Arch Hand Microsurg.
2024 Sep;29(3):203-209. 10.12790/ahm.24.0003.
Radial nerve palsy associated with fractures of the humerus shaft: a review of the literature and current treatment trends
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Inje University Haeundae Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- 2Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Medical Research Institute, Pusan National University Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- 3Busan Micro Hospital, Busan, Korea
- KMID: 2558746
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12790/ahm.24.0003
Abstract
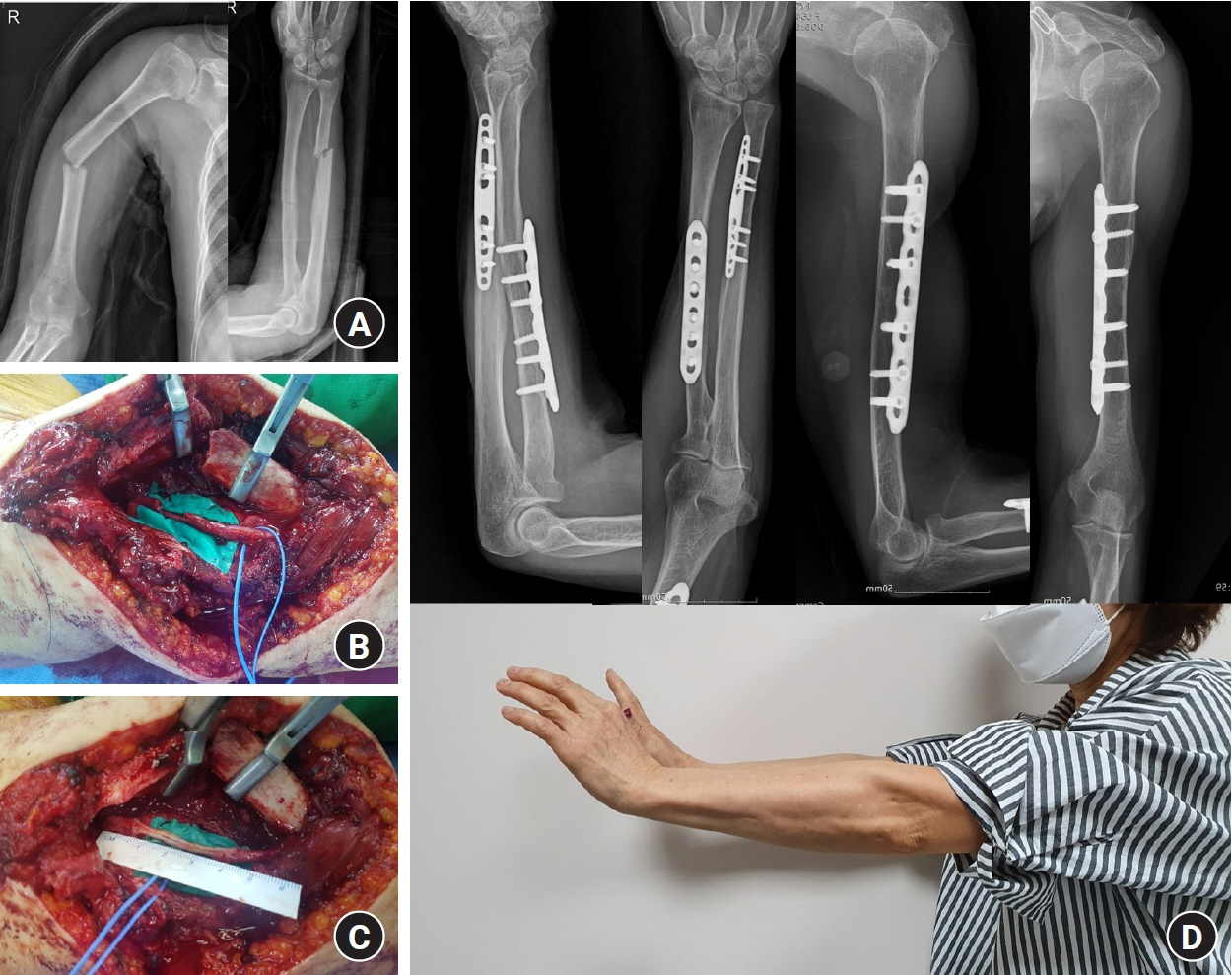
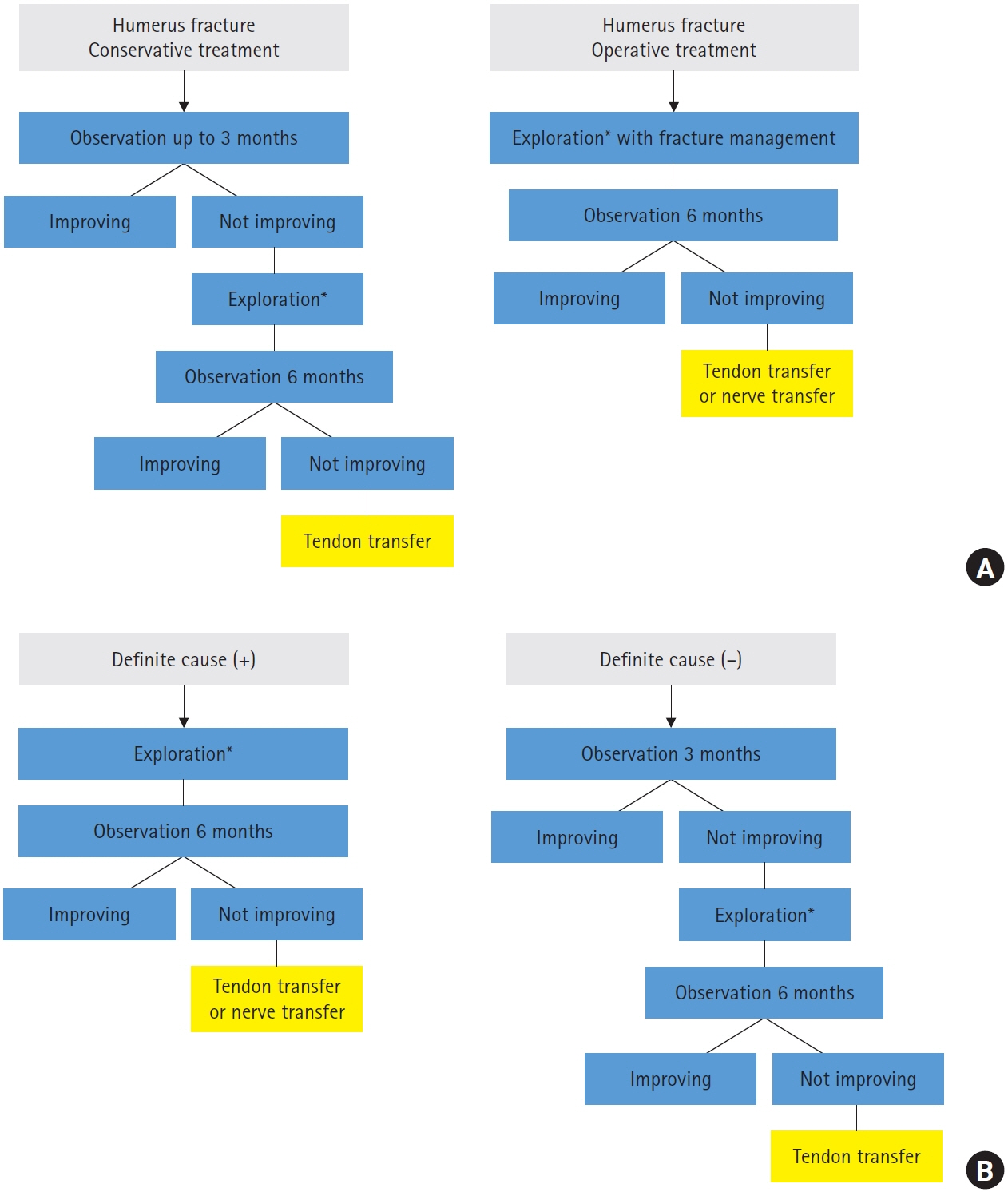
- Due to the anatomical characteristics of the radial nerve, a humeral shaft fracture can induce radial nerve palsy. Although the treatment for radial nerve palsy remains debatable, the options can be broadly classified as early exploratory surgery and initial expectant treatment. In cases of secondary paralysis, the definitive treatment primarily depends on the causative factor, with appropriate consideration of other important factors, such as the fracture characteristics and the patient's age and occupational factors, and after adequate discussion with the patient. However, if radial nerve function does not recover, a tendon or nerve transfer may be considered.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Shao YC, Harwood P, Grotz MR, Limb D, Giannoudis PV. Radial nerve palsy associated with fractures of the shaft of the humerus: a systematic review. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005; 87:1647–52.2. Prodromo J, Goitz RJ. Management of radial nerve palsy associated with humerus fracture. J Hand Surg Am. 2013; 38:995–8.3. Li Y, Ning G, Wu Q, Wu Q, Li Y, Feng S. Review of literature of radial nerve injuries associated with humeral fractures-an integrated management strategy. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e78576.
Article4. Wang JP, Shen WJ, Chen WM, Huang CK, Shen YS, Chen TH. Iatrogenic radial nerve palsy after operative management of humeral shaft fractures. J Trauma. 2009; 66:800–3.
