J Rhinol.
2024 Jul;31(2):101-105. 10.18787/jr.2024.00020.
Insufficient Diagnostic Value of Serum Galactomannan and (1,3)-β-D-Glucan in Paranasal Sinus Fungus Balls
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Jeju National University Hospital, Jeju National University College of Medicine, Jeju, Republic of Korea
- 2Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Gwangmyeong Hospital, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Gwangmyeong, Republic of Korea
- 3Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Yongin Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Yongin, Republic of Korea
- 4Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
- 5The Airway Mucus Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
- KMID: 2558236
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.18787/jr.2024.00020
Abstract
- Background and Objectives
The serum galactomannan test (GM test) and the (1,3)-β-D-glucan test (G test) are utilized in diagnosing invasive fungal sinusitis. However, their effectiveness in detecting paranasal sinus fungus balls (FBs) has not been established. This study aimed to explore their diagnostic value in patients with FBs.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 105 patients (42 with FBs and 63 with chronic rhinosinusitis [CRS]) who underwent serum GM and G tests between June 2020 and May 2021. Olfactory test results and demographics were also analyzed.
Results
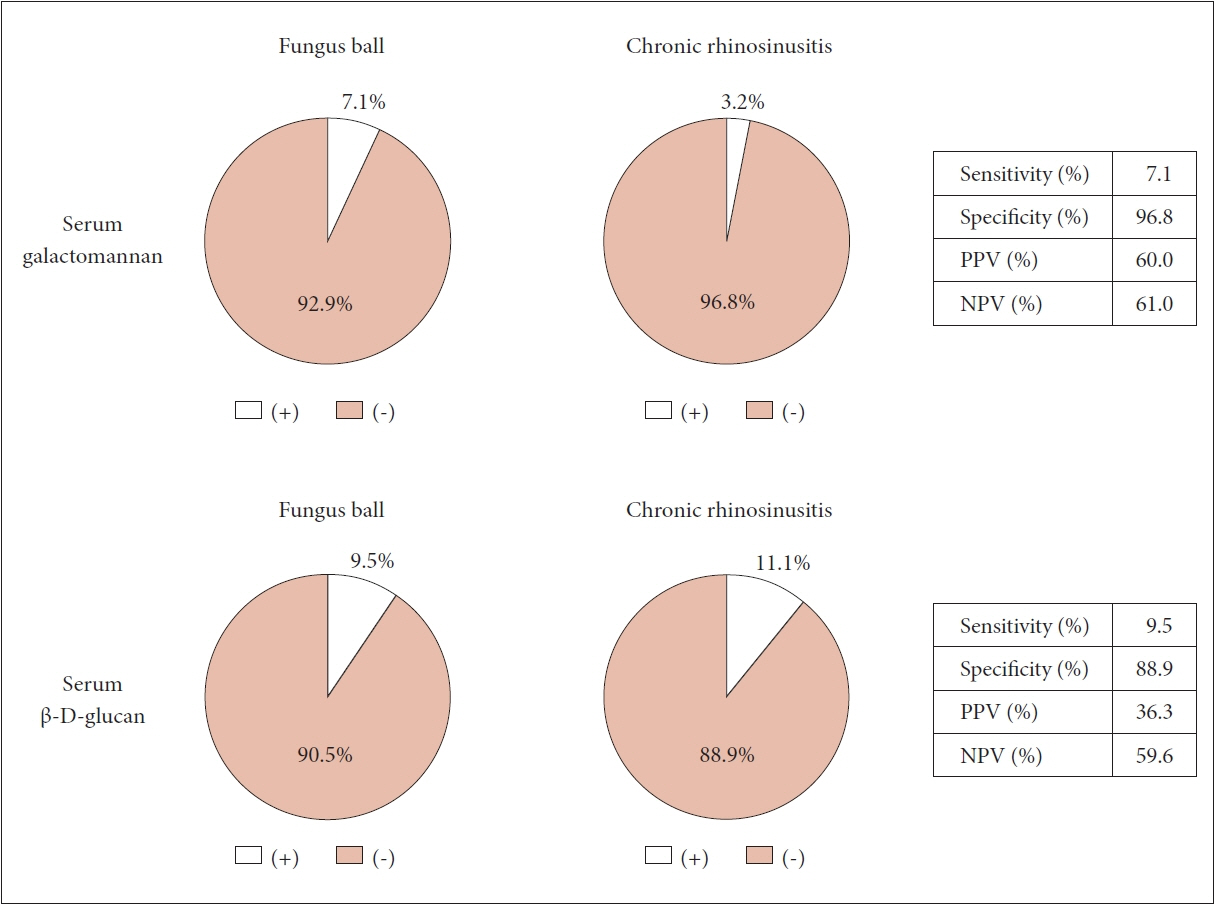
There were 42 FB patients (10 men, 32 women) and 63 CRS patients (27 men, 36 women). The positivity rates for serum GM (7.1% in the FB group vs. 3.2% in the CRS group, p=0.640) and G test (9.5% in the FB group vs. 11.1% in the CRS group, p=0.482) did not differ significantly between groups. The sensitivities of the GM and G tests were 7.1% and 9.5%, respectively, and their specificities were 96.8% and 88.9%, respectively. The positive predictive values were 60.0% for the GM test and 36.3% for the G test, and the negative predictive values were 61.0% for the GM test and 59.6% for the G test.
Conclusion
Serum GM and G tests demonstrated low sensitivity and high specificity, indicating limited effectiveness in differentiating between patients with FBs and those with CRS. Histological examination remains the gold standard for the definitive diagnosis of FBs.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Kim DW, Kim YM, Min JY, Kim JW, Kim JK, Mo JH, et al. Clinicopathologic characteristics of paranasal sinus fungus ball: retrospective, multicenter study in Korea. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2020; 277(3):761–5.2. Liu X, Liu C, Wei H, He S, Dong S, Zhou B, et al. A retrospective analysis of 1,717 paranasal sinus fungus ball cases from 2008 to 2017. Laryngoscope. 2020; 130(1):75–9.3. Cho HJ, Hong SD, Kim HY, Chung SK, Dhong HJ. Clinical implications of serum galactomannan measurement in patients with acute invasive fungal rhinosinusitis. Rhinology. 2016; 54(4):336–41.4. Theel ES, Doern CD. β-D-glucan testing is important for diagnosis of invasive fungal infections. J Clin Microbiol. 2013; 51(11):3478–83.5. Kostamo K, Richardson M, Eerola E, Rantakokko-Jalava K, Meri T, Malmberg H, et al. Negative impact of Aspergillus galactomannan and DNA detection in the diagnosis of fungal rhinosinusitis. J Med Microbiol. 2007; 56(Pt 10):1322–7.6. Kauffmann-Lacroix C, Rodier MH, Jacquemin JL, Goujon JM, Klossek JM. Detection of galactomannan for diagnosis of fungal rhinosinusitis. J Clin Microbiol. 2001; 39(12):4593–4.7. Lee HW, Kang SH, Jang KH, Kim DS, Shin SH, Ye MK. [Changes in etiologies and clinical characteristics of operated unilateral sinus diseases: comparison study between 2005 and 2015]. J Rhinol. 2017; 24(1):26–30. Korean.8. Klossek JM, Serrano E, Péloquin L, Percodani J, Fontanel JP, Pessey JJ. Functional endoscopic sinus surgery and 109 mycetomas of paranasal sinuses. Laryngoscope. 1997; 107(1):112–7.9. Ledderose GJ, Braun T, Betz CS, Stelter K, Leunig A. Functional endoscopic surgery of paranasal fungus ball: clinical outcome, patient benefit and health-related quality of life. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2012; 269(10):2203–8.10. Han SA, Kim S, Seo Y, Yang SK, Rhee CS, Han DH. Dental implant as a potential risk factor for maxillary sinus fungus ball. Sci Rep. 2024; 14(1):2483.
Article11. Melancon CC, Lindsey J, Russell GB, Clinger JD. The role of galactomannan Aspergillus antigen in diagnosing acute invasive fungal sinusitis. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2019; 9(1):60–6.12. Park SY, Lee SO, Choi SH, Jeong JY, Sung H, Kim MN, et al. Serum and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid galactomannan assays in patients with pulmonary aspergilloma. Clin Infect Dis. 2011; 52(7):e149–52.13. Boonsarngsuk V, Niyompattama A, Teosirimongkol C, Sriwanichrak K. False-positive serum and bronchoalveolar lavage Aspergillus galactomannan assays caused by different antibiotics. Scand J Infect Dis. 2010; 42(6-7):461–8.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Multiple Discrete Fungus Balls of the Bilateral Paranasal Sinuses
- Two Cases of Bilateral Paranasal Sinus Fungus Balls with Sphenoid Sinus Involvement
- Clinical Features of Bilateral Paranasal Sinus Fungus Ball
- A Case of Allergic Fungal Rhinosinusitis with Concurrently Occuring Fungus Ball
- Two Cases of Fungus Ball in Bilateral Paranasal Sinuses