Korean J Pain.
2024 Oct;37(4):332-342. 10.3344/kjp.24172.
Effect of ultrasound-guided ilioinguinaliliohypogastric nerve block on chronic pain in patients undergoing open inguinal hernia surgery under spinal anesthesia: a randomized doubleblind study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology, Pain & Palliative Care, Kalinga Institute of Medical Sciences, KIIT Deemed To be University, Bhubaneswar, Odisha, India
- 2Department of Anaesthesiology, Kalinga Institute of Medical Sciences, KIIT Deemed To be University, Bhubaneswar, Odisha, India
- 3Department of Physiology, Kalinga Institute of Medical Sciences, KIIT Deemed To be University, Bhubaneswar, Odisha, India
- KMID: 2559695
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.24172
Abstract
- Background
Pre-operative ilioinguinal-iliohypogastric nerve block (II-IHNB) has a proven role in lessening acute postoperative pain and opioid consumption following hernia repair. However, its role in preventing post-herniorrhaphy groin pain (PHGP) is still unknown. The current study aims to assess pre-operative II-IHNB's impact on PHGP three and six months after open inguinal hernia repair under spinal anesthesia.
Methods
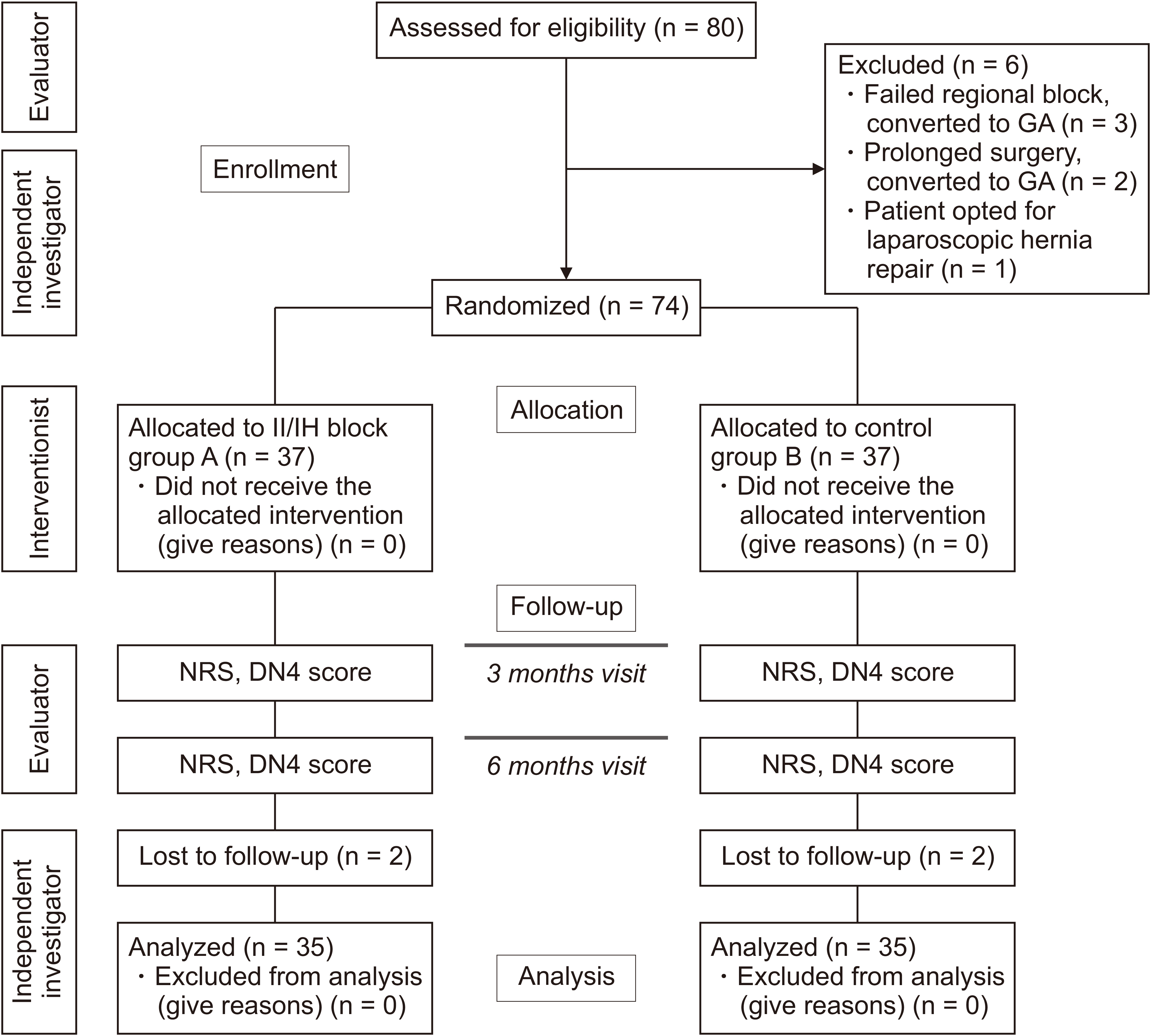
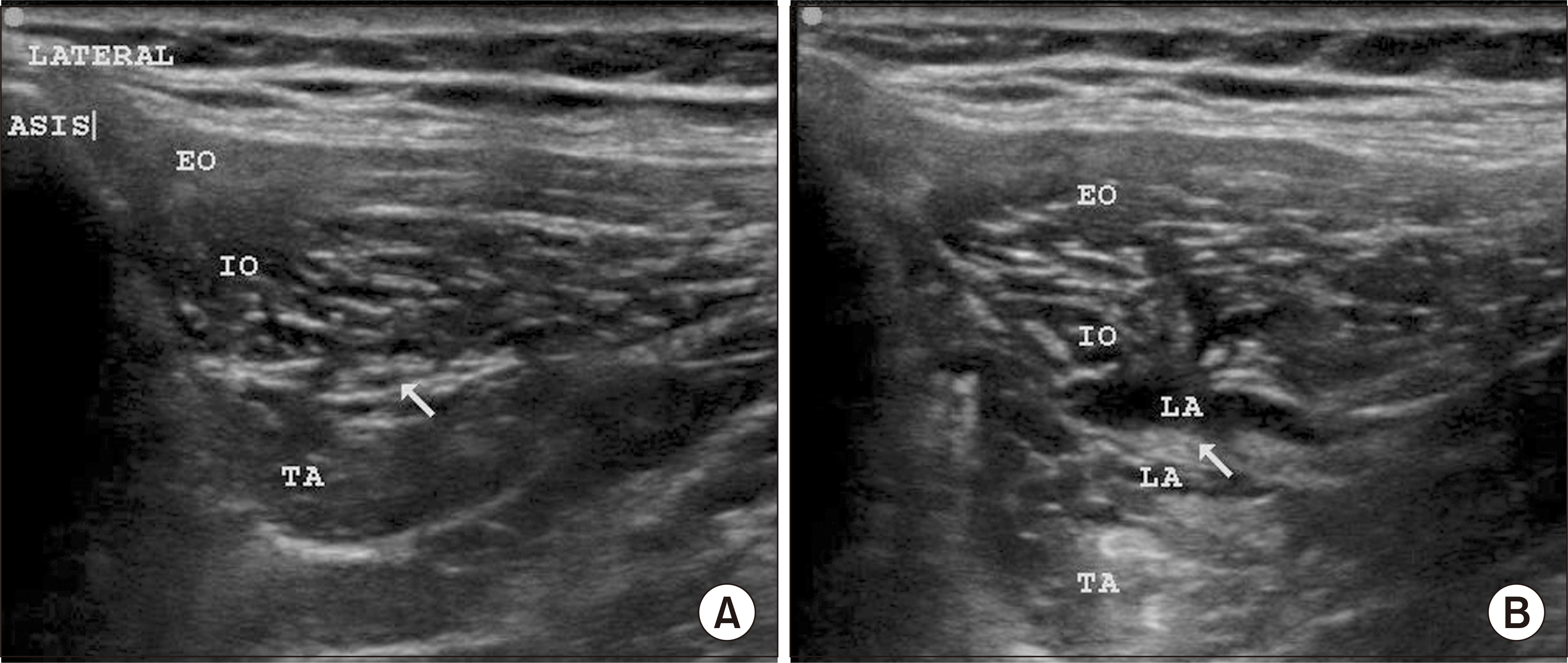
Seventy patients posted for inguinal hernia surgery were randomly allocated into group A (received ultrasound-guided II-IHNB with 10 mL of 0.5% ropivacaine and 4 mg [1 mL] dexamethasone) and group B (received ultrasound-guided II-IHNB with 11 mL of 0.9% normal saline). The time to first analgesic request, pain scores, opioid consumption, DN4 score, and PHGP at 3 and 6 months were analyzed using appropriate statistical tests.
