Ann Lab Med.
2024 Nov;44(6):497-506. 10.3343/alm.2023.0425.
Diagnostic Accuracy of Plasma Renin Concentration and Renin Activity in Predicting Mortality and Kidney Outcomes in Patients With Septic Shock and Hypoperfusion or Hypotension: A Multicenter, Prospective, Observational Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Emergency Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Emergency Medicine, College of Medicine, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon, Korea
- 3Department of Emergency Medicine, College of Medicine, Hanyang University, Seoul, Korea
- 4Department of Critical Care Medicine, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 5Department of Critical Care Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 6Department of Emergency Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2560796
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2023.0425
Abstract
- Background
Lactate is a commonly used biomarker for sepsis, although it has limitations in certain cases, suggesting the need for novel biomarkers. We evaluated the diagnostic accuracy of plasma renin concentration and renin activity for mortality and kidney outcomes in patients with sepsis with hypoperfusion or hypotension.
Methods
This was a multicenter, prospective, observational study of 117 patients with septic shock treated at three tertiary emergency departments between September 2021 and October 2022. The accuracy of renin activity, renin, and lactate concentrations in predicting 28-day mortality, acute kidney injury (AKI), and renal replacement requirement was assessed using the area under the ROC curve (AUC) analysis.
Results
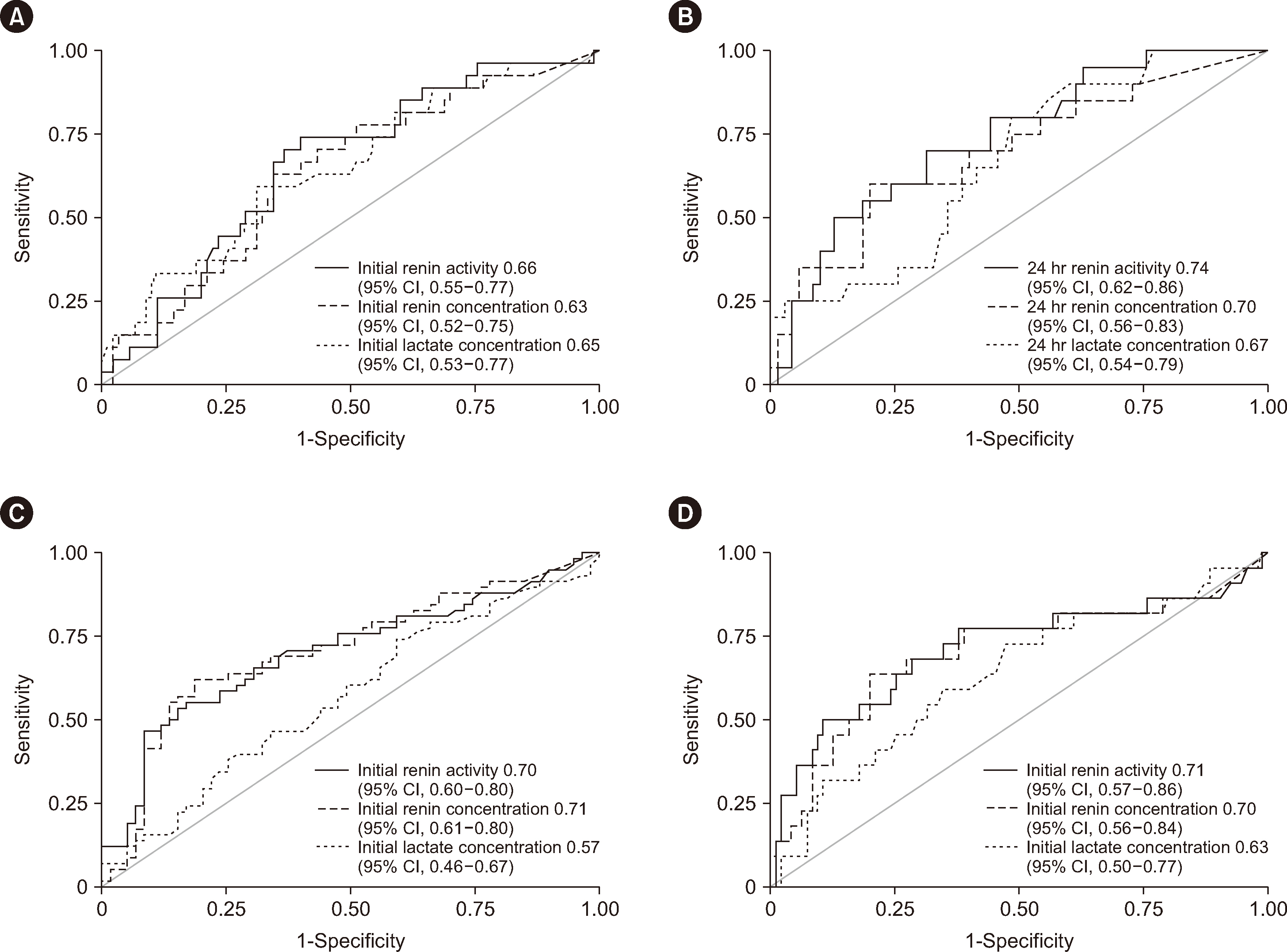
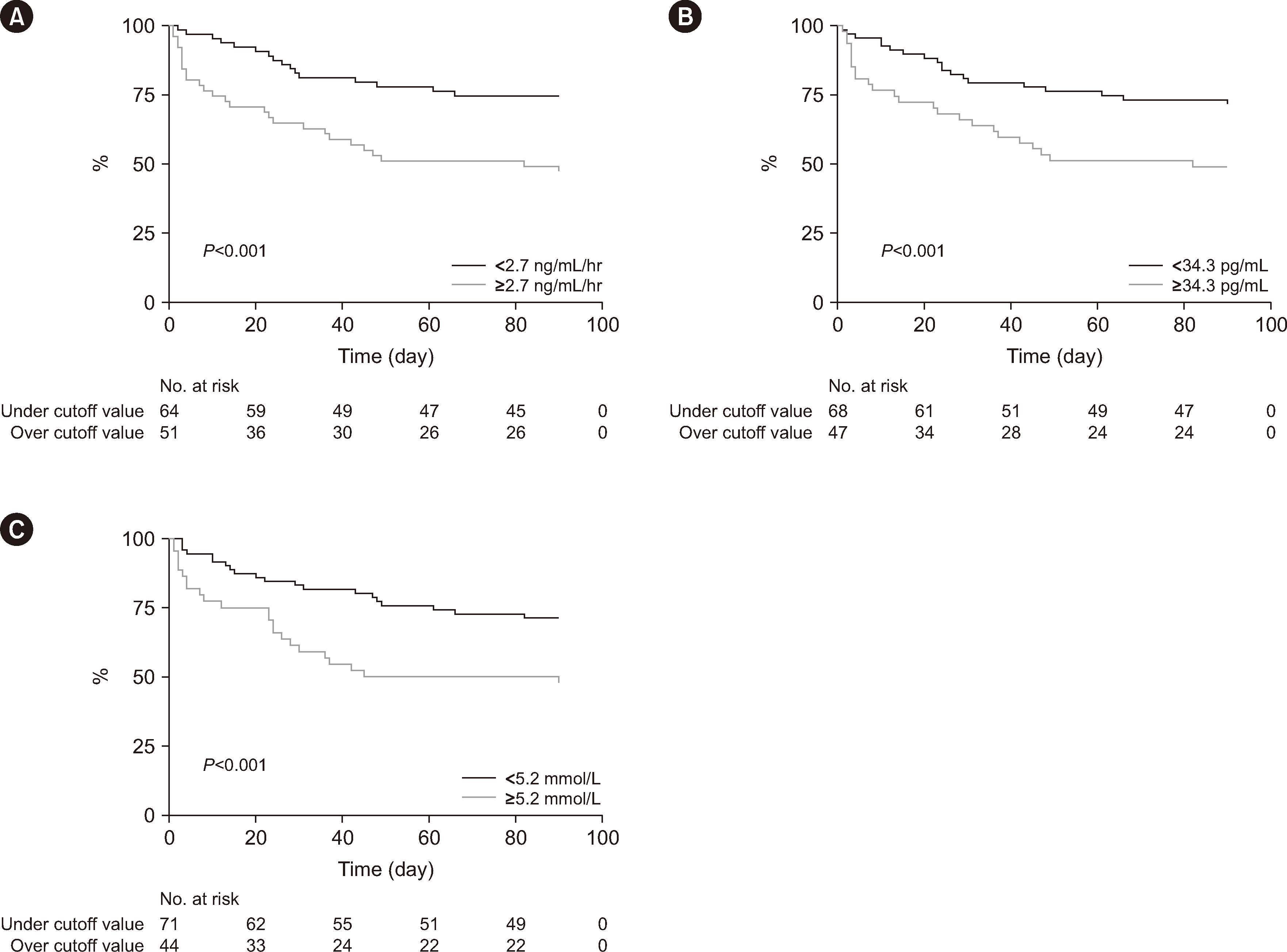
The AUCs of initial renin activity, renin, and lactate concentrations for predicting 28-day mortality were 0.66 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.55–0.77), 0.63 (95% CI, 0.52–0.75), and 0.65 (95% CI, 0.53–0.77), respectively, and those at 24 hrs were 0.74 (95% CI, 0.62–0.86), 0.70 (95% CI, 0.56–0.83), and 0.67 (95% CI, 0.54–0.79). Renin concentrations and renin activity outperformed initial lactate concentrations in predicting AKI within 14 days. The AUCs of renin and lactate concentrations were 0.71 (95% CI, 0.61–0.80) and 0.57 (95% CI, 0.46–0.67), respectively (P = 0.030). The AUC of renin activity (0.70; 95% CI, 0.60–0.80) was also higher than that of lactate concentration (P = 0.044).
