J Rhinol.
2024 Jul;31(2):129-132. 10.18787/jr.2024.00019.
Pediatric Sinonasal Pleomorphic Adenoma: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Children’s Health Ireland at Temple Street, Dublin, Ireland
- 2Department of Histopathology, Children’s Health Ireland at Crumlin, Dublin, Ireland
- 3Department of Radiology, Children’s Health Ireland at Temple Street, Dublin, Ireland
- KMID: 2558241
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.18787/jr.2024.00019
Abstract
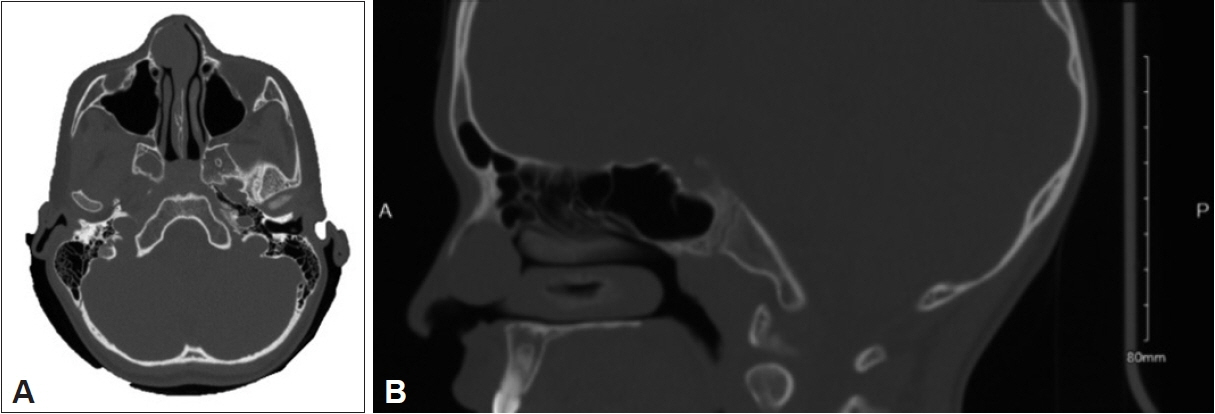
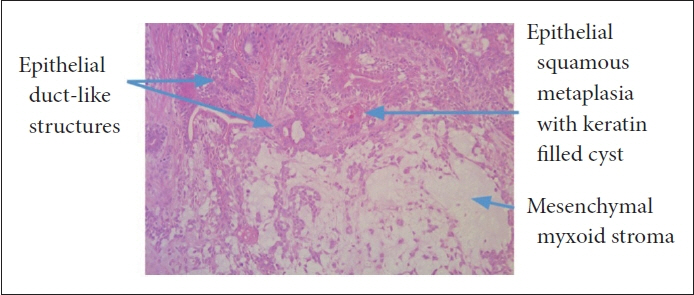
- While primarily observed in adults, this case contributes valuable insights into the manifestation and management of this benign salivary gland tumor within the pediatric population. This paper reports the first documented case of sinonasal pleomorphic adenoma in pediatric otolaryngology, presenting a unique perspective on this rare nasal tumor in a 9-year-old boy. The patient presented with progressive nasal obstruction and epistaxis and underwent a smooth endoscopic resection of a 2-cm pleomorphic adenoma on the right anterior nasal septum. The subsequent discussion covered background, histology, imaging, and management strategies. Surgical removal with clear margins, particularly through the endoscopic approach, emerged as the primary and successful treatment method, minimizing morbidity and reducing recurrence risk. Long-term clinical surveillance is recommended due to an estimated 8.8% recurrence rate. In conclusion, this paper explains the challenges and solutions in diagnosing and treating sinonasal pleomorphic adenomas in children. It emphasizes the critical importance of early diagnosis, precise surgical intervention, and continuous monitoring, which are essential for achieving optimal patient outcomes.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Sigdel B, Pokhrel A, Ranabhat S, KC S. Endoscopic management of huge pleomorphic adenoma of the nasal septum; a case report. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2022; 77:103697.2. Ritwik P, Brannon RB. A clinical analysis of nine new pediatric and adolescent cases of benign minor salivary gland neoplasms and a review of the literature. J Med Case Rep. 2012; 6:287.
Article3. Mackle T, Zahirovic A, Walsh M. Pleomorphic adenoma of the nasal septum. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2004; 113(3 Pt 1):210–1.
Article4. Rha MS, Jeong S, Cho HJ, Yoon JH, Kim CH. Sinonasal pleomorphic adenoma: a single institution case series combined with a comprehensive review of literatures. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2019; 46(2):223–9.
Article5. Konsulov S, Milkov D, Markov D, Poryazova EG. Diagnostic challenges of sinonasal pleomorphic adenoma. Cureus. 2024; 16(2):e54010.
Article6. Lazim NM, Abdullah B. Multidisciplinary approach to children with sinonasal tumors: a review. Pediatr Investig. 2019; 3(3):173–9.7. Kalwaniya DS, Meena R, Kumar D, Tolat A, Arya SV. A review of the current literature on pleomorphic adenoma. Cureus. 2023; 15(7):e42311.
Article8. Karakus MF, Ozcan KM, Dere H. Endoscopic resection of pleomorphic adenoma of the nasal septum. Tumori. 2007; 93(3):300–1.
Article9. Kuan EC, Diaz MF, Chiu AG, Bergsneider M, Wang MB, Suh JD. Sinonasal and skull base pleomorphic adenoma: a case series and literature review. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2015; 5(5):460–8.
Article10. Mead K, Kuhar H, Ibrahim N, Adelman M, Zehr B, Schoenfield L, et al. Pleomorphic adenoma of the nasal cavity: a case study. Otolaryngol Case Rep. 2023; 23:100408.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pleomorphic adenoma of the cheek in the young patient: report of a case
- Metastasizing Pleomorphic Adenoma: Report of a Case
- High-Grade Mucoepidermoid Carcinoma Ex Metastasizing Pleomorphic Adenomas in the Parotid Gland and Parapharyngeal Space: a Case Report and Literature Review
- A Case of Pleomorphic Adenoma Occurred on Philtrum
- A Case of Pleomorphic Adenoma Manifested as a Subcutaneous Nodule