Results
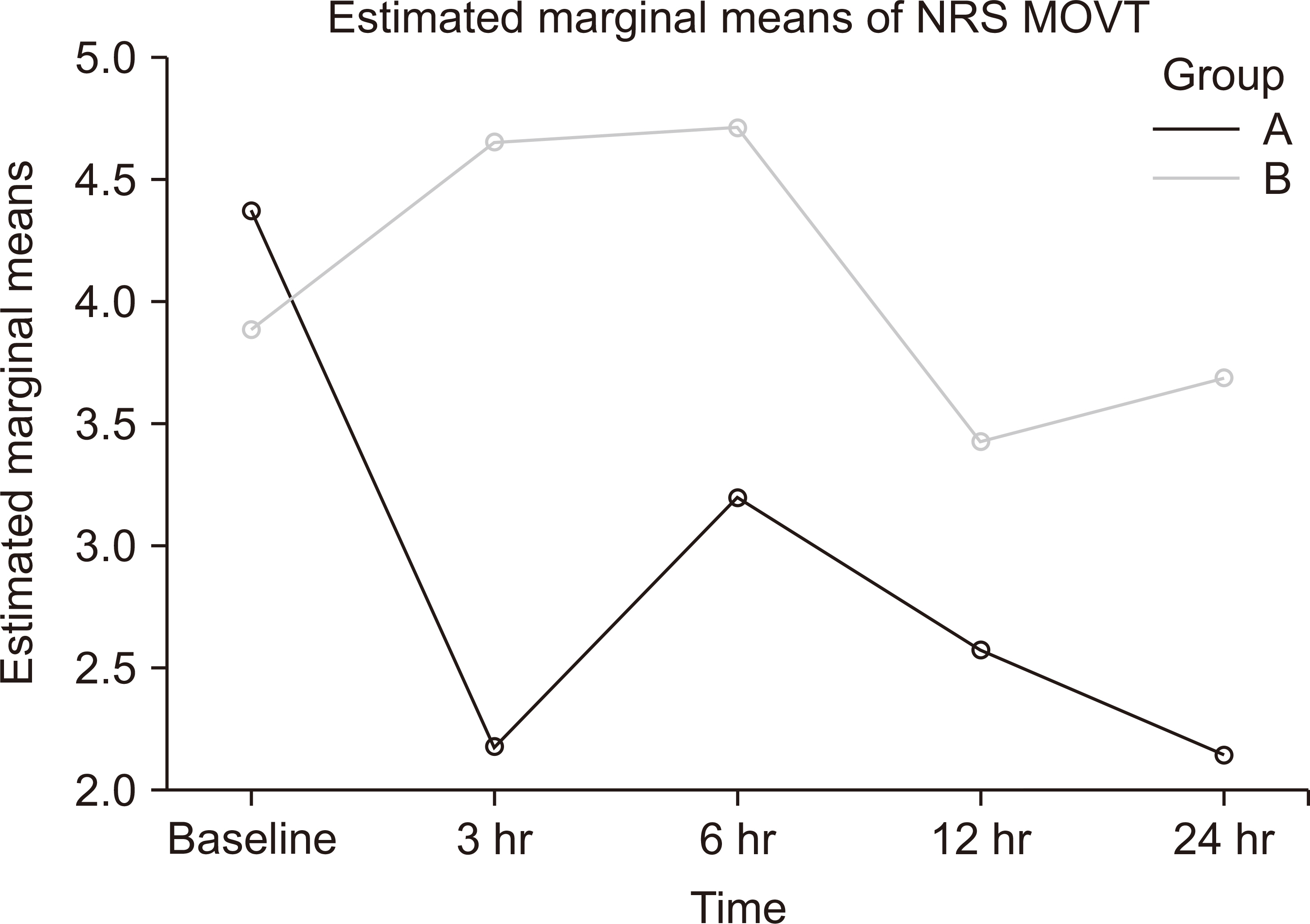
The numerical pain rating scale at movement in group A was significantly reduced at all the time intervals of 3, 6, 12, and 24 hours compared to group B. Total opioid usage was lower in group A (3.71 mg [3.90]) versus group B (12.14 mg [4.90]) with a mean difference of –8.43 mg (95% CI –10.54, –6.32), P < 0.001. The time required for the first rescue analgesic was significantly longer in group A (360 min [180–360]) versus (180 min [180–360]) in group B (P < 0.001). However, there was no difference in the incidence of PHGP at three and six months between the two groups.