Article5. Reichert P, Wnukiewicz W, Witkowski J, et al. Causes of secondary radial nerve palsy and results of treatment. Med Sci Monit. 2016; 22:554–62.
Article6. Hendrickx LA, Hilgersom NF, Alkaduhimi H, Doornberg JN, van den Bekerom MP. Radial nerve palsy associated with closed humeral shaft fractures: a systematic review of 1758 patients. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2021; 141:561–8.
Article7. Szalay E, Rockwood CA Jr. The Holstein-Lewis fracture revisited. Orthop Trans. 1983; 7:516.8. Pollock FH, Drake D, Bovill EG, Day L, Trafton PG. Treatment of radial neuropathy associated with fractures of the humerus. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1981; 63:239–43.
Article9. Noaman H, Khalifa AR, El-Deen MA, Shiha A. Early surgical exploration of radial nerve injury associated with fracture shaft humerus. Microsurgery. 2008; 28:635–42.
Article10. Han SH, Cho JW, Ryu HS. Treatment of radial nerve palsy associated with humeral shaft fracture. Arch Hand Microsurg. 2020; 25:60–6.
Article11. Heckler MW, Bamberger HB. Humeral shaft fractures and radial nerve palsy: to explore or not to explore...That is the question. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2008; 37:415–9.12. Giordano V, Belangero W, Pires RE, Labronici PJ; Clinical Decision Rules Group. Humerus shaft fracture associated with traumatic radial nerve palsy: an international survey among orthopedic trauma surgeons from Latin America and Asia/Pacific. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2017; 25:2309499017727914.
Article13. Kong CG, Sur YJ, Jung JW, Park HY. Primary radial nerve palsy associated with humeral shaft fractures according to injury mechanism: is early exploration needed? J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2021; 30:2862–8.
Article14. Burnett MG, Zager EL. Pathophysiology of peripheral nerve injury: a brief review. Neurosurg Focus. 2004; 16:E1.
Article15. Seddon H. Factors influencing indications for operation. In : Seddon H, editor. Surgical disorders of the peripheral nerves. Baltimore, MD: Williams & Wilkins;1972. p. 240–5.16. Garcia A Jr, Maeck BH. Radial nerve injuries in fractures of the shaft of the humerus. Am J Surg. 1960; 99:625–7.
Article17. Duncan DM, Johnson KA, Monkman GR. Fracture of the humerus and radial nerve palsy. Minn Med. 1974; 57:659–62.18. Shah JJ, Bhatti NA. Radial nerve paralysis associated with fractures of the humerus: a review of 62 cases. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1983; (172):171–6.19. Böstman O, Bakalim G, Vainionpää S, Wilppula E, Pätiälä H, Rokkanen P. Radial palsy in shaft fracture of the humerus. Acta Orthop Scand. 1986; 57:316–9.
Article20. Naalla R, Singhal M. Single incision modified jones transfer for radial nerve paralysis: an aesthetic alternative. Indian J Plast Surg. 2020; 53:452–3.
Article21. Narakas AO, Hentz VR. Neurotization in brachial plexus injuries: indication and results. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1988; (237):43–56.22. Davidge KM, Yee A, Kahn LC, Mackinnon SE. Median to radial nerve transfers for restoration of wrist, finger, and thumb extension. J Hand Surg Am. 2013; 38:1812–27.
Article23. Mackinnon SE, Roque B, Tung TH. Median to radial nerve transfer for treatment of radial nerve palsy: case report. J Neurosurg. 2007; 107:666–71.24. Patterson JM, Russo SA, El-Haj M, Novak CB, Mackinnon SE. Radial nerve palsy: nerve transfer versus tendon transfer to restore function. Hand (N Y). 2022; 17:1082–9.
Article25. Mackinnon SE, Dellon AL. The overlap pattern of the lateral antebrachial cutaneous nerve and the superficial branch of the radial nerve. J Hand Surg Am. 1985; 10:522–6.
Article26. Han SH, Hong IT, Lee HJ, Lee SJ, Kim U, Kim DW. Primary exploration for radial nerve palsy associated with unstable closed humeral shaft fracture. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg. 2017; 23:405–9.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Associated Factors of Radial Nerve Palsy Combined with Humerus Shaft Fracture
- Radial Nerve Palsy Complicating Humerus Shaft Fracture
- Medial Transposition of Radial Nerve in Distal Humerus Shaft Fracture: A Report of Six Cases
- Surgical Treatment of Old Radial Nerve Palsy Associated with Nonunion of Humeral Shaft Fractures
- Contributing Factors of Radial Nerve Palsy Associated with Humeral Shaft Fracture