Korean J Gastroenterol.
2024 Sep;84(3):132-137. 10.4166/kjg.2024.083.
A Case of Colonic Intussusception with Post-polypectomy Electrocoagulation Syndrome and Review of Literature: How to Manage Intussusception Following Colonoscopy?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Departments of Surgery, Daejeon Eulji Medical Center, Eulji University, Daejeon, Korea
- 2Departments of Internal Medicine, Daejeon Eulji Medical Center, Eulji University, Daejeon, Korea
- 3Departments of Radiology, Daejeon Eulji Medical Center, Eulji University, Daejeon, Korea
- 4Departments of Pathology, Daejeon Eulji Medical Center, Eulji University, Daejeon, Korea
- KMID: 2559847
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2024.083
Abstract
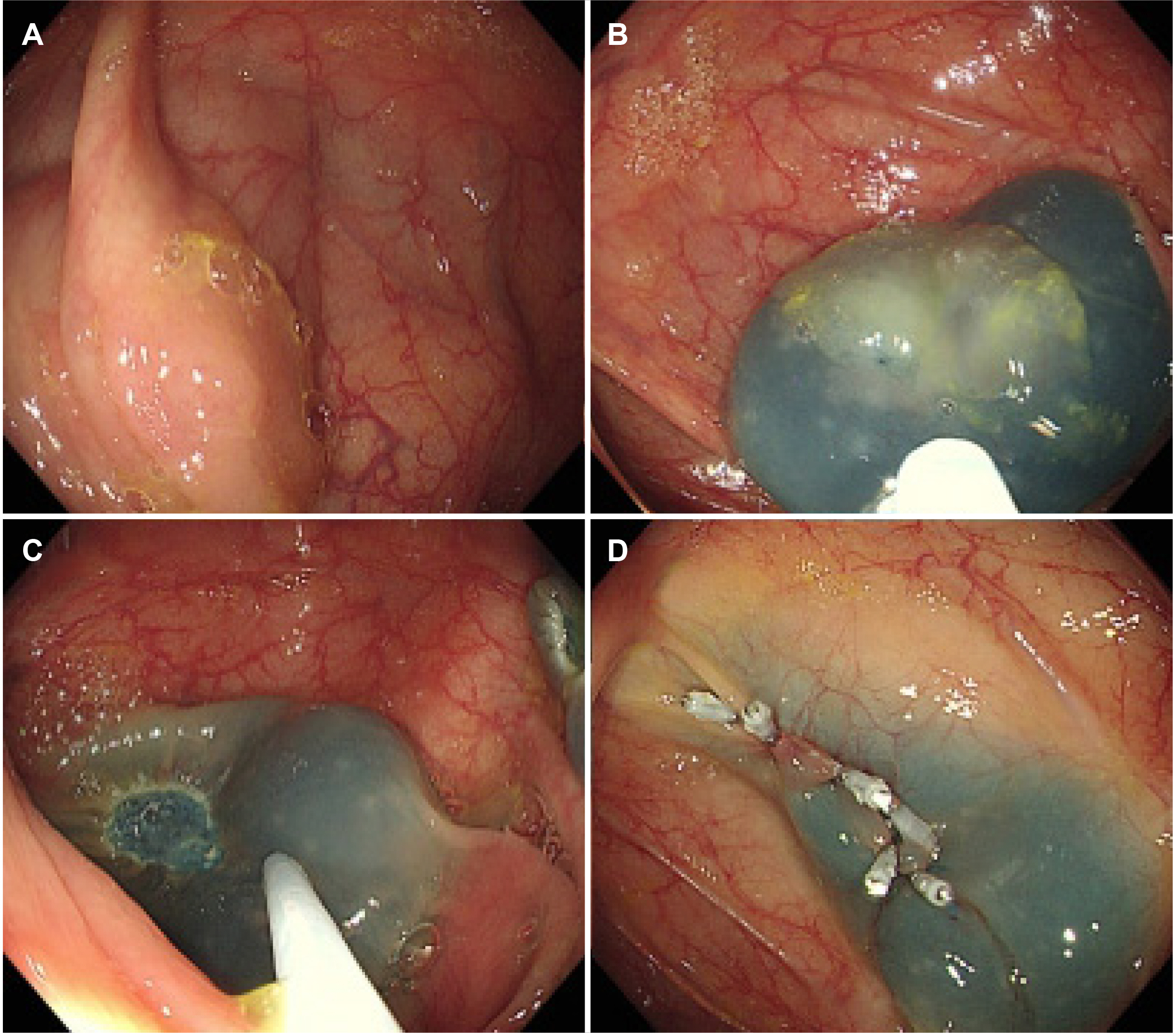
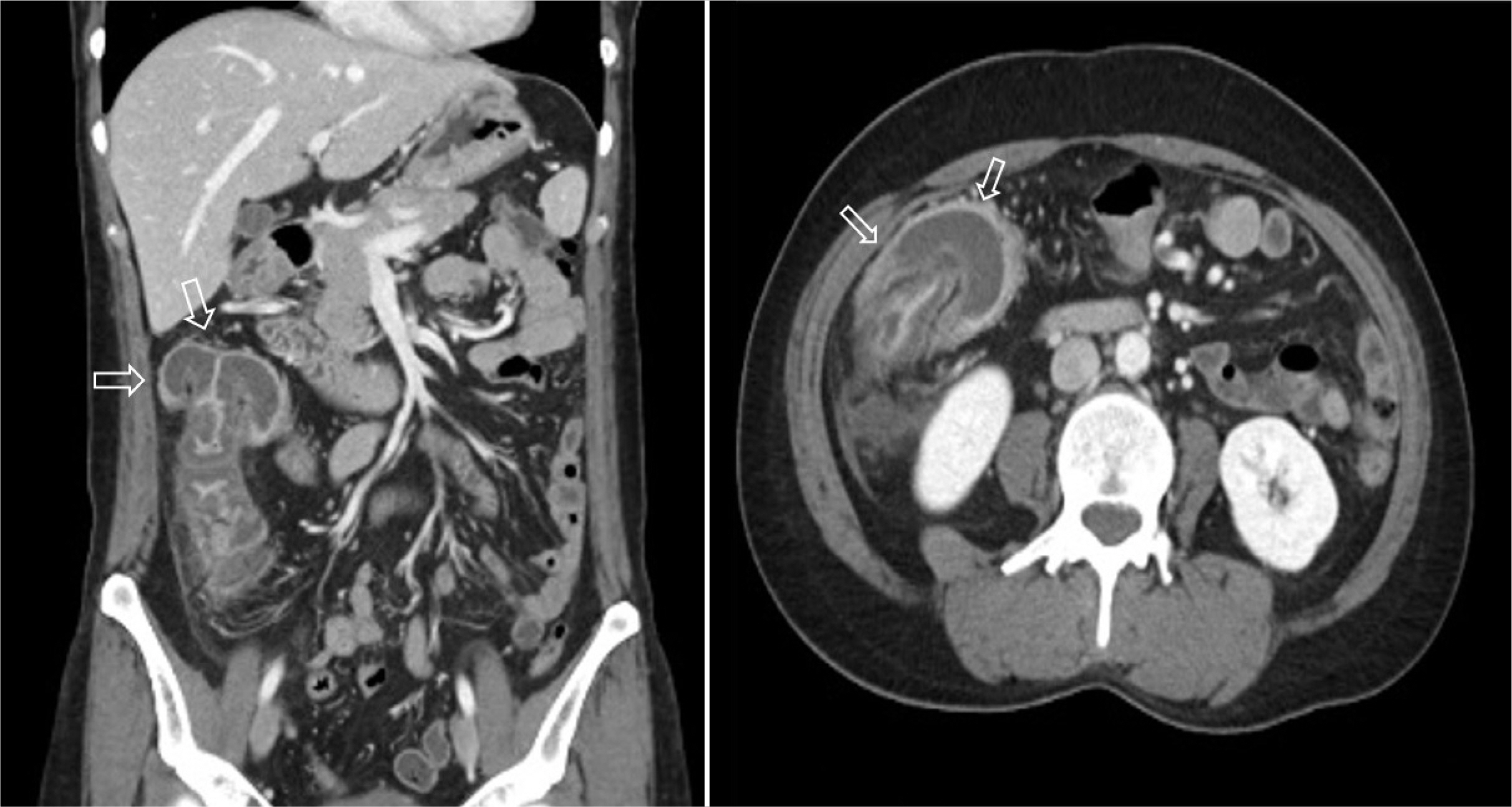
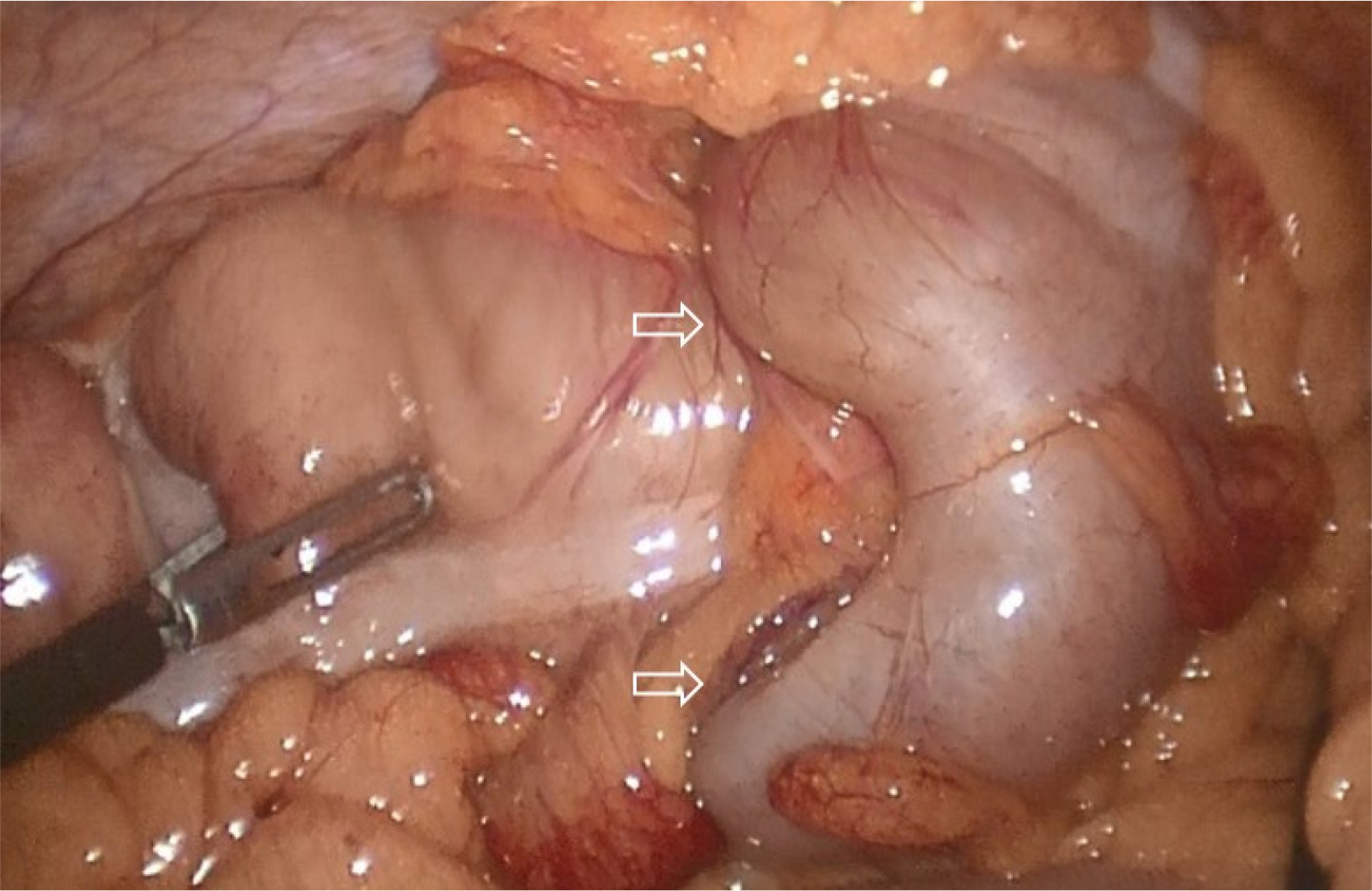
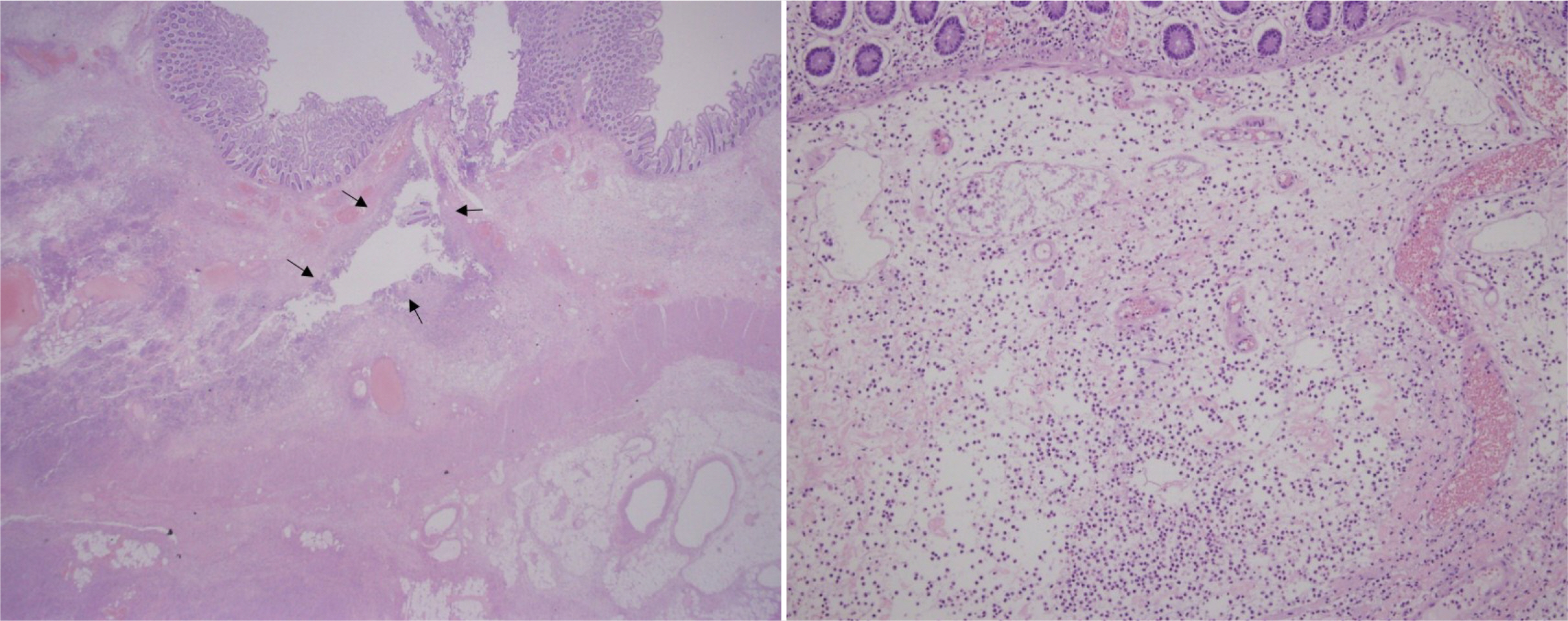
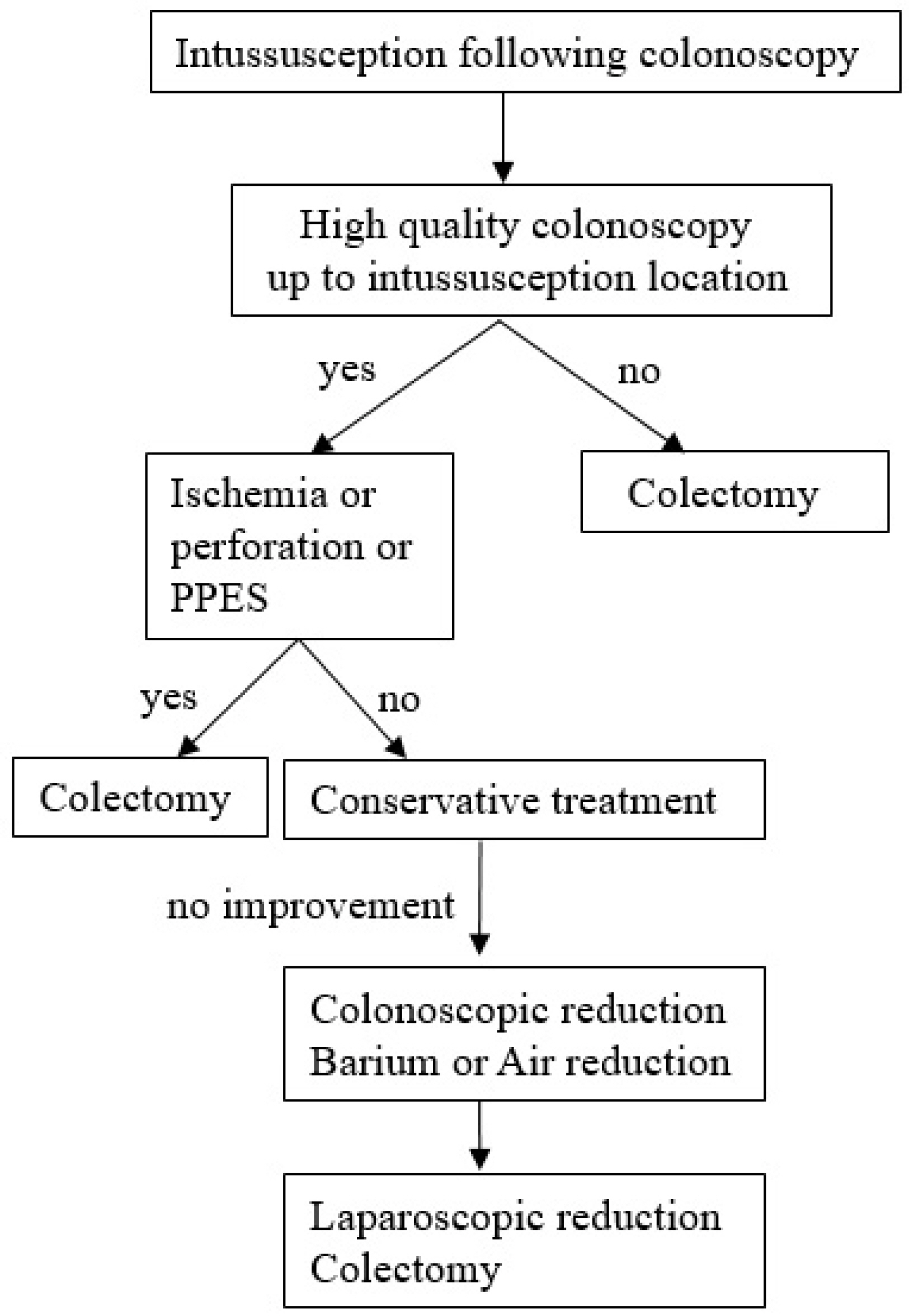
- Colonic intussusception is often reported to be related to malignancy in adults. Colonoscopy itself with or without polypectomy is known to be a rare cause of colonic intussusception. We encountered a case in which an individual was diagnosed with intussusception following colonoscopy. The patient was a 44-year-old female who, on the same day, had undergone a colonoscopy including endoscopic mucosal resection for a polyp in the ascending colon. She visited the emergency room with complaints of right-sided abdominal pain. Abdominal examination revealed peritoneal irritation in the right upper quadrant. Abdominal CT revealed colocolic intussusception near the hepatic flexure. This was suspected to have been induced by post-polypectomy electrocoagulation syndrome. A laparoscopic right hemicolectomy was performed because conducting a reduction trial through colonoscopy involves a high risk of peritonitis, in addition to a low likelihood of spontaneous reduction of intussusception due to the additional edema and ischemia resulting from the polypectomy. The patient was discharged without complications six days after the surgery. Though some cases have been reported, there is no treatment strategy for intussusception following colonoscopy. Therefore, we report this case of colonic intussusception following colonoscopy, which was found to be caused by Post-polypectomy Electrocoagulation Syndrome, with a literature review.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Marsicovetere P, Ivatury SJ, White B, Holubar SD. 2017; Intestinal intussusception: etiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 30:30–39. DOI: 10.1055/s-0036-1593429. PMID: 28144210. PMCID: PMC5179276.2. Aydin N, Roth A, Misra S. 2016; Surgical versus conservative management of adult intussusception: Case series and review. Int J Surg Case Rep. 20:142–146. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2016.01.019. PMID: 26859872. PMCID: PMC4818310.3. Weilbaecher D, Bolin JA, Hearn D, Ogden W 2nd. 1971; Intussusception in adults. Review of 160 cases. Am J Surg. 121:531–535. DOI: 10.1016/0002-9610(71)90133-4. PMID: 5557762.4. Reijnen HA, Joosten HJ, de Boer HH. 1989; Diagnosis and treatment of adult intussusception. Am J Surg. 158:25–28. DOI: 10.1016/0002-9610(89)90309-7. PMID: 2662787.5. Sanders GB, Hagan WH, Kinnaird DW. 1958; Adult intussusception and carcinoma of the colon. Ann Surg. 147:796–804. PMID: 13534248. PMCID: PMC1450734.6. Eisen LK, Cunningham JD, Aufses AH Jr. 1999; Intussusception in adults: institutional review. J Am Coll Surg. 188:390–395. DOI: 10.1016/S1072-7515(98)00331-7. PMID: 10195723.7. Begos DG, Sandor A, Modlin IM. 1997; The diagnosis and management of adult intussusception. Am J Surg. 173:88–94. DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9610(96)00419-9. PMID: 9074370.8. Hassan WAW, Teoh W. 2018; Intussusception after colonoscopy: A case report and review of literature. Clin Endosc. 51:591–595. DOI: 10.5946/ce.2018.056. PMID: 30300987. PMCID: PMC6283765.9. Vadakkenchery Varghese E, Steen C, Juszczyk K, An V. 2022; Splenic flexure intussusception: a rare complication post colonoscopy. ANZ J Surg. 92:1545–1546. DOI: 10.1111/ans.17325. PMID: 34694677.10. Lasithiotakis K, Grisbolaki E, Filis D, Athanasakis I, Zoras O, Chalkiadakis G. 2012; Ileocolic intussusception precipitated by diagnostic colonoscopy: a case report. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 22:e161–e163. DOI: 10.1097/SLE.0b013e31824b230f. PMID: 22678343.11. Ho MM, Park JJ, Prasad LM. 2010; Post colonoscopy colonic intussusception reduced via a laparoscopic approach. JSLS. 14:596–599. DOI: 10.4293/108680810X12924466008727. PMID: 21605531. PMCID: PMC3083058.12. Yamazaki T, Okamoto H, Suda T, et al. 2000; Intussusception in an adult after colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 51:356–357. DOI: 10.1016/S0016-5107(00)70371-3. PMID: 10699791.13. Min MX, Sklow B, Vaughn BP. 2017; Intussusception after routine colonoscopy: A rare complication. ACG Case Rep J. 4:e63. DOI: 10.14309/crj.2017.63. PMID: 28462240. PMCID: PMC5407360.14. Ahmed A, Zhang J, Anas K. 2020; Intussusception in a routine colonoscopy. ACG Case Rep J. 7:e00422. DOI: 10.14309/crj.0000000000000422. PMID: 32766364. PMCID: PMC7357705.15. Nachnani J, Burns E, Margolin D, Clarkston WK. 2012; Colocolonic intussusception after colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 75:223–225. DOI: 10.1016/j.gie.2011.01.046. PMID: 21481863.16. Moon JY, Lee MR, Yim SK, Ha GW. 2022; Colo-colonic intussusception with post-polypectomy electrocoagulation syndrome: A case report. World J Clin Cases. 10:8939–8944. DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i25.8939. PMID: 36157670. PMCID: PMC9477040.17. Lee CK, Shim JJ, Jang JY. 2013; Ceco-colic intussusception with subsequent bowel infarction as a rare complication of colonoscopic polypectomy. Endoscopy. 45 Suppl 2:E106–E107. DOI: 10.1055/s-0032-1326345. PMID: 23526500.18. He H, Rambhujun V, DeMaria M, Ali M, Vrabie R. 2020; Early postendoscopic transverse colo-colonic intussusception. Case Rep Gastroenterol. 14:1–6. DOI: 10.1159/000505228. PMID: 32009867. PMCID: PMC6984140.19. Yamashina T, Takeuchi Y, Uedo N, et al. 2016; Features of electrocoagulation syndrome after endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal neoplasm. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 31:615–620. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.13052. PMID: 26202127.20. Jehangir A, Bennett KM, Rettew AC, Fadahunsi O, Shaikh B, Donato A. 2015; Post-polypectomy electrocoagulation syndrome: a rare cause of acute abdominal pain. J Community Hosp Intern Med Perspect. 5:29147. DOI: 10.3402/jchimp.v5.29147. PMID: 26486121. PMCID: PMC4612487.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Colonic Intussusception Occurring after Colonoscopic Polypectomy
- Colonic Intussusception as a Complication after Colonoscopic Polypectomy
- Colonoscopic Diagnosis of Appendiceal Intussusception: A Case Report
- Intussusception after Colonoscopy: A Case Report and Review of Literature
- Two Cases of Malignant Lymphomas in the Terminal Ileum Causing Intussusception: Diagnosis and Reduction of Intussusception by Colonoscopy