Endocrinol Metab.
2024 Aug;39(4):622-631. 10.3803/EnM.2024.1965.
Financial Benefits of Renal Dose-Adjusted Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University Dongtan Sacred Heart Hospital, College of Medicine, Hallym University, Hwaseong, Korea
- 3Department of Applied Statistics, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea
- 4Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 5Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea
- 6Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea
- 7College of Nursing, Gachon University, Incheon, Korea
- 8Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University Anam Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 9Cardiovascular Center, Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University Anam Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 10Department of Internal Medicine, Ewha Womans University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 11Division of Infectious Disease, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University Anam Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 12Department of Transdisciplinary Medicine, Institute of Convergence Medicine with Innovative Technology, Seoul, Korea
- 13Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2558946
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2024.1965
Abstract
- Background
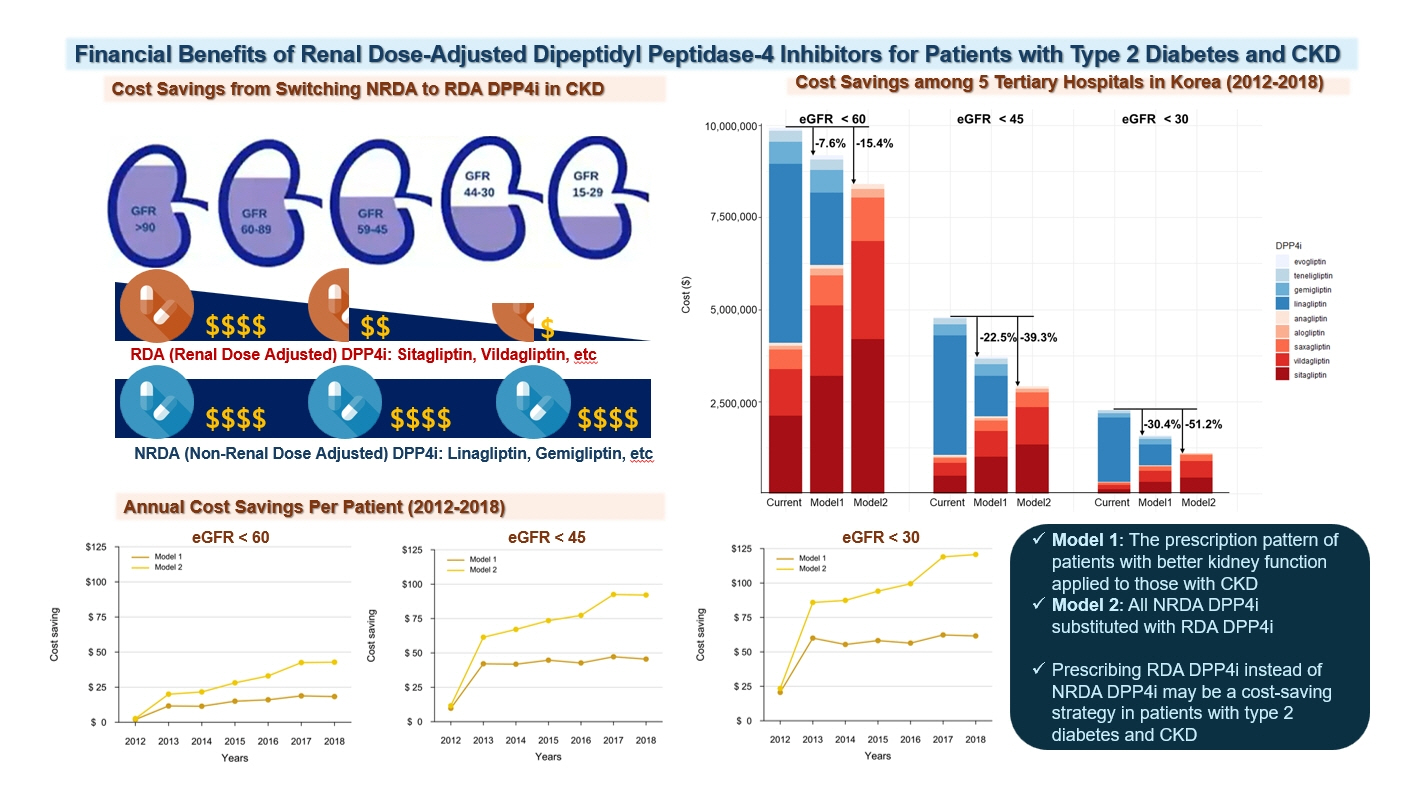
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP4) inhibitors are frequently prescribed for patients with type 2 diabetes; however, their cost can pose a significant barrier for those with impaired kidney function. This study aimed to estimate the economic benefits of substituting non-renal dose-adjusted (NRDA) DPP4 inhibitors with renal dose-adjusted (RDA) DPP4 inhibitors in patients with both impaired kidney function and type 2 diabetes.
