J Korean Foot Ankle Soc.
2024 Sep;28(3):96-101. 10.14193/jkfas.2024.28.3.96.
Predictive Factors for Secondary Revasculation Procedures in Patients with Diabetic Foot Gangrene Undergoing Transtibial Amputation Following Revascularization
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- KMID: 2559638
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14193/jkfas.2024.28.3.96
Abstract
- Purpose
Diabetic foot ulcers and gangrene are major complications of diabetes, often accompanied by peripheral vascular occlusion. Revascularization is performed to restore blood flow and reduce complications such as amputation surgery. Nevertheless, reocclusion, a frequently reported complication after revascularization, often necessitates further lower limb amputations to facilitate rehabilitation and ambulation. This study examined the factors influencing the performance of secondary revascularization procedures in patients with diabetic foot gangrene who even underwent transtibial amputation (TTA) following revascularization.
Materials and Methods
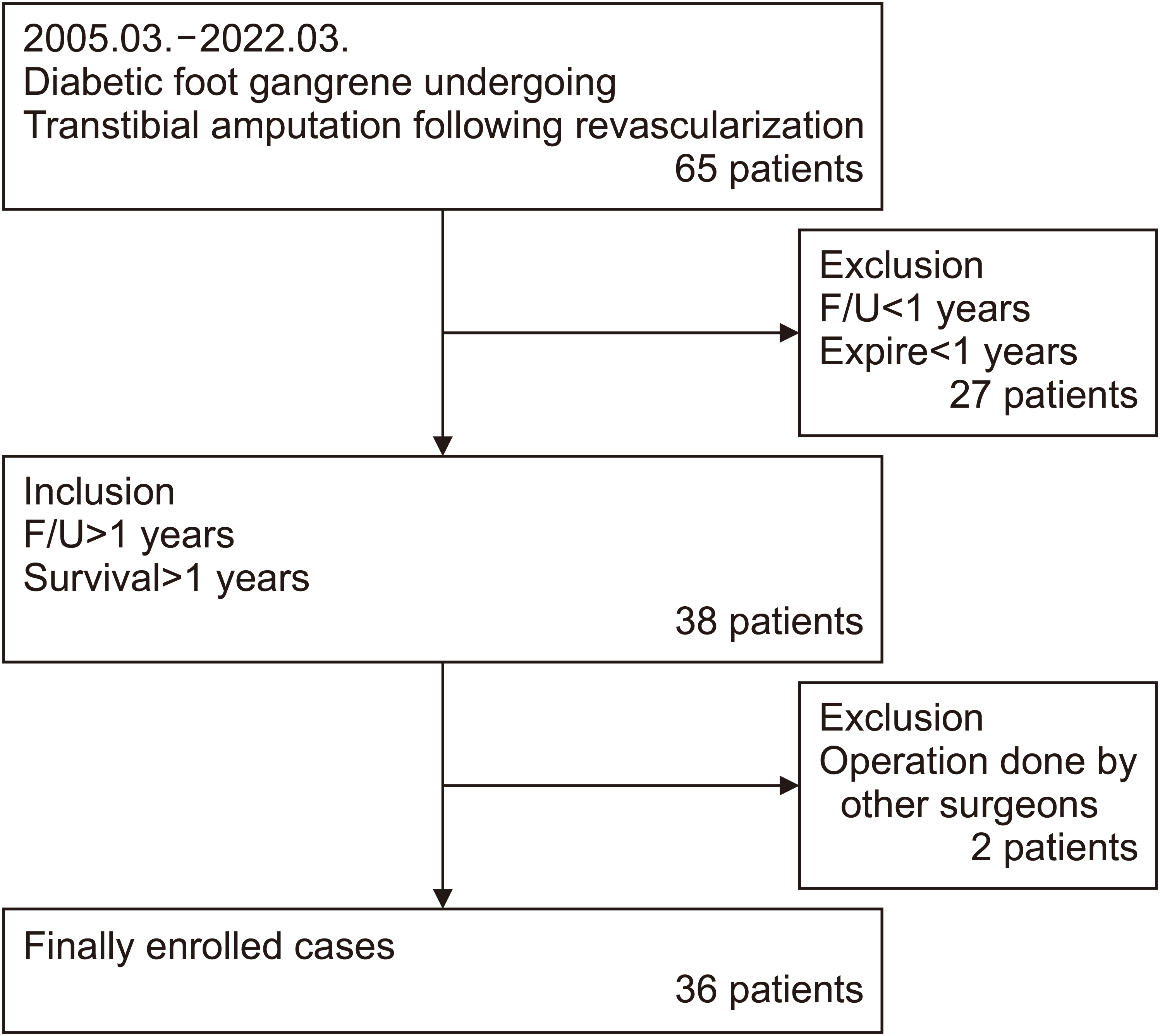
A retrospective study was conducted on 36 patients with diabetic foot gangrene who underwent TTA after revascularization from March 2005 to March 2022. The factors influencing restenosis were classified into three categories: revascularization factors, preoperative factors, and intraoperative factors. The revascularization factors were categorized based on whether percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA) or bypass surgery had been performed. Preoperative factors included the patient’s age, gender, body mass index (BMI), hypertension, and other relevant factors. Intraoperative factors included surgery duration, blood loss, and transfusion. The study examined the factors influencing secondary revascularization in these three categories.
