Arch Hand Microsurg.
2024 Sep;29(3):140-145. 10.12790/ahm.24.0027.
Comparative analysis of inpatient costs for the surgical treatment of distal radial fractures in children and adults: a retrospective cohort study from a single surgeon’s experience
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Chungnam National University Hospital, Chungnam National University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Chungnam National University Sejong Hospital, Chungnam National University College of Medicine, Sejong, Korea
- KMID: 2558737
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12790/ahm.24.0027
Abstract
- Purpose
Distal radial fractures are common in children and older adults, and numerous studies have analyzed their medical costs. However, no study has attempted to compare the medical costs of distal radial fractures in children and adults requiring surgical treatment in Korea. We therefore investigated this issue for the first time.
Methods
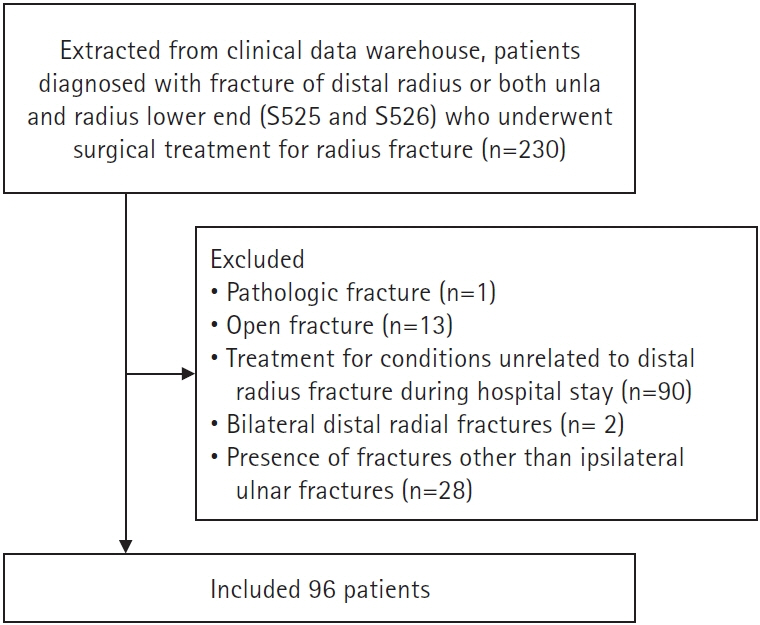
The study retrospectively analyzed 96 pediatric and adult patients who underwent surgery for distal radial fractures performed by a single surgeon between January 2021 and January 2023. Patients were divided into adult (>16 years) and pediatric (≤16 years) groups. We examined patients’ demographic factors, surgical details, and inpatient costs.
Results
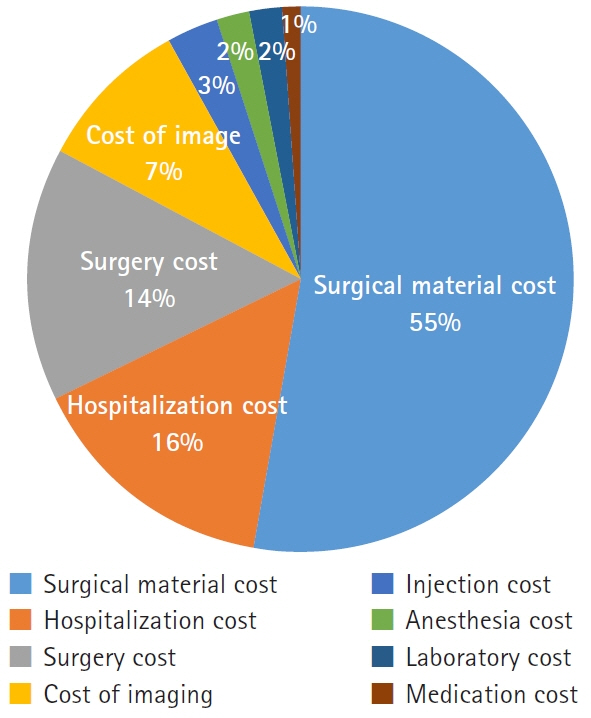
The average total inpatient cost in the pediatric group was 1,640,000 Korean won (KRW), compared to 2,940,000 KRW in the adult group. The largest difference was in surgical material costs, which were approximately 700,000 KRW more expensive in adults. Kirschner wires were mainly used during surgery for pediatric patients, whereas volar locking plates were mainly used for adults. The number of C-arm fluoroscopy images obtained during surgery was higher in pediatric patients than in adults. The reoperation rate was higher in pediatric patients.
