Korean J Pain.
2024 Jul;37(3):201-210. 10.3344/kjp.23358.
The pros and cons of ultrasound-guided procedures in pain medicine
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2557724
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.23358
Abstract
- The application of ultrasound (US) in pain medicine has been a rapidly growing field since the 2000s. Musculoskeletal injections, peripheral nerve blocks, and neuraxial injections under US guidance have been acknowledged for managing chronic pain. Although many studies on US-guided pain procedures have been published, there needs to be a classification system to evaluate which image device, the US or fluoroscopy, is clinically and technically better in various pain interventions. Therefore, this narrative review introduces the classification system for the US-guided pain procedures according to their clinical and technical outcomes and designates US-guided pain procedures into one of the four categories by reviewing previous prospective randomized comparative trials.
Keyword
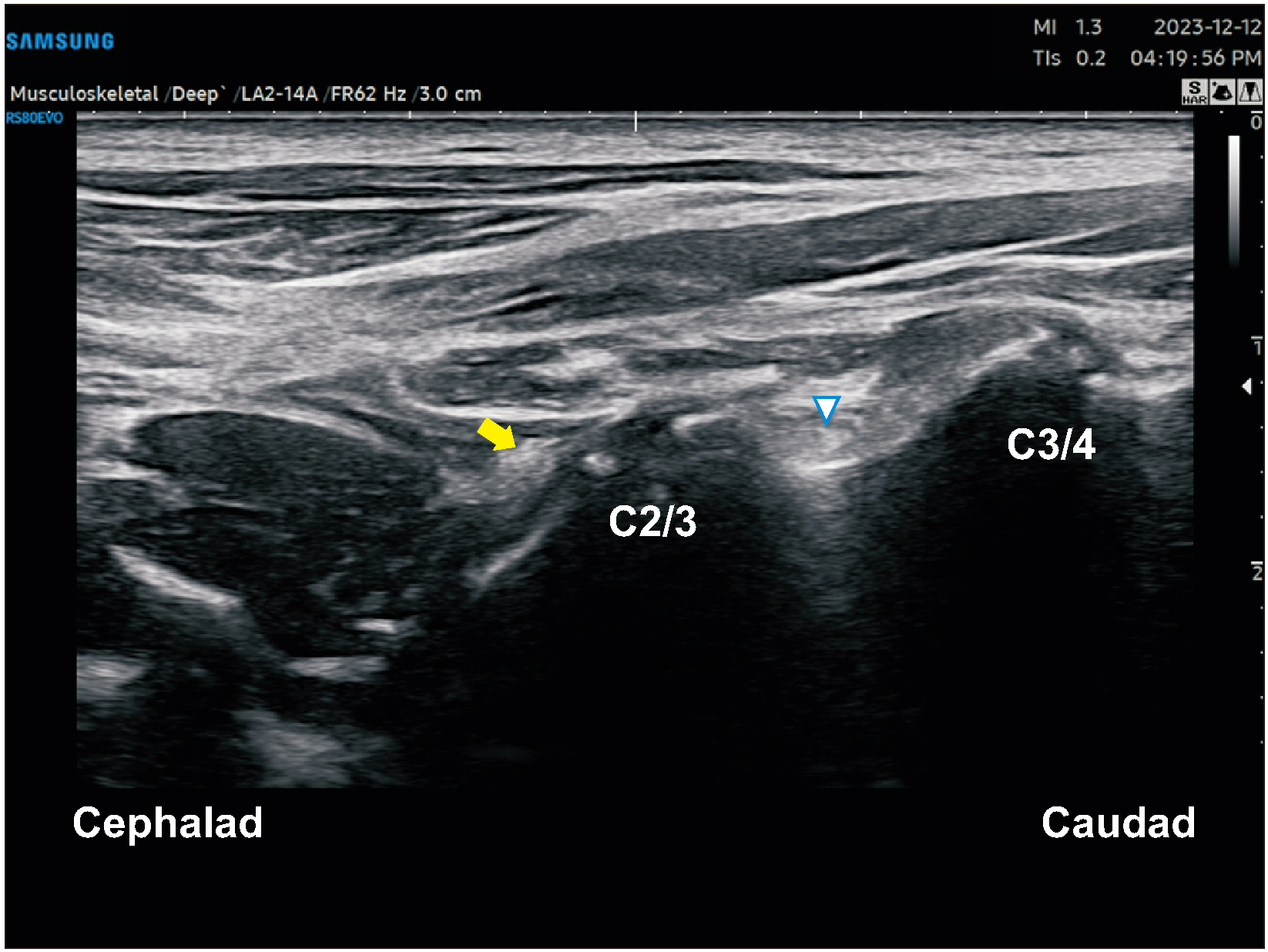
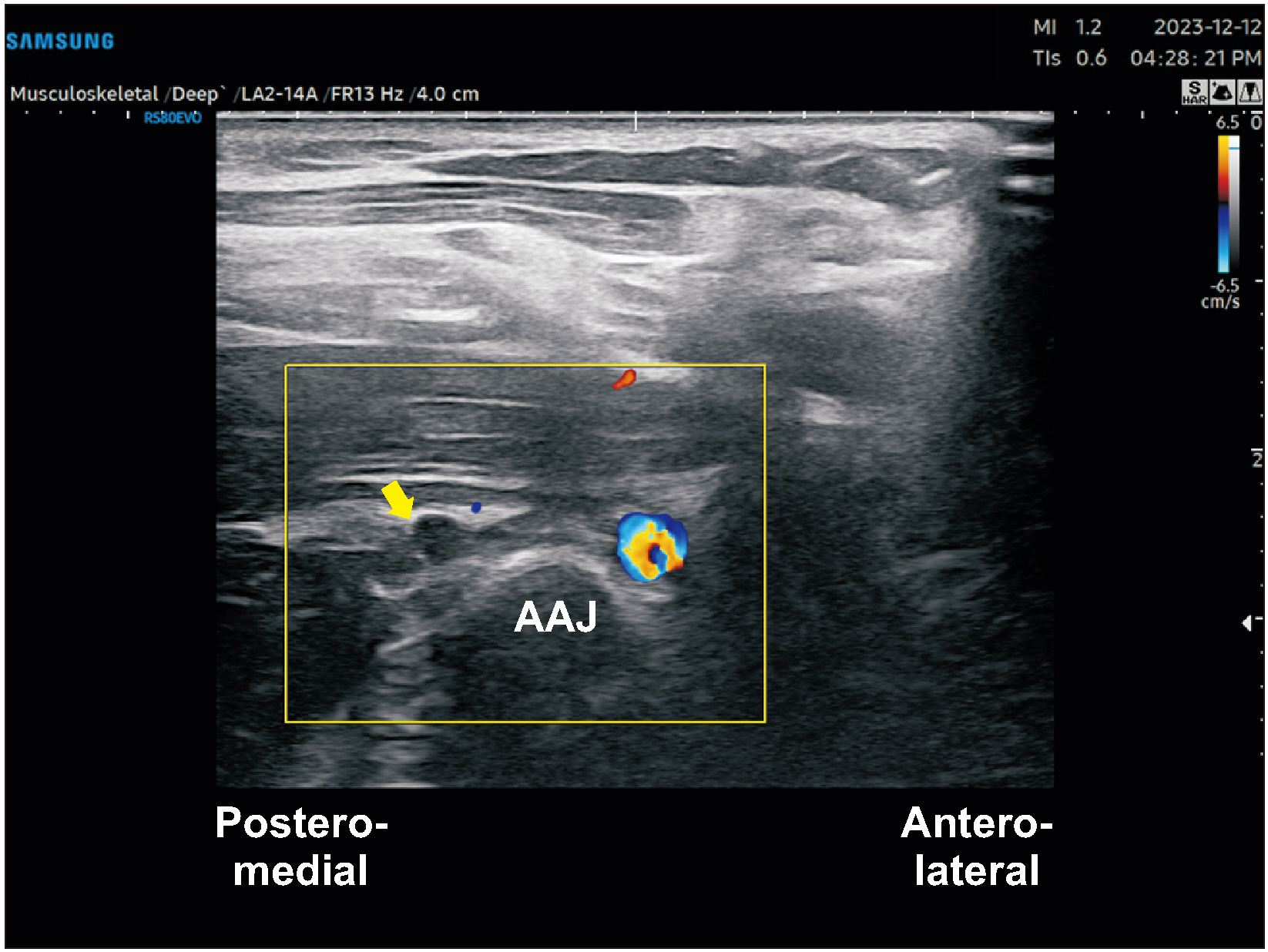
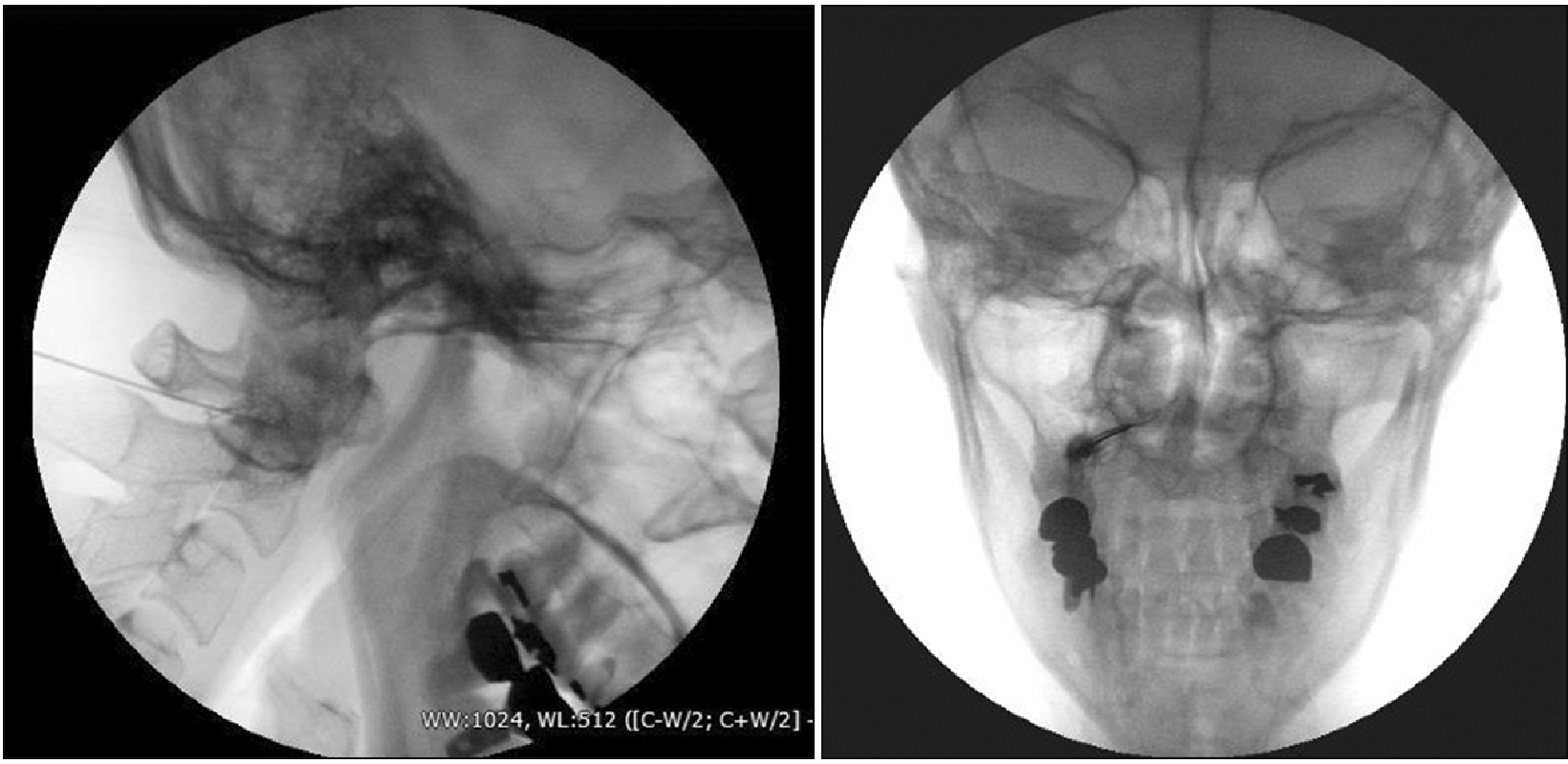
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Ultrasound-guided pain management: pros, cons, and benefits for the Philippines
John Patrick C. Toledo
Korean J Pain. 2025;38(1):79-80. doi: 10.3344/kjp.24246.