Results
Among the 36 patients in the study, 27.8% (11 patients) underwent secondary revascularization procedures. There was no significant correlation between the performance of secondary revascularization and the type of revascularization procedure, whether PTA or bypass surgery (p>0.05). Similarly, no significant differences were observed in preoperative factors (including age, BMI, smoking status, HbA1c, and underlying diseases) and intraoperative factors (surgery duration, blood loss, and transfusion). On the other hand, regarding gender, all patients who underwent revascularization procedures were male, indicating a statistically significant result (p=0.039).
Conclusion
This study suggests that while most clinical variables showed no association with reocclusion, the fact that all patients who underwent secondary revascularization procedures were male indicates that gender may be a significant predictive factor of revascularization.
Keyword
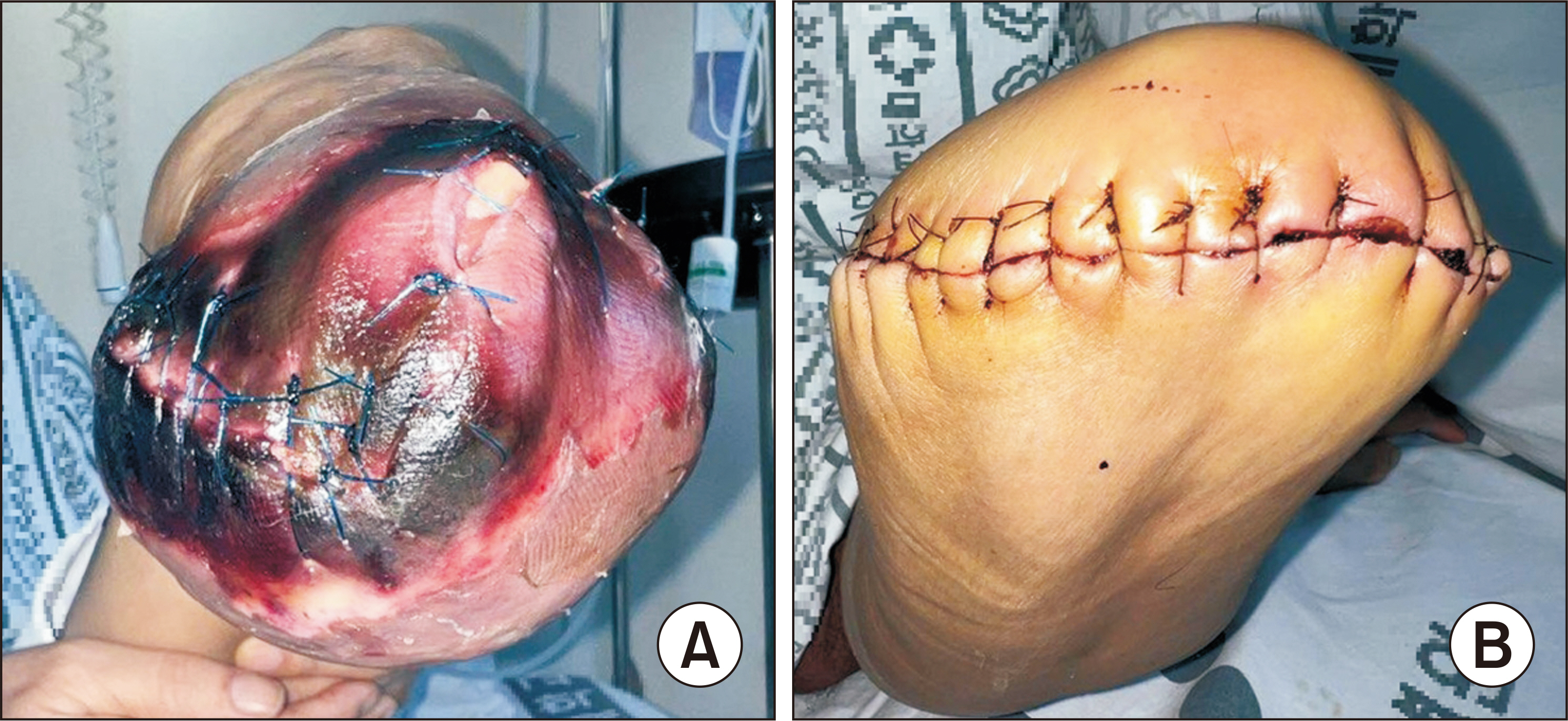
Figure
Reference
-
1. Boulton AJ, Meneses P, Ennis WJ. 1999; Diabetic foot ulcers: a framework for prevention and care. Wound Repair Regen. 7:7–16. doi: 10.1046/j.1524-475x.1999.00007.x. DOI: 10.1046/j.1524-475x.1999.00007.x. PMID: 10231501.2. American Diabetes Association. 1999; Consensus development conference on diabetic foot wound care: 7-8 April 1999, Boston, Massachusetts. Diabetes Care. 22:1354–60. doi: 10.2337/diacare.22.8.1354. DOI: 10.2337/diacare.22.8.1354. PMID: 10480782.3. Ramsey SD, Newton K, Blough D, McCulloch DK, Sandhu N, Reiber GE, et al. 1999; Incidence, outcomes, and cost of foot ulcers in patients with diabetes. Diabetes Care. 22:382–7. doi: 10.2337/diacare.22.3.382. DOI: 10.2337/diacare.22.3.382. PMID: 10097914.4. Stone PA, Back MR, Armstrong PA, Flaherty SK, Keeling WB, Johnson BL, et al. 2005; Midfoot amputations expand limb salvage rates for diabetic foot infections. Ann Vasc Surg. 19:805–11. doi: 10.1007/s10016-005-7973-3. DOI: 10.1007/s10016-005-7973-3. PMID: 16205848.5. LoGerfo FW, Gibbons GW, Pomposelli FB Jr, Campbell DR, Miller A, Freeman DV, et al. 1992; Trends in the care of the diabetic foot. Expanded role of arterial reconstruction. Arch Surg. 127:617–20. discussion 620-1. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1992.01420050145019. DOI: 10.1001/archsurg.1992.01420050145019. PMID: 1575632.6. Weitz JI, Byrne J, Clagett GP, Farkouh ME, Porter JM, Sackett DL, et al. 1996; Diagnosis and treatment of chronic arterial insufficiency of the lower extremities: a critical review. Circulation. 94:3026–49. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.94.11.3026. DOI: 10.1161/01.CIR.94.11.3026. PMID: 8941154.7. Rosenblum BI, Pomposelli FB Jr, Giurini JM, Gibbons GW, Freeman DV, Chrzan JS, et al. 1994; Maximizing foot salvage by a combined approach to foot ischemia and neuropathic ulceration in patients with diabetes. A 5-year experience. Diabetes Care. 17:983–7. doi: 10.2337/diacare.17.9.983. DOI: 10.2337/diacare.17.9.983. PMID: 7988319.8. Faglia E, Favales F, Quarantiello A, Calia P, Brambilla G, Rampoldi A, et al. 1996; Feasibility and effectiveness of peripheral percutaneous transluminal balloon angioplasty in diabetic subjects with foot ulcers. Diabetes Care. 19:1261–4. doi: 10.2337/diacare.19.11.1261. DOI: 10.2337/diacare.19.11.1261. PMID: 8908391.9. Hanna GP, Fujise K, Kjellgren O, Feld S, Fife C, Schroth G, et al. 1997; Infrapopliteal transcatheter interventions for limb salvage in diabetic patients: importance of aggressive interventional approach and role of transcutaneous oximetry. J Am Coll Cardiol. 30:664–9. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(97)00216-7. DOI: 10.1016/S0735-1097(97)00216-7. PMID: 9283523.10. Park CM, Huh SH, Kim DI, Lee BB. 2003; Clinical experiences of lower limb amputation in ischemic arterial disease. Korean J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 19:57–61.11. Matsi PJ, Manninen HI, Vanninen RL, Suhonen MT, Oksala I, Laakso M, et al. 1994; Femoropopliteal angioplasty in patients with claudication: primary and secondary patency in 140 limbs with 1-3-year follow-up. Radiology. 191:727–33. doi: 10.1148/radiology.191.3.8184053. DOI: 10.1148/radiology.191.3.8184053. PMID: 8184053.12. Szilagyi DE, Hageman JH, Smith RF, Elliott JP, Brown F, Dietz P. 1979; Autogenous vein grafting in femoropopliteal atherosclerosis: the limits of its effectiveness. Surgery. 86:836–51. doi: 10.5555/uri:pii:0039606079901818. PMID: 515951.13. Kacoyanis GP, Whittemore AD, Couch NP, Mannick JA. 1981; Femorotibial and femoroperoneal bypass vein grafts. A 15-year experience. Arch Surg. 116:1529–34. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1981.01380240019003. DOI: 10.1001/archsurg.1981.01380240019003. PMID: 7316751.14. Kretschmer G, Wenzl E, Wagner O, Polterauer P, Ehringer H, Minar E, et al. 1986; Influence of anticoagulant treatment in preventing graft occlusion following saphenous vein bypass for femoropopliteal occlusive disease. Br J Surg. 73:689–92. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800730903. DOI: 10.1002/bjs.1800730903. PMID: 3530366.15. McCollum C, Alexander C, Kenchington G, Franks PJ, Greenhalgh R. 1991; Antiplatelet drugs in femoropopliteal vein bypasses: a multicenter trial. J Vasc Surg. 13:150–61. discussion 161-2. DOI: 10.1016/0741-5214(91)90022-M. PMID: 1987387.16. Yang YB, Shen J, Wang SH, Song JB, Ge F, Xie JP, et al. 2020; A risk predictor of restenosis after superficial femoral artery stent implantation: relevance of mean platelet volume. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 20:361. doi: 10.1186/s12872-020-01633-8. DOI: 10.1186/s12872-020-01633-8. PMID: 32770951. PMCID: PMC7414580.17. Takahara M, Kaneto H, Iida O, Gorogawa S, Katakami N, Matsuoka TA, et al. 2010; The influence of glycemic control on the prognosis of Japanese patients undergoing percutaneous transluminal angioplasty for critical limb ischemia. Diabetes Care. 33:2538–42. doi: 10.2337/dc10-0939. DOI: 10.2337/dc10-0939. PMID: 20843974. PMCID: PMC2992184.18. Holtman D, Gahtan V. 2008; Peripheral Arterial Perfusion: Is it Adequate for Wound Healing? Wounds. 20:230–5. PMID: 25941794.19. Schmiegelow MT, Sode N, Riis T, Lauritzen JB, Duus BR, Lindberg-Larsen M. 2018; Re-amputations and mortality after below-knee, through-knee and above-knee amputations. Dan Med J. 65:A5520. PMID: 30511636.20. van der Zaag ES, Legemate DA, Prins MH, Reekers JA, Jacobs MJ. 2004; Angioplasty or bypass for superficial femoral artery disease? A randomised controlled trial. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 28:132–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2004.04.003. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2004.04.003. PMID: 15234692.21. Rieß HC, Debus ES, Heidemann F, Stoberock K, Grundmann RT, Behrendt CA. 2017; Gender differences in endovascular treatment of infrainguinal peripheral artery disease. Vasa. 46:296–303. doi: 10.1024/0301-1526/a000634. DOI: 10.1024/0301-1526/a000634. PMID: 28448207.22. Jelani QU, Petrov M, Martinez SC, Holmvang L, Al-Shaibi K, Alasnag M. 2018; Peripheral arterial disease in women: an overview of risk factor profile, clinical features, and outcomes. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 20:40. doi: 10.1007/s11883-018-0742-x. DOI: 10.1007/s11883-018-0742-x. PMID: 29858704. PMCID: PMC5984648.23. Morrison A, Aday AW. 2022; Sex as a key determinant of peripheral artery disease: epidemiology, differential outcomes, and proposed biological mechanisms. Can J Cardiol. 38:601–11. doi: 10.1016/j.cjca.2022.02.021. DOI: 10.1016/j.cjca.2022.02.021. PMID: 35231552. PMCID: PMC9090953.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Precipitating Factors of Amputation as Initial Treatment in Diabetic Foot
- Managing Complicated Diabetic Foot Ulcers with Peripheral Arterial Disease
- The Usefulness of Infrapopliteal Percutaneous Transluminal Angioplasty in the Treatment of Diabetic Gangrene
- Clinical Analysis of Diabetic Gangrene
- Amputation in Diabetic Foot Ulcer and Infection