and evaluation process for the ddPCR assay and to apply it to the detection of BRAF V600E in fine-needle aspiration (FNA) specimens of thyroid nodules, as an example.
Methods
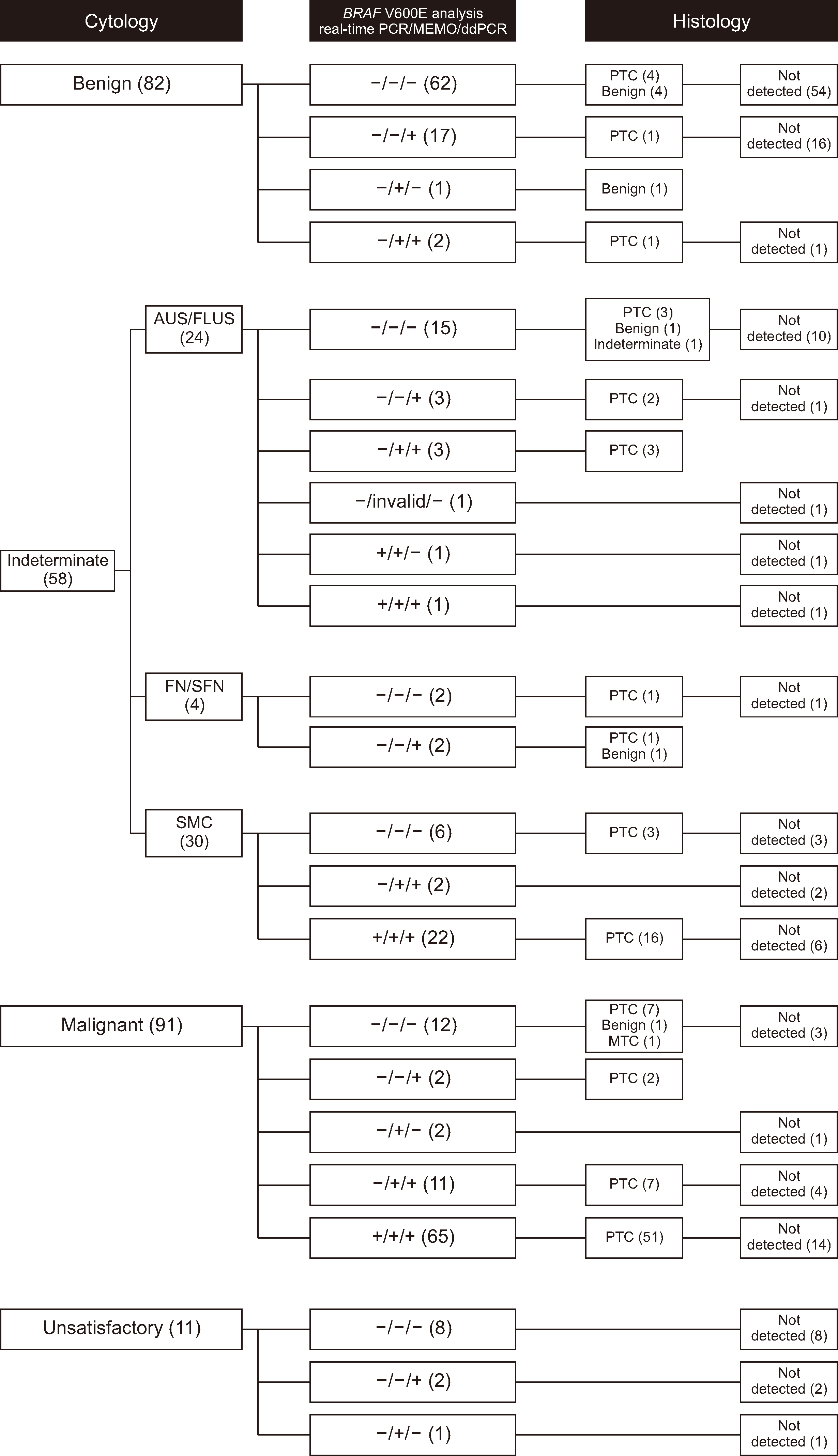
We optimized seven ddPCR parameters that can affect “rain.” Analytical and clinical performance were analyzed based on histological diagnosis after thyroidectomy using a consecutive prospective series of 242 FNA specimens.
