Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg.
2024 May;28(2):262-265. 10.14701/ahbps.23-109.
The duodenal window approach to pancreatoduodenectomy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Digestive and Emergency Surgery Unit, S. Maria Hospital Trust, Terni, Italy
- KMID: 2555936
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14701/ahbps.23-109
Abstract
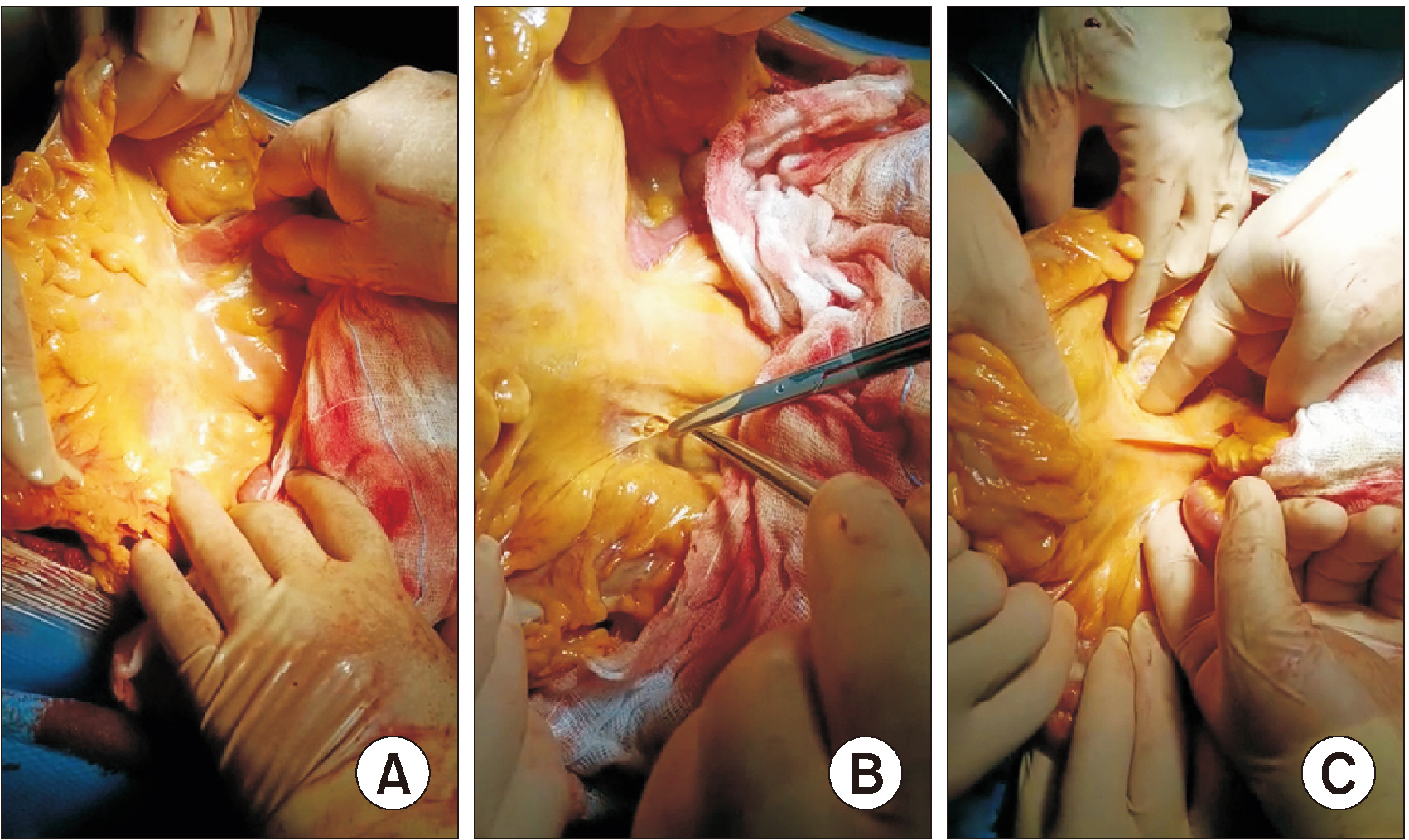
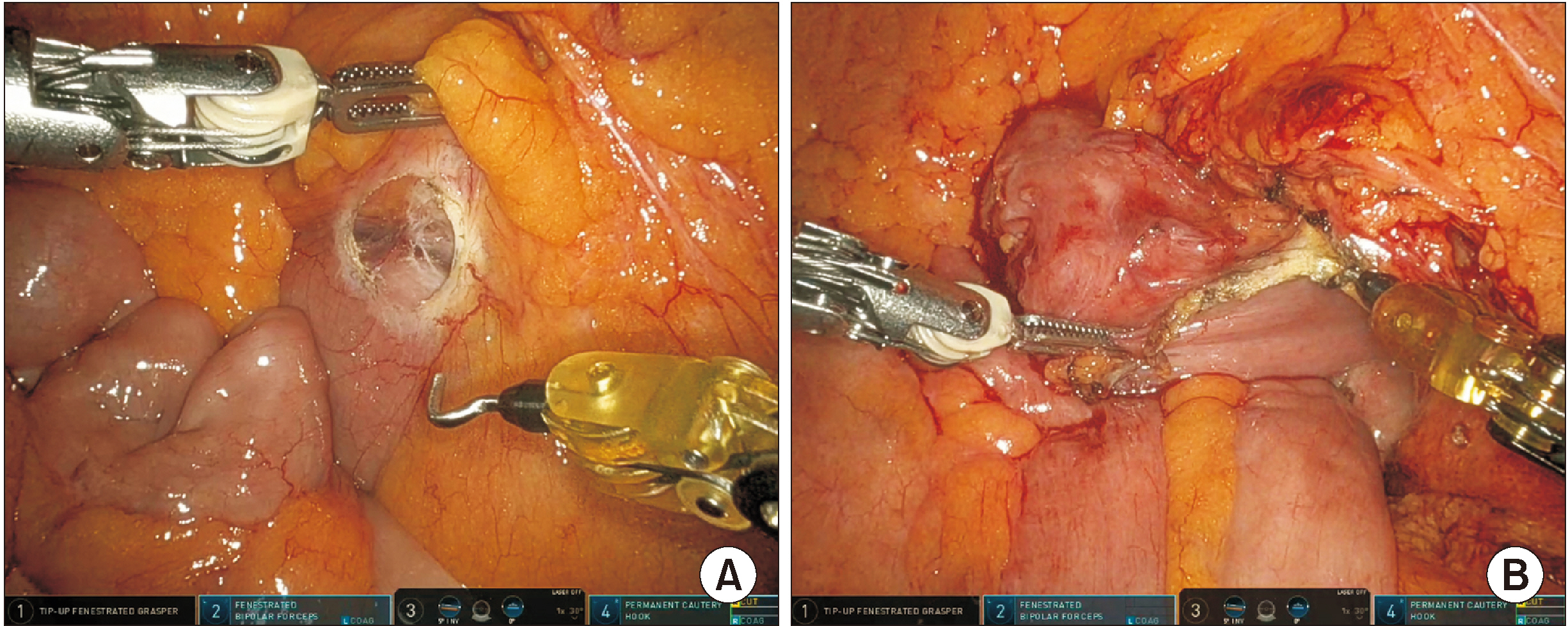
- The pancreatoduodenectomy (PD) technique is yet to be standardized. One of the most difficult passages in PD is the mobilization of the second, third, and fourth parts of the duodenum. This maneuver is classically performed from the supramesocolic space after the division of the gastrocolic ligament, but traction on the transverse mesocolon and the superior mesenteric pedicle can cause bleeding from the venous and arterial branches of the pancreatic head and uncinate process. We hereby describe a technique to access and mobilize the distal duodenum and proximal jejunum (D2 to J1) through the duodenal window and the Treitz’s foramen, performing an almost complete Kocher’s maneuver before opening the gastrocolic ligament and mobilizing the hepatic flexure. The anatomical basis and the surgical technique of the duodenal-window-first PD are discussed. The duodenal-window-first approach is a standardizable step of PD that allows an easy and safe mobilization of D2 to J1. This technique has been applied to 15 cases of PD, both open and robotic, with no specific morbidity. Therefore, we propose the adoption of the duodenal-window-first technique as a routine standardized step of PD.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Schnelldorfer T, Sarr MG. 2009; Alessandro Codivilla and the fist pancreatoduodenectomy. Arch Surg. 144:1179–1184. DOI: 10.1001/archsurg.2009.219. PMID: 20026839.
