J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2024 Jul;67(4):431-441. 10.3340/jkns.2023.0177.
Feasibility of Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Brain Arteriovenous Malformations According to Nidus Type
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea
- KMID: 2556740
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2023.0177
Abstract
Objective
: Gamma Knife radiosurgery (GKRS) is an effective and noninvasive treatment for high-risk arteriovenous malformations (AVMs). Since differences in GKRS outcomes by nidus type are unknown, this study evaluated GKRS feasibility and safety in patients with brain AVMs.
Methods
: This single-center retrospective study included patients with AVM who underwent GKRS between 2008 and 2021. Patients were divided into compact- and diffuse-type groups according to nidus characteristics. We excluded patients who performed GKRS and did not follow-up evaluation with magnetic resonance imaging or digital subtraction angiography within 36 months from the study. We used univariate and multivariate analyses to characterize associations of nidus type with obliteration rate and GKRS-related complications.
Results
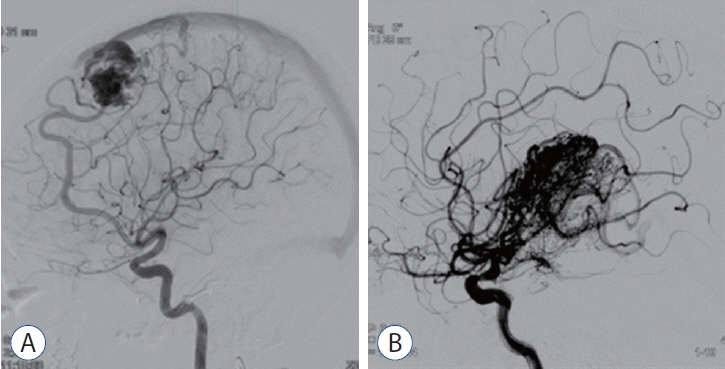
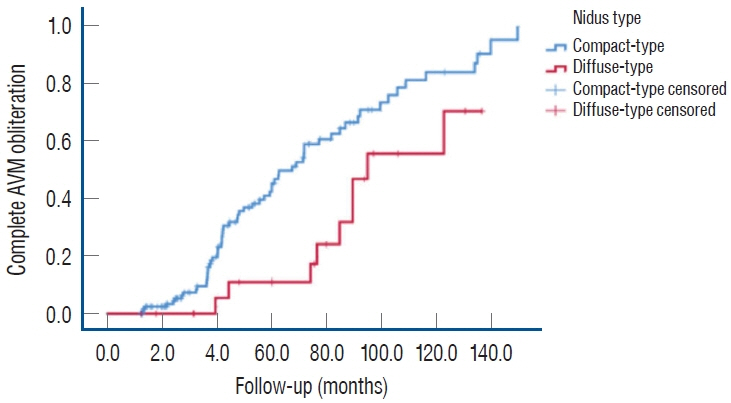
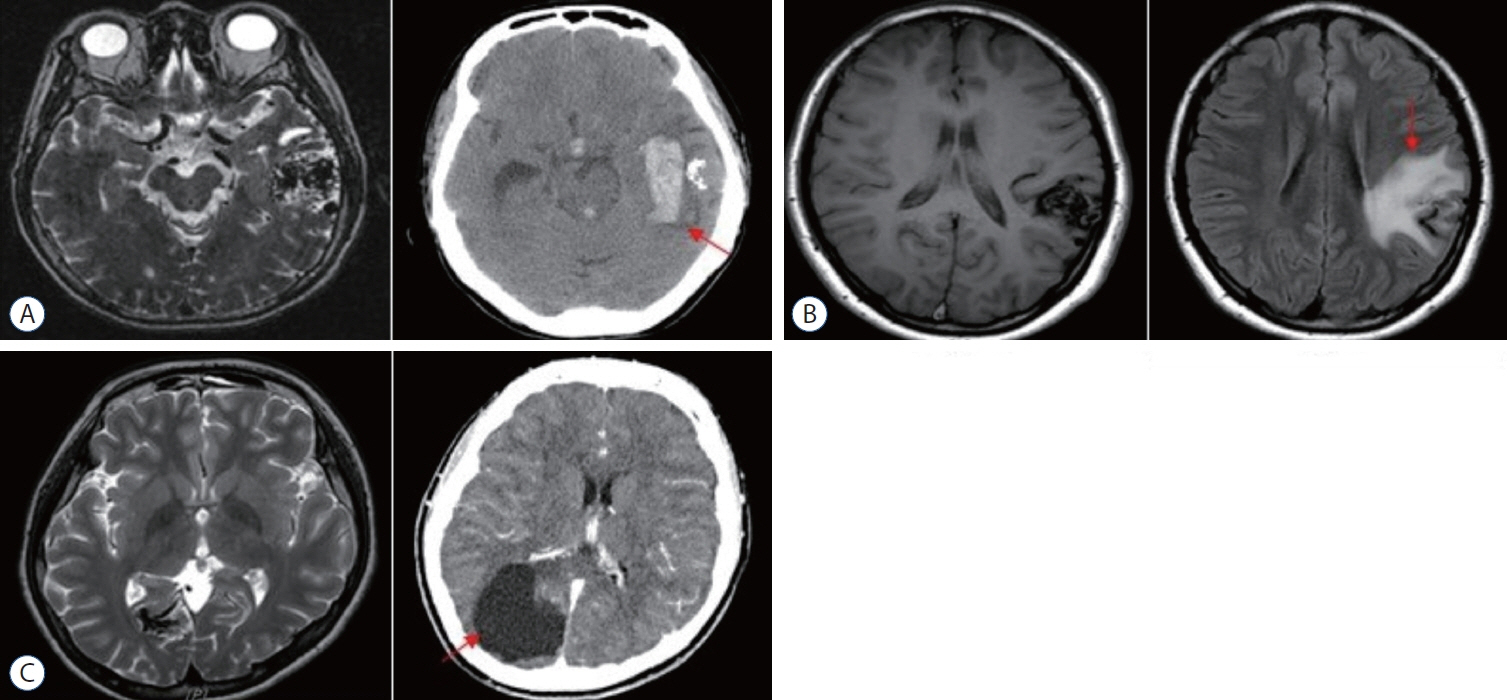
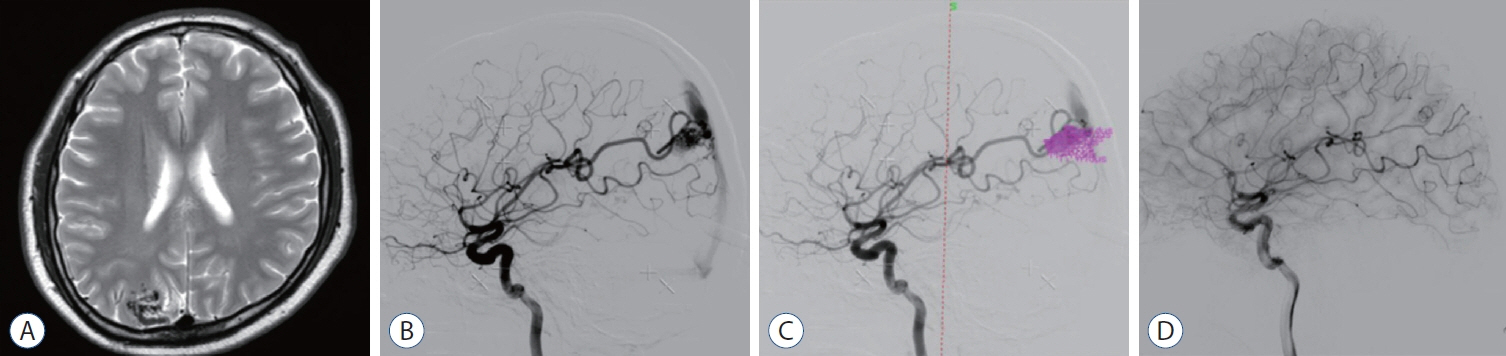
: We enrolled 154 patients (mean age, 32.14±17.17 years; mean post-GKRS follow-up, 52.10±33.67 months) of whom 131 (85.1%) had compact- and 23 (14.9%) diffuse-type nidus AVMs. Of all AVMs, 89 (57.8%) were unruptured, and 65 (42.2%) had ruptured. The mean Spetzler-Martin AVM grades were 2.03±0.95 