J Korean Med Sci.
2024 Oct;39(40):e266. 10.3346/jkms.2024.39.e266.
Efficacy of Bifidobacterium longum and Lactobacillus plantarum (NVP-1703) in Children With Allergic Rhinitis: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea
- 2PB Department, NVP Healthcare Co., Ltd., Suwon, Korea
- 3Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2560664
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2024.39.e266
Abstract
- Background
There is increasing evidence that probiotics are effective in treating allergic rhinitis (AR), while some controversies remain. This study was performed to evaluate the therapeutic effect and safety of a mixture of Bifidobacterium longum and Lactobacillus plantarum (NVP-1703) in children with AR.
Methods
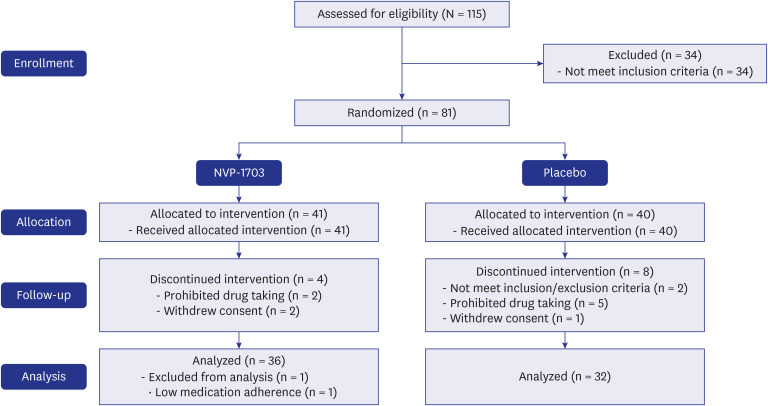
In a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study, children aged 6 to 19 years with perennial AR were treated with NVP-1703 at a dose of 1 × 1010 CFU/day or placebo once a day for 4 weeks. Total nasal symptom score (TNSS), nasal symptom duration score (NSDS), quality of life (QoL), allergic inflammatory markers, and safety parameters were evaluated.
Results
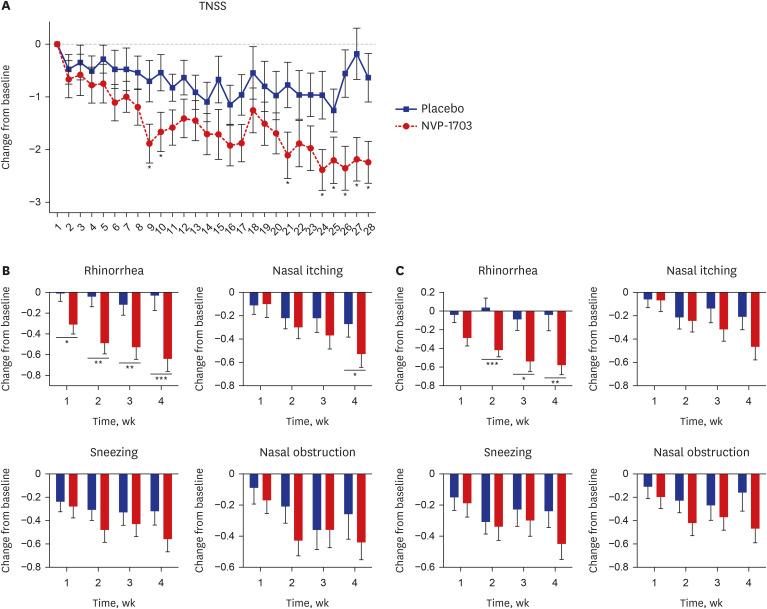
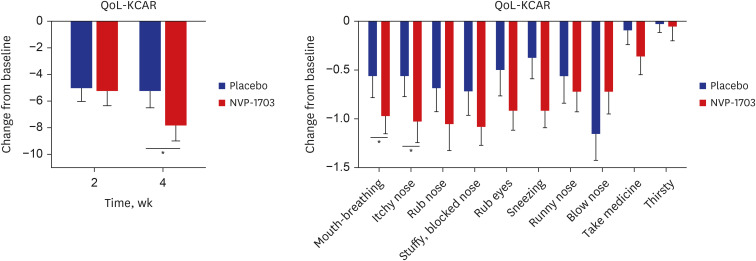
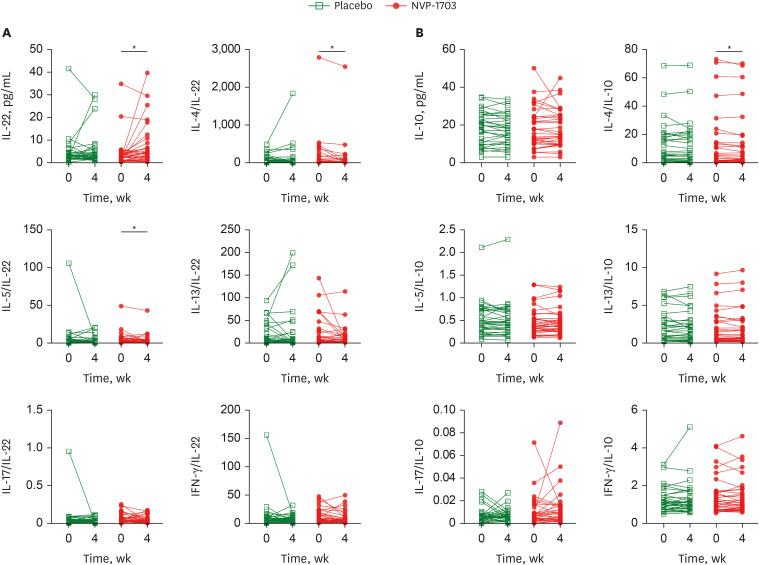
After 4 weeks of treatment, the TNSS in the NVP-1703 group significantly decreased compared to that in the placebo group (P = 0.011), both in the morning and the evening (P = 0.031 and P = 0.004, respectively). The NSDS also significantly decreased in the NVP-1703 group compared to that in the placebo group (P = 0.018). QoL scores, particularly those related to mouth breathing and itchy nose, showed a significant improvement in the NVP-1703 group compared to the placebo group. The ratios of interleukin (IL)-4/IL-22 and IL-5/IL-22 were significantly reduced in the NVP-1703 group after the treatment compared to the baseline values. No notable adverse events were reported in the NVP-1703 group.
Conclusion
Oral administration of a mixture of B. longum and L. plantarum (NVP-1703) improved both AR symptoms and QoL in children with perennial AR, accompanied by decreases in the ratios of T helper 2 cytokines to IL-22.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Meltzer EO. Allergic rhinitis: burden of illness, quality of life, comorbidities, and control. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2016; 36(2):235–248. PMID: 27083099.2. D’Elia C, Gozal D, Bruni O, Goudouris E, Meira E Cruz M. Allergic rhinitis and sleep disorders in children - coexistence and reciprocal interactions. J Pediatr (Rio J). 2022; 98(5):444–454. PMID: 34979134.3. Yamasaki A, Burks CA, Bhattacharyya N. Cognitive and quality of life-related burdens of illness in pediatric allergic airway disease. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020; 162(4):566–571. PMID: 32122241.4. Rusu E, Enache G, Cursaru R, Alexescu A, Radu R, Onila O, et al. Prebiotics and probiotics in atopic dermatitis. Exp Ther Med. 2019; 18(2):926–931. PMID: 31384325.5. West CE, Jenmalm MC, Kozyrskyj AL, Prescott SL. Probiotics for treatment and primary prevention of allergic diseases and asthma: looking back and moving forward. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2016; 12(6):625–639. PMID: 26821735.6. Jeong K, Kim M, Jeon SA, Kim YH, Lee S. A randomized trial of Lactobacillus rhamnosus IDCC 3201 tyndallizate (RHT3201) for treating atopic dermatitis. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2020; 31(7):783–792. PMID: 32363613.7. Farahmandi K, Mohr AE, McFarland LV. Effects of probiotics on allergic rhinitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2022; 36(4):440–450. PMID: 35099301.8. Ried K, Travica N, Paye Y, Sali A. Effects of a probiotic formulation on Seasonal allergic rhinitis in adults-a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial: the probiotics for hay fever trial. Front Nutr. 2022; 9:887978. PMID: 35677549.9. Yang J, Bae J, Choi CY, Choi SP, Yun HS, Chun T. Oral administration of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum NR16 isolated from Kimchi ameliorates murine allergic rhinitis. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2022; 75(1):152–160. PMID: 35388497.10. Ren J, Zhao Y, Huang S, Lv D, Yang F, Lou L, et al. Immunomodulatory effect of Bifidobacterium breve on experimental allergic rhinitis in BALB/c mice. Exp Ther Med. 2018; 16(5):3996–4004. PMID: 30344677.11. Ahmed M, Billoo AG, Iqbal K. Efficacy of probiotic in perennial allergic rhinitis under five year children: a randomized controlled trial. Pak J Med Sci. 2019; 35(6):1538–1543. PMID: 31777489.12. Anania C, Di Marino VP, Olivero F, De Canditiis D, Brindisi G, Iannilli F, et al. Treatment with a probiotic mixture containing Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. Lactis BB12 and Enterococcus faecium L3 for the prevention of allergic rhinitis symptoms in children: a randomized controlled trial. Nutrients. 2021; 13(4):1315. PMID: 33923532.13. Kim WG, Kang GD, Kim HI, Han MJ, Kim DH. Bifidobacterium longum IM55 and Lactobacillus plantarum IM76 alleviate allergic rhinitis in mice by restoring Th2/Treg imbalance and gut microbiota disturbance. Benef Microbes. 2019; 10(1):55–67. PMID: 30465441.14. Kang MG, Han SW, Kang HR, Hong SJ, Kim DH, Choi JH. Probiotic NVP-1703 alleviates allergic rhinitis by inducing IL-10 expression: a four-week clinical trial. Nutrients. 