Results
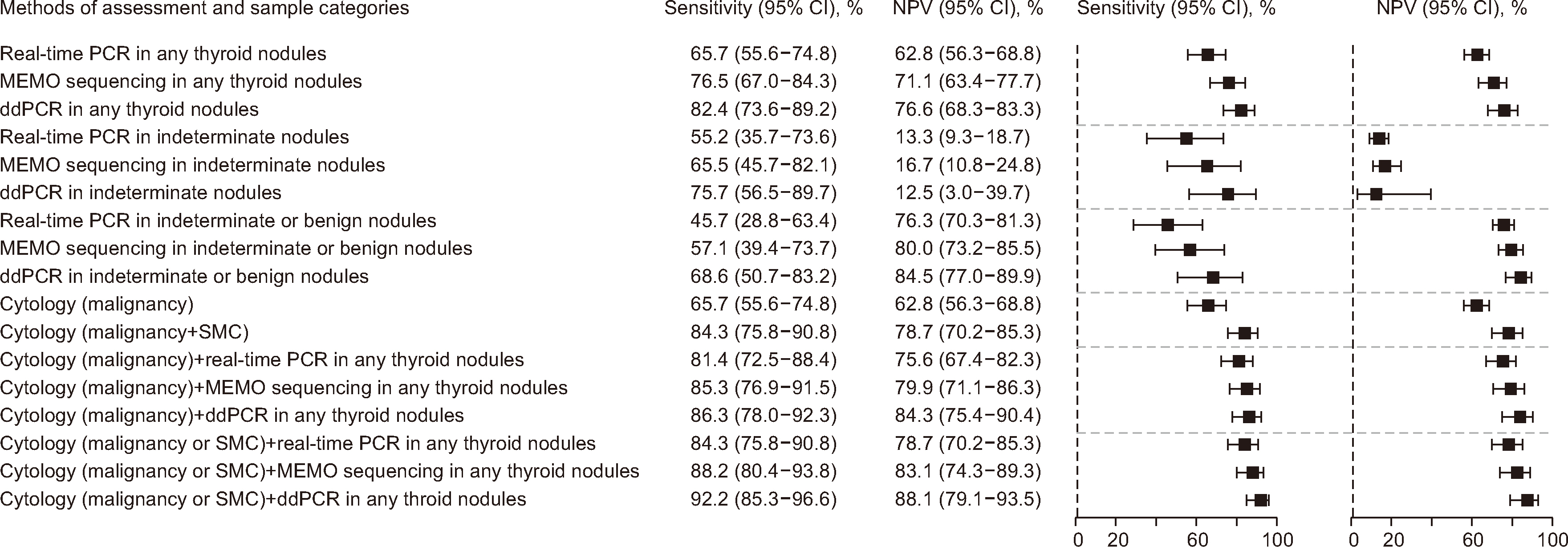
The annealing time and temperature, number of PCR cycles, and primer and probe concentrations were found to be more important considerations for assay optimization than the denaturation time and ramp rate. The limit of blank and 95% limit of detection were 0% and 0.027%, respectively. The sensitivity of ddPCR for histological papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC) was 82.4% (95% confidence interval [CI], 73.6%–89.2%). The pooled sensitivity of BRAF V600E in FNA specimens for histological PTC was 78.6% (95% CI, 75.9%–81.2%, I 2 = 60.6%).
Conclusions
We present a practical approach for optimizing ddPCR parameters that affect the separation of positive and negative droplets to reduce rain. Our approach to optimizing ddPCR parameters can be expanded to general ddPCR assays for specific mutations in clinical laboratories. The highly sensitive ddPCR can compensate for uncertainty in cytological diagnosis by detecting low levels of BRAF V600E.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Huggett JF, Cowen S, Foy CA. 2015; Considerations for digital PCR as an accurate molecular diagnostic tool. Clin Chem. 61:79–88. DOI: 10.1373/clinchem.2014.221366. PMID: 25338683.2. Sreejith KR, Ooi CH, Jin J, Dao DV, Nguyen NT. 2018; Digital polymerase chain reaction technology - recent advances and future perspectives. Lab Chip. 18:3717–32. DOI: 10.1039/C8LC00990B. PMID: 30402632.3. Cao L, Cui X, Hu J, Li Z, Choi JR, Yang Q, et al. 2017; Advances in digital polymerase chain reaction (dPCR) and its emerging biomedical applications. Biosens Bioelectron. 90:459–74. DOI: 10.1016/j.bios.2016.09.082. PMID: 27818047.4. Taylor SC, Carbonneau J, Shelton DN, Boivin G. 2015; Optimization of droplet digital PCR from RNA and DNA extracts with direct comparison to RT-qPCR: clinical implications for quantification of oseltamivir-resistant subpopulations. J Virol Methods. 224:58–66. DOI: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2015.08.014. PMID: 26315318.5. Jones M, Williams J, Gärtner K, Phillips R, Hurst J, Frater J. 2014; Low copy target detection by Droplet Digital PCR through application of a novel open access bioinformatic pipeline, 'definetherain'. J Virol Methods. 202:46–53. DOI: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2014.02.020. PMID: 24598230. PMCID: PMC4003534.6. Gerdes L, Iwobi A, Busch U, Pecoraro S. 2016; Optimization of digital droplet polymerase chain reaction for quantification of genetically modified organisms. Biomol Detect Quantif. 7:9–20. DOI: 10.1016/j.bdq.2015.12.003. PMID: 27077048. PMCID: PMC4827695.7. Hindson BJ, Ness KD, Masquelier DA, Belgrader P, Heredia NJ, Makarewicz AJ, et al. 2011; High-throughput droplet digital PCR system for absolute quantitation of DNA copy number. Anal Chem. 83:8604–10. DOI: 10.1021/ac202028g. PMID: 22035192. PMCID: PMC3216358.8. Witte AK, Mester P, Fister S, Witte M, Schoder D, Rossmanith P. 2016; A systematic investigation of parameters influencing droplet rain in the Listeria monocytogenes prfA assay - reduction of ambiguous results in ddPCR. PLoS One. 11:e0168179. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0168179. PMID: 27992475. PMCID: PMC5167268. PMID: 30f535116df4400e99868a27cff3b017.9. Maier J, Lange T, Cross M, Wildenberger K, Niederwieser D, Franke GN. 2019; Optimized digital droplet PCR for BCR-ABL. J Mol Diagn. 