Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab.
2024 Aug;29(4):234-241. 10.6065/apem.2346182.091.
New-onset diabetes in children during the COVID-19 Pandemic: an assessment of biomarkers and psychosocial risk factors at play in Mississippi
- Affiliations
-
- 1Arkansas Children's Hospital, Little Rock, AR, USA
- 2University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson, MS, USA
- 3Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, MA, USA
- KMID: 2559451
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.6065/apem.2346182.091
Abstract
- Purpose
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic has led to an association between COVID-19 and pediatric diabetes. Studies have indicated the increased likelihood of children with COVID-19 infection developing diabetes. Our objective was to assess not only the increase in pediatric diabetes at our hospital and identify possible risk factors, but also to correlate the psychosocial changes resulting from the pandemic with new-onset diabetes.
Methods
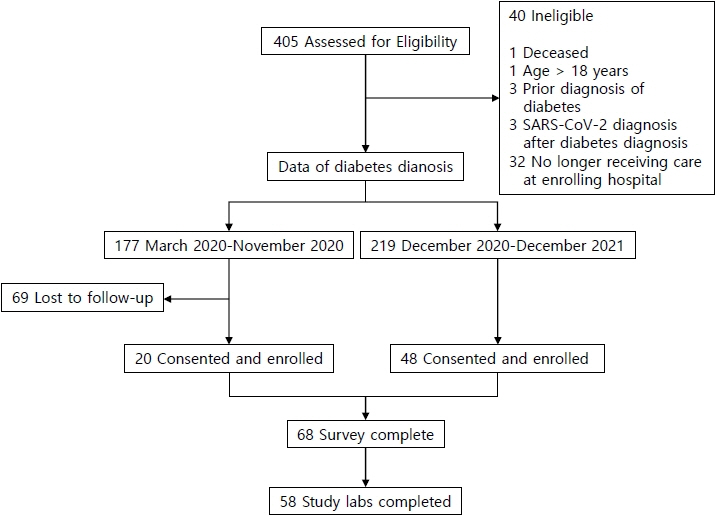
We analyzed data from 58 children aged 1 to 18 years admitted to our hospital with new-onset diabetes between March 2020 and December 2021. The data included inflammatory biomarkers and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) antibodies (Abs), as well as the results of a lifestyle questionnaire.
Results
The average number of hospital admissions per month for new-onset diabetes increased from 10 to 18 with the start of the pandemic. Of the 58 children in our analysis, 33% had positive SARS-CoV-2 IgG Ab, 31% had type 1 diabetes mellitus, and 62% had type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). More than half (54%) were experiencing diabetic ketoacidosis. Those with T2DM were older, majority African American, had higher median body mass index (BMI) percentiles, and lower vitamin D levels. There were no significant correlations between any psychosocial risk factors and either diabetes type or SARS-CoV2 Ab status.
Conclusion
Despite the increased incidence of new-onset diabetes among children in Mississippi during the pandemic, this study was unable to demonstrate a significant correlation between COVID-19 infection and new-onset diabetes. The findings of this study highlighted the correlation between increased BMI and type 2 diabetes, underscoring the significant problems of obesity and diabetes in our study region. Further research is warranted.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Commentary on "New-onset diabetes in children during the COVID-19 Pandemic: an assessment of biomarkers and psychosocial risk factors at play in Mississippi"
Se Young Kim
Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2024;29(4):209-210. doi: 10.6065/apem.24223091edi04.
Reference
-
References
1. Gottesman BL, Yu J, Tanaka C, Longhurst CA, Kim JJ. Incidence of new-onset type 1 diabetes among US children during the COVID-19 global pandemic. JAMA Pediatr. 2022; 176:414–5.
Article2. Vlad A, Serban V, Timar R, Sima A, Botea V, Albai O, et al. Increased incidence of type 1 diabetes during the COVID-19 pandemic in Romanian children. Medicina (Kaunas). 2021; 57:973.