Reference
-
1. Narouze SN. 2012; Ultrasound-guided cervical spine injections: ultrasound "prevents" whereas contrast fluoroscopy "detects" intravascular injections. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 37:127–30. DOI: 10.1097/AAP.0b013e31823f3c80. PMID: 22354064.2. Finlayson RJ, Gupta G, Alhujairi M, Dugani S, Tran DQ. 2012; Cervical medial branch block: a novel technique using ultrasound guidance. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 37:219–23. DOI: 10.1097/AAP.0b013e3182374e24. PMID: 22030725.3. Finlayson RJ, Etheridge JP, Vieira L, Gupta G, Tran DQ. 2013; A randomized comparison between ultrasound- and fluoroscopy-guided third occipital nerve block. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 38:212–7. DOI: 10.1097/AAP.0b013e31828b25bc. PMID: 23558370.
Article4. Narouze SN, Vydyanathan A, Kapural L, Sessler DI, Mekhail N. 2009; Ultrasound-guided cervical selective nerve root block: a fluoroscopy-controlled feasibility study. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 34:343–8. DOI: 10.1097/AAP.0b013e3181ac7e5c. PMID: 19574867.5. Baig S, Moon JY, Shankar H. 2017; Review of sympathetic blocks: anatomy, sonoanatomy, evidence, and techniques. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 42:377–91. DOI: 10.1097/AAP.0000000000000591. PMID: 28272291.6. Jung H, Bae J, Kim J, Yoo Y, Lee HJ, Rho H, et al. 2022; Can the rhomboid major muscle be used to identify the thoracic spinal segment on ultrasonography? A prospective observational study. Pain Med. 23:1670–8. DOI: 10.1093/pm/pnac043. PMID: 35289904.
Article7. Finlayson RJ, Etheridge JP, Tiyaprasertkul W, Nelems B, Tran DQ. 2015; A randomized comparison between ultrasound- and fluoroscopy-guided c7 medial branch block. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 40:52–7. DOI: 10.1097/AAP.0000000000000186. PMID: 25478757.
Article8. Finlayson RJ, Etheridge JB, Elgueta MF, Thonnagith A, De Villiers F, Nelems B, et al. 2017; A randomized comparison between ultrasound- and fluoroscopy-guided sacral lateral branch blocks. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 42:400–6. DOI: 10.1097/AAP.0000000000000569. PMID: 28178092.
Article9. Petscavage-Thomas J, Gustas C. 2016; Comparison of ultrasound-guided to fluoroscopy-guided biceps tendon sheath therapeutic injection. J Ultrasound Med. 35:2217–21. DOI: 10.7863/ultra.15.08076. PMID: 27582534.
Article10. Shamshery C, Kumar VV, Agarwal A, Aggarwal A, Madabushi R. 2021; Comparative evaluation of efficacy of fluoroscopy and ultrasound for iliopsoas block: a randomised trial. Turk J Anaesthesiol Reanim. 49:284–91. DOI: 10.5152/TJAR.2021.454. PMID: 35110009. PMCID: PMC10335524.11. Hughey S, Schafer J, Cole J, Booth G, Tuttle R, Stedje-Larsen E. 2021; Ultrasound versus fluoroscopy for stellate ganglion block: a cadaveric study. Pain Med. 22:2307–10. DOI: 10.1093/pm/pnab182. PMID: 34051103.12. Jee H, Lee JH, Kim J, Park KD, Lee WY, Park Y. 2013; Ultrasound-guided selective nerve root block versus fluoroscopy-guided transforaminal block for the treatment of radicular pain in the lower cervical spine: a randomized, blinded, controlled study. Skeletal Radiol. 42:69–78. DOI: 10.1007/s00256-012-1434-1. PMID: 22609989.