Conclusion
The inpatient costs of surgical treatment for pediatric patients with distal radius fractures were lower than for adults, primarily due to differences in the costs of surgical materials. However, the reoperation rate was higher in the pediatric group, and radiation exposure was also greater. Policy adjustments may be necessary to address these unique challenges in the treatment of pediatric wrist fractures.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Jo YH, Lee BG, Kim HS, et al. Incidence and seasonal variation of distal radius fractures in Korea: a population-based study. J Korean Med Sci. 2018; 33:e48.
Article2. Ando J, Takahashi T, Ae R, et al. Epidemiology of distal radius fracture: a regional population-based study in Japan. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2023; 24:478.
Article3. Cheng JC, Shen WY. Limb fracture pattern in different pediatric age groups: a study of 3,350 children. J Orthop Trauma. 1993; 7:15–22.4. Kwon GD, Jang S, Lee A, et al. Incidence and mortality after distal radius fractures in adults aged 50 years and older in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2016; 31:630–4.
Article5. Kim EG, Bae G, Kwon HY, Yang H. Aging and direct medical costs of osteoporotic fractures. J Bone Miner Metab. 2021; 39:589–97.
Article6. Kim HY, Ha YC, Kim TY, et al. Healthcare costs of osteoporotic fracture in Korea: information from the National Health Insurance Claims Database, 2008-2011. J Bone Metab. 2017; 24:125–33.
Article7. Shyamalan G, Theokli C, Pearse Y, Tennent D. Volar locking plates versus Kirschner wires for distal radial fractures: a cost analysis study. Injury. 2009; 40:1279–81.
Article8. Toon DH, Premchand RA, Sim J, Vaikunthan R. Outcomes and financial implications of intra-articular distal radius fractures: a comparative study of open reduction internal fixation (ORIF) with volar locking plates versus nonoperative management. J Orthop Traumatol. 2017; 18:229–34.
Article9. Rajan PV, Qudsi RA, Dyer GS, Losina E. The cost-effectiveness of surgical fixation of distal radial fractures: a computer model-based evaluation of three operative modalities. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2018; 100:e13.10. Karantana A, Scammell BE, Davis TR, Whynes DK. Cost-effectiveness of volar locking plate versus percutaneous fixation for distal radial fractures: economic evaluation alongside a randomised clinical trial. Bone Joint J. 2015; 97-B:1264–70.11. Jo YH, Lee BG, Kim JH, et al. National surgical trends for distal radius fractures in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2017; 32:1181–6.
Article12. Huetteman HE, Zhong L, Chung KC. Cost of surgical treatment for distal radius fractures and the implications of episode-based bundled payments. J Hand Surg Am. 2018; 43:720–30.
Article13. Mulders MA, Walenkamp MM, van Dieren S, Goslings JC, Schep NW; VIPER Trial Collaborators. Volar plate fixation in adults with a displaced extra-articular distal radial fracture is cost-effective. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2020; 102:609–16.
Article14. Kazmers NH, Judson CH, Presson AP, Xu Y, Tyser AR. Evaluation of factors driving cost variation for distal radius fracture open reduction internal fixation. J Hand Surg Am. 2018; 43:606–14.
Article15. Kallini JR, Fu EC, Shah AS, Waters PM, Bae DS. Growth disturbance following intra-articular distal radius fractures in the skeletally immature patient. J Pediatr Orthop. 2020; 40:e910–5.16. Liu DS, Murray MM, Bae DS, May CJ. Pediatric and adolescent distal radius fractures: current concepts and treatment recommendations. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2024; May 29 [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.5435/JAAOS-D-23-01233.
Article17. Cannata G, De Maio F, Mancini F, Ippolito E. Physeal fractures of the distal radius and ulna: long-term prognosis. J Orthop Trauma. 2003; 17:172–80.
Article