Article2. Whipple AO, Parsons WB, Mullins CR. 1935; Treatment of carcinoma of the ampulla of Vater. Ann Surg. 102:763–779. DOI: 10.1097/00000658-193510000-00023. PMID: 17856666. PMCID: PMC1391173.3. Traverso LW, Longmire WP. 1978; Preservation of the pylorus in pancreaticoduodenectomy. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 146:959–962.
Article4. Giulianotti PC, Sbrana F, Bianco FM, Elli EF, Shah G, Addeo P, et al. 2010; Robot-assisted pancreatic surgery: single-surgeon experience. Surg Endosc. 24:1646–1657. DOI: 10.1007/s00464-009-0825-4. PMID: 20063016.
Article5. Tebala GD, Di Saverio S, Gallo G, Cirocchi R, Milani MS, Bond-Smith G. 2021; Importance of the duodenal window and Fredet's fascia in laparoscopic right colectomy: technical note. Surg Technol Int. 39:173–175. DOI: 10.52198/21.STI.39.CR1511. PMID: 34736289.6. Machado MC, da Cunha JE, Bacchella T, Bove P. 1976; A modified technique for the reconstruction of the alimentary tract after pancreatoduodenectomy. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 143:271–272.7. Cattell RB, Braasch JW. 1960; A technique for the exposure of the third and fourth portion of the duodenum. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 111:378–379.8. Akita M, Yamasaki M, Miyake T, Mimura K, Maeda E, Nishimura T, et al. 2020; Cattell-Braasch maneuver facilitates the artery-first approach and complete excision of the mesopancreas for pancreatoduodenectomy. J Surg Oncol. 121:1126–1131. DOI: 10.1002/jso.25892. PMID: 32141084.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pancreatoduodenectomy following neoadjuvant chemotherapy in duodenal adenocarcinoma
- Laparoscopic pancreas-preserving near total duodenectomy for large villous adenoma in patients with total colectomy for familial adenomatous polyposis
- The Significance of Drain Amylase Level for Diagnosis of Pancreatic Leakage after Pancreatoduodenectomy
- A Case of Resolution of Duodenal Obstruction Caused by Duodenal Ulcer after the Eradication of Helicobacter pylori Infection
- Insights of window-bsed mechanism approach to visualize composite bioData point in feature spaces