and 3.39±1.23 for the compact- and diffuse-type groups, respectively (p<0.001). During the follow-up period, AVM-related hemorrhages occurred in four individuals (2.6%), three of whom had compact nidi. Substantial radiation-induced changes and cyst formation were observed in 21 (13.6%) and one patient (0.6%), respectively. The AVM complete obliteration rate was 46.1% across both groups. Post-GKRS complication and complete obliteration rates were not significantly different between nidus types. For diffuse-type nidus AVMs, larger AVM size and volume (p<0.001), lower radiation dose (p<0.001), eloquent area location (p=0.015), and higher Spetzler-Martin grade (p<0.001) were observed.
Conclusion
: GKRS is a safe and feasible treatment for brain AVMs characterized by both diffuse- and compact-type nidi.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Chang JH, Chang JW, Park YG, Chung SS. Factors related to complete occlusion of arteriovenous malformations after gamma knife radiosurgery. J Neurosurg 93 Suppl. 3:96–101. 2000.
Article2. China M, Vastani A, Hill CS, Tancu C, Grover PJ. Gamma knife radiosurgery for cerebral arteriovenous malformations: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosurg Rev. 45:1987–2004. 2022.
Article3. Cohen-Inbar O, Ding D, Chen CJ, Sheehan JP. Stereotactic radiosurgery for deep intracranial arteriovenous malformations, part 1: brainstem arteriovenous malformations. J Clin Neurosci. 24:30–36. 2016.
Article4. Ding D, Xu Z, Shih HH, Starke RM, Yen CP, Sheehan JP. Stereotactic radiosurgery for partially resected cerebral arteriovenous malformations. World Neurosurg. 85:263–272. 2016.