2020; 12(5):1427. PMID: 32429063.15. Meltzer EO, Kunjibettu S, Hall N, Wingertzahn MA, Murcia C, Berger W, et al. Efficacy and safety of ciclesonide, 200 microg once daily, for the treatment of perennial allergic rhinitis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2007; 98(2):175–181. PMID: 17304887.16. Zhang Y, Wei P, Chen B, Li X, Luo X, Chen X, et al. Intranasal fluticasone furoate in pediatric allergic rhinitis: randomized controlled study. Pediatr Res. 2021; 89(7):1832–1839. PMID: 33007780.17. Jung JW, Kang HR, Ji GE, Park MS, Song WJ, Kim MH, et al. Therapeutic effects of fermented red ginseng in allergic rhinitis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2011; 3(2):103–110. PMID: 21461249.18. Lin WY, Fu LS, Lin HK, Shen CY, Chen YJ. Evaluation of the effect of Lactobacillus paracasei (HF.A00232) in children (6-13 years old) with perennial allergic rhinitis: a 12-week, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Pediatr Neonatol. 2014; 55(3):181–188. PMID: 24269033.19. Giovannini M, Agostoni C, Riva E, Salvini F, Ruscitto A, Zuccotti GV, et al. A randomized prospective double blind controlled trial on effects of long-term consumption of fermented milk containing Lactobacillus casei in pre-school children with allergic asthma and/or rhinitis. Pediatr Res. 2007; 62(2):215–220. PMID: 17597643.20. Lue KH, Sun HL, Lu KH, Ku MS, Sheu JN, Chan CH, et al. A trial of adding Lactobacillus johnsonii EM1 to levocetirizine for treatment of perennial allergic rhinitis in children aged 7-12 years. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2012; 76(7):994–1001. PMID: 22513081.21. Miraglia Del Giudice M, Indolfi C, Capasso M, Maiello N, Decimo F, Ciprandi G. Bifidobacterium mixture (B longum BB536, B infantis M-63, B breve M-16V) treatment in children with seasonal allergic rhinitis and intermittent asthma. Ital J Pediatr. 2017; 43(1):25. PMID: 28270216.22. Ivory K, Chambers SJ, Pin C, Prieto E, Arqués JL, Nicoletti C. Oral delivery of Lactobacillus casei Shirota modifies allergen-induced immune responses in allergic rhinitis. Clin Exp Allergy. 2008; 38(8):1282–1289. PMID: 18510694.23. Singh A, Hacini-Rachinel F, Gosoniu ML, Bourdeau T, Holvoet S, Doucet-Ladeveze R, et al. Immune-modulatory effect of probiotic Bifidobacterium lactis NCC2818 in individuals suffering from seasonal allergic rhinitis to grass pollen: an exploratory, randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2013; 67(2):161–167. PMID: 23299716.24. Wolk K, Haugen HS, Xu W, Witte E, Waggie K, Anderson M, et al. IL-22 and IL-20 are key mediators of the epidermal alterations in psoriasis while IL-17 and IFN-gamma are not. J Mol Med (Berl). 2009; 87(5):523–536. PMID: 19330474.25. Zenewicz LA, Yancopoulos GD, Valenzuela DM, Murphy AJ, Stevens S, Flavell RA. Innate and adaptive interleukin-22 protects mice from inflammatory bowel disease. Immunity. 