Arch Hand Microsurg.
2024 Sep;29(3):163-172. 10.12790/ahm.23.0056.
Paraffinoma of the hands: a case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2558740
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12790/ahm.23.0056
Abstract
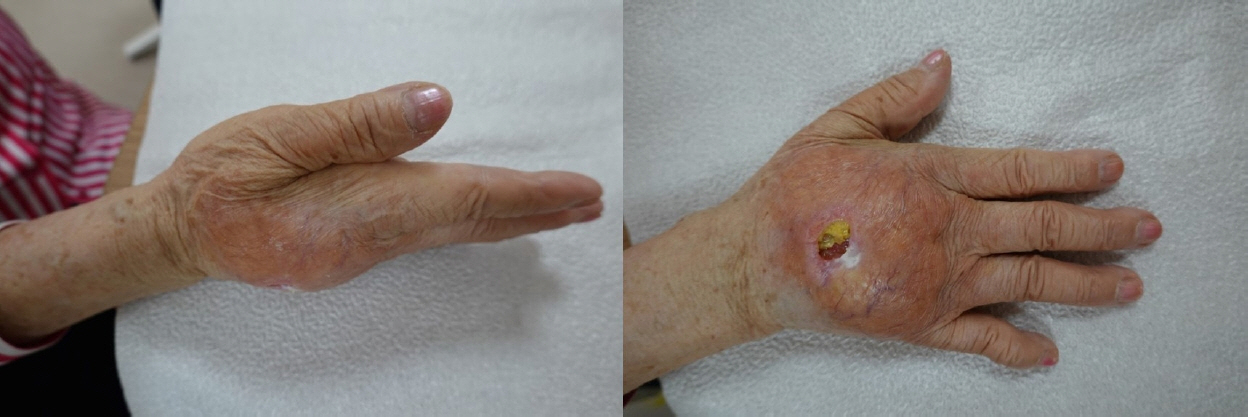
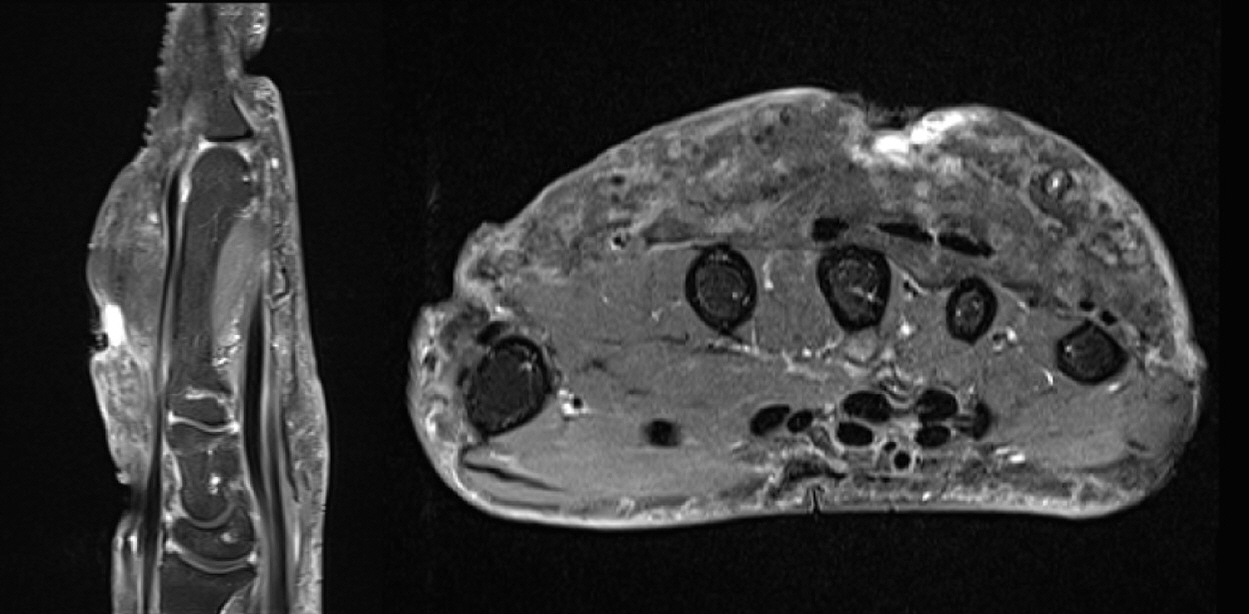
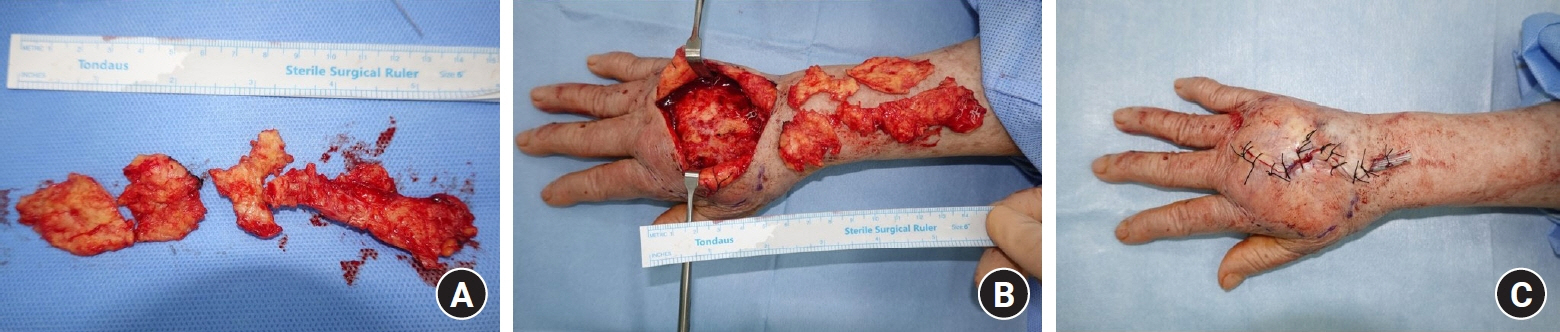
