J Rheum Dis.
2024 Oct;31(4):200-211. 10.4078/jrd.2024.0051.
Early human migration determines the risk of being attacked by wolves: ethnic gene diversity on the development of systemic lupus erythematosus
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Rheumatology, Hanyang University Guri Hospital, Guri, Korea
- 2Hanyang University Institute for Rheumatology Research and Hanyang University Hospital for Rheumatic Diseases, Seoul, Korea
- 3Division of Rheumatology, Regional Rheumatoid & Degenerative Arthritis Center, Chungnam National University Hospital, Daejeon, Korea
- KMID: 2559889
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2024.0051
Abstract
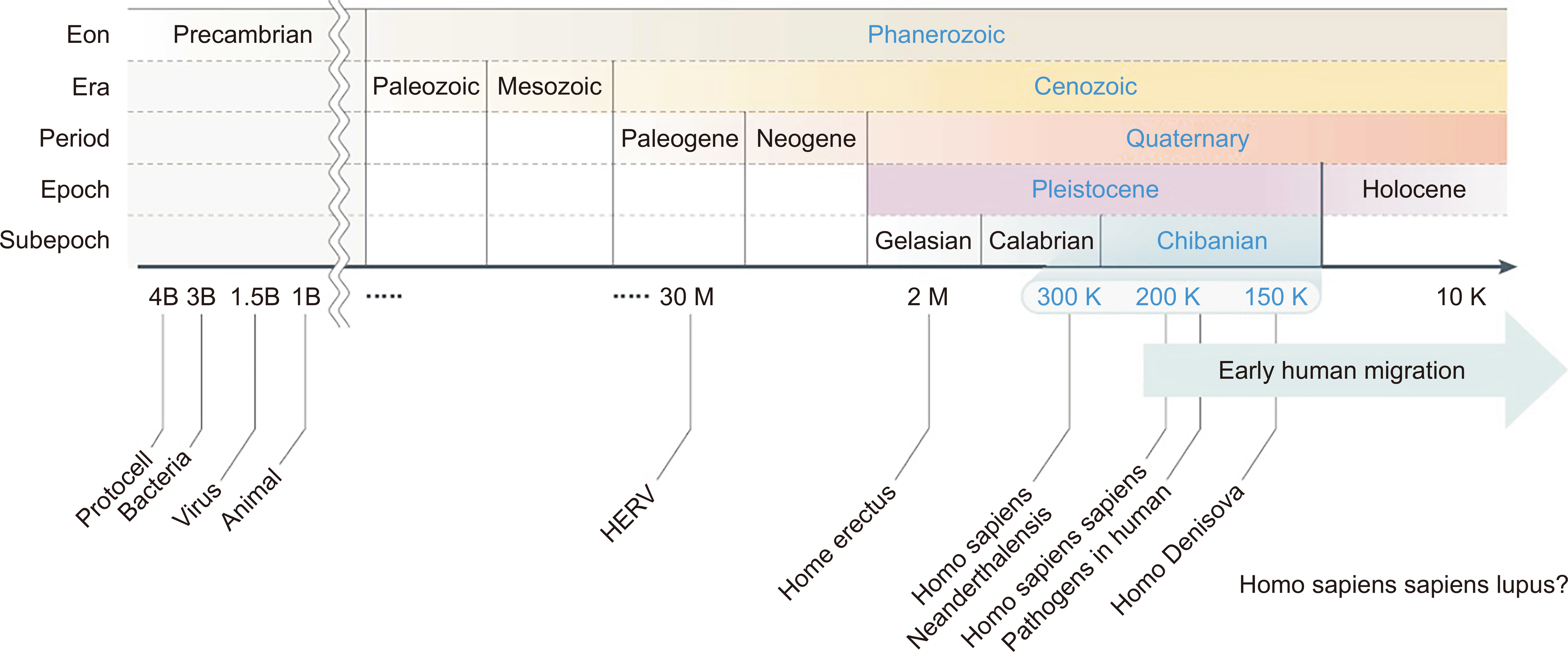
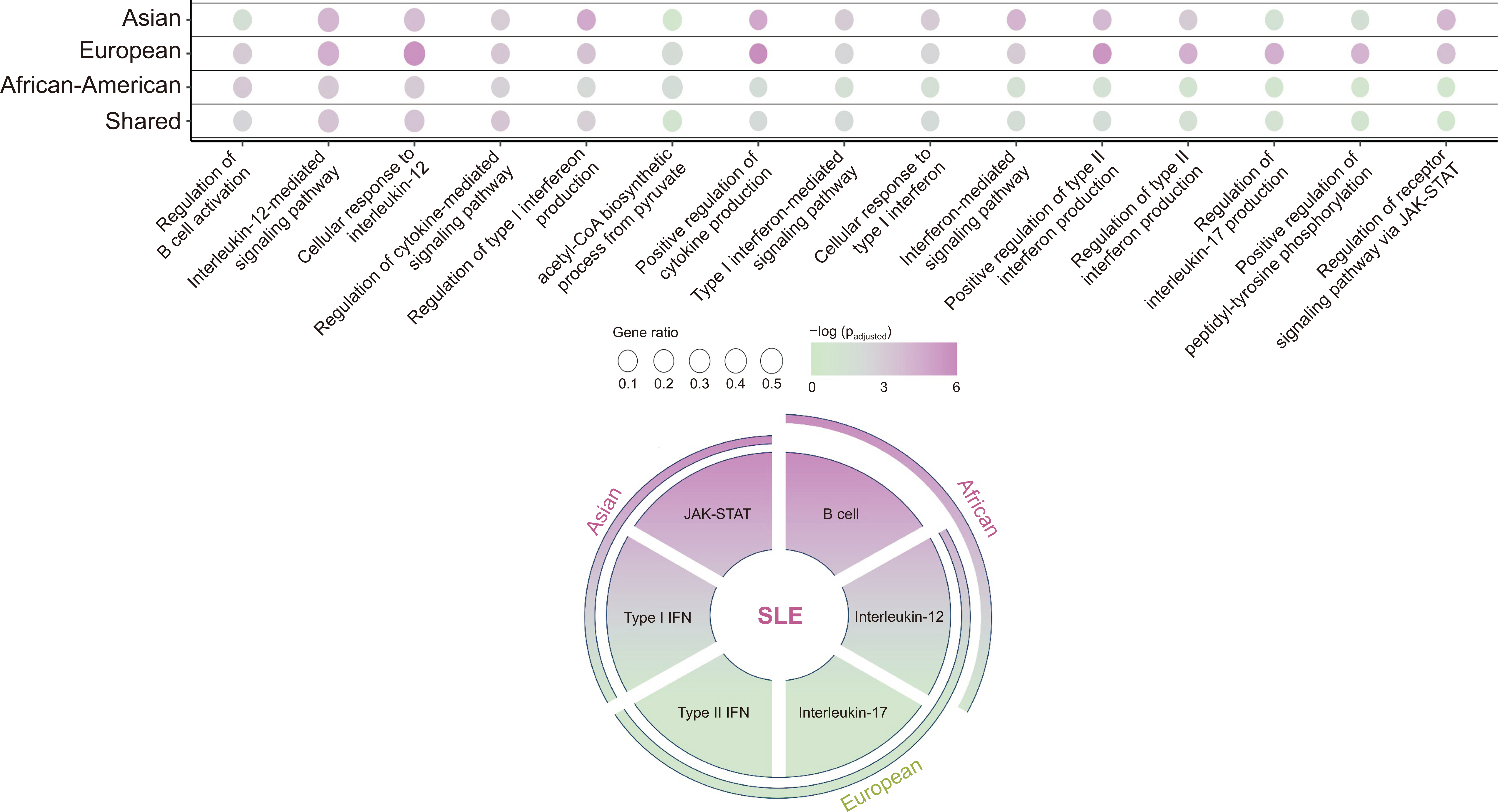
- The prevalence of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) varies significantly based on ethnicity rather than geographic distribution; thus, the prevalence is higher in Asian, Hispanic, and Black African populations than in European populations. The risk of developing lupus nephritis (LN) is the highest among Asian populations. Therefore, we hypothesize that human genetic diversity between races has occurred through the early human migration and human genetic adaptation to various environments, with a particular focus on pathogens. Additionally, we compile the currently available evidence on the ethnic gene diversity of SLE and how it relates to disease severity. The human leukocyte antigen (HLA) locus is well established as associated with susceptibility to SLE; specific allele distributions have been observed across diverse populations. Notably, specific amino acid residues within these HLA loci demonstrate significant associations with SLE risk. The non-HLA genetic loci associated with SLE risk also varies across diverse ancestries, implicating distinct immunological pathways, such as the type-I interferon and janus kinase–signal transducers and activators of transcription (JAK–STAT) pathways in Asians, the type-II interferon signaling pathway in Europeans, and B cell activation pathway in Africans. Furthermore, assessing individual genetic susceptibility using genetic risk scores (GRS) for SLE helps to reveal the diverse prevalence, age of onset, and clinical phenotypes across different ethnicities. A higher GRS increases the risk of LN and the severity of SLE. Therefore, understanding ethnic gene diversity is crucial for elucidating disease mechanisms and SLE severity, which could enable the development of novel drugs specific to each race.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Liu Z, Davidson A. 2012; Taming lupus-a new understanding of pathogenesis is leading to clinical advances. Nat Med. 18:871–82. DOI: 10.1038/nm.2752. PMID: 22674006. PMCID: PMC3607103.2. Barber MRW, Drenkard C, Falasinnu T, Hoi A, Mak A, Kow NY, et al. 2021; Global epidemiology of systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 17:515–32. DOI: 10.1038/s41584-021-00668-1. PMID: 34345022. PMCID: PMC8982275.3. Izmirly PM, Wan I, Sahl S, Buyon JP, Belmont HM, Salmon JE, et al. 2017; The incidence and prevalence of systemic lupus erythematosus in New York County (Manhattan), New York: the Manhattan lupus surveillance program. Arthritis Rheumatol. 69:2006–17. DOI: 10.1002/art.40192. PMID: 28891252. PMCID: PMC11102806.4. Lewis MJ, Jawad AS. 2017; The effect of ethnicity and genetic ancestry on the epidemiology, clinical features and outcome of systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology (Oxford). 