Korean J Sports Med.
2024 Jun;42(2):99-104. 10.5763/kjsm.2024.42.2.99.
Infectious Skin Diseases of Korean National Wrestlers: A Cross-sectional Observational Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Family Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Family Medicine, SMG-SNU Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- 3Team Doctor Rehabilitation Clinic, Seoul, Korea
- 4H+ Yangji Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 5Department of Physical Education, Dongguk University, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2556274
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5763/kjsm.2024.42.2.99
Abstract
- Purpose
Wrestlers have a lot of direct skin-to-skin contact between wrestlers during matches, and many studies show that wrestlers are vulnerable to the spread of skin infections. However, there have been few studies on skin infections in Korean wrestlers. The purpose of this study was to compare the characteristics of skin diseases in wrestlers and other athletes.
Methods
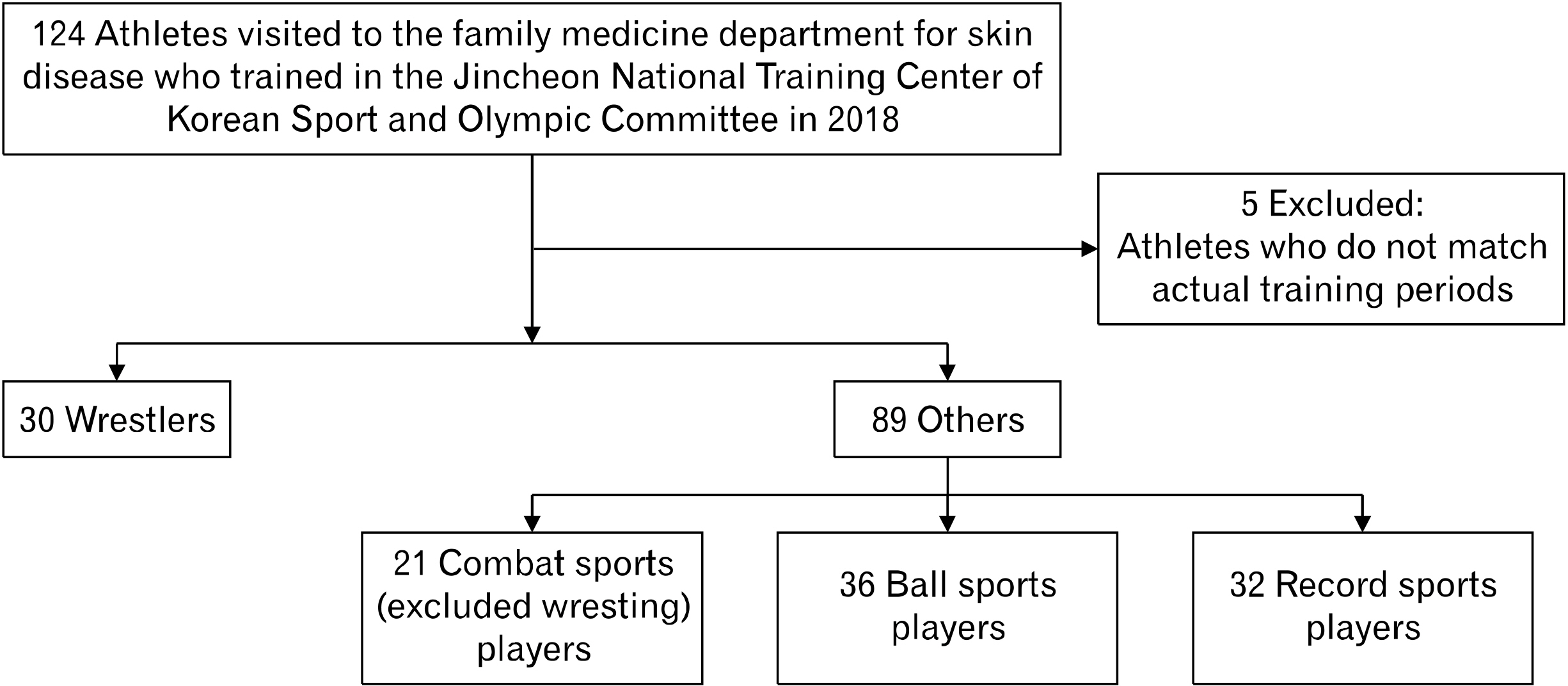
Athletes who visited for skin diseases in the Department of Family Medicine in the Jincheon National Training Center in 2018 were investigated. We calculated the duration of skin disease per training period (DSD/TP) as the number of visits×7 days×1,000/official training days. Athletes with a DSD/TP above the median value or equal to were defined as the high DSD/TP group, and the others were defined as the low DSD/TP group. A chi-square test was used to compare the odds ratio [OR] for these groups about infectious and noninfectious skin diseases.
Results
Thirty wrestlers and 89 other sports players visited the infirmary with skin diseases. The probability of belonging to the high DSD/TP group was significantly higher when the wrestlers visited for skin infections than the other athletes (OR, 7.714; 95% confidence interval [CI], 2.699–22.048). However, there was no significant difference in noninfectious skin diseases between wrestling and other sports (OR, 0.569; 95% CI, 0.246–1.320).
Conclusion
This is the first study that shows Korean national wrestlers with skin diseases receive more treatment for infectious skin diseases than other sports. This study can provide important information on the prevention of wrestlers for skin infections.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Adams BB. 2002; Dermatologic disorders of the athlete. Sports Med. 32:309–21. DOI: 10.2165/00007256-200232050-00003. PMID: 11929358.
Article2. Agel J, Ransone J, Dick R, Oppliger R, Marshall SW. 2007; Descriptive epidemiology of collegiate men's wrestling injuries: National Collegiate Athletic Association Injury Surveillance System, 1988-1989 through 2003-2004. J Athl Train. 42:303–10.3. Hradil E, Hersle K, Nord4in P, Faergemann J. 1995; An epidemic of tinea corporis caused by Trichophyton tonsurans among wrestlers in Sweden. Acta Derm Venereol. 75:305–6. DOI: 10.2340/0001555575305306. PMID: 8578955.
Article4. Adams BB. 2000; Tinea corporis gladiatorum: a cross-sectional study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 43:1039–41. DOI: 10.1067/mjd.2000.109284. PMID: 11100020.
Article5. Peterson AR, Nash E, Anderson BJ. 2019; Infectious disease in contact sports. Sports Health. 11:47–58. DOI: 10.1177/1941738118789954. PMID: 30106670. PMCID: PMC6299350.
Article6. Jun JB, Kim YD. 2004; The epidemiological, clinical and mycological studies on trichophytosis gladiatorum prevailing among Korean wrestlers. Korean J Med Mycol. 9:28–44.7. Kaynar O. 2021; Infectious dermatological diseases findings of the wrestlers according to regions. Ann Med Res. 25:65–9.
Article8. Champion AE, Goodwin TA, Brolinson PG, Werre SR, Prater MR, Inzana TJ. 2014; Prevalence and characterization of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates from healthy university student athletes. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 13:33. DOI: 10.1186/s12941-014-0033-5. PMID: 25085442. PMCID: PMC4362218.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Severe Knee, Ankle, and Shoulder Injuries among Korean Men and Women Freestyle Wrestlers: A Survey-based Cross-Sectional Study
- Prevalence, Characteristics of Ear Deformity and Treatment Tendency for Auricular Hematoma in Elite Wrestlers
- Febrile Illness with Skin Rashes
- Severe Injuries in Elite Korean Male Wrestlers: A Comparison Study between Wrestling Styles
- The Impact of Inflammatory and Infectious Diseases of Vulvar on Quality of Life