Methods
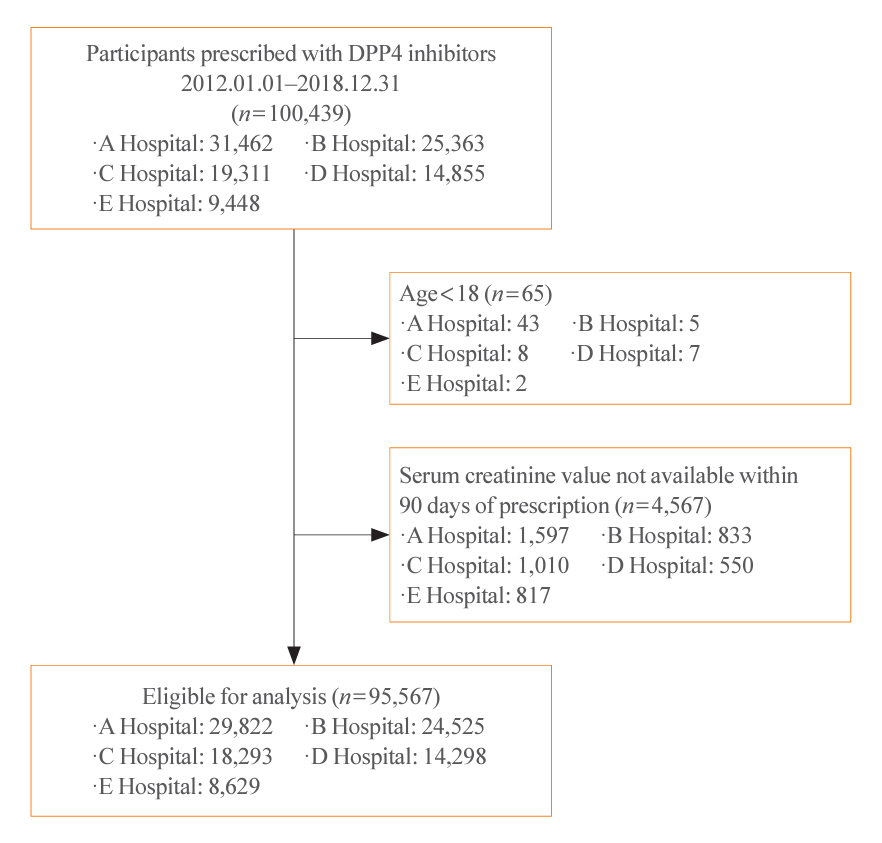
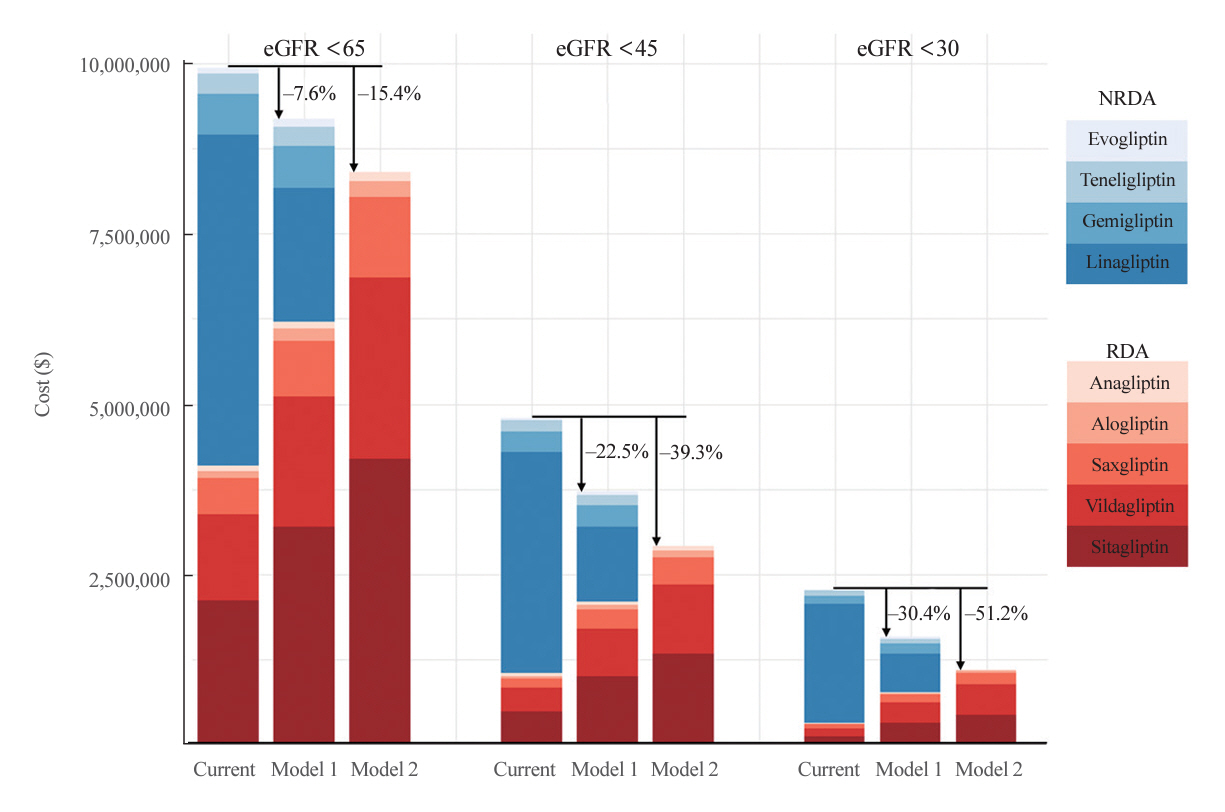
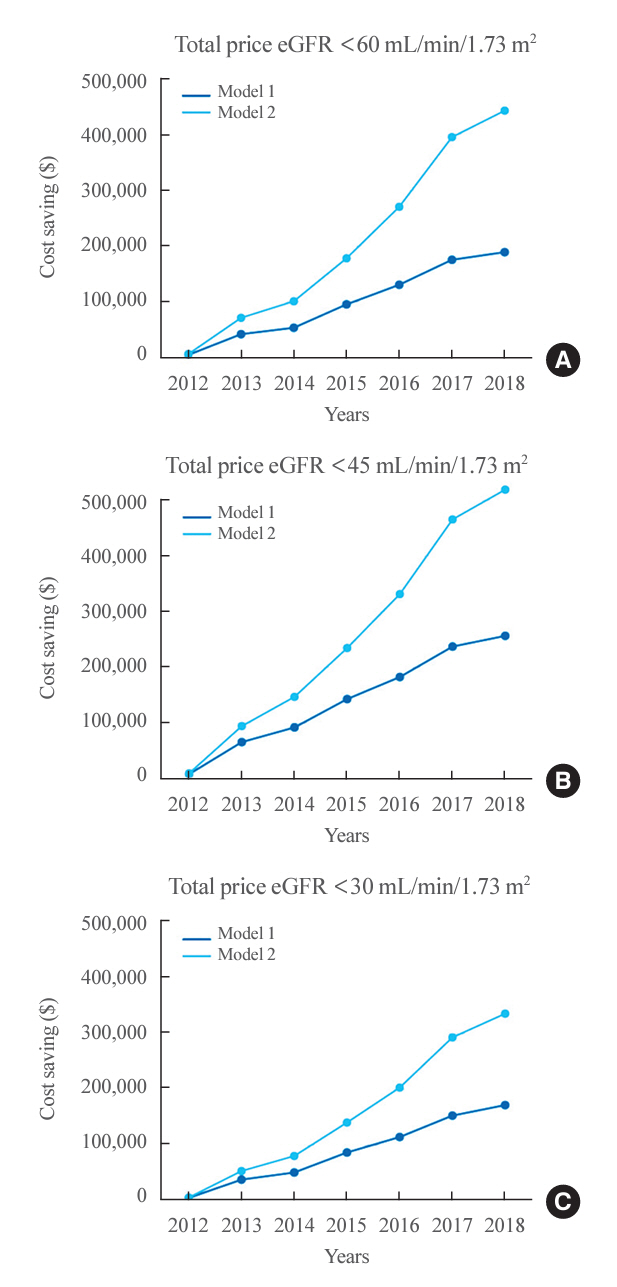
This retrospective cohort study was conducted from January 1, 2012 to December 31, 2018, using data obtained from common data models of five medical centers in Korea. Model 1 applied the prescription pattern of participants with preserved kidney function to those with impaired kidney function. In contrast, model 2 replaced all NRDA DPP4 inhibitors with RDA DPP4 inhibitors, adjusting the doses of RDA DPP4 inhibitors based on individual kidney function. The primary outcome was the cost difference between the two models.
Results
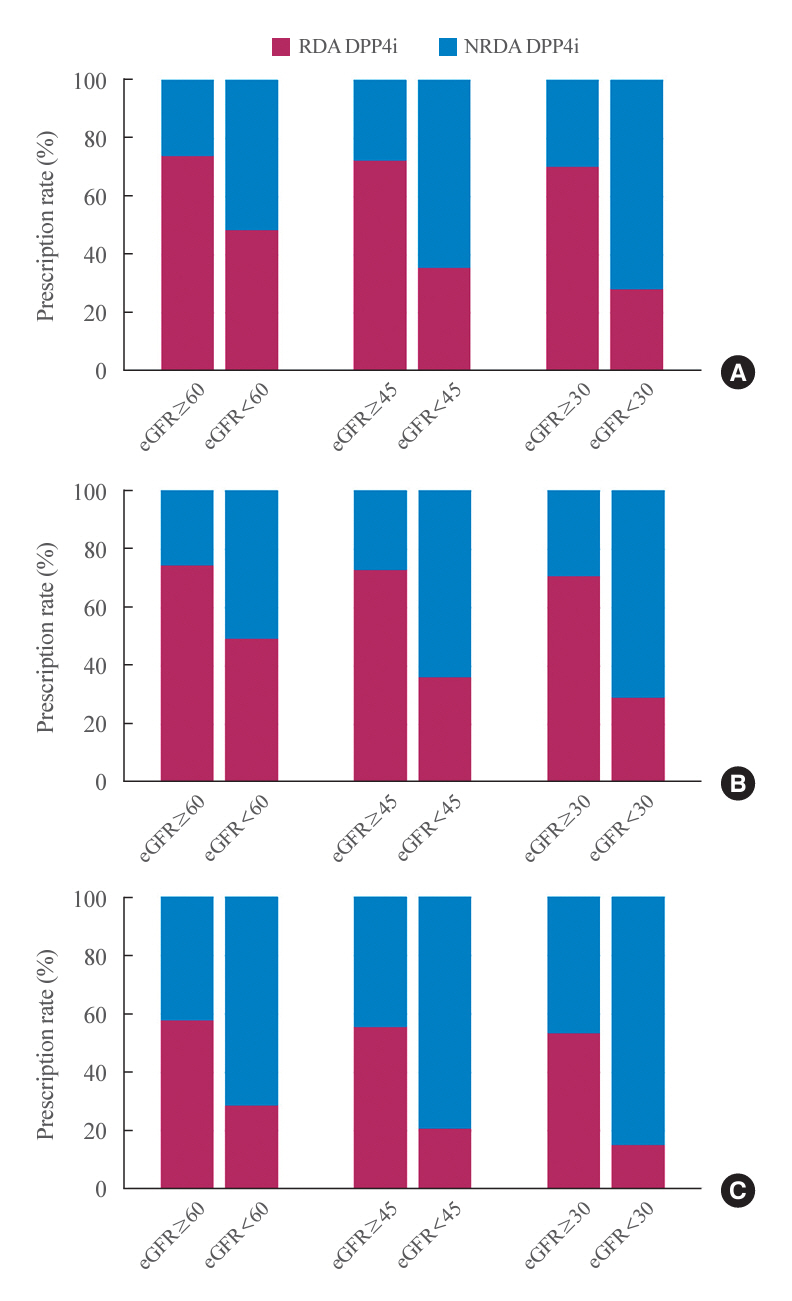
In total, 67,964,996 prescription records were analyzed. NRDA DPP4 inhibitors were more frequently prescribed to patients with impaired kidney function than in those with preserved kidney function (25.7%, 51.3%, 64.3%, and 71.6% in patients with estimated glomerular filtration rates [eGFRs] of ≥60, <60, <45, and <30 mL/min/1.73 m2, respectively). When model 1 was applied, the cost savings per year were 7.6% for eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m2 and 30.4% for eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73 m2. According to model 2, 15.4% to 51.2% per year could be saved depending on kidney impairment severity.
Conclusion
Adjusting the doses of RDA DPP4 inhibitors based on individual kidney function could alleviate the economic burden associated with medical expenses.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Parving HH, Lewis JB, Ravid M, Remuzzi G, Hunsicker LG; DEMAND investigators. Prevalence and risk factors for microalbuminuria in a referred cohort of type II diabetic patients: a global perspective. Kidney Int. 2006; 69:2057–63.
Article2. Thomas MC, Weekes AJ, Broadley OJ, Cooper ME, Mathew TH. The burden of chronic kidney disease in Australian patients with type 2 diabetes (the NEFRON study). Med J Aust. 2006; 185:140–4.3. Furuta S, Smart C, Hackett A, Benning R, Warrington S. Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of [14C]anagliptin, a novel dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, in humans. Xenobiotica. 2013; 43:432–42.
Article4. Kim SH, Yoo JH, Lee WJ, Park CY. Gemigliptin: an update of its clinical use in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab J. 2016; 40:339–53.
Article5. Graefe-Mody U, Friedrich C, Port A, Ring A, Retlich S, Heise T, et al. Effect of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor linagliptin(*). Diabetes Obes Metab. 2011; 13:939–46.
Article6. Moon SJ, Cho YM. Economic benefit of prescribing an adjusted renal dose of dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors in type 2 diabetes patients with chronic kidney disease. J Diabetes. 2020; 12:645–8.7. Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, et al. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.4. Cochrane; 2023. Chapter 6, Choosing effect measures and computing estimates of effect [cited. 2024; May. 9. [cited 2024 May 9]. Available from: https://training.cochrane.org/handbook/current/chapter-06.8. Hampp C, Borders-Hemphill V, Moeny DG, Wysowski DK. Use of antidiabetic drugs in the U.S., 2003-2012. Diabetes Care. 2014; 37:1367–74.9. Bae JH, Han KD, Ko SH, Yang YS, Choi JH, Choi KM, et al. Diabetes fact sheet in Korea 2021. Diabetes Metab J. 2022; 46:417–26.
Article10. Nishimura R, Kato H, Kisanuki K, Oh A, Hiroi S, Onishi Y, et al. Treatment patterns, persistence and adherence rates in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Japan: a claims-based cohort study. BMJ Open. 2019; 9:e025806.