56(Suppl 1):i67–77. DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/kew399. PMID: 27940583.5. Askanase A, Khalili L, Tang W, Mertz P, Scherlinger M, Sebbag E, et al. 2023; New and future therapies: changes in the therapeutic armamentarium for SLE. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 37:101865. DOI: 10.1016/j.berh.2023.101865. PMID: 37633826.6. Han Y, Liu L, Zang B, Liang R, Zhao X, Liu B. 2023; Advances in natural products and antibody drugs for SLE: new therapeutic ideas. Front Pharmacol. 14:1235440. DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1235440. PMID: 37492083. PMCID: PMC10363611.7. Appel GB, Contreras G, Dooley MA, Ginzler EM, Isenberg D, Jayne D, et al. Aspreva Lupus Management Study Group. 2009; Mycophenolate mofetil versus cyclophosphamide for induction treatment of lupus nephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 20:1103–12. DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2008101028. PMID: 19369404. PMCID: PMC2678035.8. Isenberg D, Appel GB, Contreras G, Dooley MA, Ginzler EM, Jayne D, et al. 2010; Influence of race/ethnicity on response to lupus nephritis treatment: the ALMS study. Rheumatology (Oxford). 49:128–40. DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/kep346. PMID: 19933596. PMCID: PMC2789586.9. Merrill JT, Neuwelt CM, Wallace DJ, Shanahan JC, Latinis KM, Oates JC, et al. 2010; Efficacy and safety of rituximab in moderately-to-severely active systemic lupus erythematosus: the randomized, double-blind, phase II/III systemic lupus erythematosus evaluation of rituximab trial. Arthritis Rheum. 62:222–33. DOI: 10.1002/art.27233. PMID: 20039413. PMCID: PMC4548300.10. Catalina MD, Bachali P, Yeo AE, Geraci NS, Petri MA, Grammer AC, et al. 2020; Patient ancestry significantly contributes to molecular heterogeneity of systemic lupus erythematosus. JCI Insight. 5:e140380. DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.140380. PMID: 32759501. PMCID: PMC7455079.11. Wolpoff MH, Hawks J, Frayer DW, Hunley K. 2001; Modern human ancestry at the peripheries: a test of the replacement theory. Science. 291:293–7. DOI: 10.1126/science.291.5502.293. PMID: 11209077.12. Price M. 2020; Africans, too, carry Neanderthal genetic legacy. Science. 367:497. DOI: 10.1126/science.367.6477.497. PMID: 32001636.13. Wolf AB, Akey JM. 2018; Outstanding questions in the study of archaic hominin admixture. PLoS Genet. 14:e1007349. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007349. PMID: 29852022. PMCID: PMC5978786.14. Hunter P. 2014; The genetics of human migrations: our ancestors migration out of Africa has left traces in our genomes that explain how they adapted to new environments. EMBO Rep. 15:1019–22. DOI: 10.15252/embr.201439469. PMID: 25216943. PMCID: PMC4253842.15. Narbonne GM. 2005; The Ediacara biota: neoproterozoic origin of animals and their ecosystems. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci. 33:421–42. DOI: 10.1146/annurev.earth.33.092203.122519.16. Karlsson EK, Kwiatkowski DP, Sabeti PC. 2014; Natural selection and infectious disease in human populations. Nat Rev Genet. 15:379–93. DOI: 10.1038/nrg3734. PMID: 24776769. PMCID: PMC4912034.17. Casanova JL, Abel L. 2005; Inborn errors of immunity to infection: the rule rather than the exception. J Exp Med. 202:197–201. DOI: 10.1084/jem.20050854. PMID: 16027233. PMCID: PMC2212996.18. Allison AC. 1954; Protection afforded by sickle-cell trait against subtertian malarial infection. Br Med J. 1:290–4. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.1.4857.290.19. Parkes M, Cortes A, Van Heel DA, Brown MA. 2013; Genetic insights into common pathways and complex relationships among immune-mediated diseases. Nat Rev Genet. 14:661–73. DOI: 10.1038/nrg3502. PMID: 23917628.20. Abel L, Alcaïs A, Schurr E. 2014; The dissection of complex susceptibility to infectious disease: bacterial, viral and parasitic infections. Curr Opin Immunol. 30:72–8. DOI: 10.1016/j.coi.2014.07.002. PMID: 25083600.21. Quintana-Murci L, Clark AG. 2013; Population genetic tools for dissecting innate immunity in humans. Nat Rev Immunol. 13:280–93. DOI: 10.1038/nri3421. PMID: 23470320. PMCID: PMC4015519.22. Konstantinoudis G, Cameletti M, Gómez-Rubio V, Gómez IL, Pirani M, Baio G, et al. 2022; Regional excess mortality during the 2020 COVID-19 pandemic in five European countries. Nat Commun. 13:482. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-28157-3. PMID: 35079022. PMCID: PMC8789777.23. Landoni G, Maimeri N, Fedrizzi M, Fresilli S, Kuzovlev A, Likhvantsev V, et al. 2021; Why are Asian countries outperforming the Western world in controlling COVID-19 pandemic? Pathog Glob Health. 115:70–2. DOI: 10.1080/20477724.2020.1850982. PMID: 33241776. PMCID: PMC7850376.24. Fodil N, Langlais D, Gros P. 2016; Primary immunodeficiencies and inflammatory disease: a growing genetic intersection. Trends Immunol. 37:126–40. DOI: 10.1016/j.it.2015.12.006. PMID: 26791050. PMCID: PMC4738049.25. Langefeld CD, Ainsworth HC, Cunninghame Graham DS, Kelly JA, Comeau ME, Marion MC, et al. 2017; Transancestral mapping and genetic load in systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Commun. 8:16021. DOI: 10.1038/ncomms16021. PMID: 28714469. PMCID: PMC5520018.26. Fumagalli M, Pozzoli U, Cagliani R, Comi GP, Riva S, Clerici M, et al. 2009; Parasites represent a major selective force for interleukin genes and shape the genetic predisposition to autoimmune conditions. J Exp Med. 206:1395–408. DOI: 10.1084/jem.20082779. PMID: 19468064. PMCID: PMC2715056.27. Zhernakova A, Elbers CC, Ferwerda B, Romanos J, Trynka G, Dubois PC, et al. 2010; Evolutionary and functional analysis of celiac risk loci reveals SH2B3 as a protective factor against bacterial infection. Am J Hum Genet. 86:970–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2010.05.004. PMID: 20560212. PMCID: PMC3032060.28. Jostins L, Ripke S, Weersma RK, Duerr RH, McGovern DP, Hui KY, et al. 2012; Host-microbe interactions have shaped the genetic architecture of inflammatory bowel disease. Nature. 491:119–24. DOI: 10.1038/nature11582. PMID: 23128233. PMCID: PMC3491803.29. Prugnolle F, Manica A, Charpentier M, Guégan JF, Guernier V, Balloux F. 2005; Pathogen-driven selection and worldwide HLA class I diversity. Curr Biol. 15:1022–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.04.050. PMID: 15936272.30. Ryder LP, Svejgaard A, Dausset J. 1981; Genetics of HLA disease association. Annu Rev Genet. 15:169–87. DOI: 10.1146/annurev.ge.15.120181.001125. PMID: 7039493.31. Gough SC, Simmonds MJ. 2007; The HLA region and autoimmune disease: associations and mechanisms of action. Curr Genomics. 8:453–65. DOI: 10.2174/138920207783591690. PMID: 19412418. PMCID: PMC2647156.32. Chen H, Hayashi G, Lai OY, Dilthey A, Kuebler PJ, Wong TV, et al. 2012; Psoriasis patients are enriched for genetic variants that protect against HIV-1 disease. PLoS Genet. 8:e1002514. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002514. PMID: 22577363. PMCID: PMC3343879.33. Matzaraki V, Kumar V, Wijmenga C, Zhernakova A. 2017; The MHC locus and genetic susceptibility to autoimmune and infectious diseases. Genome Biol. 18:76. DOI: 10.1186/s13059-017-1207-1. PMID: 28449694. PMCID: PMC5406920.34. Ritari J, Koskela S, Hyvärinen K, FinnGen , Partanen J. 2022; HLA-disease association and pleiotropy landscape in over 235,000 Finns. Hum Immunol. 83:391–8. DOI: 10.1016/j.humimm.2022.02.003. PMID: 35221124.35. Tsoi LC, Spain SL, Knight J, Ellinghaus E, Stuart PE, Capon F, et al. 2012; Identification of 15 new psoriasis susceptibility loci highlights the role of innate immunity. Nat Genet. 44:1341–8. DOI: 10.1038/ng.2467. PMID: 23143594. PMCID: PMC3510312.36. Cortes A, Hadler J, Pointon JP, Robinson PC, Karaderi T, Leo P, et al. 2013; Identification of multiple risk variants for ankylosing spondylitis through high-density genotyping of immune-related loci. Nat Genet. 45:730–8. DOI: 10.1038/ng.2667. PMID: 23749187. PMCID: PMC3757343.37. Diogo D, Bastarache L, Liao KP, Graham RR, Fulton RS, Greenberg JD, et al. 2015; TYK2 protein-coding variants protect against rheumatoid arthritis and autoimmunity, with no evidence of major pleiotropic effects on non-autoimmune complex traits. PloS one. 10:e0122271. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0122271. PMID: 25849893. PMCID: PMC4388675.38. Dendrou CA, Cortes A, Shipman L, Evans HG, Attfield KE, Jostins L, et al. 2016; Resolving TYK2 locus genotype-to-phenotype differences in autoimmunity. Sci Transl Med. 8:363ra149. DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aag1974. PMID: 27807284. PMCID: PMC5737835.39. Boisson-Dupuis S, Ramirez-Alejo N, Li Z, Patin E, Rao G, Kerner G, et al. 2018; Tuberculosis and impaired IL-23-dependent IFN-γ immunity in humans homozygous for a common TYK2 missense variant. Sci Immunol. 3:eaau8714. DOI: 10.3410/f.734676937.793572033. PMID: 30578352. PMCID: PMC6341984.40. Kerner G, Ramirez-Alejo N, Seeleuthner Y, Yang R, Ogishi M, Cobat A, et al. 2019; Homozygosity for TYK2 P1104A underlies tuberculosis in about 1% of patients in a cohort of European ancestry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 116:10430–4. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1903561116. PMID: 31068474. PMCID: PMC6534977.41. Kerner G, Laval G, Patin E, Boisson-Dupuis S, Abel L, Casanova JL, et al. 2021; Human ancient DNA analyses reveal the high burden of tuberculosis in Europeans over the last 2,000 years. Am J Hum Genet. 108:517–24. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2021.02.009. PMID: 33667394. PMCID: PMC8008489.42. Lindesmith L, Moe C, Marionneau S, Ruvoen N, Jiang X, Lindblad L, et al. 2003; Human susceptibility and resistance to Norwalk virus infection. Nat Med. 9:548–53. DOI: 10.1038/nm860. PMID: 12692541.43. Panda D, Gjinaj E, Bachu M, Squire E, Novatt H, Ozato K, et al. 2019; IRF1 maintains optimal constitutive expression of antiviral genes and regulates the early antiviral response. Front Immunol. 10:1019. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01019. PMID: 31156620. PMCID: PMC6529937.44. Nunes-Santos CJ, Kuehn HS, Rosenzweig SD. 2020; IKAROS family zinc finger 1-associated diseases in primary immunodeficiency patients. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 40:461–70. DOI: 10.1016/j.iac.2020.04.004. PMID: 32654692. PMCID: PMC7394939.45. Rascovan N, Sjögren KG, Kristiansen K, Nielsen R, Willerslev E, Desnues C, et al. 2019; Emergence and spread of basal lineages of Yersinia pestis during the Neolithic decline. Cell. 176:295–305.e10. DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.11.005. PMID: 30528431.46. Andrades Valtueña A, Neumann GU, Spyrou MA, Musralina L, Aron F, Beisenov A, et al. 2022; Stone Age Yersinia pestis genomes shed light on the early evolution, diversity, and ecology of plague. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 119:e2116722119. DOI: 10.3410/f.742004133.793592836. PMID: 35412864. PMCID: PMC9169917.47. Trowsdale J. 2011; The MHC, disease and selection. Immunol Lett. 137:1–8. DOI: 10.1016/j.imlet.2011.01.002. PMID: 21262263.48. Spurgin LG, Richardson DS. 2010; How pathogens drive genetic diversity: MHC, mechanisms and misunderstandings. Proc Biol Sci. 277:979–88. DOI: 10.1098/rspb.2009.2084. PMID: 20071384. PMCID: PMC2842774.49. Satta Y, O'HUigin C, Takahata N, Klein J. 1994; Intensity of natural selection at the major histocompatibility complex loci. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 91:7184–8. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.91.15.7184. PMID: 8041766. PMCID: PMC44363.50. Robinson J, Halliwell JA, Hayhurst JD, Flicek P, Parham P, Marsh SG. 2015; The IPD and IMGT/HLA database: allele variant databases. Nucleic Acids Res. 43:D423–31. DOI: 10.1093/nar/gku1161. PMID: 25414341. PMCID: PMC4383959.51. Yasukochi Y, Satta Y. 2013; Current perspectives on the intensity of natural selection of MHC loci. Immunogenetics. 65:479–83. DOI: 10.1007/s00251-013-0693-x. PMID: 23549729. PMCID: PMC3651823.52. Yasukochi Y, Satta Y. 2014; A human-specific allelic group of the MHC DRB1 gene in primates. J Physiol Anthropol. 33:14. DOI: 10.1186/1880-6805-33-14. PMID: 24928070. PMCID: PMC4072476.53. Quintana-Murci L. 2016; Understanding rare and common diseases in the context of human evolution. Genome Biol. 17:225. DOI: 10.1186/s13059-016-1093-y. PMID: 27821149. PMCID: PMC5098287.54. Fernández-Viña MA, Klein JP, Haagenson M, Spellman SR, Anasetti C, Noreen H, et al. 2013; Multiple mismatches at the low expression HLA loci DP, DQ, and DRB3/4/5 associate with adverse outcomes in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood. 121:4603–10. DOI: 10.1182/blood-2013-02-481945. PMID: 23596045. PMCID: PMC3668493.55. Paul S, Weiskopf D, Angelo MA, Sidney J, Peters B, Sette A. 2013; HLA class I alleles are associated with peptide-binding repertoires of different size, affinity, and immunogenicity. J Immunol. 191:5831–9. DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1302101. PMID: 24190657. PMCID: PMC3872965.56. Kaufman J. 2018; Generalists and specialists: a new view of how MHC class I molecules fight infectious pathogens. Trends Immunol. 39:367–79. DOI: 10.1016/j.it.2018.01.001. PMID: 29396014. PMCID: PMC5929564.57. Manczinger M, Boross G, Kemény L, Müller V, Lenz TL, Papp B, et al. 2019; Pathogen diversity drives the evolution of generalist MHC-II alleles in human populations. PLoS Biol. 17:e3000131. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000131. PMID: 30703088. PMCID: PMC6372212.58. Crump JA, Luby SP, Mintz ED. 2004; The global burden of typhoid fever. Bull World Health Organ. 