2008; 29(6):947–957. PMID: 19100701.26. Nakagome K, Imamura M, Kawahata K, Harada H, Okunishi K, Matsumoto T, et al. High expression of IL-22 suppresses antigen-induced immune responses and eosinophilic airway inflammation via an IL-10-associated mechanism. J Immunol. 2011; 187(10):5077–5089. PMID: 21998459.27. Pennino D, Bhavsar PK, Effner R, Avitabile S, Venn P, Quaranta M, et al. IL-22 suppresses IFN-γ-mediated lung inflammation in asthmatic patients. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013; 131(2):562–570. PMID: 23174657.28. Johnson JR, Nishioka M, Chakir J, Risse PA, Almaghlouth I, Bazarbashi AN, et al. IL-22 contributes to TGF-β1-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition in asthmatic bronchial epithelial cells. Respir Res. 2013; 14(1):118. PMID: 24283210.29. Tang J, Xiao P, Luo X, Bai J, Xia W, Chen W, et al. Increased IL-22 level in allergic rhinitis significantly correlates with clinical severity. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2014; 28(6):197–201. PMID: 25514475.30. Torre E, Sola D, Caramaschi A, Mignone F, Bona E, Fallarini S. A pilot study on clinical scores, immune cell modulation, and microbiota composition in allergic patients with rhinitis and asthma treated with a probiotic preparation. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2022; 183(2):186–200. PMID: 34673641.31. Costa DJ, Marteau P, Amouyal M, Poulsen LK, Hamelmann E, Cazaubiel M, et al. Efficacy and safety of the probiotic Lactobacillus paracasei LP-33 in allergic rhinitis: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial (GA2LEN Study). Eur J Clin Nutr. 2014; 68(5):602–607. PMID: 24569538.32. Yonekura S, Okamoto Y, Okawa T, Hisamitsu M, Chazono H, Kobayashi K, et al. Effects of daily intake of Lactobacillus paracasei strain KW3110 on Japanese cedar pollinosis. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2009; 30(4):397–405. PMID: 19772761.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Efficacy of Probiotic Therapy on Atopic Dermatitis in Children: A Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Trial
- Effect of administration of synbiotics mixture containing Bifidobacterium longum and xylooligosaccharide on fecal microbiota and defecation characteristics in healthy volunteers
- Efficacy of Quadruple-coated Probiotics in Patients With Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled, Parallel-group Study
- A Case of Sepsis by Bifidobacterium longum
- The effects of mask applied aromatherapy on allergic rhinitis symptoms, fatigue, and quality of life related to allergic rhinitis in the COVID-19 era: a randomized controlled trial