Article13. Cui X, Zhang D, Zhao Y, Song Y, He L, Zhang J. 2022; An open-label non-inferiority randomized trail comparing the effectiveness and safety of ultrasound-guided selective cervical nerve root block and fluoroscopy-guided cervical transforaminal epidural block for cervical radiculopathy. Ann Med. 54:2681–91. DOI: 10.1080/07853890.2022.2124445. PMID: 36164681. PMCID: PMC9553110.
Article14. Wan Q, Yang H, Li X, Lin C, Ke S, Wu S, et al. 2017; Ultrasound-guided versus fluoroscopy-guided deep cervical plexus block for the treatment of cervicogenic headache. Biomed Res Int. 2017:4654803. DOI: 10.1155/2017/4654803. PMID: 28326321. PMCID: PMC5343221.15. Ha DH, Shim DM, Kim TK, Kim YM, Choi SS. 2010; Comparison of ultrasonography- and fluoroscopy-guided facet joint block in the lumbar spine. Asian Spine J. 4:15–22. DOI: 10.4184/asj.2010.4.1.15. PMID: 20622950. PMCID: PMC2900164.
Article16. Yun DH, Kim HS, Yoo SD, Kim DH, Chon JM, Choi SH, et al. 2012; Efficacy of ultrasonography-guided injections in patients with facet syndrome of the low lumbar spine. Ann Rehabil Med. 36:66–71. DOI: 10.5535/arm.2012.36.1.66. PMID: 22506237. PMCID: PMC3309334.17. Nisolle ML, Ghoundiwal D, Engelman E, El Founas W, Gouwy J, Guntz E, et al. 2023; Comparison of the effectiveness of ultrasound-guided versus fluoroscopy-guided medial lumbar bundle branch block on pain related to lumbar facet joints: a multicenter randomized controlled non-inferiority study. BMC Anesthesiol. 23:76. Erratum in: BMC Anesthesiol 2023; 23: 157. DOI: 10.1186/s12871-023-02029-9. PMID: 36906521. PMCID: PMC10007783.18. Soneji N, Bhatia A, Seib R, Tumber P, Dissanayake M, Peng PW. 2016; Comparison of fluoroscopy and ultrasound guidance for sacroiliac joint injection in patients with chronic low back pain. Pain Pract. 16:537–44. DOI: 10.1111/papr.12304. PMID: 25988390.19. Bellingham GA, Bhatia A, Chan CW, Peng PW. 2012; Randomized controlled trial comparing pudendal nerve block under ultrasound and fluoroscopic guidance. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 37:262–6. DOI: 10.1097/AAP.0b013e318248c51d. PMID: 22430025.
Article20. Fowler IM, Tucker AA, Weimerskirch BP, Moran TJ, Mendez RJ. 2014; A randomized comparison of the efficacy of 2 techniques for piriformis muscle injection: ultrasound-guided versus nerve stimulator with fluoroscopic guidance. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 39:126–32. DOI: 10.1097/AAP.0000000000000056. PMID: 24509422.21. Kim DH, Lee MS, Lee S, Yoon SH, Shin JW, Choi SS. 2019; A prospective randomized comparison of the efficacy of ultrasound- vs fluoroscopy-guided genicular nerve block for chronic knee osteoarthritis. Pain Physician. 22:139–46. DOI: 10.36076/ppj/2019.22.139.22. Yang G, Liu J, Ma L, Cai Z, Meng C, Qi S, et al. 2016; Ultrasound-guided versus fluoroscopy-controlled lumbar transforaminal epidural injections: a prospective randomized clinical trial. Clin J Pain. 32:103–8. DOI: 10.1097/AJP.0000000000000237. PMID: 25803759.23. Falsafi M, Baghianimoghadam B, Bahrami-Freiduni M, Esmaeilnejad-Ganji SM. 2021; Examining the accuracy of ultrasound-guided lumbar transforaminal injection controlled by fluoroscopic imaging in patients with lumbar radiculopathy: a modified technique. Turk Neurosurg. 31:582–6. DOI: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.32660-20.1. PMID: 33978216.