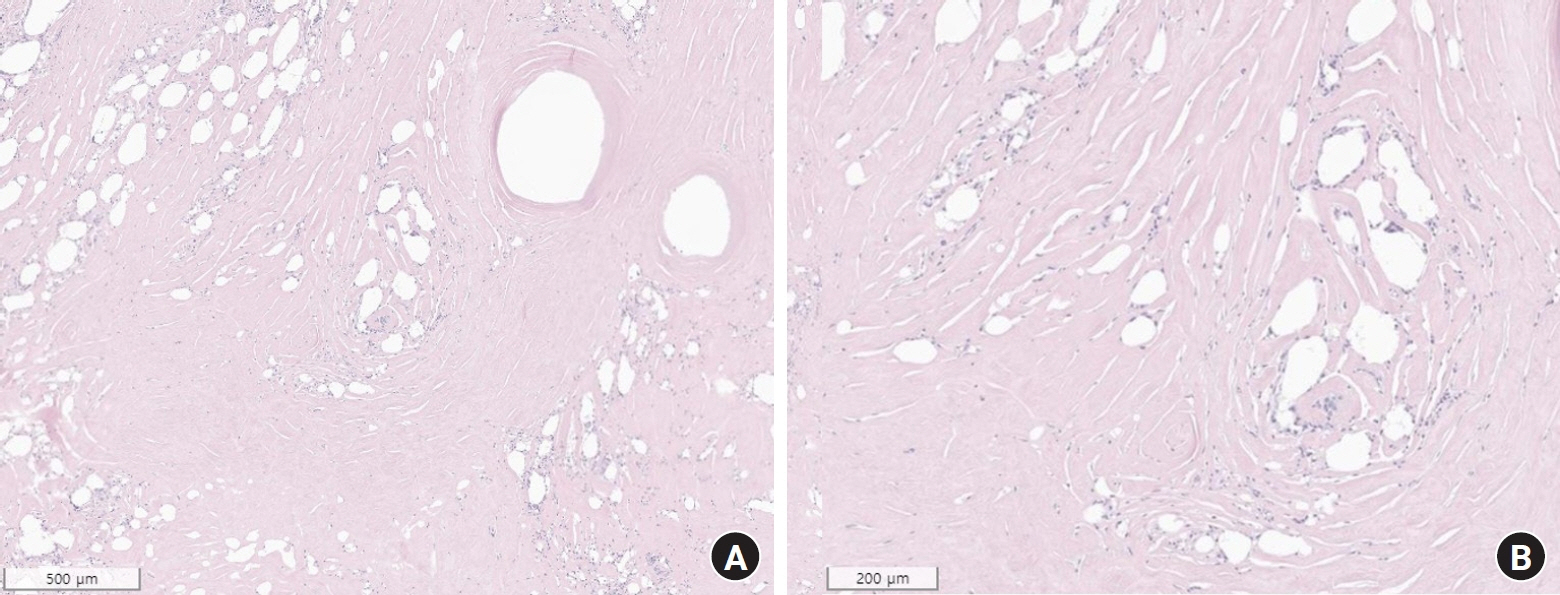
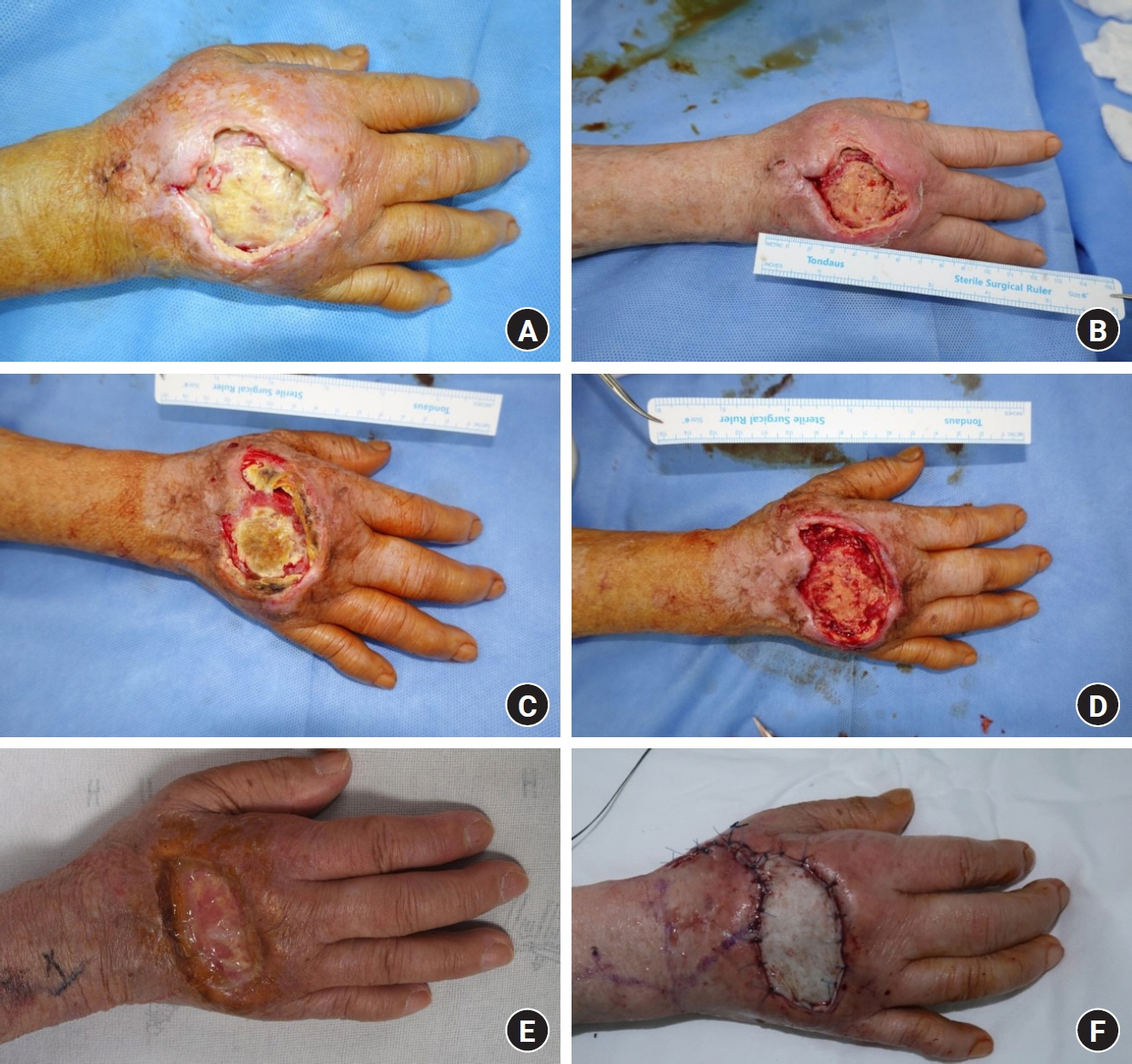
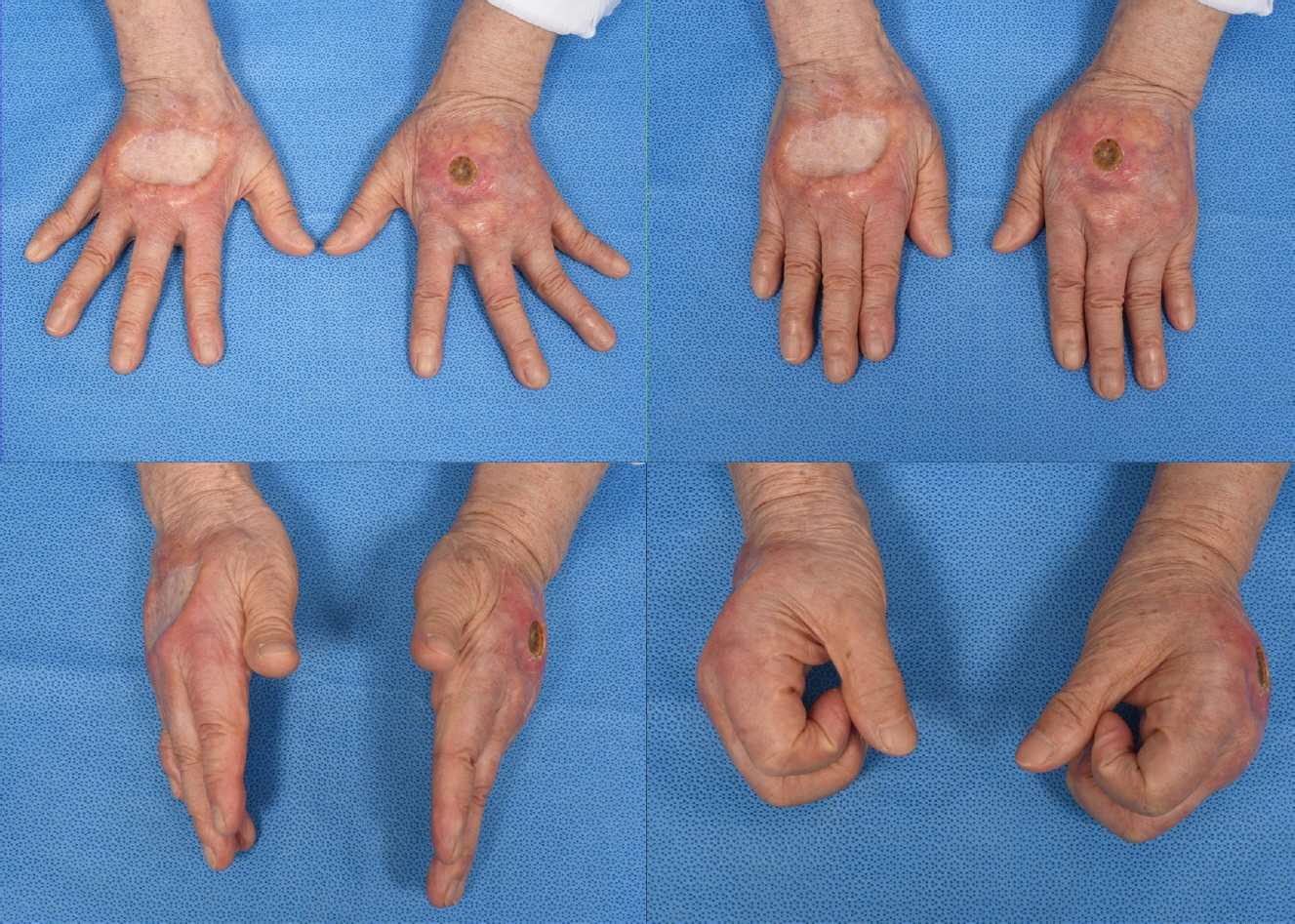
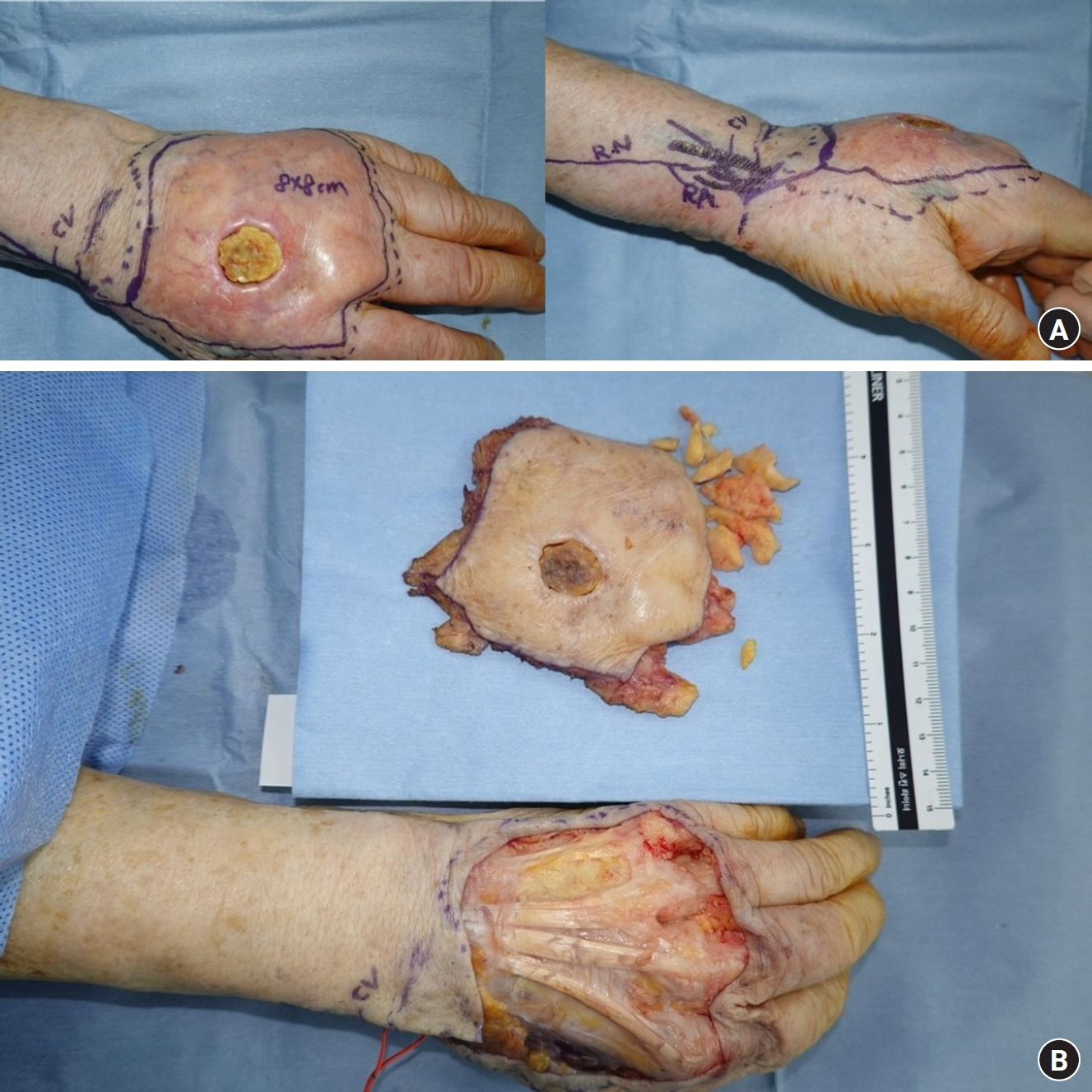
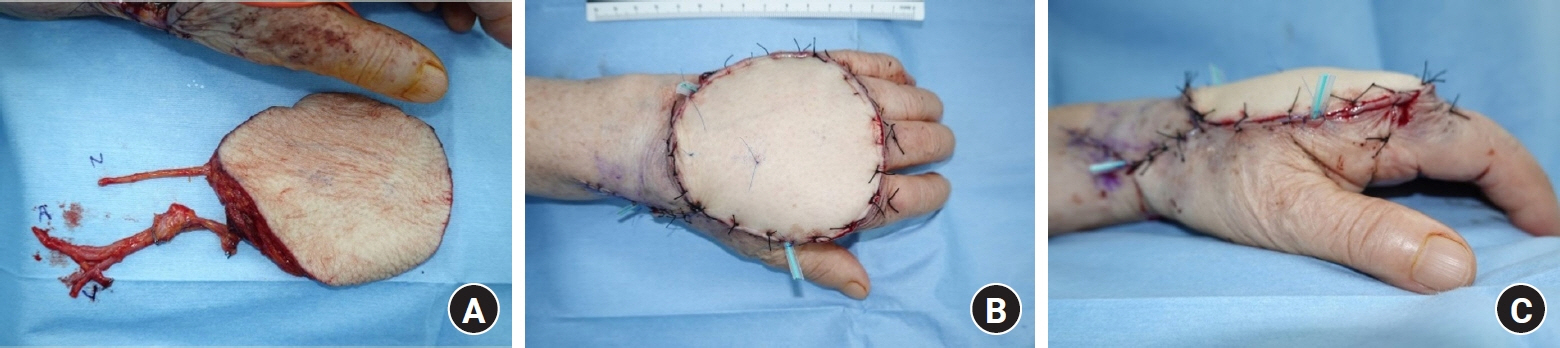
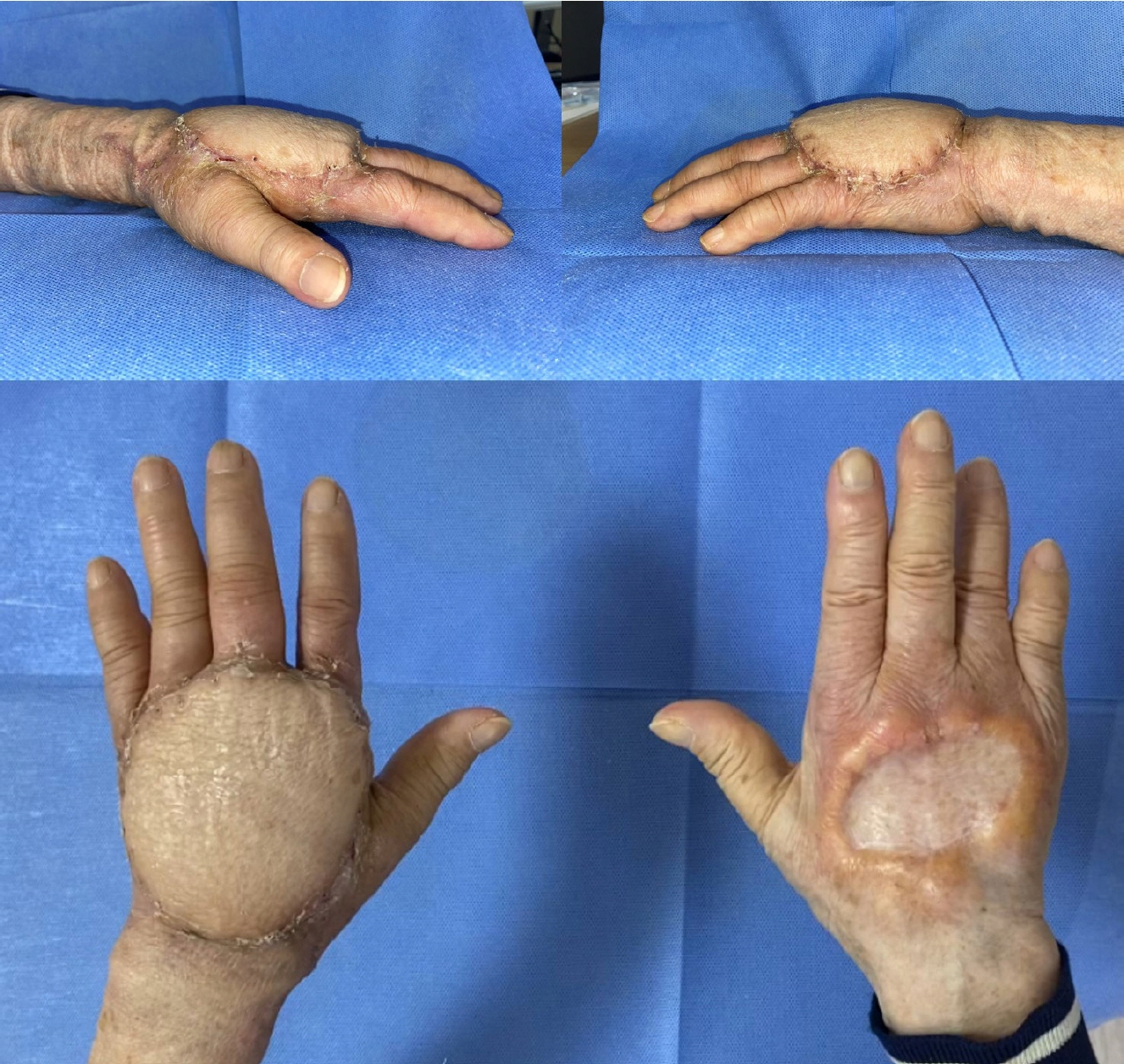
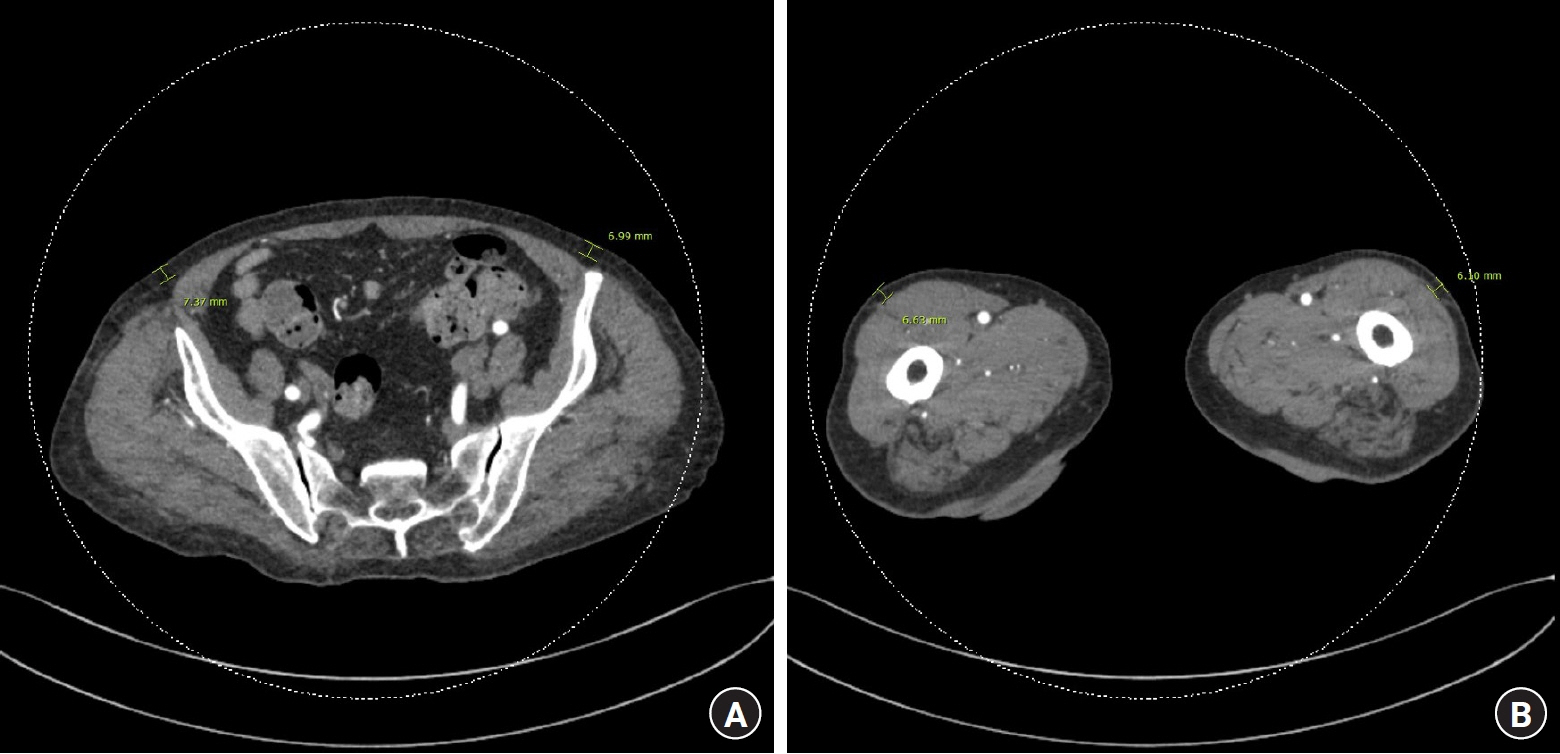
- Paraffin injection has been widely used to improve body contouring or to augment various body parts, although