Article11. ElSayed NA, Aleppo G, Aroda VR, Bannuru RR, Brown FM, Bruemmer D, et al. 13. Older adults: standards of care in diabetes-2023. Diabetes Care. 2023; 46(Suppl 1):S216–29.12. Tebboth A, Lee S, Scowcroft A, Bingham-Gardiner P, Spencer W, Bolodeoku J, et al. Demographic and clinical characteristics of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus initiating dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors: a retrospective study of UK general practice. Clin Ther. 2016; 38:1825–32.
Article13. Patorno E, Gopalakrishnan C, Bartels DB, Brodovicz KG, Liu J, Schneeweiss S. Preferential prescribing and utilization trends of diabetes medications among patients with renal impairment: emerging role of linagliptin and other dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab. 2017; 1:e00005.
Article14. Huang H, Shetty S, Bauer E, Lang K. Concordance with prescribing information dosage recommendations for dipeptidyl-peptidase-4 inhibitors among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with moderate to severe chronic kidney disease. Curr Med Res Opin. 2018; 34:1021–7.
Article15. Spanopoulos D, Barrett B, Busse M, Roman T, Poole C. Prescription of DPP-4 inhibitors to type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with renal impairment: a UK primary care experience. Clin Ther. 2018; 40:152–4.
Article16. Verbeeck RK, Musuamba FT. Pharmacokinetics and dosage adjustment in patients with renal dysfunction. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2009; 65:757–73.
Article17. Davis TM. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors: pharmacokinetics, efficacy, tolerability and safety in renal impairment. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014; 16:891–9.
Article18. Covington P, Christopher R, Davenport M, Fleck P, Mekki QA, Wann ER, et al. Pharmacokinetic, pharmacodynamic, and tolerability profiles of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor alogliptin: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multiple-dose study in adult patients with type 2 diabetes. Clin Ther. 2008; 30:499–512.
Article19. Araki E, Kawamori R, Inagaki N, Watada H, Hayashi N, Horie Y, et al. Long-term safety of linagliptin monotherapy in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013; 15:364–71.
Article20. Rosenstock J, Sankoh S, List JF. Glucose-lowering activity of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor saxagliptin in drug-naive patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2008; 10:376–86.
Article21. Aschner P, Kipnes MS, Lunceford JK, Sanchez M, Mickel C, Williams-Herman DE, et al. Effect of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor sitagliptin as monotherapy on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2006; 29:2632–7.
Article22. Bergman AJ, Cote J, Yi B, Marbury T, Swan SK, Smith W, et al. Effect of renal insufficiency on the pharmacokinetics of sitagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor. Diabetes Care. 2007; 30:1862–4.
Article23. Hong S, Han K, Park CY. Outcomes for inappropriate renal dose adjustment of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: population-based study. Mayo Clin Proc. 2020; 95:101–12.
Article24. Franch-Nadal J, Gatius JR, Mata-Cases M, Ortega E, Valles JA, Vlacho B, et al. Compliance with the DPP-4 inhibitors dose adjustment recommendations based on renal function in a population database. Endocrinol Diabetes Nutr (Engl Ed). 2022; 69:83–91.
Article25. Heerspink HJ, Stefansson BV, Correa-Rotter R, Chertow GM, Greene T, Hou FF, et al. Dapagliflozin in patients with chronic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 2020; 383:1436–46.
Article26. The EMPA-KIDNEY Collaborative Group, Herrington WG, Staplin N, Wanner C, Green JB, Hauske SJ, et al. Empagliflozin in patients with chronic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 2023; 388:117–27.
Article27. Cherney DZ, Cooper ME, Tikkanen I, Pfarr E, Johansen OE, Woerle HJ, et al. Pooled analysis of phase III trials indicate contrasting influences of renal function on blood pressure, body weight, and HbA1c reductions with empagliflozin. Kidney Int. 2018; 93:231–44.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors on Cardiovascular Outcome
- Emerging Safety Issues of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors and Sodium Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors: How to Interpret and Apply in Clinical Practice
- Novel Therapies for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibitor, an Update
- Soluble Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Levels Are Associated with Decreased Renal Function in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus