Clin Transplant Res.
2024 Jun;38(2):71-89. 10.4285/ctr.24.0006.
Polyomavirus nephropathy: diagnosis, histologic features, and differentiation from acute rejection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA, USA
- KMID: 2557601
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4285/ctr.24.0006
Abstract
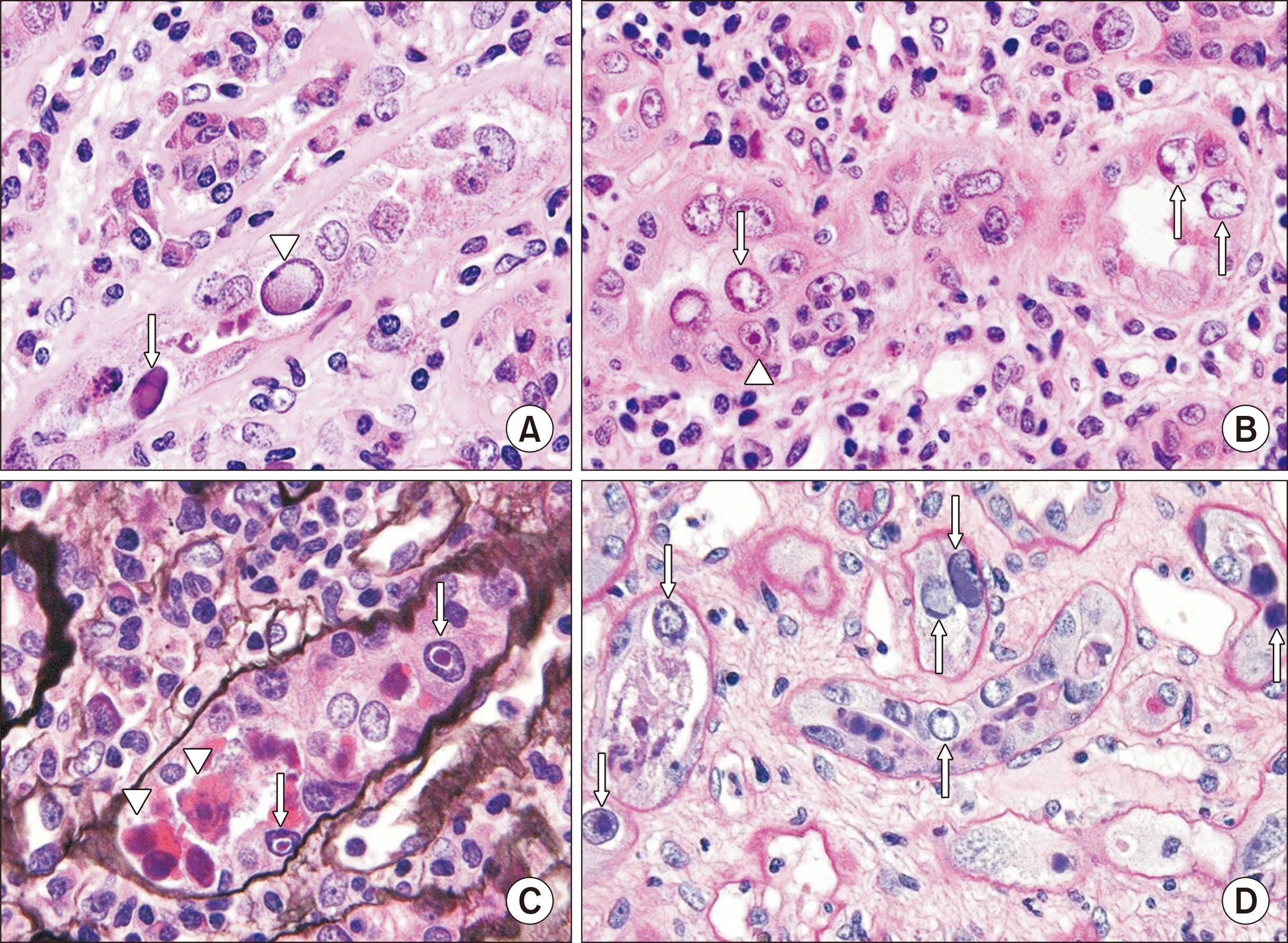
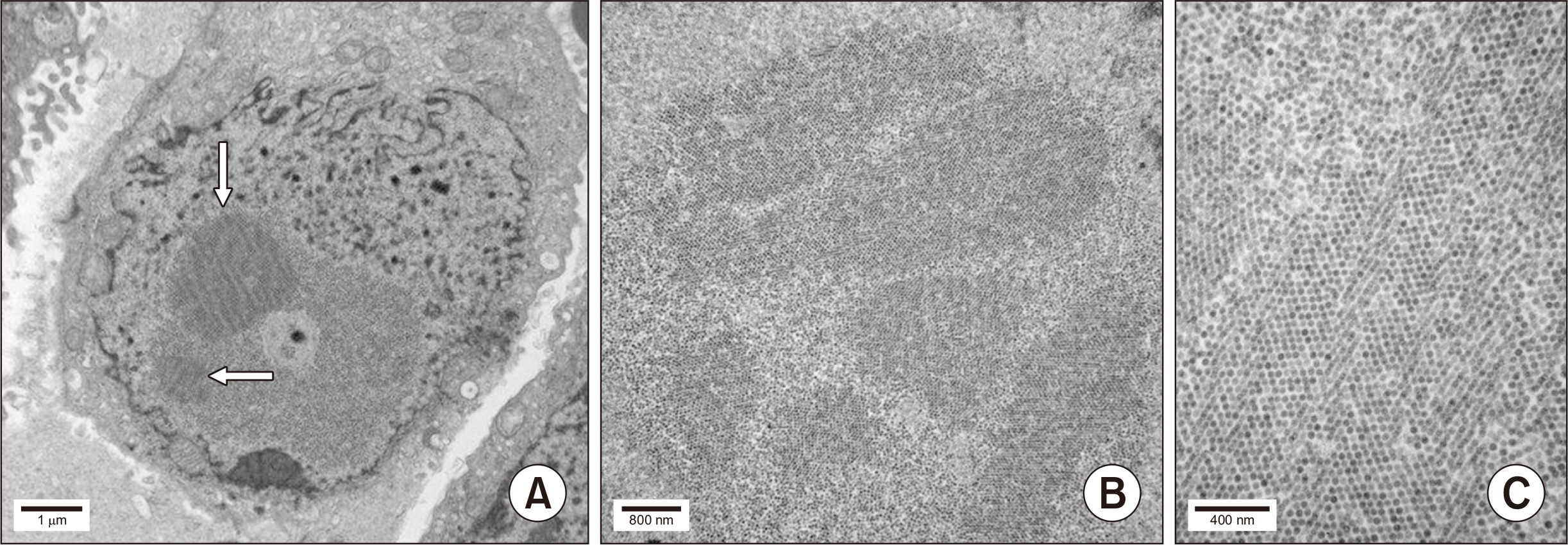
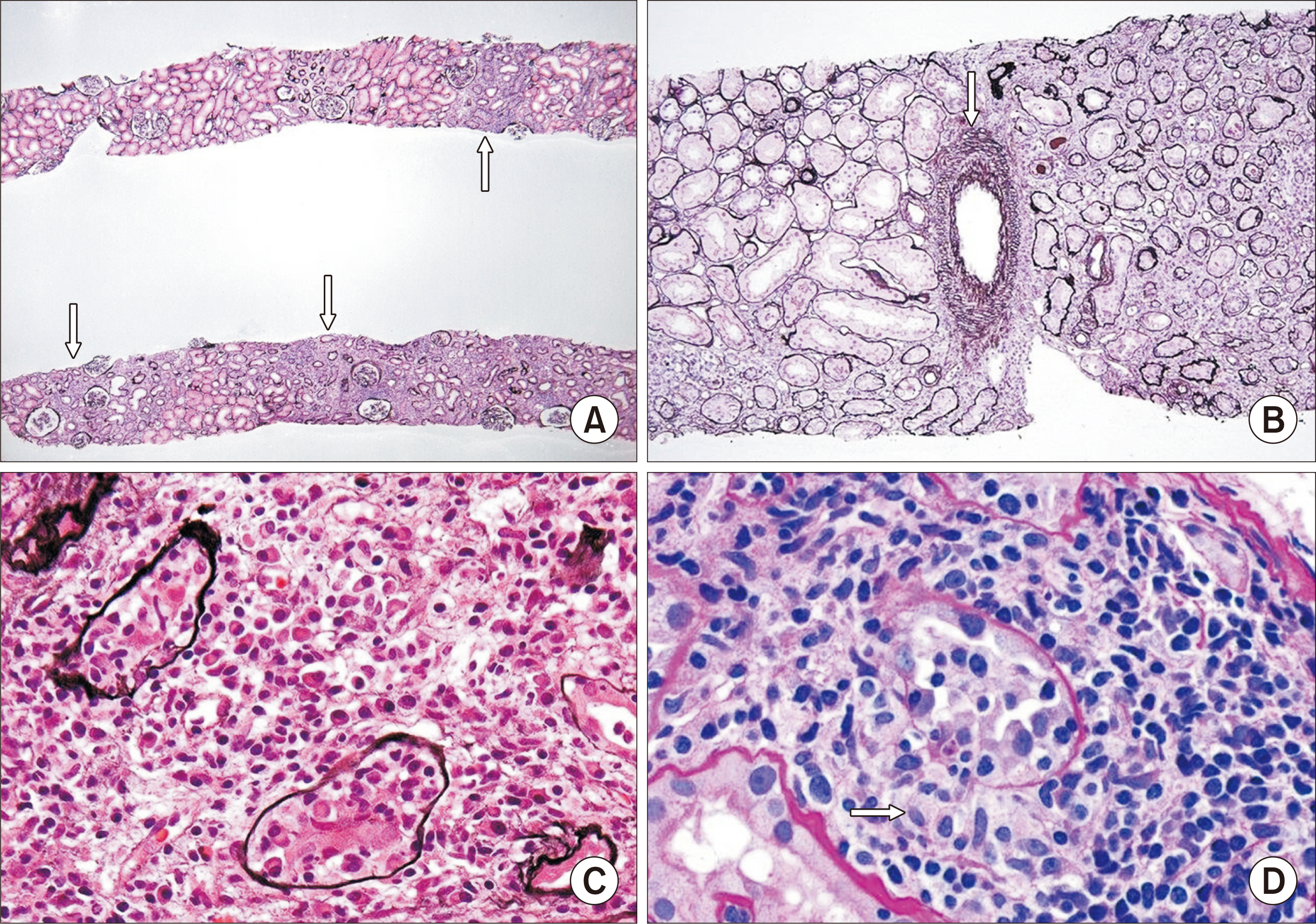
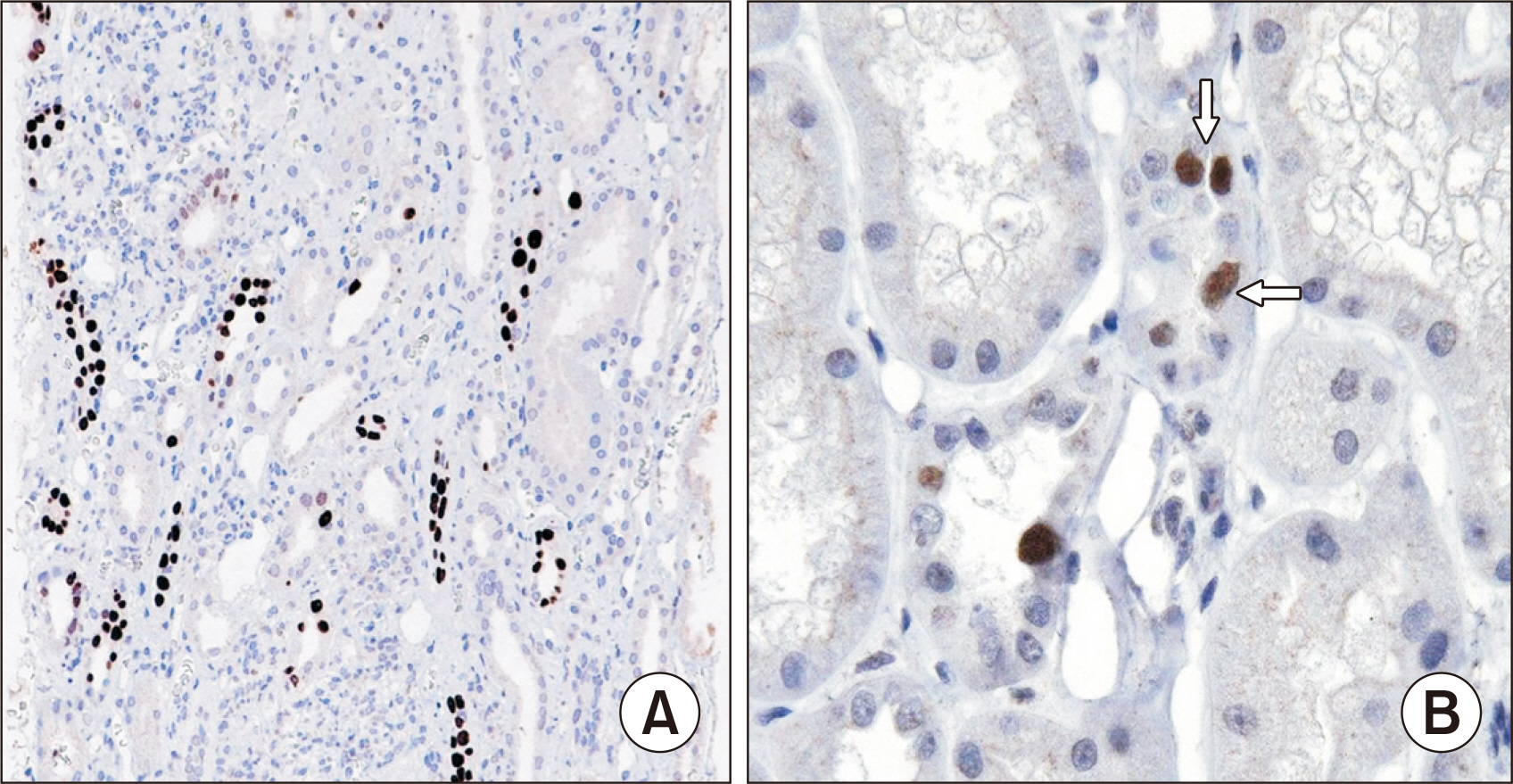
- Polyomaviruses, particularly BK virus, are ubiquitous latent infections that may reactivate with immunosuppression during kidney transplantation, resulting in polyomavirus nephropathy (PVN). The levels of viruria and viremia serve as tools for screening and making a presumptive diagnosis of PVN, respectively, while a definitive diagnosis requires a kidney biopsy. There are histologic classifications of PVN based on the extent of tubular cell viral infection, interstitial fibrosis, and interstitial inflammation. These classifications correlate to some degree with graft function and loss, aiding in determining treatment efficacy and prognostication. PVN has histologic overlap with acute cell-mediated rejection, making the differential diagnosis challenging, although there are suggestive features for these different causes of graft dysfunction. This article reviews the diagnosis, histologic findings, and classifications of PVN, and discusses how to differentiate viral nephropathy from acute rejection.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Knowles WA. 2006; Discovery and epidemiology of the human polyomaviruses BK virus (BKV) and JC virus (JCV). Adv Exp Med Biol. 577:19–45. DOI: 10.1007/0-387-32957-9_2. PMID: 16626025.
Article2. Koukoulaki M, Grispou E, Pistolas D, Balaska K, Apostolou T, Anagnostopoulou M, et al. 2009; Prospective monitoring of BK virus replication in renal transplant recipients. Transpl Infect Dis. 11:1–10. DOI: 10.1111/j.1399-3062.2008.00342.x. PMID: 18811631.
Article3. Hirsch HH, Vincenti F, Friman S, Tuncer M, Citterio F, Wiecek A, et al. 2013; Polyomavirus BK replication in de novo kidney transplant patients receiving tacrolimus or cyclosporine: a prospective, randomized, multicenter study. Am J Transplant. 13:136–45. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2012.04320.x. PMID: 23137180. PMCID: PMC3563214.4. Malik O, Saleh S, Suleiman B, Ashqar B, Maibam A, Yaseen M, et al. 2019; Prevalence, risk factors, treatment, and overall impact of BK viremia on kidney transplantation. Transplant Proc. 51:1801–9. DOI: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2019.03.035. PMID: 31399166.5. Yoon SH, Cho JH, Jung HY, Choi JY, Park SH, Kim YL, et al. 2015; Clinical impact of BK virus surveillance on outcomes in kidney transplant recipients. Transplant Proc. 47:660–5. DOI: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2014.11.051. PMID: 25891706.
Article6. Shen CL, Wu BS, Lien TJ, Yang AH, Yang CY. 2021; BK polyomavirus nephropathy in kidney transplantation: balancing rejection and infection. Viruses. 13:487. DOI: 10.3390/v13030487. PMID: 33809472. PMCID: PMC7998398.
