Ann Rehabil Med.
2024 Aug;48(4):239-248. 10.5535/arm.240005.
Effect of Pre- and Post-Dialysis Exercise on Functional Capacity Using Portable Ergometer in Chronic Kidney Disease Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Jeonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju, Korea
- 2Research Institute of Clinical Medicine of Jeonbuk National University–Biomedical Research Institute of Jeonbuk National University Hospital, Jeonju, Korea
- KMID: 2558730
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.240005
Abstract
Objective
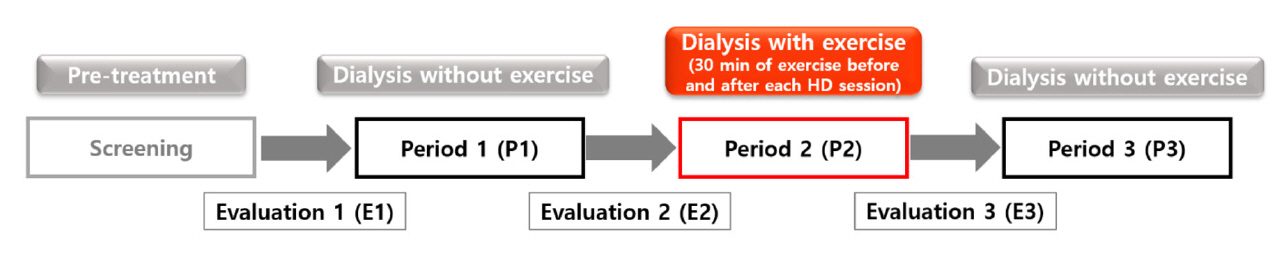
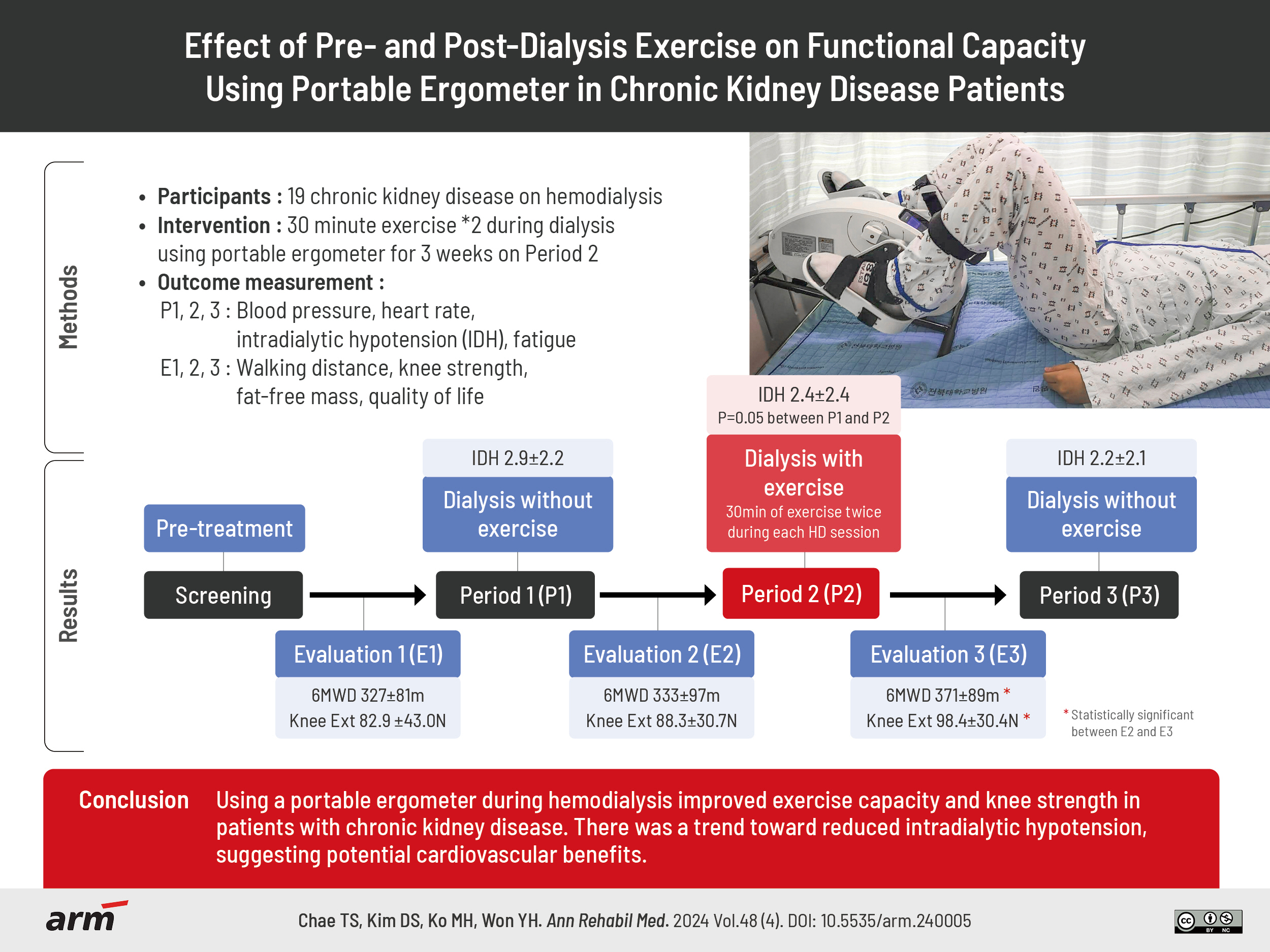
To assess whether performing exercises during hemodialysis reduces the risk of developing intradialytic hypotension and enhances exercise capacity in patients with chronic kidney disease.