21:27–37. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2018.08.012. PMID: 30347270.10. Xu X, Ma X, Zhang X, Cao G, Tang Y, Deng X, et al. 2019; Detection of BRAF V600E mutation in fine-needle aspiration fluid of papillary thyroid carcinoma by droplet digital PCR. Clin Chim Acta. 491:91–6. DOI: 10.1016/j.cca.2019.01.017. PMID: 30682328.11. Lee ST, Kim SW, Ki CS, Jang JH, Shin JH, Oh YL, et al. 2012; Clinical implication of highly sensitive detection of the BRAF V600E mutation in fine-needle aspirations of thyroid nodules: a comparative analysis of three molecular assays in 4585 consecutive cases in a BRAF V600E mutation-prevalent area. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 97:2299–306. DOI: 10.1210/jc.2011-3135. PMID: 22500044.12. Park KS, Oh YL, Ki CS, Kim JW. 2015; Evaluation of the Real-Q BRAF V600E detection assay in fine-needle aspiration samples of thyroid nodules. J Mol Diagn. 17:431–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmoldx.2015.03.006. PMID: 25937618.13. Choi R, Park KS, Kim JW, Ki CS. 2015; Evaluation of the Anyplex BRAF V600E real-time detection assay using dual-priming oligonucleotide technology in fine-needle aspirates of thyroid nodules. Ann Lab Med. 35:624–9. DOI: 10.3343/alm.2015.35.6.624. PMID: 26354351. PMCID: PMC4579107.14. CLSI. 2020. Evaluation of detection capability for clinical laboratory measurement procedures; approved guideline. 2nd ed. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;Wayne, PA: CLSI EP17-A2.15. CLSI. 2004. Evaluation of precision performance of quantitative measurement methods; approved guideline. 2nd ed. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;Wayne, PA: CLSI EP5-A2.16. Cibas ES, Ali SZ. 2017; The 2017 Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology. Thyroid. 27:1341–6. DOI: 10.1089/thy.2017.0500. PMID: 29091573.17. Alexander EK, Cibas ES. 2022; Diagnosis of thyroid nodules. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 10:533–9. DOI: 10.1016/S2213-8587(22)00101-2. PMID: 35752200.18. Krauss EA, Mahon M, Fede JM, Zhang L. 2016; Application of the Bethesda classification for thyroid fine-needle aspiration: institutional experience and meta-analysis. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 140:1121–31. DOI: 10.5858/arpa.2015-0154-SA. PMID: 27684984.19. Nikiforov YE, Ohori NP, Hodak SP, Carty SE, LeBeau SO, Ferris RL, et al. 2011; Impact of mutational testing on the diagnosis and management of patients with cytologically indeterminate thyroid nodules: a prospective analysis of 1056 FNA samples. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 96:3390–7. DOI: 10.1210/jc.2011-1469. PMID: 21880806. PMCID: PMC3205883.20. Patel KN, Angell TE, Babiarz J, Barth NM, Blevins T, Duh QY, et al. 2018; Performance of a genomic sequencing classifier for the preoperative diagnosis of cytologically indeterminate thyroid nodules. JAMA Surg. 153:817–24. DOI: 10.1001/jamasurg.2018.1153. PMID: 29799911. PMCID: PMC6583881.21. Steward DL, Carty SE, Sippel RS, Yang SP, Sosa JA, Sipos JA, et al. 2019; Performance of a multigene genomic classifier in thyroid nodules with indeterminate cytology: a prospective blinded multicenter study. JAMA Oncol. 