it has now been abandoned owing to serious complications. Paraffin injection may lead to complications after a long latency period, ranging from several years to several decades. Here, we present the rare case of a 77-year-old woman who suffered from recurrent wound problems after a bilateral paraffin injection into her hands 40 years ago. Initially, conservative debridement was carried out due to the patient’s reluctance to undergo extensive surgery and cost concerns. However, this resulted in recurrent wound dehiscence and infection. After serial debridement procedures, a skin graft was performed on her right hand. The patient complained of a depressed contour and numbness at the skin graft site, and tightness and discomfort of her right hand during flexion of the metacarpophalangeal joint. Three years later, the patient presented with a highly similar wound on her left hand. Thorough excision of the soft tissue infiltrated by paraffin was performed, followed by reconstruction using a sensate free anterolateral thigh flap. The patient responded well postoperatively without complications, displaying a fair range of motion without discomfort, sensory restoration of the flap, and satisfaction with the contour of the dorsum. This case report highlights the importance of complete excision of soft tissues infiltrated by paraffin for definitive treatment. Among the various reconstruction options, a sensate free flap is a good choice for achieving favorable functional and esthetic outcomes in hand reconstruction after radical excision of a paraffinoma.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Boo-Chai K. The complications of augmentation mammaplasty by silicone injection. Br J Plast Surg. 1969; 22:281–5.
Article2. Di Benedetto G, Pierangeli M, Scalise A, Bertani A. Paraffin oil injection in the body: an obsolete and destructive procedure. Ann Plast Surg. 2002; 49:391–6.