Conclusions
Pre-operative ultrasound-guided II-IHNB reduces postoperative analgesic requirement but does not reduce the incidence of chronic PHGP following hernia surgery at 6 months.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kurzer M, Kark A, Hussain ST. 2009; Day-case inguinal hernia repair in the elderly: a surgical priority. Hernia. 13:131–6. DOI: 10.1007/s10029-008-0452-3. PMID: 19034602.2. Gram-Hanssen A, Öberg S, Rosenberg J. 2023; A critical appraisal of the chronic pain rate after inguinal hernia repair. J Abdom Wall Surg. 2:10972. DOI: 10.3389/jaws.2023.10972. PMID: 38312409. PMCID: PMC10831660.3. Schug SA, Lavand'homme P, Barke A, Korwisi B, Rief W. Treede RD; IASP Taskforce for the Classification of Chronic Pain. 2019; The IASP classification of chronic pain for ICD-11: chronic postsurgical or posttraumatic pain. Pain. 160:45–52. DOI: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001413. PMID: 30586070.4. Khan JS, Rai A, Sundara Rajan R, Jackson TD, Bhatia A. 2016; A scoping review of perineural steroids for the treatment of chronic postoperative inguinal pain. Hernia. 20:367–76. DOI: 10.1007/s10029-016-1487-5. PMID: 27033854.5. Rosenberger DC, Pogatzki-Zahn EM. 2022; Chronic post-surgical pain - update on incidence, risk factors and preventive treatment options. BJA Educ. 22:190–6. DOI: 10.1016/j.bjae.2021.11.008. PMID: 35496645. PMCID: PMC9039436.6. Nienhuijs S, Staal E, Strobbe L, Rosman C, Groenewoud H, Bleichrodt R. 2007; Chronic pain after mesh repair of inguinal hernia: a systematic review. Am J Surg. 194:394–400. DOI: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2007.02.012. PMID: 17693290.7. Aasvang E, Kehlet H. 2005; Chronic postoperative pain: the case of inguinal herniorrhaphy. Br J Anaesth. 95:69–76. DOI: 10.1093/bja/aei019. PMID: 15531621.8. Thomassen I, van Suijlekom HA, van der Gaag A, Nienhuijs SW. 2012; Intervention techniques for chronic post herniorrhaphy pain. Eur Surg. 44:132–7. DOI: 10.1007/s10353-011-0035-x.9. Thapa P, Euasobhon P. 2018; Chronic postsurgical pain: current evidence for prevention and management. Korean J Pain. 31:155–73. DOI: 10.3344/kjp.2018.31.3.155. PMID: 30013730. PMCID: PMC6037807.10. Kamal K, Jain P, Bansal T, Ahlawat G. 2018; A comparative study to evaluate ultrasound-guided transversus abdominis plane block versus ilioinguinal iliohypogastric nerve block for post-operative analgesia in adult patients undergoing inguinal hernia repair. Indian J Anaesth. 62:292–7. DOI: 10.4103/ija.IJA_548_17. PMID: 29720755. PMCID: PMC5907435.11. Eichenberger U, Greher M, Kirchmair L, Curatolo M, Moriggl B. 2006; Ultrasound-guided blocks of the ilioinguinal and iliohypogastric nerve: accuracy of a selective new technique confirmed by anatomical dissection. Br J Anaesth. 97:238–43. DOI: 10.1093/bja/ael103. PMID: 16698865.12. Bouhassira D, Attal N, Alchaar H, Boureau F, Brochet B, Bruxelle J, et al. 2005; Comparison of pain syndromes associated with nervous or somatic lesions and development of a new neuropathic pain diagnostic questionnaire (DN4). Pain. 114:29–36. DOI: 10.1016/j.pain.2004.12.010. PMID: 15733628.13. Onur T, Ökmen K, Terkanlıoğlu S, Onur A. Karaca Ümran. 2022; The effects of ilioinguinal nerve block on acute and chronic neuropathic pain in patients following inguinal hernia repair with spinal anesthesia: a prospective cohort study. J Surg Med. 6:120–4. DOI: 10.28982/josam.891954.14. Cunningham J, Temple WJ, Mitchell P, Nixon JA, Preshaw RM, Hagen NA. 1996; Cooperative hernia study. Pain in the postrepair patient. Ann Surg. 224:598–602. DOI: 10.1097/00000658-199611000-00003. PMID: 8916874. PMCID: PMC1235436.15. Kehlet H, Bay-Nielsen M, Kingsnorth A. 2002; Chronic postherniorrhaphy pain--a call for uniform assessment. Hernia. 