Article24. Thompson BF, Pingree MJ, Qu W, Murthy NS, Lachman N, Hurdle MF. 2018; Descriptive cadaveric study comparing the accuracy of ultrasound versus fluoroscopic guidance for first sacral transforaminal injections: a comparison study. PM R. 10:382–90. DOI: 10.1016/j.pmrj.2017.09.008. PMID: 28943459.
Article25. Burnham TR, Smith A, McCormick ZL, Teramoto M, Burnham R. 2022; Evaluation of an ultrasound-assisted longitudinal axis lateral crest approach to radiofrequency ablation of the sacroiliac joint. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 101:26–31. DOI: 10.1097/PHM.0000000000001733. PMID: 34915543.
Article26. Moon JY, Choi JK, Shin JY, Chon SW, Dev S. 2017; A brief report on a technical description of ultrasound-guided lumbar sympathetic block. Korean J Pain. 30:66–70. DOI: 10.3344/kjp.2017.30.1.66. PMID: 28119774. PMCID: PMC5256261.
Article27. Ryu JH, Lee CS, Kim YC, Lee SC, Shankar H, Moon JY. 2018; Ultrasound-assisted versus fluoroscopic-guided lumbar sympathetic ganglion block: a prospective and randomized study. Anesth Analg. 126:1362–8. DOI: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000002640. PMID: 29189275.
Article28. Abdelghaffar NA, Farahat TE. 2022; Fluoroscopic anterior approach versus ultrasound guided superior hypogastric plexus neurolysis in cancer pelvic pain: a randomized controlled study. BMC Anesthesiol. 22:403. DOI: 10.1186/s12871-022-01948-3. PMID: 36575390. PMCID: PMC9793506.
Article29. Senkal S, Sir E. 2021; Comparison of ultrasonography and conventional fluoroscopy guided caudal epidural injection in chronic low back pain. Turk Neurosurg. 31:119–23. DOI: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.31515-20.2. PMID: 33372261.30. Poutoglidou F, Metaxiotis D, Vasiliadis AV, Alvanos D, Mpeletsiotis A. 2021; Caudal epidural injections in lumbar spinal stenosis: comparison of nonimage, ultrasonography-, and fluoroscopy-guided techniques. A randomized clinical trial. Perm J. 25:20.321. DOI: 10.7812/TPP/20.321. PMID: 35348084. PMCID: PMC8784067.
Article31. Kim JY, Lee JS, Kim JY, Baek JW, Kim HS, Kim DH. 2024; Comparison of the incidence of intravascular injection using the Tuohy and Quincke needles during ultrasound-guided caudal epidural block: a prospective randomized controlled study. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 49:17–22. DOI: 10.1136/rapm-2023-104504. PMID: 37169489.
Article32. Park Y, Lee JH, Park KD, Ahn JK, Park J, Jee H. 2013; Ultrasound-guided vs. fluoroscopy-guided caudal epidural steroid injection for the treatment of unilateral lower lumbar radicular pain: a prospective, randomized, single-blind clinical study. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 92:575–86. DOI: 10.1097/PHM.0b013e318292356b. PMID: 23636087.33. Kim DH, Lee JH, Sim JH, Jeong W, Lee D, Kwon HM, et al. 2021; Real-time ultrasound-guided low thoracic epidural catheter placement: technical consideration and fluoroscopic evaluation. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 46:512–7. DOI: 10.1136/rapm-2021-102578. PMID: 33893174.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Ultrasound-guided pain management: pros, cons, and benefits for the Philippines
- Ultrasound-Guided Intervention for Breast Lesions
- Ultrasound Findings and Procedures for Knee and Distal Femur Pathologies
- Ultrasound-guided interventions for spinal pain
- Robotic Thyroidectomy: Pros and Cons of Various Surgical Approaches