5:204–12. DOI: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.4616. PMID: 30419129. PMCID: PMC6439562.22. Cancer Genome Atlas Network. 2014; Integrated genomic characterization of papillary thyroid carcinoma. Cell. 159:676–90. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.09.050. PMID: 25417114. PMCID: PMC4243044.23. Nikiforov YE, Nikiforova MN. 2011; Molecular genetics and diagnosis of thyroid cancer. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 7:569–80. DOI: 10.1038/nrendo.2011.142. PMID: 21878896.24. Xing M. 2013; Molecular pathogenesis and mechanisms of thyroid cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:184–99. DOI: 10.1038/nrc3431. PMID: 23429735. PMCID: PMC3791171.25. Huggett JF, Foy CA, Benes V, Emslie K, Garson JA, Haynes R, et al. 2013; The digital MIQE guidelines: minimum information for publication of quantitative digital PCR experiments. Clin Chem. 59:892–902. DOI: 10.1373/clinchem.2013.206375. PMID: 23570709.26. Huggett JF. dMIQE Group. 2020; The digital MIQE guidelines update: minimum information for publication of quantitative digital PCR experiments for 2020. Clin Chem. 66:1012–29. DOI: 10.1093/clinchem/hvaa125. PMID: 32746458.27. Fnais N, Soobiah C, Al-Qahtani K, Hamid JS, Perrier L, Straus SE, et al. 2015; Diagnostic value of fine needle aspiration BRAF(V600E) mutation analysis in papillary thyroid cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hum Pathol. 46:1443–54. DOI: 10.1016/j.humpath.2015.06.001. PMID: 26232865.28. Li C, Lee KC, Schneider EB, Zeiger MA. 2012; BRAF V600E mutation and its association with clinicopathological features of papillary thyroid cancer: a meta-analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 97:4559–70. DOI: 10.1210/jc.2012-2104. PMID: 23055546. PMCID: PMC3513529.29. Liu C, Chen T, Liu Z. 2016; Associations between BRAF(V600E) and prognostic factors and poor outcomes in papillary thyroid carcinoma: a meta-analysis. World J Surg Oncol. 14:241. DOI: 10.1186/s12957-016-0979-1. PMID: 27600854. PMCID: PMC5012084.30. Moon S, Song YS, Kim YA, Lim JA, Cho SW, Moon JH, et al. 2017; Effects of coexistent BRAFV600E and TERT promoter mutations on poor clinical outcomes in papillary thyroid cancer: a meta-analysis. Thyroid. 27:651–60. DOI: 10.1089/thy.2016.0350. PMID: 28181854.31. Xing M, Alzahrani AS, Carson KA, Shong YK, Kim TY, Viola D, et al. 2015; Association between BRAF V600E mutation and recurrence of papillary thyroid cancer. J Clin Oncol. 33:42–50. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2014.56.8253. PMID: 25332244. PMCID: PMC4268252.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evaluation of the Anyplex BRAF V600E Real-Time Detection Assay Using Dual-Priming Oligonucleotide Technology in Fine-Needle Aspirates of Thyroid Nodules
- Role of BRAF(V600E) Mutation Analysis for Thyroid Nodules Classified as Indeterminate on Ultrasonography
- Diagnostic value of BRAF(V600E) mutation analysis in fine needle aspiration for evaluation of thyroid nodules
- Analysis of the BRAF(V600E) Mutation in Thyroid Nodules: the Preoperative Diagnostic Role of Fine-needle Aspiration Biopsy for Patients with Papillary Thyroid Cancer and Its Impact on Patient Care
- Prevalence of the B Type Raf Kinase V600E Mutation in Cytologically Indeterminate Thyroid Nodules: Correlation with Ultrasonographic and Pathologic Features