Methods
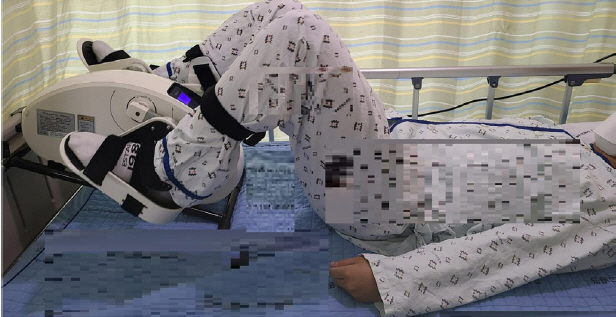
This study included patients aged ≥18 years undergoing hemodialysis. Participants performed exercises using a portable lower extremity ergometer during hemodialysis sessions for 3 weeks. Data regarding walking distance, knee strength, quality of life, fat-free mass, arterial pressure, blood pressure, heart rate, frequency of intradialytic hypotension, fatigue, and duration of hemodialysis were collected and analyzed.
Results
Significant improvements in walking distance and knee strength were observed following the implementation of exercise training during hemodialysis. Although there was no significant reduction in the frequency of intradialytic hypotension, a decreasing trend was noted. Other parameters such as quality of life and fatigue did not show significant changes.
Conclusion
Using a portable ergometer during hemodialysis improved exercise capacity and knee strength in patients with chronic kidney disease. There was a trend toward reduced intradialytic hypotension, suggesting potential cardiovascular benefits. Further research with larger sample sizes is needed to confirm these findings.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Painter P, Carlson L, Carey S, Paul SM, Myll J. Physical functioning and health-related quality-of-life changes with exercise training in hemodialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis. 2000; 35:482–92.
Article2. Suh MR, Jung HH, Kim SB, Park JS, Yang WS. Effects of regular exercise on anxiety, depression, and quality of life in maintenance hemodialysis patients. Ren Fail. 2002; 24:337–45.
Article3. Laupacis A, Muirhead N, Keown P, Wong C. A disease-specific questionnaire for assessing quality of life in patients on hemodialysis. Nephron. 1992; 60:302–6.
Article4. Leypoldt JK, Cheung AK, Delmez JA, Gassman JJ, Levin NW, Lewis JA, et al. Relationship between volume status and blood pressure during chronic hemodialysis. Kidney Int. 2002; 61:266–75.
Article5. Agarwal R. How can we prevent intradialytic hypotension? Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2012; 21:593–9.
Article6. Palmer BF, Henrich WL. Recent advances in the prevention and management of intradialytic hypotension. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008; 19:8–11.
Article7. Tai DJ, Conley J, Ravani P, Hemmelgarn BR, MacRae JM. Hemodialysis prescription education decreases intradialytic hypotension. J Nephrol. 2013; 26:315–22.
Article8. Zhou YL, Liu HL, Duan XF, Yao Y, Sun Y, Liu Q. Impact of sodium and ultrafiltration profiling on haemodialysis-related hypotension. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2006; 21:3231–7.
Article9. Karmiel JC. The rehab exercise "E": a natural role for renal dietitians. J Ren Nutr. 1999; 9:214–9.
Article10. Gołębiowski T, Kusztal M, Weyde W, Dziubek W, Woźniewski M, Madziarska K, et al. A program of physical rehabilitation during hemodialysis sessions improves the fitness of dialysis patients. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2012; 35:290–6.
Article11. Anding K, Bär T, Trojniak-Hennig J, Kuchinke S, Krause R, Rost JM, et al. A structured exercise programme during haemodialysis for patients with chronic kidney disease: clinical benefit and long-term adherence. BMJ Open. 2015; 5:e008709.
Article12. Stewart P. Exercise and a cycle of life: help us help ourselves. Adv Ren Replace Ther. 1999; 6:184–6.
Article13. Varon J. The diagnosis and treatment of hypertensive crises. Postgrad Med. 2009; 121:5–13.
Article14. Vannorsdall MD, Hariachar S, Hewitt LA. A randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 2 study of the efficacy and safety of droxidopa in patients with intradialytic hypotension. Postgrad Med. 2015; 127:133–43.
Article15. Saghiv MS, Sagiv MS. Blood pressure. In : Saghiv MS, Sagiv MS, editors. Basic exercise physiology: clinical and laboratory perspectives. Springer;2020. p. 251–84.16. Kono K, Nishida Y, Moriyama Y, Yabe H, Taoka M, Sato T. Investigation of factors affecting the six-minute walk test results in hemodialysis patients. Ther Apher Dial. 2014; 18:623–7.
Article17. DeMers D, Wachs D. Physiology, mean arterial pressure. StatPearls Publishing;2019.18. Kersten P, Küçükdeveci AA, Tennant A. The use of the visual analogue scale (VAS) in rehabilitation outcomes. J Rehabil Med. 2012; 44:609–10.
Article19. National Kidney Foundation. K/DOQI clinical practice guidelines for chronic kidney disease: evaluation, classification, and stratification. Am J Kidney Dis. 2002; 39(2 Suppl 1):S1–266.20. Hays RD, Kallich JD, Mapes DL, Coons SJ, Carter WB. Development of the kidney disease quality of life (KDQOL) instrument. Qual Life Res. 1994; 3:329–38.
Article21. Knight EL, Ofsthun N, Teng M, Lazarus JM, Curhan GC. The association between mental health, physical function, and hemodialysis mortality. Kidney Int. 2003; 63:1843–51.
Article22. Fukuhara S, Lopes AA, Bragg-Gresham JL, Kurokawa K, Mapes DL, Akizawa T, Worldwide Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study, et al. Health-related quality of life among dialysis patients on three continents: the dialysis outcomes and practice patterns study. Kidney Int. 2003; 64:1903–10.
Article23. McFarlane PA, Bayoumi AM, Pierratos A, Redelmeier DA. The quality of life and cost utility of home nocturnal and conventional in-center hemodialysis. Kidney Int. 2003; 64:1004–11.
Article24. Flythe JE, Kimmel SE, Brunelli SM. Rapid fluid removal during dialysis is associated with cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. Kidney Int. 2011; 79:250–7.
Article25. Mandic S, Myers J, Selig SE, Levinger I. Resistance versus aerobic exercise training in chronic heart failure. Curr Heart Fail Rep. 2012; 9:57–64.
Article26. Kurella Tamura M, Covinsky KE, Chertow GM, Yaffe K, Landefeld CS, McCulloch CE. Functional status of elderly adults before and after initiation of dialysis. N Engl J Med. 2009; 361:1539–47.
Article27. Dobsak P, Homolka P, Svojanovsky J, Reichertova A, Soucek M, Novakova M, et al. Intra-dialytic electrostimulation of leg extensors may improve exercise tolerance and quality of life in hemodialyzed patients. Artif Organs. 2012; 36:71–8.
Article28. Kuipers J, Oosterhuis JK, Krijnen WP, Dasselaar JJ, Gaillard CA, Westerhuis R, et al. Prevalence of intradialytic hypotension, clinical symptoms and nursing interventions--a three-months, prospective study of 3818 haemodialysis sessions. BMC Nephrol. 2016; 17:21.29. Cheema B, Abas H, Smith B, O'Sullivan A, Chan M, Patwardhan A, et al. Randomized controlled trial of intradialytic resistance training to target muscle wasting in ESRD: the progressive exercise for anabolism in kidney disease (PEAK) study. Am J Kidney Dis. 2007; 50:574–84.
Article30. Miller BW, Cress CL, Johnson ME, Nichols DH, Schnitzler MA. Exercise during hemodialysis decreases the use of antihypertensive medications. Am J Kidney Dis. 2002; 39:828–33.
Article31. Parsons TL, Toffelmire EB, King-VanVlack CE. Exercise training during hemodialysis improves dialysis efficacy and physical performance. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2006; 87:680–7.
Article32. Anding-Rost K, von Gersdorff G, von Korn P, Ihorst G, Josef A, Kaufmann M, et al. Exercise during hemodialysis in patients with chronic kidney failure. NEJM Evid. 2023; 2:EVIDoa2300057.
Article33. Lambert K, Lightfoot CJ, Jegatheesan DK, Gabrys I, Bennett PN. Physical activity and exercise recommendations for people receiving dialysis: a scoping review. PLoS One. 2022; 17:e0267290.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effectiveness of exercise for improving physical and renal function in older adults with pre-dialysis chronic kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Validity and Utility of 6-minute-walk Test and WALK(Walking-Stair-Climbing) Test to Assess the Exercise Capacity in Hemodialysis Patients
- Effect of Kegel Exercise on Vital Capacity According to the Position: A Preliminary Study
- The Effects of Assisted Ergometer Training With a Functional Electrical Stimulation on Exercise Capacity and Functional Ability in Subacute Stroke Patients
- The Effect of Pulmonary Rehabilitation in Patients with Chronic Lung Disease