Clin Transplant Res.
2024 Mar;38(1):7-12. 10.4285/kjt.23.0059.
Surgical techniques for robotic right donor hepatectomy, part 1: robotic hilar dissection and right lobe mobilization
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Transplantation, Department of Surgery, Houston Methodist Hospital, Houston, TX, USA
- KMID: 2555991
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4285/kjt.23.0059
Abstract
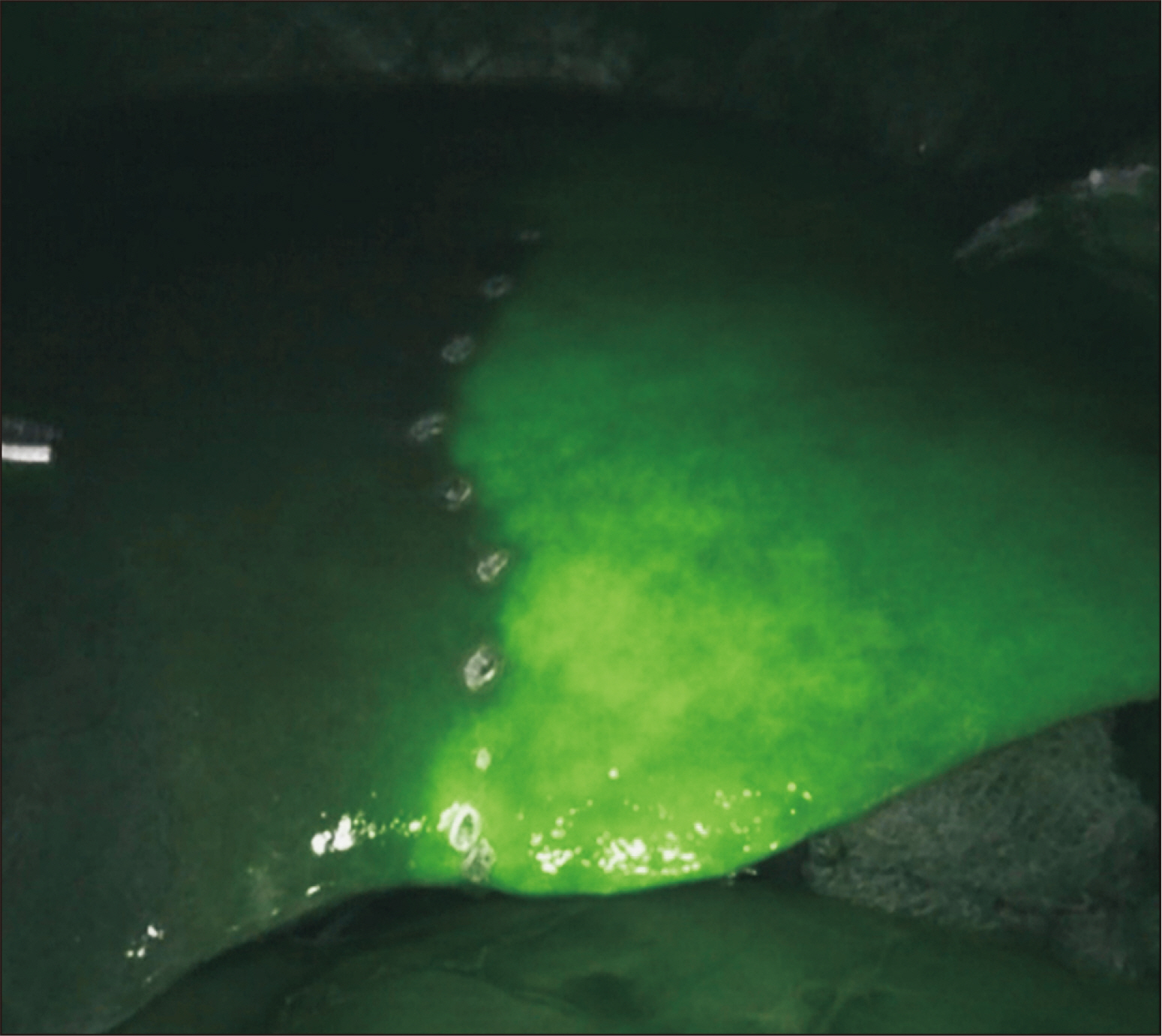
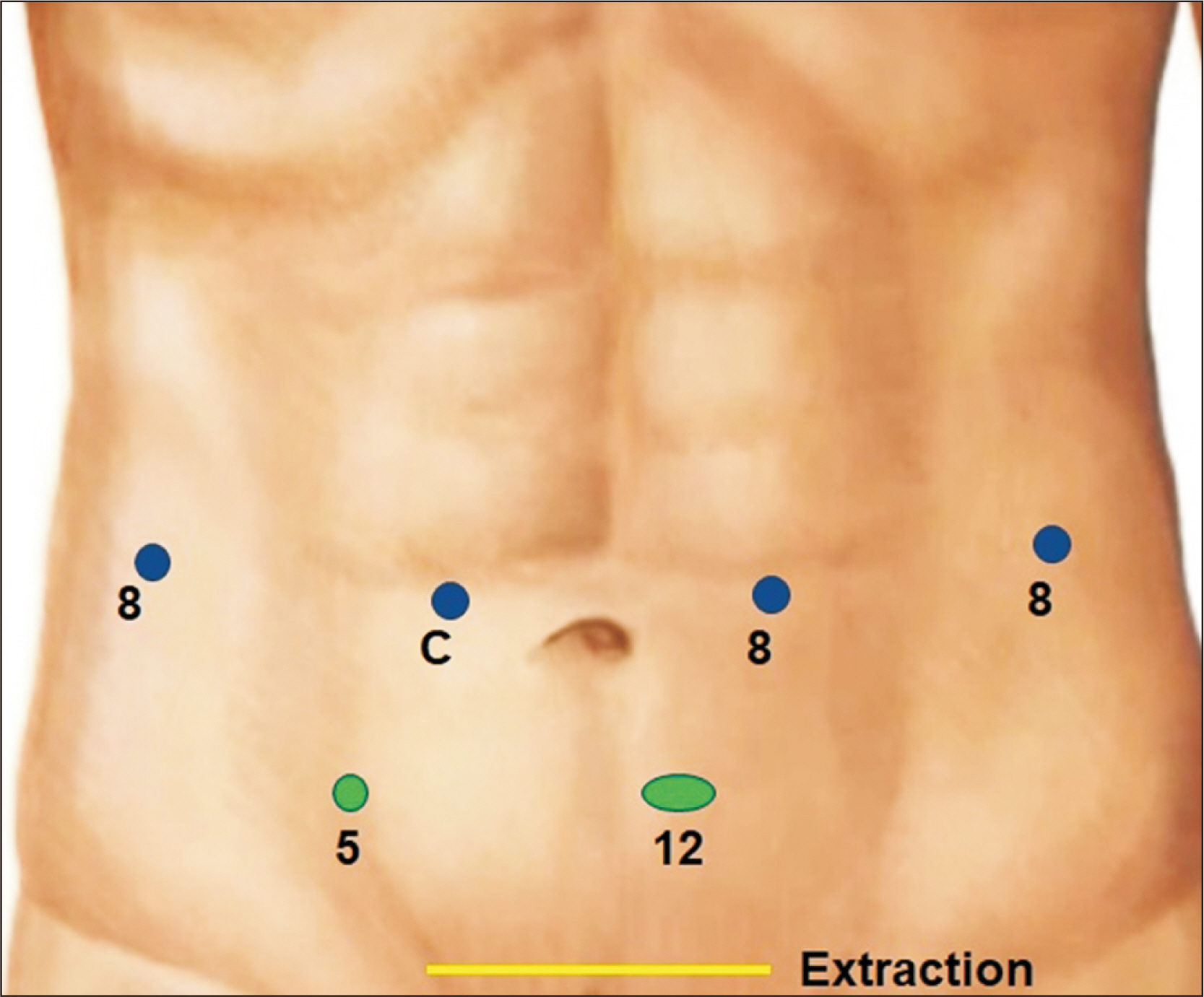
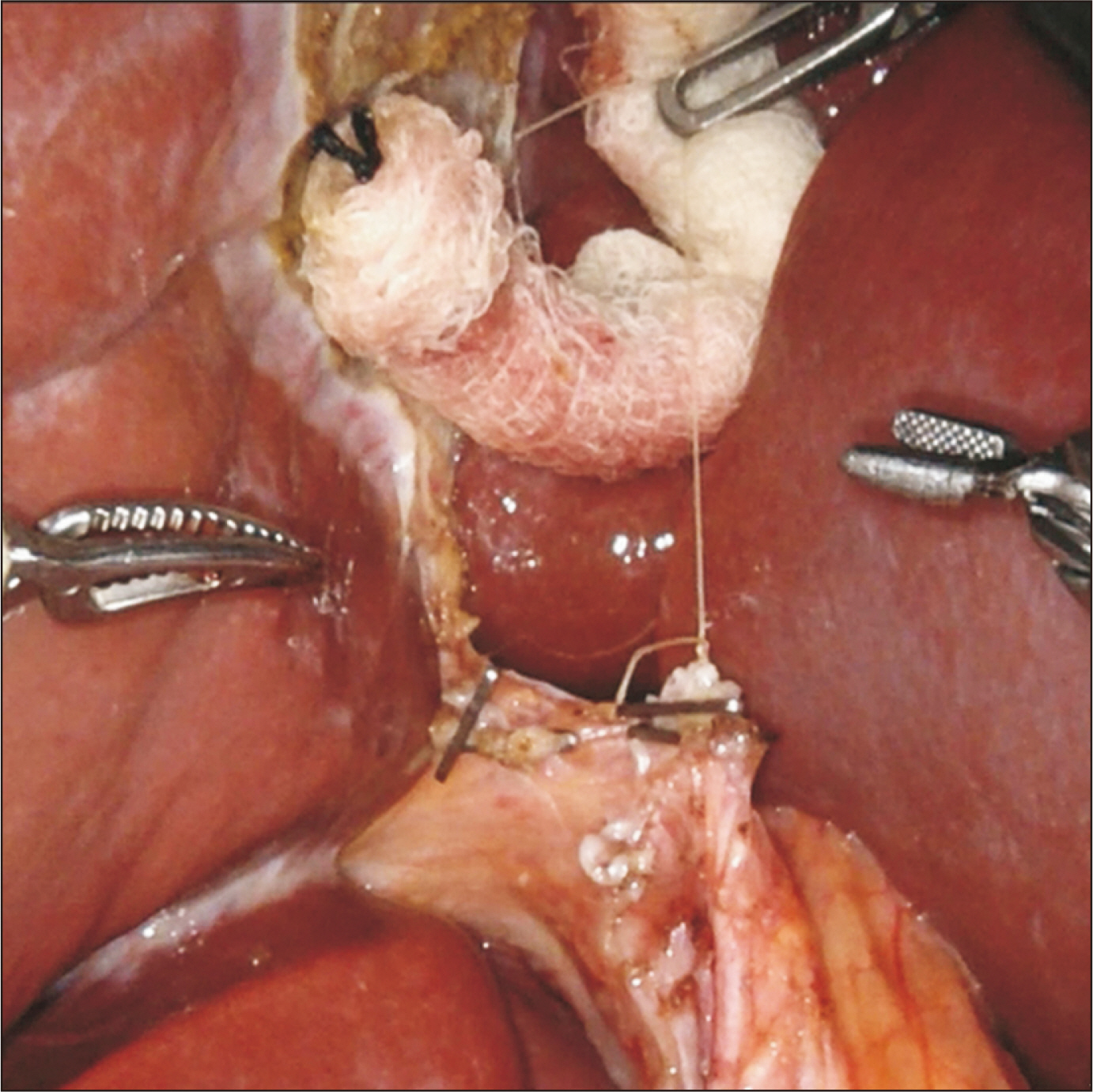
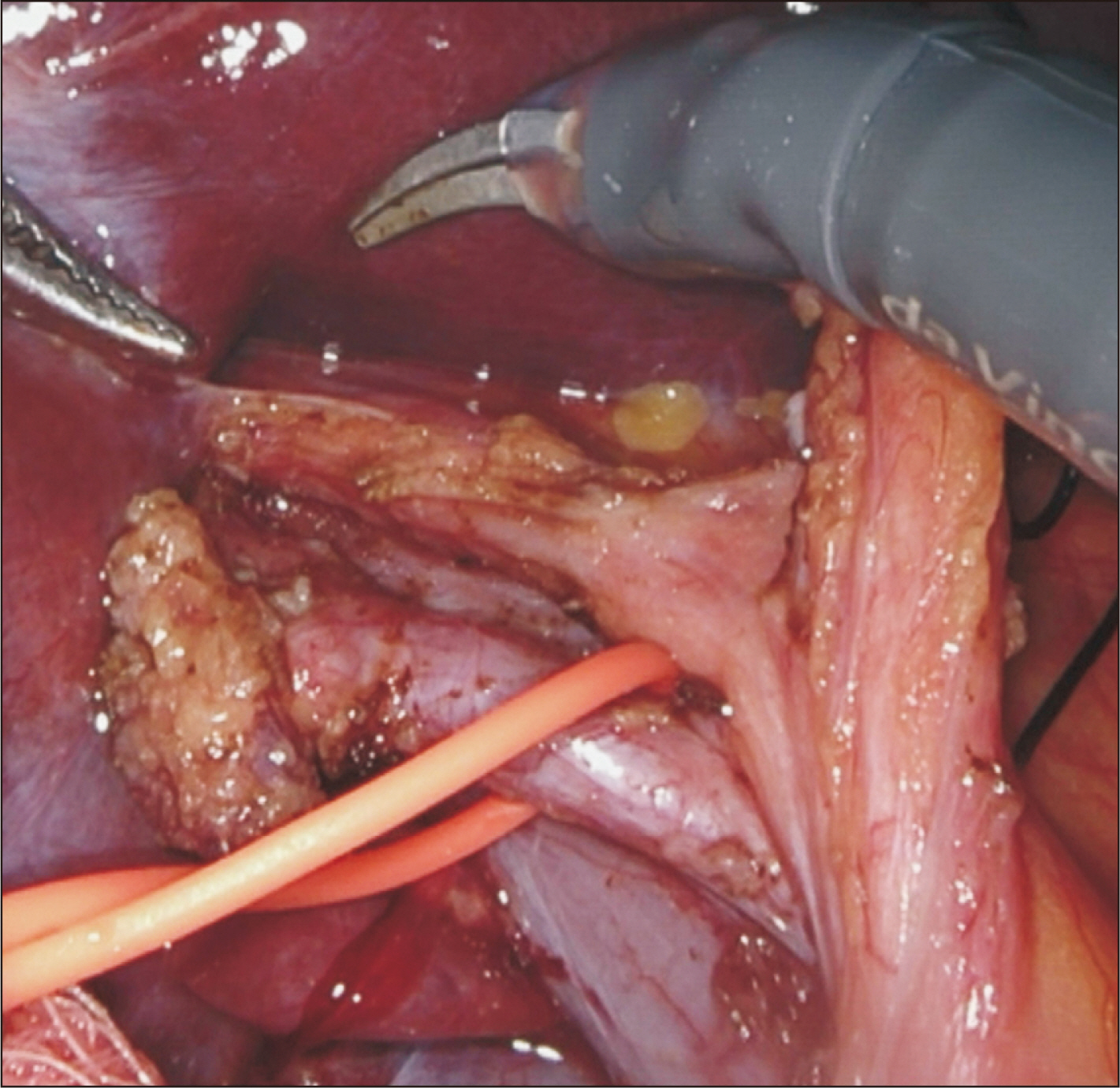
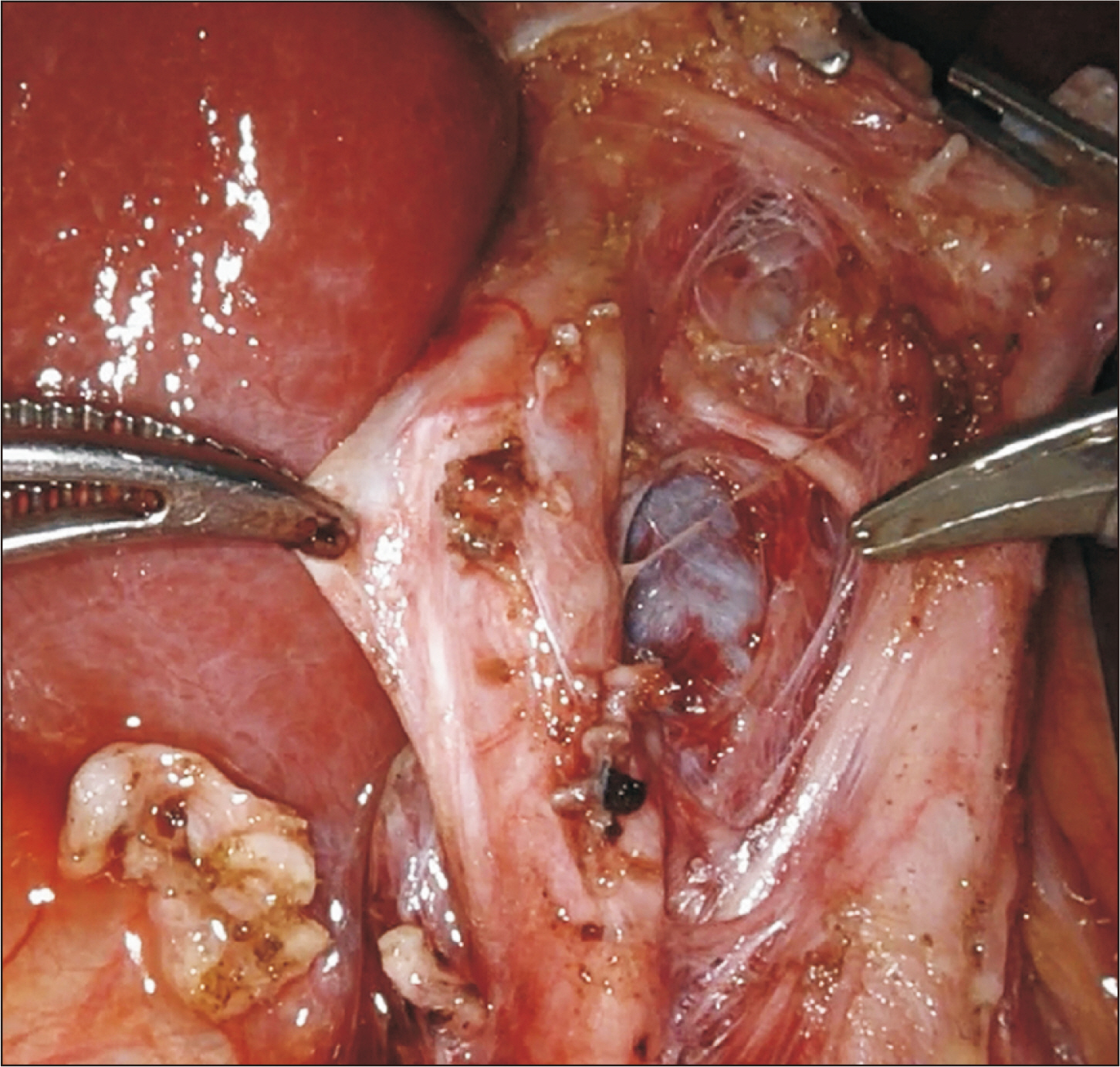
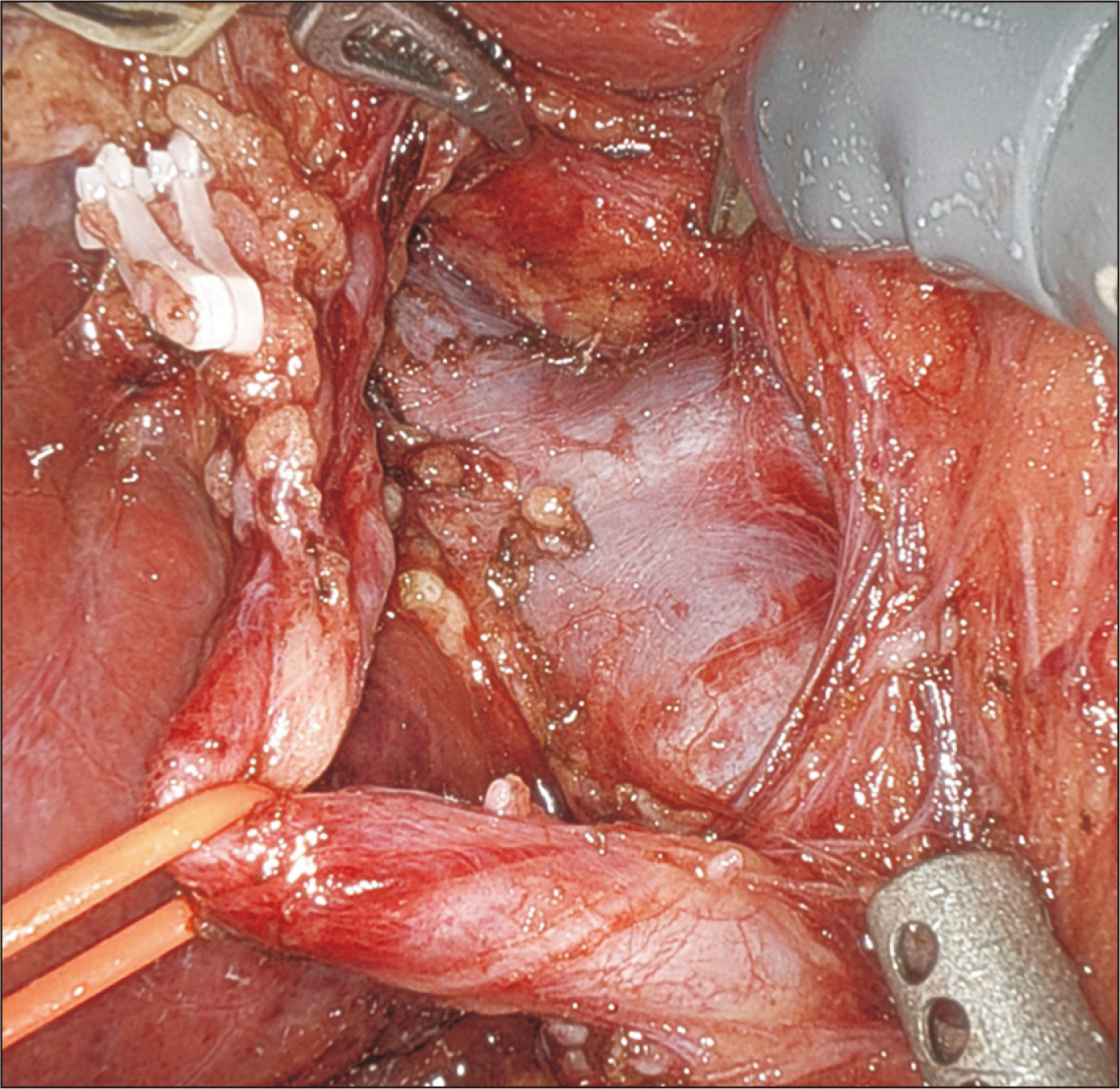
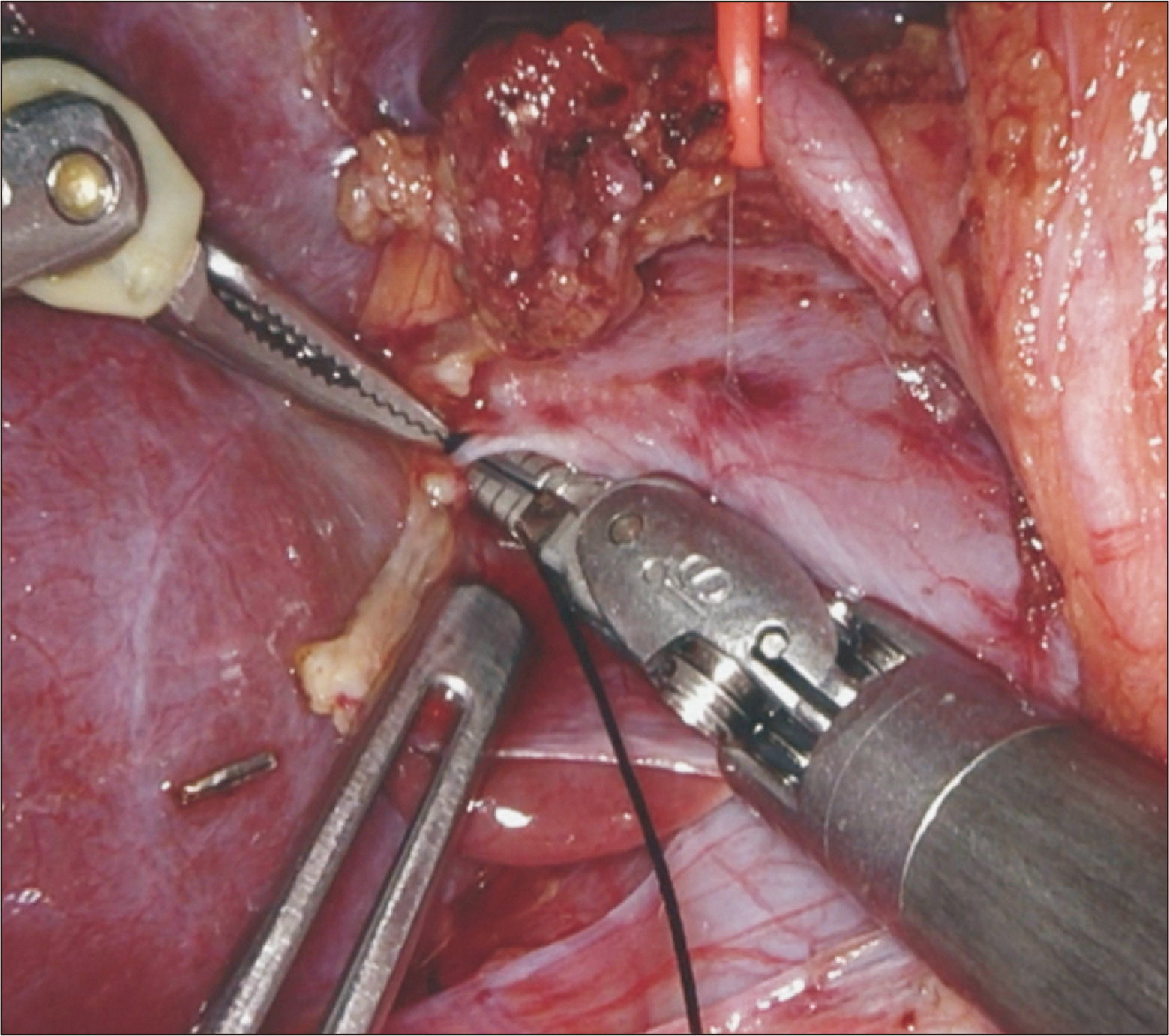
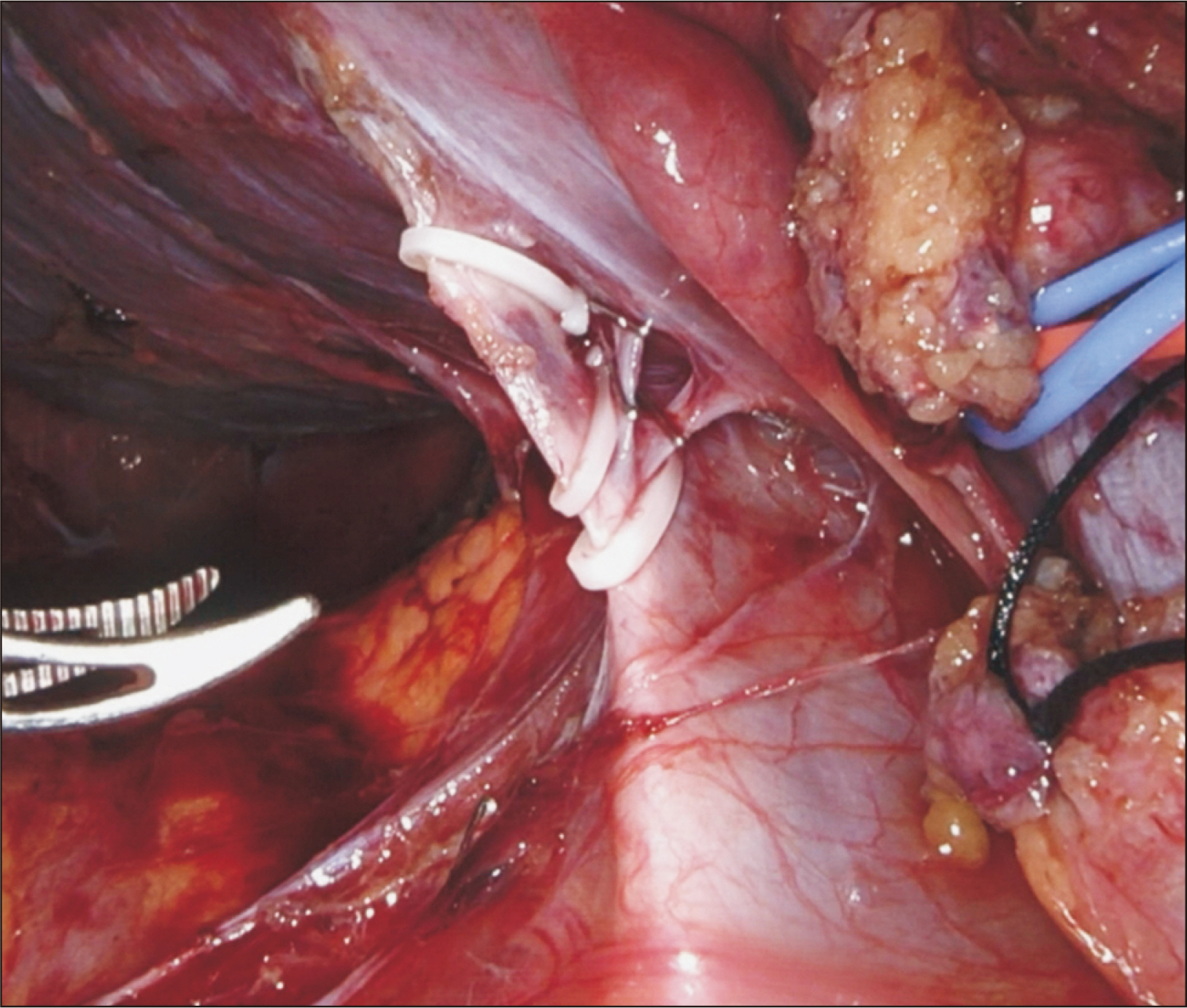
- Robotic surgery is emerging as a feasible minimally invasive approach for donor hepatectomy at specialized centers. The aim of this article is to systematically describe the surgical techniques for robotic hilar dissection and right lobe mobilization in right donor hepatectomy. The setup of the robotic arms, the dissection of inflow vessels and retrohepatic inferior vena cava, and the pearls and pitfalls of these two parts of the operation are detailed.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Rho SY, Lee JG, Joo DJ, Kim MS, Kim SI, Han DH, et al. 2022; Outcomes of robotic living donor right hepatectomy from 52 consecutive cases: comparison with open and laparoscopy-assisted donor hepatectomy. Ann Surg. 275:e433–42. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000004067. PMID: 32773621.
Article2. Broering D, Sturdevant ML, Zidan A. 2022; Robotic donor hepatectomy: a major breakthrough in living donor liver transplantation. Am J Transplant. 22:14–23. DOI: 10.1111/ajt.16889. PMID: 34783439.
Article3. Chandran B, Varghese CT, Balakrishnan D, Nair K, Mallick S, Mathew JS, et al. 2022; Technique of robotic right donor hepatectomy. J Minim Access Surg. 18:157–60. DOI: 10.4103/jmas.JMAS_35_21. PMID: 35017406. PMCID: PMC8830578.
Article4. Chen PD, Wu CY, Hu RH, Chen CN, Yuan RH, Liang JT, et al. 2017; Robotic major hepatectomy: is there a learning curve? Surgery. 161:642–9. DOI: 10.1016/j.surg.2016.09.025. PMID: 27884614.5. Choi GH, Chong JU, Han DH, Choi JS, Lee WJ. 2017; Robotic hepatectomy: the Korean experience and perspective. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 6:230–8. DOI: 10.21037/hbsn.2017.01.14. PMID: 28848745. PMCID: PMC5554764.
Article6. Choi TW, Chung JW, Kim HC, Lee M, Choi JW, Jae HJ, et al. 2021; Anatomic variations of the hepatic artery in 5625 patients. Radiol Cardiothorac Imaging. 3:e210007. DOI: 10.1148/ryct.2021210007. PMID: 34498005. PMCID: PMC8415139.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Surgical techniques for robotic right donor hepatectomy, part 2: robotic parenchymal transection and bile duct division
- Current status of robotic surgery for liver transplantation
- Totally Robotic Esophagectomy
- The method of using robotic Harmonic ACE curved shears for parenchymal transection in robotic hepatectomy
- Robotic-assisted right hepatectomy via anterior approach for intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma