J Korean Med Sci.
2024 Oct;39(38):e298. 10.3346/jkms.2024.39.e298.
Outpatient Renal Function Screening Before Contrast-Enhanced CT Examinations
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2559788
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2024.39.e298
Abstract
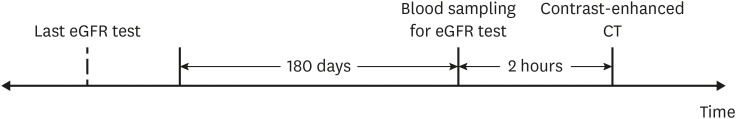
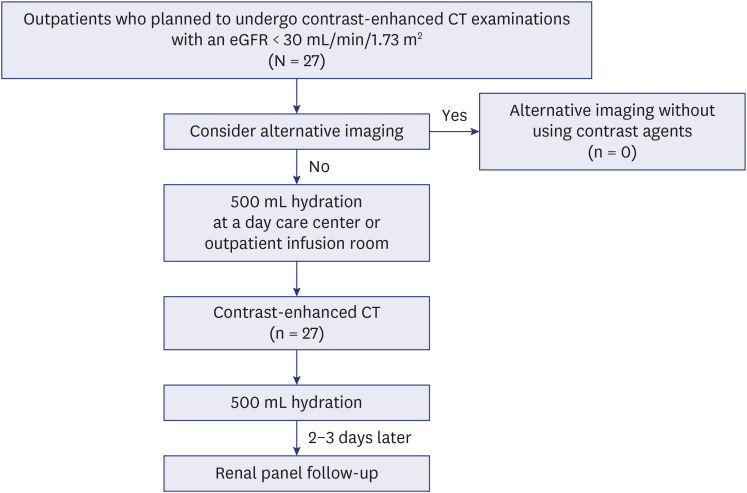
- Intravascular administration of iodinated contrast media can cause contrast-induced acute kidney injury, especially in patients with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) less than 30 mL/min/1.73 m 2 . The American College of Radiology (ACR) and the European Society of Urogenital Radiology (ESUR) guidelines recommend renal function screening based on medical history, but their effectiveness has been under-evaluated. This retrospective study included 2,560 consecutive adult outpatients without eGFR measurements within 180 days before contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) at a single tertiary hospital from July through September 2023. On the day of CT, they underwent eGFR tests and 1.1% had an eGFR < 30 mL/min/1.73 m 2 , preferentially with histories of gout and renal disease. According to the ACR and ESUR strategies, 16.9% and 38.8% of all study participants were positive, respectively, identifying 92.6% and 96.3% of patients with renal insufficiency. Both strategies demonstrated high negative predictive values. These results support selective renal function screening before contrast-enhanced examinations.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Schöckel L, Jost G, Seidensticker P, Lengsfeld P, Palkowitsch P, Pietsch H. Developments in X-ray contrast media and the potential impact on computed tomography. Invest Radiol. 2020; 55(9):592–597. PMID: 32701620.2. Maioli M, Toso A, Leoncini M, Gallopin M, Musilli N, Bellandi F. Persistent renal damage after contrast-induced acute kidney injury: incidence, evolution, risk factors, and prognosis. Circulation. 2012; 125(25):3099–3107. PMID: 22592896.3. Bahrainwala JZ, Leonberg-Yoo AK, Rudnick MR. Contrast-induced acute kidney injury: epidemiology, risk stratification, and prognosis. Rangaswami J, Lerma EV, McCullough PA, editors. Kidney Disease in the Cardiac Catheterization Laboratory: a Practical Approach. Cham, Switzerland: Springer Cham;2020. p. 183–207.4. Seeliger E, Sendeski M, Rihal CS, Persson PB. Contrast-induced kidney injury: mechanisms, risk factors, and prevention. Eur Heart J. 2012; 33(16):2007–2015. PMID: 22267241.5. Morcos R, Kucharik M, Bansal P, Al Taii H, Manam R, Casale J, et al. Contrast-induced acute kidney injury: review and practical update. Clin Med Insights Cardiol. 2019; 13:1179546819878680. PMID: 31700251.6. Aubry P, Brillet G, Catella L, Schmidt A, Bénard S. Outcomes, risk factors and health burden of contrast-induced acute kidney injury: an observational study of one million hospitalizations with image-guided cardiovascular procedures. BMC Nephrol. 2016; 17(1):167. PMID: 27821094.7. Zuo T, Jiang L, Mao S, Liu X, Yin X, Guo L. Hyperuricemia and contrast-induced acute kidney injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Cardiol. 2016; 224:286–294. PMID: 27665399.8. ACR manual on contrast media. Updated 2024. Accessed November 4, 2023. https://www.acr.org/-/media/ACR/Files/Clinical-Resources/Contrast_Media.pdf .9. Davenport MS, Khalatbari S, Cohan RH, Dillman JR, Myles JD, Ellis JH. Contrast material-induced nephrotoxicity and intravenous low-osmolality iodinated contrast material: risk stratification by using estimated glomerular filtration rate. Radiology. 2013; 268(3):719–728. PMID: 23579046.10. Ellis JH, Khalatbari S, Yosef M, Cohan RH, Davenport MS. Influence of clinical factors on risk of contrast-induced nephrotoxicity from IV iodinated low-osmolality contrast material in patients with a low estimated glomerular filtration rate. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2019; 213(5):W188–W193. PMID: 31268731.11. ESUR guidelines on contrast agents. 10.0. Updated 2018. Accessed November 4, 2023. https://www.esur.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/ESUR-Guidelines-10_0-Final-Version.pdf .12. Abbasi N, Glazer DI, Saini S, Sharma A, Khorasani R. Utility of patient-reported risk factors for identifying advanced chronic kidney disease before outpatient CT: comparison with recent ACR/NKF consensus criteria. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2022; 219(3):462–470. PMID: 35383485.13. Ledermann HP, Mengiardi B, Schmid A, Froehlich JM. Screening for renal insufficiency following ESUR (European Society of Urogenital Radiology) guidelines with on-site creatinine measurements in an outpatient setting. Eur Radiol. 2010; 20(8):1926–1933. PMID: 20309560.14. Choyke PL, Cady J, DePollar SL, Austin H. Determination of serum creatinine prior to iodinated contrast media: is it necessary in all patients? Tech Urol. 1998; 4(2):65–69. PMID: 9623618.15. Tippins RB, Torres WE, Baumgartner BR, Baumgarten DA. Are screening serum creatinine levels necessary prior to outpatient CT examinations? Radiology. 2000; 216(2):481–484. PMID: 10924574.16. Too CW, Ng WY, Tan CC, Mahmood MI, Tay KH. Screening for impaired renal function in outpatients before iodinated contrast injection: comparing the Choyke questionnaire with a rapid point-of-care-test. Eur J Radiol. 2015; 84(7):1227–1231. PMID: 25933722.17. O’Hare AM, Choi AI, Bertenthal D, Bacchetti P, Garg AX, Kaufman JS, et al. Age affects outcomes in chronic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007; 18(10):2758–2765. PMID: 17855638.18. Eriksen BO, Ingebretsen OC. The progression of chronic kidney disease: a 10-year population-based study of the effects of gender and age. Kidney Int. 2006; 69(2):375–382. PMID: 16408129.19. Iseki K, Oshiro S, Tozawa M, Iseki C, Ikemiya Y, Takishita S. Significance of hyperuricemia on the early detection of renal failure in a cohort of screened subjects. Hypertens Res. 2001; 24(6):691–697. PMID: 11768729.20. Kang DH, Nakagawa T. Uric acid and chronic renal disease: possible implication of hyperuricemia on progression of renal disease. Semin Nephrol. 2005; 25(1):43–49. PMID: 15660334.21. Mallat SG, Al Kattar S, Tanios BY, Jurjus A. Hyperuricemia, hypertension, and chronic kidney disease: an emerging association. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2016; 18(10):74. PMID: 27696189.22. Ruilope LM, Garcia-Puig J. Hyperuricemia and renal function. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2001; 3(3):197–202. PMID: 11353569.23. Oh SW, Park SY, Yong HS, Choi YH, Cha MJ, Kim TB, et al. Korean clinical practice guidelines for adverse reactions to intravenous iodinate and MRI-gadolinium contrast agents: revised clinical consensus and recommendations (3rd edition, 2022). J Korean Soc Radiol. 2022; 83(2):254–264.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Diagnostic Value of Contrast-Enhanced CT in Acute Bilateral Renal Cortical Necrosis: A Case Report
- GB Opacification at CT by Contrast Media Injected a Few Hours Earlier in Adult with Normal Renal Function
- Evaluation of Residual Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization: Comparison between Contrast-Enhanced Helical CT and Contrast-Enhanced Power Doppler Ultrasonography
- Assessment of Cystic Renal Masses Based on Bosniak Classification: Comparison of CT, Contrast-enhanced US, and MR Imaging
- Multislice computed tomography/contrast-enhanced ultrasound image fusion as a tool for evaluating unclear renal cysts