82:346–53. PMID: 15298225. PMCID: PMC2622843.59. Sun H, Yang Z, Lin K, Liu S, Huang K, Wang X, et al. 2015; The adaptive change of HLA-DRB1 allele frequencies caused by natural selection in a Mongolian population that migrated to the South of China. PLoS One. 10:e0134334. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0134334. PMID: 26230582. PMCID: PMC4521750.60. Villesen P, Aagaard L, Wiuf C, Pedersen FS. 2004; Identification of endogenous retroviral reading frames in the human genome. Retrovirology. 1:32. DOI: 10.1186/1742-4690-1-32. PMID: 15476554. PMCID: PMC524368.61. Belshaw R, Pereira V, Katzourakis A, Talbot G, Pačes J, Burt A, et al. 2004; Long-term reinfection of the human genome by endogenous retroviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 101:4894–9. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0307800101. PMID: 15044706. PMCID: PMC387345.62. Sekigawa I, Ogasawara H, Kaneko H, Hishikawa T, Hashimoto H. 2001; Retroviruses and autoimmunity. Intern Med. 40:80–6. DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.40.80. PMID: 11300167.63. Stearrett N, Dawson T, Rahnavard A, Bachali P, Bendall ML, Zeng C, et al. 2021; Expression of human endogenous retroviruses in systemic lupus erythematosus: multiomic integration with gene expression. Front Immunol. 12:661437. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.661437. PMID: 33986751. PMCID: PMC8112243.64. Adelman MK, Marchalonis JJ. 2002; Endogenous retroviruses in systemic lupus erythematosus: candidate lupus viruses. Clin Immunol. 102:107–16. DOI: 10.1006/clim.2001.5153. PMID: 11846452.65. Katoh I, Kurata S. 2013; Association of endogenous retroviruses and long terminal repeats with human disorders. Front Oncol. 3:234. DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2013.00234. PMID: 24062987. PMCID: PMC3769647.66. Mustelin T, Ukadike KC. 2020; How retroviruses and retrotransposons in our genome may contribute to autoimmunity in rheumatological conditions. Front Immunol. 11:593891. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.593891. PMID: 33281822. PMCID: PMC7691656.67. Greenig M. 2019; HERVs, immunity, and autoimmunity: understanding the connection. PeerJ. 7:e6711. DOI: 10.7717/peerj.6711. PMID: 30984482. PMCID: PMC6452852.68. Talotta R, Atzeni F, Laska MJ. 2020; Retroviruses in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus: are they potential therapeutic targets? Autoimmunity. 53:177–91. DOI: 10.1080/08916934.2020.1755962. PMID: 32321325.69. Perl A, Colombo E, Dai H, Agarwal R, Mark KA, Banki K, et al. 1995; Antibody reactivity to the HRES-1 endogenous retroviral element identifies a subset of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and overlap syndromes. Correlation with antinuclear antibodies and HLA class II alleles. Arthritis Rheum. 38:1660–71. DOI: 10.1002/art.1780381119. PMID: 7488288.70. Chen CJ, Lin KH, Lin SC, Tsai WC, Yen JH, Chang SJ, et al. 2005; High prevalence of immunoglobulin A antibody against Epstein-Barr virus capsid antigen in adult patients with lupus with disease flare: case control studies. J Rheumatol. 32:44–7. PMID: 15630723.71. Marchini J, Howie B. 2010; Genotype imputation for genome-wide association studies. Nat Rev Genet. 11:499–511. DOI: 10.1038/nrg2796. PMID: 20517342.72. Guerra SG, Vyse TJ, Cunninghame Graham DS. 2012; The genetics of lupus: a functional perspective. Arthritis Res Ther. 14:211. DOI: 10.1186/ar3844. PMID: 22640752. PMCID: PMC3446495.73. Yin X, Kim K, Suetsugu H, Bang SY, Wen L, Koido M, et al. 2021; Meta-analysis of 208370 East Asians identifies 113 susceptibility loci for systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 80:632–40. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-219209. PMID: 33272962. PMCID: PMC8053352.74. Morris DL, Taylor KE, Fernando MM, Nititham J, Alarcón-Riquelme ME, Barcellos LF, et al. 2012; Unraveling multiple MHC gene associations with systemic lupus erythematosus: model choice indicates a role for HLA alleles and non-HLA genes in Europeans. Am J Hum Genet. 91:778–93. DOI: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.08.026. PMID: 23084292. PMCID: PMC3487133.75. Kim K, Bang SY, Lee HS, Okada Y, Han B, Saw WY, et al. 2014; The HLA-DRβ1 amino acid positions 11-13-26 explain the majority of SLE-MHC associations. Nat Commun. 5:5902. DOI: 10.1038/ncomms6902. PMID: 25533202.76. Bang SY, Choi JY, Park S, Choi J, Hong SJ, Lee HS, et al. 2016; Brief report: influence of HLA-DRB1 susceptibility alleles on the clinical subphenotypes of systemic lupus erythematosus in Koreans. Arthritis Rheumatol. 68:1190–6. DOI: 10.1002/art.39539. PMID: 26663868.77. Sun C, Molineros JE, Looger LL, Zhou XJ, Kim K, Okada Y, et al. 2016; High-density genotyping of immune-related loci identifies new SLE risk variants in individuals with Asian ancestry. Nat Genet. 48:323–30. DOI: 10.1038/ng.3496. PMID: 26808113. PMCID: PMC4767573.78. Gonzalez-Galarza FF, McCabe A, Santos EJMD, Jones J, Takeshita L, Ortega-Rivera ND, et al. 2020; Allele frequency net database (AFND) 2020 update: gold-standard data classification, open access genotype data and new query tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 48:D783–8. DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkz1029. PMID: 31722398. PMCID: PMC7145554.79. Morris DL, Sheng Y, Zhang Y, Wang YF, Zhu Z, Tombleson P, et al. 2016; Genome-wide association meta-analysis in Chinese and European individuals identifies ten new loci associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Genet. 48:940–6. DOI: 10.1038/ng.3603. PMID: 27399966. PMCID: PMC4966635.80. Lessard CJ, Sajuthi S, Zhao J, Kim K, Ice JA, Li H, et al. 2016; Identification of a systemic lupus erythematosus risk locus spanning ATG16L2, FCHSD2, and P2RY2 in Koreans. Arthritis Rheumatol. 68:1197–209. DOI: 10.1002/art.39548. PMID: 26663301. PMCID: PMC4981330.81. Molineros JE, Looger LL, Kim K, Okada Y, Terao C, Sun C, et al. 2019; Amino acid signatures of HLA class-I and II molecules are strongly associated with SLE susceptibility and autoantibody production in Eastern Asians. PLoS Genet. 15:e1008092. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008092. PMID: 31022184. PMCID: PMC6504188.82. Geh D, Gordon C. 2018; Epratuzumab for the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 14:245–58. DOI: 10.1080/1744666X.2018.1450141. PMID: 29542345.83. Wallace DJ, Furie RA, Tanaka Y, Kalunian KC, Mosca M, Petri MA, et al. 2018; Baricitinib for systemic lupus erythematosus: a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet. 392:222–31. DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31363-1. PMID: 30043749.84. He J, Zhang R, Shao M, Zhao X, Miao M, Chen J, et al. 2020; Efficacy and safety of low-dose IL-2 in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 79:141–9. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-215396. PMID: 31537547. PMCID: PMC6937406.85. Morand EF, Furie R, Tanaka Y, Bruce IN, Askanase AD, Richez C, et al. 2020; Trial of anifrolumab in active systemic lupus erythematosus. N Engl J Med. 382:211–21. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1912196. PMID: 31851795.86. van Vollenhoven RF, Hahn BH, Tsokos GC, Lipsky P, Fei K, Gordon RM, et al. 2020; Maintenance of efficacy and safety of ustekinumab through one year in a phase II multicenter, prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover trial of patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 72:761–8. DOI: 10.1002/art.41179. PMID: 31769212.87. Isenberg D, Furie R, Jones NS, Guibord P, Galanter J, Lee C, et al. 2021; Efficacy, safety, and pharmacodynamic effects of the Bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibitor fenebrutinib (GDC-0853) in systemic lupus erythematosus: results of a phase II, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Rheumatol. 73:1835–46. DOI: 10.1002/art.41811. PMID: 34042314.88. Furie RA, Aroca G, Cascino MD, Garg JP, Rovin BH, Alvarez A, et al. 2022; B-cell depletion with obinutuzumab for the treatment of proliferative lupus nephritis: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 81:100–7. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2021-220920. PMID: 34615636. PMCID: PMC8762029.89. Morand E, Pike M, Merrill JT, van Vollenhoven R, Werth VP, Hobar C, et al. 2023; Deucravacitinib, a tyrosine kinase 2 inhibitor, in systemic lupus erythematosus: a phase II, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Rheumatol. 75:242–52. DOI: 10.1002/art.42391. PMID: 36369798. PMCID: PMC10100399.90. Webb R, Kelly JA, Somers EC, Hughes T, Kaufman KM, Sanchez E, et al. 2011; Early disease onset is predicted by a higher genetic risk for lupus and is associated with a more severe phenotype in lupus patients. Ann Rheum Dis. 70:151–6. DOI: 10.1136/ard.2010.141697. PMID: 20881011. PMCID: PMC3034281.91. Joo YB, Lim J, Tsao BP, Nath SK, Kim K, Bae SC. 2018; Genetic variants in systemic lupus erythematosus susceptibility loci, XKR6 and GLT1D1 are associated with childhood-onset SLE in a Korean cohort. Sci Rep. 8:9962. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-28128-z. PMID: 29967481. PMCID: PMC6028392.92. Reid S, Alexsson A, Frodlund M, Morris D, Sandling JK, Bolin K, et al. 2020; High genetic risk score is associated with early disease onset, damage accrual and decreased survival in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis. 79:363–9. DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-216227. PMID: 31826855. PMCID: PMC7034364.93. Kwon YC, Ha E, Kwon HH, Park DJ, Shin JM, Joo YB, et al. 2023; Higher genetic risk loads confer more diverse manifestations and higher risk of lupus nephritis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 75:1566–72. DOI: 10.1002/art.42516. PMID: 37011055.94. Darwin C. 1859. On the origin of species by means of natural selection, or the preservation of favored races in the struggle for life. John Murray;London: DOI: 10.5962/bhl.title.68064.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Incidence of Anti - Ro Antibodies in Patients with Systemic Lupus Crythematosus
- Multiple Dermatofibromas in a woman with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- A Case of Transverse Myelitis as a First Manifestation of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- A Case Of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Associated With Hyperthyroidism And Severe Retinopathy
- Pulmonary Hemorrhage with Hemoptysis in Systemic Lupus Erythematosis