Article7. Nickeleit V, Singh HK. 2015; Polyomaviruses and disease: is there more to know than viremia and viruria? Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 20:348–58. DOI: 10.1097/MOT.0000000000000192. PMID: 25933251. PMCID: PMC4927320.8. Imlay H, Whitaker K, Fisher CE, Limaye AP. 2018; Clinical characteristics and outcomes of late-onset BK virus nephropathy in kidney and kidney-pancreas transplant recipients. Transpl Infect Dis. 20:e12928. DOI: 10.1111/tid.12928. PMID: 29809315.9. Ramos E, Drachenberg CB, Wali R, Hirsch HH. 2009; The decade of polyomavirus BK-associated nephropathy: state of affairs. Transplantation. 87:621–30. DOI: 10.1097/TP.0b013e318197c17d. PMID: 19295303.
Article10. Hirsch HH, Randhawa P. AST Infectious Diseases Community of Practice. 2009; BK virus in solid organ transplant recipients. Am J Transplant. 9 Suppl 4:S136–46. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2009.02904.x. PMID: 20070673.
Article11. Zakaria ZE, Elokely AM, Ghorab AA, Bakr AI, Halim MA, Gheith OA, et al. 2019; Screening for BK viremia/viruria and the impact of management of BK virus nephropathy in renal transplant recipients. Exp Clin Transplant. 17(Suppl 1):83–91. DOI: 10.6002/ect.MESOT2018.O17. PMID: 30777529.12. Hirsch HH. 2002; Polyomavirus BK nephropathy: a (re-)emerging complication in renal transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2:25–30. DOI: 10.1034/j.1600-6143.2002.020106.x. PMID: 12095052.13. Cannon RM, Ouseph R, Jones CM, Hughes MG, Eng M, Marvin MR. 2011; BK viral disease in renal transplantation. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 16:576–9. DOI: 10.1097/MOT.0b013e32834cd666. PMID: 22027587.
Article14. Myint TM, Chong CH, Wyld M, Nankivell B, Kable K, Wong G. 2022; Polyoma BK virus in kidney transplant recipients: screening, monitoring, and management. Transplantation. 106:e76–89. DOI: 10.1097/TP.0000000000003801. PMID: 33908382.
Article15. Gras J, Le Flécher A, Dupont A, Vérine J, Amara A, Delaugerre C, et al. 2023; Characteristics, risk factors and outcome of BKV nephropathy in kidney transplant recipients: a case-control study. BMC Infect Dis. 23:74. DOI: 10.1186/s12879-023-08043-z. PMID: 36747162. PMCID: PMC9903532.
Article16. Womer KL, Huang Y, Herren H, Dibadj K, Peng R, Murawski M, et al. 2010; Dendritic cell deficiency associated with development of BK viremia and nephropathy in renal transplant recipients. Transplantation. 89:115–23. DOI: 10.1097/TP.0b013e3181bc6096. PMID: 20061927.
Article17. Bauman Y, Nachmani D, Vitenshtein A, Tsukerman P, Drayman N, Stern-Ginossar N, et al. 2011; An identical miRNA of the human JC and BK polyoma viruses targets the stress-induced ligand ULBP3 to escape immune elimination. Cell Host Microbe. 9:93–102. DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2011.01.008. PMID: 21320692.18. Ambalathingal GR, Francis RS, Smyth MJ, Smith C, Khanna R. 2017; BK polyomavirus: clinical aspects, immune regulation, and emerging therapies. Clin Microbiol Rev. 30:503–28. DOI: 10.1128/CMR.00074-16. PMID: 28298471. PMCID: PMC5355639.
Article19. Comoli P, Hirsch HH, Ginevri F. 2008; Cellular immune responses to BK virus. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 13:569–74. DOI: 10.1097/MOT.0b013e3283186b93. PMID: 19060544.
Article20. van Aalderen MC, Heutinck KM, Huisman C, ten Berge IJ. 2012; BK virus infection in transplant recipients: clinical manifestations, treatment options and the immune response. Neth J Med. 70:172–83. PMID: 22641625.21. Zhou W, Sharma M, Martinez J, Srivastava T, Diamond DJ, Knowles W, et al. 2007; Functional characterization of BK virus-specific CD4+ T cells with cytotoxic potential in seropositive adults. Viral Immunol. 20:379–88. DOI: 10.1089/vim.2007.0030. PMID: 17931108.22. Trydzenskaya H, Sattler A, Müller K, Schachtner T, Dang-Heine C, Friedrich P, et al. 2011; Novel approach for improved assessment of phenotypic and functional characteristics of BKV-specific T-cell immunity. Transplantation. 92:1269–77. DOI: 10.1097/TP.0b013e318234e0e5. PMID: 22124284.
Article23. Renner FC, Dietrich H, Bulut N, Celik D, Freitag E, Gaertner N, et al. 2013; The risk of polyomavirus-associated graft nephropathy is increased by a combined suppression of CD8 and CD4 cell-dependent immune effects. Transplant Proc. 45:1608–10. DOI: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2013.01.026. PMID: 23726630.
Article24. Prince O, Savic S, Dickenmann M, Steiger J, Bubendorf L, Mihatsch MJ. 2009; Risk factors for polyoma virus nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 24:1024–33. DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfn671. PMID: 19073658. PMCID: PMC2644630.
Article25. Gonzalez S, Escobar-Serna DP, Suarez O, Benavides X, Escobar-Serna JF, Lozano E. 2015; BK virus nephropathy in kidney transplantation: an approach proposal and update on risk factors, diagnosis, and treatment. Transplant Proc. 47:1777–85. DOI: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2015.05.010. PMID: 26293050.26. Abend JR, Low JA, Imperiale MJ. 2007; Inhibitory effect of gamma interferon on BK virus gene expression and replication. J Virol. 81:272–9. DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01571-06. PMID: 17035315. PMCID: PMC1797268.
Article27. Comoli P, Cioni M, Basso S, Gagliardone C, Potenza L, Verrina E, et al. 2013; Immunity to polyomavirus BK infection: immune monitoring to regulate the balance between risk of BKV nephropathy and induction of alloimmunity. Clin Dev Immunol. 2013:256923. DOI: 10.1155/2013/256923. PMID: 24000288. PMCID: PMC3755406.28. Bohl DL, Storch GA, Ryschkewitsch C, Gaudreault- Keener M, Schnitzler MA, Major EO, et al. 2005; Donor origin of BK virus in renal transplantation and role of HLA C7 in susceptibility to sustained BK viremia. Am J Transplant. 5:2213–21. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2005.01000.x. PMID: 16095500.
Article29. Mbianda C, El-Meanawy A, Sorokin A. 2015; Mechanisms of BK virus infection of renal cells and therapeutic implications. J Clin Virol. 71:59–62. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcv.2015.08.003. PMID: 26295751. PMCID: PMC4572911.
Article30. Schwarz A, Linnenweber-Held S, Heim A, Framke T, Haller H, Schmitt C. 2016; Viral origin, clinical course, and renal outcomes in patients with BK virus infection after living-donor renal transplantation. Transplantation. 100:844–53. DOI: 10.1097/TP.0000000000001066. PMID: 26720302.
Article31. Sawinski D, Goral S. 2015; BK virus infection: an update on diagnosis and treatment. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 30:209–17. DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfu023. PMID: 24574543.
Article32. Hirsch HH, Randhawa P. AST Infectious Diseases Community of Practice. 2013; BK polyomavirus in solid organ transplantation. Am J Transplant. 13 Suppl 4:179–88. DOI: 10.1111/ajt.12110. PMID: 23465010.33. Favi E, Puliatti C, Sivaprakasam R, Ferraresso M, Ambrogi F, Delbue S, et al. 2019; Incidence, risk factors, and outcome of BK polyomavirus infection after kidney transplantation. World J Clin Cases. 7:270–90. DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i3.270. PMID: 30746369. PMCID: PMC6369392.
Article34. Borriello M, Ingrosso D, Perna AF, Lombardi A, Maggi P, Altucci L, et al. 2022; BK virus infection and BK-virus-associated nephropathy in renal transplant recipients. Genes (Basel). 13:1290. DOI: 10.3390/genes13071290. PMID: 35886073. PMCID: PMC9323957.
Article35. Wang J, Li J, Chen Z, Xu M, Yang C, Rong R, et al. 2022; A nomogram for predicting BK virus activation in kidney transplantation recipients using clinical risk factors. Front Med (Lausanne). 9:770699. DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.770699. PMID: 35223891. PMCID: PMC8866320.
Article36. Sharif A, Alachkar N, Bagnasco S, Geetha D, Gupta G, Womer K, et al. 2012; Incidence and outcomes of BK virus allograft nephropathy among ABO- and HLA-incompatible kidney transplant recipients. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 7:1320–7. DOI: 10.2215/CJN.00770112. PMID: 22626962. PMCID: PMC3408120.
Article37. Imlay H, Baum P, Brennan DC, Hanson KE, Hodges MR, Hodowanec AC, et al. 2022; Consensus definitions of BK polyomavirus nephropathy in renal transplant recipients for clinical trials. Clin Infect Dis. 75:1210–6. DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciac071. PMID: 35100619. PMCID: PMC9525067.38. Hirsch HH, Randhawa PS. AST Infectious Diseases Community of Practice. 2019; BK polyomavirus in solid organ transplantation-guidelines from the American Society of Transplantation Infectious Diseases Community of Practice. Clin Transplant. 33:e13528. DOI: 10.1111/ctr.13528. PMID: 30859620.
Article39. Hirsch HH, Brennan DC, Drachenberg CB, Ginevri F, Gordon J, Limaye AP, et al. 2005; Polyomavirus-associated nephropathy in renal transplantation: interdisciplinary analyses and recommendations. Transplantation. 79:1277–86. DOI: 10.1097/01.TP.0000156165.83160.09. PMID: 15912088.
Article40. Demir E, Turkmen A, Sever MS. 2021; Risk factors, pathogenesis, presentation and management of BK virus infection in kidney transplantation. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 36:985–7. DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfz214. PMID: 34047340.
Article41. Hirsch HH, Babel N, Comoli P, Friman V, Ginevri F, Jardine A, et al. 2014; European perspective on human polyomavirus infection, replication and disease in solid organ transplantation. Clin Microbiol Infect. 20 Suppl 7:74–88. DOI: 10.1111/1469-0691.12538. PMID: 24476010.
Article42. Nickeleit V, Singh HK, Randhawa P, Drachenberg CB, Bhatnagar R, Bracamonte E, et al. 2018; The Banff Working Group classification of definitive polyomavirus nephropathy: morphologic definitions and clinical correlations. J Am Soc Nephrol. 29:680–93. DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2017050477. PMID: 29279304. PMCID: PMC5791071.43. Nickeleit V, Singh HK, Dadhania D, Cornea V, El-Husseini A, Castellanos A, et al. 2021; The 2018 Banff Working Group classification of definitive polyomavirus nephropathy: a multicenter validation study in the modern era. Am J Transplant. 21:669–80. DOI: 10.1111/ajt.16189. PMID: 32654412. PMCID: PMC7891590.
Article44. Sawinski D, Trofe-Clark J. 2018; BK virus nephropathy. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 13:1893–6. DOI: 10.2215/CJN.04080318. PMID: 30242026. PMCID: PMC6302319.
Article45. Koh MJ, Lim BJ, Noh S, Kim YH, Jeong HJ. 2012; Urinary decoy cell grading and its clinical implications. Korean J Pathol. 46:233–6. DOI: 10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2012.46.3.233. PMID: 23110008. PMCID: PMC3479773.
Article46. Sekito T, Araki M, Yoshinaga K, Maruyama Y, Sadahira T, Nishimura S, et al. 2021; Presence of decoy cells for 6 months on urine cytology efficiently predicts BK virus nephropathy in renal transplant recipients. Int J Urol. 28:1240–6. DOI: 10.1111/iju.14679. PMID: 34467590.47. Ramos E, Drachenberg CB, Portocarrero M, Wali R, Klassen DK, Fink JC, et al. 2002; BK virus nephropathy diagnosis and treatment: experience at the University of Maryland Renal Transplant Program. Clin Transpl. 143–53. PMID: 12971444.48. Hassan S, Mittal C, Amer S, Khalid F, Patel A, Delbusto R, et al. 2014; Currently recommended BK virus (BKV) plasma viral load cutoff of ≥4 log10/mL underestimates the diagnosis of BKV-associated nephropathy: a single transplant center experience. Transpl Infect Dis. 16:55–60. DOI: 10.1111/tid.12164. PMID: 24283677.
Article49. Elfadawy N, Flechner SM, Schold JD, Srinivas TR, Poggio E, Fatica R, et al. 2014; Transient versus persistent BK viremia and long-term outcomes after kidney and kidney-pancreas transplantation. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 9:553–61. DOI: 10.2215/CJN.08420813. PMID: 24408118. PMCID: PMC3944774.
Article50. Demey B, Descamps V, Presne C, Helle F, Francois C, Duverlie G, et al. 2021; BK polyomavirus micro-RNAs: time course and clinical relevance in kidney transplant recipients. Viruses. 13:351. DOI: 10.3390/v13020351. PMID: 33672313. PMCID: PMC7926448.
Article51. Govind S, Hockley J, Morris C, Almond N. Collaborative Study Group. 2019; The development and establishment of the 1st WHO BKV International Standard for nucleic acid based techniques. Biologicals. 60:75–84. DOI: 10.1016/j.biologicals.2019.04.004. PMID: 31105020.
Article52. Govind S, Fritzsche M, Jenkins A, Cleveland MH, Vallone PM, Almond N, et al. 2023; Deep sequencing and molecular characterisation of BK virus and JC virus WHO international reference materials for clinical diagnostic use. Viruses. 15:1289. DOI: 10.3390/v15061289. PMID: 37376589. PMCID: PMC10302978.53. World Health Organization (WHO). 2015. Collaborative Study to establish the 1st WHO IS for BKV DNA for nucleic acid amplification technique (NAT)-based assays [Internet]. WHO;Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/WHO-BS-2015.2270. cited 2023 Oct 8.54. Ginevri F, Azzi A, Hirsch HH, Basso S, Fontana I, Cioni M, et al. 2007; Prospective monitoring of polyomavirus BK replication and impact of pre-emptive intervention in pediatric kidney recipients. Am J Transplant. 7:2727–35. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2007.01984.x. PMID: 17908275.
Article55. Schaub S, Hirsch HH, Dickenmann M, Steiger J, Mihatsch MJ, Hopfer H, et al. 2010; Reducing immunosuppression preserves allograft function in presumptive and definitive polyomavirus-associated nephropathy. Am J Transplant. 10:2615–23. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2010.03310.x. PMID: 21114642.
Article56. Elfadawy N, Flechner SM, Liu X, Schold J, Tian D, Srinivas TR, et al. 2013; The impact of surveillance and rapid reduction in immunosuppression to control BK virus-related graft injury in kidney transplantation. Transpl Int. 26:822–32. DOI: 10.1111/tri.12134. PMID: 23763289.
Article57. Cleenders E, Koshy P, Van Loon E, Lagrou K, Beuselinck K, Andrei G, et al. 2023; An observational cohort study of histological screening for BK polyomavirus nephropathy following viral replication in plasma. Kidney Int. 104:1018–34. DOI: 10.1016/j.kint.2023.07.025. PMID: 37598855.
Article58. Liptak P, Kemeny E, Ivanyi B. 2006; Primer: histopathology of polyomavirus-associated nephropathy in renal allografts. Nat Clin Pract Nephrol. 2:631–6. DOI: 10.1038/ncpneph0319. PMID: 17066055.59. Herrera GA, Veeramachaneni R, Turbat-Herrera EA. 2005; Electron microscopy in the diagnosis of BK-polyoma virus infection in the transplanted kidney. Ultrastruct Pathol. 29:469–74. DOI: 10.1080/01913120500323399. PMID: 16316947.
Article60. Nankivell BJ, Renthawa J, Sharma RN, Kable K, O'Connell PJ, Chapman JR. 2017; BK virus nephropathy: histological evolution by sequential pathology. Am J Transplant. 17:2065–77. DOI: 10.1111/ajt.14292. PMID: 28371308.
Article61. Kemény E, Hirsch HH, Eller J, Dürmüller U, Hopfer H, Mihatsch MJ. 2010; Plasma cell infiltrates in polyomavirus nephropathy. Transpl Int. 23:397–406. DOI: 10.1111/j.1432-2277.2009.01001.x. PMID: 19912590.
Article62. Drachenberg CB, Papadimitriou JC, Chaudhry MR, Ugarte R, Mavanur M, Thomas B, et al. 2017; Histological evolution of BK virus-associated nephropathy: importance of integrating clinical and pathological findings. Am J Transplant. 17:2078–91. DOI: 10.1111/ajt.14314. PMID: 28422412.
Article63. Hever A, Nast CC. 2008; Polyoma virus nephropathy with simian virus 40 antigen-containing tubular basement membrane immune complex deposition. Hum Pathol. 39:73–9. DOI: 10.1016/j.humpath.2007.05.006. PMID: 17949777.64. Bracamonte E, Leca N, Smith KD, Nicosia RF, Nickeleit V, Kendrick E, et al. 2007; Tubular basement membrane immune deposits in association with BK polyomavirus nephropathy. Am J Transplant. 7:1552–60. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2007.01794.x. PMID: 17425622.
Article65. Rosales IA, Collins AB, do Carmo PA, Tolkoff-Rubin N, Smith RN, Colvin RB. 2016; Immune complex tubulointerstitial nephritis due to autoantibodies to the proximal tubule brush border. J Am Soc Nephrol. 27:380–4. DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2015030334. PMID: 26334028. PMCID: PMC4731130.
Article66. Drachenberg CB, Papadimitriou JC, Hirsch HH, Wali R, Crowder C, Nogueira J, et al. 2004; Histological patterns of polyomavirus nephropathy: correlation with graft outcome and viral load. Am J Transplant. 4:2082–92. DOI: 10.1046/j.1600-6143.2004.00603.x. PMID: 15575913.
Article67. Nankivell BJ, Renthawa J, Shingde M, Khan A. 2020; The importance of kidney medullary tissue for the accurate diagnosis of BK virus allograft nephropathy. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 15:1015–23. DOI: 10.2215/CJN.13611119. PMID: 32601093. PMCID: PMC7341776.
Article68. Ding R, Medeiros M, Dadhania D, Muthukumar T, Kracker D, Kong JM, et al. 2002; Noninvasive diagnosis of BK virus nephritis by measurement of messenger RNA for BK virus VP1 in urine. Transplantation. 74:987–94. DOI: 10.1097/00007890-200210150-00016. PMID: 12394843.69. Dadhania D, Snopkowski C, Ding R, Muthukumar T, Lee J, Bang H, et al. 2010; Validation of noninvasive diagnosis of BK virus nephropathy and identification of prognostic biomarkers. Transplantation. 90:189–97. DOI: 10.1097/TP.0b013e3181e2a932. PMID: 20526237. PMCID: PMC2989149.
Article70. Singh HK, Andreoni KA, Madden V, True K, Detwiler R, Weck K, et al. 2009; Presence of urinary Haufen accurately predicts polyomavirus nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 20:416–27. DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2008010117. PMID: 19158358. PMCID: PMC2637054.
Article71. Singh HK, Reisner H, Derebail VK, Kozlowski T, Nickeleit V. 2015; Polyomavirus nephropathy: quantitative urinary polyomavirus-Haufen testing accurately predicts the degree of intrarenal viral disease. Transplantation. 99:609–15. DOI: 10.1097/TP.0000000000000367. PMID: 25136849. PMCID: PMC4347732.72. Nickeleit V, Davis VG, Thompson B, Singh HK. 2021; The urinary polyomavirus-haufen test: a highly predictive non-invasive biomarker to distinguish "presumptive" from "definitive" polyomavirus nephropathy: how to use it-when to use it-how does it compare to PCR based assays? Viruses. 13:135. DOI: 10.3390/v13010135. PMID: 33477927. PMCID: PMC7833404.
Article73. Huang Y, Chen XT, Yang SC, Yang HF, Hou XT, Chen WF, et al. 2020; Detection of proximal tubule involvement by BK polyomavirus in kidney transplant recipients with urinary sediment double-immunostaining. Front Immunol. 11:582678. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.582678. PMID: 33072129. PMCID: PMC7539630.74. Kant S, Bromberg J, Haas M, Brennan D. 2020; Donor-derived cell-free DNA and the prediction of BK virus-associated nephropathy. Transplant Direct. 6:e622. DOI: 10.1097/TXD.0000000000001061. PMID: 33134498. PMCID: PMC7587413.
Article75. Tan CS, Gabardi S, Pavlakis M. 2019; Survey of BK virus screening practices by American Society of Transplantation members. Clin Transplant. 33:e13620. DOI: 10.1111/ctr.13620. PMID: 31152561.
Article76. Limaye AP, Brennan DC. 2022. Kidney transplantation in adults: BK polyomavirus-associated nephropathy [Internet]. Uptodate;Available from: https://medilib.ir/uptodate/show/7338. cited 2023 Oct 15.77. Hamed R, Al Maghrabi M, Kasem MF, El Fekky MA, Al Shami AA, Mohamed NH, et al. 2023; Screening for polyomavirus nephropathy and viremia in children with renal transplantation. Pediatr Transplant. 27:e14479. DOI: 10.1111/petr.14479. PMID: 36724736.
Article78. Drachenberg RC, Drachenberg CB, Papadimitriou JC, Ramos E, Fink JC, Wali R, et al. 2001; Morphological spectrum of polyoma virus disease in renal allografts: diagnostic accuracy of urine cytology. Am J Transplant. 1:373–81. DOI: 10.1034/j.1600-6143.2001.10414.x. PMID: 12099383.79. Loupy A, Haas M, Roufosse C, Naesens M, Adam B, Afrouzian M, et al. 2020; The Banff 2019 Kidney Meeting Report (I): updates on and clarification of criteria for T cell-and antibody-mediated rejection. Am J Transplant. 20:2318–31. DOI: 10.1111/ajt.15898. PMID: 32463180. PMCID: PMC7496245.80. Gaber LW, Egidi MF, Stratta RJ, Lo A, Moore LW, Gaber AO. 2006; Clinical utility of histological features of polyomavirus allograft nephropathy. Transplantation. 82:196–204. DOI: 10.1097/01.tp.0000226176.87700.a4. PMID: 16858282.
Article81. Li P, Cheng D, Wen J, Ni X, Li X, Xie K, et al. 2019; The immunophenotyping of different stages of BK virus allograft nephropathy. Ren Fail. 41:855–61. DOI: 10.1080/0886022X.2019.1617168. PMID: 31535918. PMCID: PMC6758702.
Article82. Hariharan S. 2006; BK virus nephritis after renal transplantation. Kidney Int. 69:655–62. DOI: 10.1038/sj.ki.5000040. PMID: 16395271.
Article83. Masutani K, Shapiro R, Basu A, Tan H, Wijkstrom M, Randhawa P. 2012; The Banff 2009 Working Proposal for polyomavirus nephropathy: a critical evaluation of its utility as a determinant of clinical outcome. Am J Transplant. 12:907–18. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-6143.2012.03993.x. PMID: 22390378. PMCID: PMC3319333.84. Sar A, Worawichawong S, Benediktsson H, Zhang J, Yilmaz S, Trpkov K. 2011; Interobserver agreement for polyomavirus nephropathy grading in renal allografts using the working proposal from the 10th Banff Conference on Allograft Pathology. Hum Pathol. 42:2018–24. DOI: 10.1016/j.humpath.2011.03.008. PMID: 21733554.
Article85. Kowalewska J, El Moudden I, Perkowska-Ptasinska A, Kapp ME, Fogo AB, Lin MY, et al. 2021; Assessment of the Banff Working Group classification of definitive BK polyomavirus nephropathy. Transpl Int. 34:2286–96. DOI: 10.1111/tri.14003. PMID: 34339576.
Article86. Sanders ML, Swee M, Fraer M, Kuppachi S, Ten Eyck P, Rastogi P. 2019; BK virus histopathologic disease severity does not predict allograft outcome in renal transplant recipients. Ann Diagn Pathol. 42:1–6. DOI: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2019.06.012. PMID: 31302370.
Article87. Menter T, Mayr M, Schaub S, Mihatsch MJ, Hirsch HH, Hopfer H. 2013; Pathology of resolving polyomavirus-associated nephropathy. Am J Transplant. 13:1474–83. DOI: 10.1111/ajt.12218. PMID: 23721552.
Article88. Nickeleit V, Hirsch HH, Zeiler M, Gudat F, Prince O, Thiel G, et al. 2000; BK-virus nephropathy in renal transplants-tubular necrosis, MHC-class II expression and rejection in a puzzling game. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 15:324–32. DOI: 10.1093/ndt/15.3.324. PMID: 10692517.89. Masutani K, Tsuchimoto A, Matsukuma Y, Kurihara K, Nishiki T, Kitada H, et al. 2015; Temporal serum creatinine increase and exacerbation of tubulointerstitial inflammation during the first two months in resolving polyomavirus BK nephropathy. Nephrology (Carlton). 20 Suppl 2:45–50. DOI: 10.1111/nep.12462. PMID: 26031586.90. Subramanian KS, Srinivas BH, Nachiappa Ganesh R, Gochhait D, Ps P, Parameswaran S, et al. 2022; Revisit of polyomavirus nephropathy grading in renal allograft recipients according to the Banff 2019 Working Group classification: a study from a large transplant center in South India. Cureus. 14:e22377. DOI: 10.7759/cureus.22377. PMID: 35321062. PMCID: PMC8935362.
Article91. Bouatou Y, Nguyen TQ, Roelofs JJ, Bemelman FJ, Michielsen L, Goldschmeding R, et al. 2019; A multicenter application of the 2018 Banff Classification for BK polyomavirus-associated nephropathy in renal transplantation. Transplantation. 103:2692–700. DOI: 10.1097/TP.0000000000002712. PMID: 30896679.
Article92. Chen XT, Yang SC, Chen WF, Li J, Deng SX, Qiu J, et al. 2019; Glomerular parietal epithelial cells infection is associated with poor graft outcome in kidney transplant recipients with BK polyomavirus-associated nephropathy. J Infect Dis. 219:1879–86. DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiz022. PMID: 30649366.
Article93. Sood P, Senanayake S, Sujeet K, Medipalli R, Zhu YR, Johnson CP, et al. 2012; Management and outcome of BK viremia in renal transplant recipients: a prospective single-center study. Transplantation. 94:814–21. DOI: 10.1097/TP.0b013e31826690c6. PMID: 23018881.94. Alméras C, Vetromile F, Garrigue V, Szwarc I, Foulongne V, Mourad G. 2011; Monthly screening for BK viremia is an effective strategy to prevent BK virus nephropathy in renal transplant recipients. Transpl Infect Dis. 13:101–8. DOI: 10.1111/j.1399-3062.2011.00619.x. PMID: 21371220.
Article95. Cheungpasitporn W, Kremers WK, Lorenz E, Amer H, Cosio FG, Stegall MD, et al. 2018; De novo donor-specific antibody following BK nephropathy: the incidence and association with antibody-mediated rejection. Clin Transplant. 32:e13194. DOI: 10.1111/ctr.13194. PMID: 29315820.
Article96. Dieplinger G, Everly MJ, Briley KP, Haisch CE, Bolin P, Maldonado AQ, et al. 2015; Onset and progression of de novo donor-specific anti-human leukocyte antigen antibodies after BK polyomavirus and preemptive immunosuppression reduction. Transpl Infect Dis. 17:848–58. DOI: 10.1111/tid.12467. PMID: 26442607.97. Hod-Dvorai R, Lee R, Muluhngwi P, Raijmakers M, Shetty A, Tambur AR, et al. 2023; Development of de novo donor-specific antibodies in renal transplant recipients with BK viremia managed with immunosuppression reduction. Transpl Infect Dis. 25:e13993. DOI: 10.1111/tid.13993. PMID: 36413505.
Article98. Shanmugham S, Bhadauria D, Agrawal V, Jain M, Yaccha M, Kaul A, et al. 2022; The diagnostic and therapeutic dilemma of the co-existence of BK virus nephropathy with acute rejection - an experience from a single centre and review of the literature. Transpl Immunol. 72:101581. DOI: 10.1016/j.trim.2022.101581. PMID: 35301106.99. Kim YJ, Jeong JC, Koo TY, Kwon HY, Han M, Jeon HJ, et al. 2013; Impact of combined acute rejection on BK virus-associated nephropathy in kidney transplantation. J Korean Med Sci. 28:1711–5. DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2013.28.12.1711. PMID: 24339698. PMCID: PMC3857364.
Article100. McGregor SM, Chon WJ, Kim L, Chang A, Meehan SM. 2015; Clinical and pathological features of kidney transplant patients with concurrent polyomavirus nephropathy and rejection-associated endarteritis. World J Transplant. 5:292–9. DOI: 10.5500/wjt.v5.i4.292. PMID: 26722657. PMCID: PMC4689940.
Article101. Li X, Sun Q, Chen J, Ji S, Wen J, Cheng D, et al. 2013; Immunophenotyping in BK virus allograft nephropathy distinct from acute rejection. Clin Dev Immunol. 2013:412902. DOI: 10.1155/2013/412902. PMID: 24194773. PMCID: PMC3806154.
Article102. Chen XT, Qiu J, Wu ZX, Zhang H, Chen T, Yang SC, et al. 2022; Using both plasma and urine donor-derived cell-free DNA to identify various renal allograft injuries. Clin Chem. 68:814–25. DOI: 10.1093/clinchem/hvac053. PMID: 35587713.
Article103. Wen J, Sun R, Yang H, Ran Q, Hou Y. 2022; Detection of BK polyomavirus-associated nephropathy using plasma graft-derived cell-free DNA: development of a novel algorithm from programmed monitoring. Front Immunol. 13:1006970. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1006970. PMID: 36275762. PMCID: PMC9582120.104. Adam BA, Kikic Z, Wagner S, Bouatou Y, Gueguen J, Drieux F, et al. 2020; Intragraft gene expression in native kidney BK virus nephropathy versus T cell-mediated rejection: prospects for molecular diagnosis and risk prediction. Am J Transplant. 20:3486–501. DOI: 10.1111/ajt.15980. PMID: 32372431.
Article105. Halloran PF, Madill-Thomsen KS, Böhmig GA, Myslak M, Gupta G, Kumar D, et al. 2021; A 2-fold approach to polyoma virus (BK) nephropathy in kidney transplants: distinguishing direct virus effects from cognate T cell-mediated inflammation. Transplantation. 105:2374–84. DOI: 10.1097/TP.0000000000003884. PMID: 34310102.
Article106. Salinas T, Li C, Snopkowski C, Stryjniak G, Shankaranarayanan D, Albakry S, et al. 2023; Urinary cell mRNA profiling of kidney allograft recipients: development of a portable protocol for noninvasive diagnosis of T cell mediated rejection and BK virus nephropathy. J Immunol Methods. 512:113402. DOI: 10.1016/j.jim.2022.113402. PMID: 36493873.
Article107. Kim MS, Lim JH, Han MH, Kim SY, Kim YJ, Kim YJ. 2022; Multiplex immunofluorescence assay of infiltrating mononu-clear cell subsets in acute T-cell-mediated rejection and BK virus-associated nephropathy in the allograft kidney. Diagnostics (Basel). 12:268. DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12020268. PMID: 35204360. PMCID: PMC8870790.
Article108. Rogers NM, Russ GR, Cooper J, Coates PT. 2009; Immunophenotyping of interstitial infiltrate does not distinguish between BK virus nephropathy and acute cellular rejection. Nephrology (Carlton). 14:118–22. DOI: 10.1111/j.1440-1797.2008.01050.x. PMID: 19143944.109. van Doesum WB, Abdulahad WH, van Dijk MC, Dolff S, van Son WJ, Stegeman CA, et al. 2014; Characterization of urinary CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in kidney transplantation patients with polyomavirus BK infection and allograft rejection. Transpl Infect Dis. 16:733–43. DOI: 10.1111/tid.12273. PMID: 25092256.110. Batal I, Zainah H, Stockhausen S, Basu A, Tan H, Shapiro R, et al. 2009; The significance of renal C4d staining in patients with BK viruria, viremia, and nephropathy. Mod Pathol. 22:1468–76. DOI: 10.1038/modpathol.2009.118. PMID: 19734851.
Article111. Mohamed M, Parajuli S, Muth B, Astor BC, Panzer SE, Mandelbrot D, et al. 2016; In kidney transplant recipients with BK polyomavirus infection, early BK nephropathy, microvascular inflammation, and serum creatinine are risk factors for graft loss. Transpl Infect Dis. 18:361–71. DOI: 10.1111/tid.12530. PMID: 26998753.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Polyomavirus Disease in Kidney Transplantation
- Urinary Decoy Cell Grading and Its Clinical Implications
- The Expression of C4d and HLA-DR in Renal Allografts with the Histologic Features of Antibody-Mediated Rejection
- Polyomavirus Induced Interstital Nephritis in Renal Allograft Recipient
- A Case of Concomitant Interstitial Nephritis by BK Virus with Acute Rejection in a Renal Allograft Recipient