Article3. Unsworth R, Wallace S, Oliver NS, Yeung S, Kshirsagar A, Naidu H, et al. New-onset type 1 diabetes in children during COVID-19: multicenter regional findings in the U.K. Diabetes Care. 2020; 43:e170. –1.
Article4. Barrett CE, Koyama AK, Alvarez P, Chow W, Lundeen EA, Perrine CG, et al. Risk for newly diagnosed diabetes >30 days after SARS-CoV-2 infection among persons aged <18 years - United States, March 1, 2020-June 28, 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2022; 71:59–65.
Article5. Yang JK, Lin SS, Ji XJ, Guo LM. Binding of SARS coronavirus to its receptor damages islets and causes acute diabetes. Acta Diabetol. 2010; 47:193–9.6. Magrone T, Magrone M, Jirillo E. Focus on receptors for coronaviruses with special reference to angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 as a potential drug target - a perspective. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2020; 20:807–11.7. Jenssen BP, Kelly MK, Powell M, Bouchelle Z, Mayne SL, Fiks AG. COVID-19 and changes in child obesity. Pediatrics. 2021; 147:e2021050123.
Article8. Maurya R, Sebastian P, Namdeo M, Devender M, Gertler A. COVID-19 severity in obesity: leptin and inflammatory cytokine interplay in the link between high morbidity and mortality. Front Immunol. 2021; 12:649359.
Article9. Bode B, Garrett V, Messler J, McFarland R, Crowe J, Booth R, et al. Glycemic characteristics and clinical outcomes of COVID-19 patients hospitalized in the United States. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2020; 14:813–21.
Article10. Harris PA, Taylor R, Thielke R, Payne J, Gonzalez N, Conde JG. Research electronic data capture (REDCap)--a metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support. J Biomed Inform. 2009; 42:377–81.
Article11. Harris PA, Taylor R, Minor BL, Elliott V, Fernandez M, O'Neal L, et al. The REDCap consortium: building an international community of software platform partners. J Biomed Inform. 2019; 95:103208.
Article12. Ho J, Rosolowsky E, Pacaud D, Huang C, Lemay JA, Brockman N, et al. Diabetic ketoacidosis at type 1 diabetes diagnosis in children during the COVID-19 pandemic. Pediatr Diabetes. 2021; 22:552–7.
Article13. Chambers MA, Mecham C, Arreola EV, Sinha M. Increase in the number of pediatric new-onset diabetes and diabetic ketoacidosis cases during the COVID-19 pandemic. Endocr Pract. 2022; 28:479–85.
Article14. Xiao K, Yang H, Liu B, Pang X, Du J, Liu M, et al. Antibodies can last for more than 1 year after SARS-CoV-2 infection: a follow-up study from survivors of COVID-19. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021; 8:684864.
Article15. van der Voort PHJ, Moser J, Zandstra DF, Muller Kobold AC, Knoester M, Calkhoven CF, et al. Leptin levels in SARS-CoV-2 infection related respiratory failure: a cross-sectional study and a pathophysiological framework on the role of fat tissue. Heliyon. 2020; 6:e04696.
Article16. Jones SA, Hunter CA. Is IL-6 a key cytokine target for therapy in COVID-19? Nat Rev Immunol. 2021; 21:337–9.
Article17. Shaw J. Epidemiology of childhood type 2 diabetes and obesity. Pediatr Diabetes. 2007; 8 Suppl 9:7–15.
Article18. Zakharova I, Klimov L, Kur yaninova V, Nikitina I, Malyavskaya S, Dolbnya S, et al. Vitamin D insufficiency in overweight and obese children and adolescents. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019; 10:103.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Commentary on "New-onset diabetes in children during the COVID-19 Pandemic: an assessment of biomarkers and psychosocial risk factors at play in Mississippi"
- COVID-19 and diabetes in children
- New-onset type 1 diabetes mellitus in the Paediatric Emergency Department: impact of the COVID-19 pandemic
- Association of Sociodemographic and Psychosocial Factors With COVID-19–Related Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder Risk Group Among Medical Students
- Factors Influencing Psychosocial Well-being of General Hospital Nurses Following the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Cross-sectional Study