Article5. Ding D, Yen CP, Xu Z, Starke RM, Sheehan JP. Radiosurgery for primary motor and sensory cortex arteriovenous malformations: outcomes and the effect of eloquent location. Neurosurgery. 73:816–824. discussion 824. 2013.
Article6. Du R, Keyoung HM, Dowd CF, Young WL, Lawton MT. The effects of diffuseness and deep perforating artery supply on outcomes after microsurgical resection of brain arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurgery. 60:638–646. discussion 646-648. 2007.
Article7. Flickinger JC, Kondziolka D, Pollock BE, Maitz AH, Lunsford LD. Complications from arteriovenous malformation radiosurgery: multivariate analysis and risk modeling. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 38:485–490. 1997.
Article8. Ganz JC, Reda WA, Abdelkarim K. Adverse radiation effects after gamma knife surgery in relation to dose and volume. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 151:9–19. 2009.
Article9. Graffeo CS, Sahgal A, De Salles A, Fariselli L, Levivier M, Ma L, et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery for Spetzler-Martin grade I and II arteriovenous malformations: International Society of Stereotactic Radiosurgery (ISRS) practice guideline. Neurosurgery. 87:442–452. 2020.
Article10. Gross BA, Du R. Natural history of cerebral arteriovenous malformations: a meta-analysis. J Neurosurg. 118:437–443. 2013.
Article11. Ivanov AA, Alaraj A, Charbel FT, Aletich V, Amin-Hanjani S. Recurrence of cerebral arteriovenous malformations following resection in adults: does preoperative embolization increase the risk? Neurosurgery. 78:562–571. 2016.
Article12. Kano H, Flickinger JC, Tonetti D, Hsu A, Yang HC, Flannery TJ, et al. Estimating the risks of adverse radiation effects after gamma knife radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations. Stroke. 48.1:84–90. 2017.
Article13. Kano H, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC, Park KJ, Parry PV, Yang H, et al. : Multistaged volumetric management of large arteriovenous malformations in Niranjan A, Kano H, Lunsford LD (eds) : Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Brain Vascular Malformations. Basel : Karger Publishers, 2013, Vol 27, pp73-80.14. Klimo P Jr, Rao G, Brockmeyer D. Pediatric arteriovenous malformations: a 15-year experience with an emphasis on residual and recurrent lesions. Childs Nerv Syst. 23:31–37. 2007.
Article15. Liscák R, Vladyka V, Simonová G, Urgosík D, Novotný J Jr, Janousková L, et al. arteriovenous malformations after leksell gamma knife radiosurgery: rate of obliteration and complications. Neurosurgery. 60:1005–1014. discussion 1015-1016. 2007.16. Morgan MK, Sekhon LH, Finfer S, Grinnell V. Delayed neurological deterioration following resection of arteriovenous malformations of the brain. J Neurosurg. 90:695–701. 1999.
Article17. Pan JW, Zhou HJ, Zhan RY, Wan S, Yan M, Fan WJ, et al. Supratentorial brain AVM embolization with onyx-18 and post-embolization management. a single-center experience. Interv Neuroradiol. 15:275–282. 2009.
Article18. Park CK, Choi SK, Lee SH, Choi MK, Lim YJ. Clinical outcomes and radiosurgical considerations for pediatric arteriovenous malformation: influence of clinical features on obliteration rate. Childs Nerv Syst. 33:2137–2145. 2017.
Article19. Pollock BE, Link MJ, Stafford SL, Garces YI, Foote RL. Stereotactic radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations: the effect of treatment period on patient outcomes. Neurosurgery. 78:499–509. 2016.20. Shin M, Maruyama K, Kurita H, Kawamoto S, Tago M, Terahara A, et al. Analysis of nidus obliteration rates after gamma knife surgery for arteriovenous malformations based on long-term follow-up data: the University of Tokyo experience. J Neurosurg. 101:18–24. 2004.
Article21. Spetzler RF, Ponce FA. A 3-tier classification of cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Clinical article. J Neurosurg. 114:842–849. 2011.22. van Beijnum J, van der Worp HB, Buis DR, Al-Shahi Salman R, Kappelle LJ, Rinkel GJ, et al. Treatment of brain arteriovenous malformations: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 306:2011–2019. 2011.23. Yang HC, Peng SJ, Lee CC, Wu HM, Chen YW, Lin CJ, et al. Does the diffuseness of the nidus affect the outcome of stereotactic radiosurgery in patients with unruptured cerebral arteriovenous malformations? Stereotact Funct Neurosurg. 99:113–122. 2021.
Article24. Zipfel GJ, Bradshaw P, Bova FJ, Friedman WA. Do the morphological characteristics of arteriovenous malformations affect the results of radiosurgery? J Neurosurg. 101:393–401. 2004.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Recurrence of pediatric cerebral arteriovenous malformation after obliteration by radiosurgery: a case report
- How to use Leksell GammaPlan
- Changes of MR Images in Arteriovenous Malformations of Brain after Gamma-knife Radiosurgery
- A Case of Recurrent Expansile Cyst Formation after Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for a Cerebral Arteriovenous Malformation: Role of the Residual Nidus: Case Report
- Brain Edema after Repeat Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for a Large Arteriovenous Malformation: A Case Report