6:178–81. DOI: 10.1007/s10029-002-0082-0. PMID: 12424597.16. Molegraaf M, Lange J, Wijsmuller A. 2017; Uniformity of chronic pain assessment after inguinal hernia repair: a critical review of the literature. Eur Surg Res. 58:1–19. DOI: 10.1159/000448706. PMID: 27577699. PMCID: PMC5296927.17. HerniaSurge Group. 2018; International guidelines for groin hernia management. Hernia. 22:1–165. DOI: 10.1007/s10029-017-1668-x. PMID: 29330835. PMCID: PMC5809582.18. Alfieri S, Amid PK, Campanelli G, Izard G, Kehlet H, Wijsmuller AR, et al. 2011; International guidelines for prevention and management of post-operative chronic pain following inguinal hernia surgery. Hernia. 15:239–49. DOI: 10.1007/s10029-011-0798-9. PMID: 21365287.19. Kehlet H, Roumen RM, Reinpold W, Miserez M. 2013; Invited commentary: persistent pain after inguinal hernia repair: what do we know and what do we need to know? Hernia. 17:293–7. DOI: 10.1007/s10029-013-1109-4. PMID: 23686405.20. Andreae MH, Andreae DA. 2013; Regional anaesthesia to prevent chronic pain after surgery: a Cochrane systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Anaesth. 111:711–20. DOI: 10.1093/bja/aet213. PMID: 23811426. PMCID: PMC3793661.21. Humble SR, Dalton AJ, Li L. 2015; A systematic review of therapeutic interventions to reduce acute and chronic post-surgical pain after amputation, thoracotomy or mastectomy. Eur J Pain. 19:451–65. DOI: 10.1002/ejp.567. PMID: 25088289. PMCID: PMC4405062.22. Borghi B, D'Addabbo M, White PF, Gallerani P, Toccaceli L, Raffaeli W, et al. 2010; The use of prolonged peripheral neural blockade after lower extremity amputation: the effect on symptoms associated with phantom limb syndrome. Anesth Analg. 111:1308–15. DOI: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e3181f4e848. PMID: 20881281.23. Sentürk M, Ozcan PE, Talu GK, Kiyan E, Camci E, Ozyalçin S, et al. 2002; The effects of three different analgesia techniques on long-term postthoracotomy pain. Anesth Analg. 94:11–5. DOI: 10.1213/00000539-200201000-00003. PMID: 11772793.24. Elahwal L, Elrahwan S, Elbadry AA. 2022; Ilioinguinal and iliohypogastric nerve block for acute and chronic pain relief after caesarean section: a randomized controlled trial. Anesth Pain Med. 12:e121837. DOI: 10.5812/aapm.121837. PMID: 35991778. PMCID: PMC9375958.25. Okur O, Tekgul ZT, Erkan N. 2017; Comparison of efficacy of transversus abdominis plane block and iliohypogastric/ilioinguinal nerve block for postoperative pain management in patients undergoing inguinal herniorrhaphy with spinal anesthesia: a prospective randomized controlled open-label study. J Anesth. 31:678–85. DOI: 10.1007/s00540-017-2378-3. PMID: 28616651.26. Aveline C, Le Hetet H, Le Roux A, Vautier P, Cognet F, Vinet E, et al. 2011; Comparison between ultrasound-guided transversus abdominis plane and conventional ilioinguinal/iliohypogastric nerve blocks for day-case open inguinal hernia repair. Br J Anaesth. 106:380–6. DOI: 10.1093/bja/aeq363. PMID: 21177284.27. Hosalli V, Ayyanagouda B, Hiremath P, Ambi U, Hulkund SY. 2019; Comparative efficacy of postoperative analgesia between ultrasound-guided dual transversus abdominis plane and Ilioinguinal/Iliohypogastric nerve blocks for open inguinal hernia repair: an open label prospective randomised comparative clinical trial. Indian J Anaesth. 