Article3. Downey AP, Osman NI, Mangera A, Inman RD, Reid SV, Chapple CR. Penile paraffinoma. Eur Urol Focus. 2019; 5:894–8.
Article4. Ho WS, Chan AC, Law BK. Management of paraffinoma of the breast: 10 years' experience. Br J Plast Surg. 2001; 54:232–4.5. Yen Kok KY, Tripathi S, Telisinghe P. Breast paraffinoma: an obsolete but still important condition. Experience with 60 cases and the literature review. Asian J Surg. 2023; 46:321–7.6. Eo SR, Kim KS, Kim DY, Lee SY, Cho BH. Paraffinoma of the labia. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004; 113:1885–7.
Article7. Wibowo SA, Wijanarko S, Ismail EA, Putra MD. Total penectomy and perineal urethrostomy management of penile squamous cell carcinoma with paraffinoma in single center hospital: a rare case report. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2021; 9(C):55–8.
Article8. Pennisi VR, Capozzi A, Walsh J, Christensen N. Obscure breast carcinoma encountered in subcutaneous mastectomies. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1971; 47:17–20.
Article9. Addison PD, Beausang ES, Neligan PC. Malignant fibrous histiocytoma arising in a paraffinoma of the breast. Can J Plast Surg. 2002; 10:215–6.
Article10. Jeong JH, Shin HJ, Woo SH, Seul JH. A new repair technique for penile paraffinoma: bilateral scrotal flaps. Ann Plast Surg. 1996; 37:386–93.11. Kwon H, Jung SN, Yim YM. Paraffin injection injury of the hands: presentation and treatment. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2009; 34:400–1.
Article12. Davis BF. Paraffinoma and wax cancer. JAMA. 1920; 75:1709–11.
Article13. Obed D, Krezdorn N, Harik-Chraim E, Freystaetter C, Radtke C, Vogt PM. Complications after liquid body contouring with site-enhancing oil injections. Clin Dermatol. 2022; 40:556–63.
Article14. Gyldenløve M, Rørvig S, Skov L, Hansen D. Severe hypercalcaemia, nephrocalcinosis, and multiple paraffinomas caused by paraffin oil injections in a young bodybuilder. Lancet. 2014; 383:2098.
Article15. Pang TC. Death Following Injection of Paraffin into the Breast. Br Med J. 1957; 1:992.16. Ackerman AB. Histologic diagnosis of inflammatory skin diseases: a method by pattern analysis. Philadelphia, PA: Lea and Febiger;1978.17. Lee T, Choi HR, Lee YT, Lee YH. Paraffinoma of the penis. Yonsei Med J. 1994; 35:344–8.
Article18. Friedrich JB, Katolik LI, Vedder NB. Soft tissue reconstruction of the hand. J Hand Surg Am. 2009; 34:1148–55.
Article19. Lee SH, Mun GH. Transverse thoracodorsal artery perforator flaps: experience with 31 free flaps. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2008; 61:372–9.
Article20. Lin CT, Yang KC, Hsu KC, Liu WC, Chen JS, Chen LW. Sensate thoracodorsal artery perforator flap: a focus on its preoperative design and harvesting technique. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009; 123:163–74.
Article21. Wahood W, Ghozy S, Al-Abdulghani A, Kallmes DF. Radial artery diameter: a comprehensive systematic review of anatomy. J Neurointerv Surg. 2022; 14:1274–8.
Article22. Gholami M, Shaban B, Hejazi A, Sazegar G, Soufizadeh R. Anatomical variations of anterolateral thigh flap: a fresh cadaver dissection study. World J Plast Surg. 2021; 10:18–24.
Article23. Sinna R, Hajji H, Qassemyar Q, Perignon D, Benhaim T, Havet E. Anatomical background of the perforator flap based on the deep branch of the superficial circumflex iliac artery (SCIP Flap): a cadaveric study. Eplasty. 2010; 10:e11.24. Iida T, Yoshimatsu H, Hara H, Mihara M, Koshima I. Reconstruction of large facial defects using a sensate superficial circumflex iliac perforator flap based on the lateral cutaneous branches of the intercostal nerves. Ann Plast Surg. 2014; 72:328–31.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Eyelid Paraffinoma Misdiagnosed as a Chalazion
- One-stage Reconstruction after Partial Removal of Paraffinoma in Face with Dermofat Graft and Face Lift
- Penile paraffinoma: 39 cases
- A case of Paraffinoma in the Upper Lid
- Late-Onset Complication of Fillers: Paraffinoma of the Lower Eyelids Clinically Mimicking Xanthelasma