Conclusions
Renin concentration and renin activity show comparable performance to lactate concentration in predicting 28-day mortality in patients with septic shock but superior performance in predicting AKI.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Elbers PW, Ince C. 2006; Mechanisms of critical illness-classifying microcirculatory flow abnormalities in distributive shock. Crit Care. 10:221. DOI: 10.1186/cc4969. PMID: 16879732. PMCID: PMC1750971.2. Fleischmann C, Scherag A, Adhikari NK, Hartog CS, Tsaganos T, Schlattmann P, et al. 2016; Assessment of global incidence and mortality of hospital-treated sepsis. Current estimates and limitations. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 193:259–72. DOI: 10.1164/rccm.201504-0781OC. PMID: 26414292.3. Moore JX, Donnelly JP, Griffin R, Howard G, Safford MM, Wang HE. 2016; Defining sepsis mortality clusters in the United States. Crit Care Med. 44:1380–7. DOI: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000001665. PMID: 27105174. PMCID: PMC4911271.4. Namgung M, Ahn C, Park Y, Kwak IY, Lee J, Won M. 2023; Mortality among adult patients with sepsis and septic shock in Korea: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Exp Emerg Med. 10:157–71. DOI: 10.15441/ceem.23.005. PMID: 36882054. PMCID: PMC10350360. PMID: 419bda7536834d6eb6551c66ec5dab10.5. Suh GJ, Shin TG, Kwon WY, Kim K, Jo YH, Choi SH, et al. 2023; Hemodynamic management of septic shock: beyond the Surviving Sepsis Campaign guidelines. Clin Exp Emerg Med. 10:255–64. DOI: 10.15441/ceem.23.065. PMID: 37439141. PMCID: PMC10579730. PMID: cfdb2d2475f247518a1673ed7afb15f3.6. Evans L, Rhodes A, Alhazzani W, Antonelli M, Coopersmith CM, French C, et al. 2021; Surviving sepsis campaign: international guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock 2021. Crit Care Med. 49:e1063–143. DOI: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000005337. PMID: 34605781.7. Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW, Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, et al. 2016; The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA. 315:801–10. DOI: 10.1001/jama.2016.0287. PMID: 26903338. PMCID: PMC4968574.8. Gu WJ, Zhang Z, Bakker J. 2015; Early lactate clearance-guided therapy in patients with sepsis: a meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis of randomized controlled trials. Intensive Care Med. 41:1862–3. DOI: 10.1007/s00134-015-3955-2. PMID: 26154408.9. Simpson SQ, Gaines M, Hussein Y, Badgett RG. 2016; Early goal-directed therapy for severe sepsis and septic shock: a living systematic review. J Crit Care. 36:43–8. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2016.06.017. PMID: 27546746.10. Gómez-Ramos JJ, Marín-Medina A, Prieto-Miranda SE, Dávalos-Rodríguez IP, Alatorre-Jiménez MA, Esteban-Zubero E. 2018; Determination of plasma lactate in the emergency department for the early detection of tissue hypoperfusion in septic patients. Am J Emerg Med. 36:1418–22. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajem.2017.12.068. PMID: 29291989.11. Kraut JA, Madias NE. 2014; Lactic acidosis. N Engl J Med. 371:2309–19. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMra1309483. PMID: 25494270.12. Casserly B, Phillips GS, Schorr C, Dellinger RP, Townsend SR, Osborn TM, et al. 2015; Lactate measurements in sepsis-induced tissue hypoperfusion: results from the Surviving Sepsis Campaign database. Crit Care Med. 43:567–73. DOI: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000000742. PMID: 25479113.13. Bakker J, Nijsten MW, Jansen TC. 2013; Clinical use of lactate monitoring in critically ill patients. Ann Intensive Care. 3:12. DOI: 10.1186/2110-5820-3-12. PMID: 23663301. PMCID: PMC3654944.14. Paul M, Poyan Mehr A, Kreutz R. 2006; Physiology of local renin-angiotensin systems. Physiol Rev. 86:747–803. DOI: 10.1152/physrev.00036.2005. PMID: 16816138.15. Harrison-Bernard LM. 2009; The renal renin-angiotensin system. Adv Physiol Educ. 33:270–4. DOI: 10.1152/advan.00049.2009. PMID: 19948673.16. Fyhrquist F, Saijonmaa O. 2008; Renin-angiotensin system revisited. J Intern Med. 264:224–36. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.2008.01981.x. PMID: 18793332. PMCID: PMC7166930.17. Chung KS, Song JH, Jung WJ, Kim YS, Kim SK, Chang J, et al. 2017; Implications of plasma renin activity and plasma aldosterone concentration in critically ill patients with septic shock. Korean J Crit Care Med. 32:142–53. DOI: 10.4266/kjccm.2017.00094. PMID: 31723628. PMCID: PMC6786707. PMID: 7cfb1c9a24dc4bde8233c8ccb3f28911.18. Bellomo R, Forni LG, Busse LW, McCurdy MT, Ham KR, Boldt DW, et al. 2020; Renin and survival in patients given angiotensin II for catecholamine-resistant vasodilatory shock. A clinical trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 202:1253–61. DOI: 10.1164/rccm.201911-2172OC. PMID: 32609011. PMCID: PMC7605187.19. Gleeson PJ, Crippa IA, Mongkolpun W, Cavicchi FZ, Van Meerhaeghe T, Brimioulle S, et al. 2019; Renin as a marker of tissue-perfusion and prognosis in critically ill patients. Crit Care Med. 47:152–8. DOI: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000003544. PMID: 30653055.20. Campbell DJ, Nussberger J, Stowasser M, Danser AH, Morganti A, Frandsen E, et al. 2009; Activity assays and immunoassays for plasma renin and prorenin: information provided and precautions necessary for accurate measurement. Clin Chem. 55:867–77. DOI: 10.1373/clinchem.2008.118000. PMID: 19264850.21. Nguyen M, Denimal D, Dargent A, Guinot PG, Duvillard L, Quenot JP, et al. 2019; Plasma renin concentration is associated with hemodynamic deficiency and adverse renal outcome in septic shock. Shock. 52:e22–30. DOI: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000001285. PMID: 30407370.22. Leśnik P, Łysenko L, Krzystek-Korpacka M, Woźnica-Niesobska E, Mierzchała-Pasierb M, Janc J. 2022; Renin as a marker of tissue perfusion, septic shock and mortality in septic patients: a prospective observational study. Int J Mol Sci. 23:9133. DOI: 10.3390/ijms23169133. PMID: 36012398. PMCID: PMC9409106. PMID: 8b3457675e054b0bb7b2f171c75b4b87.23. Park H, Shin TG, Kim WY, Jo YH, Hwang YJ, Choi SH, et al. 2022; A quick Sequential Organ Failure Assessment-negative result at triage is associated with low compliance with sepsis bundles: a retrospective analysis of a multicenter prospective registry. Clin Exp Emerg Med. 9:84–92. DOI: 10.15441/ceem.22.230. PMID: 35843608. PMCID: PMC9288871. PMID: fce8323a50a3480abd838598d0ee6a85.24. GC labs. Renin activity [LC/MS-MS]. https://gclabs.co.kr/test/item/view?code=N883.25. DRG Instruments GmbH. DRG Renin (active) ELISA (EIA-5125). https://www.drg-diagnostics.de/49-1-DRG+Renin+active+ELISA.html.26. Khwaja A. 2012; KDIGO clinical practice guidelines for acute kidney injury. Nephron Clin Pract. 120:c179–84. DOI: 10.1159/000339789. PMID: 22890468.27. Závada J, Hoste E, Cartin-Ceba R, Calzavacca P, Gajic O, Clermont G, et al. 2010; A comparison of three methods to estimate baseline creatinine for RIFLE classification. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 25:3911–8. DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfp766. PMID: 20100732.28. Jentzer JC, Vallabhajosyula S, Khanna AK, Chawla LS, Busse LW, Kashani KB. 2018; Management of refractory vasodilatory shock. Chest. 154:416–26. DOI: 10.1016/j.chest.2017.12.021. PMID: 29329694.29. Lee GT, Hwang SY, Park JE, Jo IJ, Kim WY, Chung SP, et al. 2021; Diagnostic accuracy of lactate levels after initial fluid resuscitation as a predictor for 28 day mortality in septic shock. Am J Emerg Med. 46:392–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajem.2020.10.020. PMID: 33092937.30. Jeyaraju M, McCurdy MT, Levine AR, Devarajan P, Mazzeffi MA, Mullins KE, et al. 2022; Renin kinetics are superior to lactate kinetics for predicting in-hospital mortality in hypotensive critically ill patients. Crit Care Med. 50:50–60. DOI: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000005143. PMID: 34166293.31. Doerschug KC, Delsing AS, Schmidt GA, Ashare A. 2010; Renin-angiotensin system activation correlates with microvascular dysfunction in a prospective cohort study of clinical sepsis. Crit Care. 14:R24. DOI: 10.1186/cc8887. PMID: 20175923. PMCID: PMC2875539.32. Khanna A, English SW, Wang XS, Ham K, Tumlin J, Szerlip H, et al. 2017; Angiotensin II for the Treatment of Vasodilatory Shock. N Engl J Med. 377:419–30. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1704154. PMID: 28528561.33. Puskarich MA, Trzeciak S, Shapiro NI, Albers AB, Heffner AC, Kline JA, et al. 2013; Whole blood lactate kinetics in patients undergoing quantitative resuscitation for severe sepsis and septic shock. Chest. 143:1548–53. DOI: 10.1378/chest.12-0878. PMID: 23740148. PMCID: PMC3673659.34. Kang YR, Um SW, Koh WJ, Suh GY, Chung MP, Kim H, et al. 2011; Initial lactate level and mortality in septic shock patients with hepatic dysfunction. Anaesth Intensive Care. 39:862–7. DOI: 10.1177/0310057X1103900510. PMID: 21970130.35. Ha TS, Shin TG, Jo IJ, Hwang SY, Chung CR, Suh GY, et al. 2016; Lactate clearance and mortality in septic patients with hepatic dysfunction. Am J Emerg Med. 34:1011–5. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajem.2016.02.053. PMID: 26976769.36. Romejko K, Markowska M, Niemczyk S. 2023; The review of current knowledge on neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL). Int J Mol Sci. 24:10470. DOI: 10.3390/ijms241310470. PMID: 37445650. PMCID: PMC10341718. PMID: 9faf4d8310e2460aa7c6b3fd0e3c7470.37. Pan HC, Yang SY, Chiou TT, Shiao CC, Wu CH, Huang CT, et al. 2022; Comparative accuracy of biomarkers for the prediction of hospital-acquired acute kidney injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Care. 26:349. DOI: 10.1186/s13054-022-04223-6. PMID: 36371256. PMCID: PMC9652605. PMID: 4500d9b124fc471a870bcfc365d2b2f5.38. Macdonald SPJ, Stone SF, Neil CL, van Eeden PE, Fatovich DM, Arendts G, et al. 2014; Sustained elevation of resistin, NGAL and IL-8 are associated with severe sepsis/septic shock in the emergency department. PLoS One. 9:e110678. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0110678. PMID: 25343379. PMCID: PMC4208806. PMID: f0a67426bc2c49529a4e3927be22b38c.39. Macdonald SPJ, Bosio E, Neil C, Arendts G, Burrows S, Smart L, et al. 2017; Resistin and NGAL are associated with inflammatory response, endothelial activation and clinical outcomes in sepsis. Inflamm Res. 66:611–9. DOI: 10.1007/s00011-017-1043-5. PMID: 28424824.40. Zhang A, Cai Y, Wang PF, Qu JN, Luo ZC, Chen XD, et al. 2016; Diagnosis and prognosis of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin for acute kidney injury with sepsis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Care. 20:41. DOI: 10.1186/s13054-016-1212-x. PMID: 26880194. PMCID: PMC4754917.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Periperal Plasma Renin Activity in Children with Normotensive Reflux Nephropathy
- Role of vasopressin in current anesthetic practice
- Change of plasma renin activity between pre and post-ESWL
- Changes of Plasma Renin Activity by Age and its Diurnal Variation in Children
- A Study on the Change of Plasma Renin Activity(PRA) and Aldosterone Concentration(PAC) before and after Heart Operation in Children with Congenital Heart Disease