63:450–5. DOI: 10.4103/ija.IJA_153_19. PMID: 31263296. PMCID: PMC6573039.28. Faiz SHR, Nader ND, Niknejadi S, Davari-Farid S, Hobika GG, Rahimzadeh P. 2019; A clinical trial comparing ultrasound-guided ilioinguinal/iliohypogastric nerve block to transversus abdominis plane block for analgesia following open inguinal hernia repair. J Pain Res. 12:201–7. Erratum in: J Pain Res 2023; 16: 681-2. DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S179506. PMID: 36908926. PMCID: PMC9999711.29. Mostafa SF, Abdelghany MS, Elyazed MMA. 2023; Analgesic efficacy of ultrasound guided quadratus lumborum block versus ilioinguinal/iliohypogastric nerve block following pediatric open inguinal hernia repair: a prospective randomized controlled trial. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 39:134–40. DOI: 10.4103/joacp.joacp_127_21. PMID: 37250238. PMCID: PMC10220194.30. Varsha R, Desai SN, Mudakanagoudar MS, Annigeri VM. 2021; Comparison between caudal epidural and ultrasound-guided ilioinguinal-iliohypogastric block with bupivacaine and dexmedetomidine for postoperative analgesia following pediatric inguinal hernia surgeries: a prospective randomized, double-blind study. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 37:389–94. DOI: 10.4103/joacp.JOACP_175_19. PMID: 34759549. PMCID: PMC8562458.31. Fekry DM, Megahed NA, EL-Lakany MH, Yakout MMS. 2017; Ultrasound-guided ilioinguinal, iliohypogastric, and genitofemoral nerve block versus spinal subarachnoid blockade for inguinal hernia repair. Res Opin Anesth Intensive Care. 4:29–34. DOI: 10.4103/2356-9115.202693.32. Singh R, Yadav K, Singh P. 2023; Efficacy of analgesia using ilioinguinal-iliohypogastric (IIIH) nerve block, transversus abdominis plane (TAP) block and diclofenac after caesarean delivery under spinal anaesthesia: a non-randomised clinical trial. Indian J Anaesth. 67:638–43. DOI: 10.4103/ija.ija_746_22. PMID: 37601938. PMCID: PMC10436716.33. Santos Gde C, Braga GM, Queiroz FL, Navarro TP, Gomez RS. 2011; Assessment of postoperative pain and hospital discharge after inguinal and iliohypogastric nerve block for inguinal hernia repair under spinal anesthesia: a prospective study. Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992). 57:545–9. DOI: 10.1016/S0104-4230(11)70109-9. PMID: 22012289.34. Ünlütürk Z, Öztekin SNS, Alkan H, Şenol H, Betaş S, Erdoğan Ç. 2022; Which scale is more useful to detect diabetic neuropathic pain?: a cross-sectional study. BMC Endocr Disord. 22:56. DOI: 10.1186/s12902-022-00970-3. PMID: 35255868. PMCID: PMC8900336.35. Clarke H, Bonin RP, Orser BA, Englesakis M, Wijeysundera DN, Katz J. 2012; The prevention of chronic postsurgical pain using gabapentin and pregabalin: a combined systematic review and meta-analysis. Anesth Analg. 115:428–42. DOI: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e318249d36e. PMID: 22415535.36. Mishriky BM, Waldron NH, Habib AS. 2015; Impact of pregabalin on acute and persistent postoperative pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Anaesth. 114:10–31. DOI: 10.1093/bja/aeu293. PMID: 25209095.37. Martinez V, Pichard X, Fletcher D. 2017; Perioperative pregabalin administration does not prevent chronic postoperative pain: systematic review with a meta-analysis of randomized trials. Pain. 158:775–83. DOI: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000838.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Utility of ultrasound-guided transversus abdominis plane block for day-case inguinal hernia repair
- Ultrasound-guided transversalis fascia plane block versus transmuscular quadratus lumborum block for post-operative analgesia in inguinal hernia repair
- Comparison of the analgesic efficacy of the ultrasound-guided transversalis fascia plane block and erector spinae plane block in patients undergoing open inguinal hernia repair under spinal anesthesia
- The Efficacy of Ultrasound-Guided Lower Extremity Nerve Block in Trauma Patients
- Intrathecal levobupivacaine versus bupivacaine for inguinal hernia surgery: a randomized controlled trial