Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg.
2024 May;28(2):229-237. 10.14701/ahbps.23-107.
Survival benefit of neoadjuvant FOLFIRINOX for patients with borderline resectable pancreatic cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of General Surgery, Department of Surgery, Western University, London, ON, Canada
- 2Division of Medical Oncology, Department of Oncology, Western University, London, ON, Canada
- KMID: 2555933
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14701/ahbps.23-107
Abstract
- Backgrounds/Aims
While patients with borderline resectable pancreatic cancer (BRPC) are a target population for neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC), formal guidelines for neoadjuvant therapy are lacking. We assessed the perioperative and oncological outcomes in patients with BRPC undergoing NAC with FOLFIRINOX for patients undergoing upfront surgery (US).
Methods
The AHPBA criteria for borderline resectability and/or a CA19-9 level > 100 µ/mL defined borderline resectable tumors retrieved from a prospectively populated institutional registry from 2007 to 2020. The primary outcome was overall survival (OS) at 1 and 3 years. A Cox Proportional Hazard model based on intention to treat was used. A receiver–operator characteristics (ROC) curve was constructed to assess the discriminatory capability of the use of CA19-9 > 100 µ/mL to predict resectability and mortality.
Results
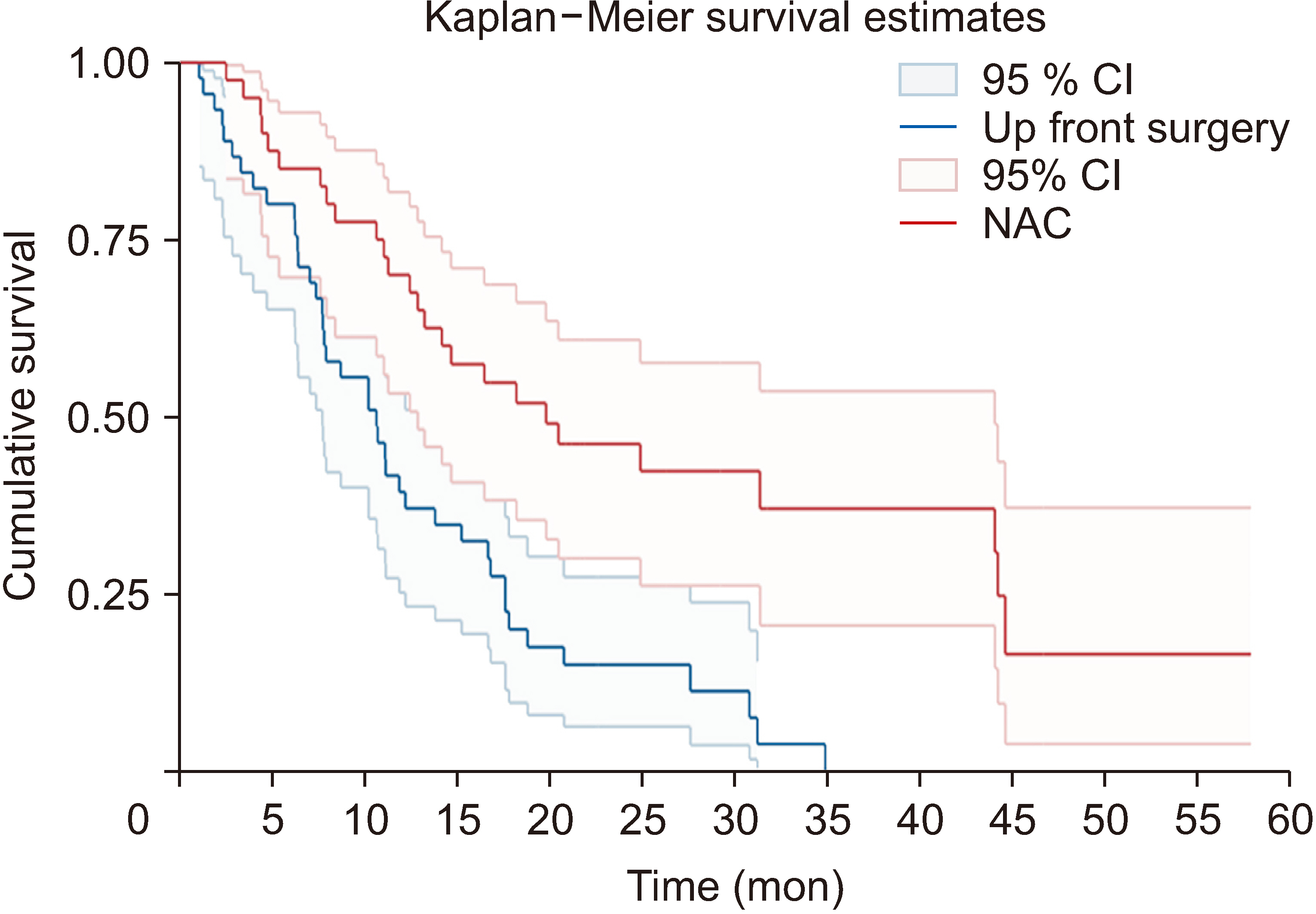
Forty BRPC patients underwent NAC, while 46 underwent US. The median OS with NAC was 19.8 months (interquartile range [IQR], 10.3−44.24) vs. 10.6 months (IQR, 6.37−17.6) with US. At 1 year, 70% of the NAC group and 41.3% of the US group survived (p = 0.008). At 3 years, 42.5 % of the NAC group and 10.9% of the US group survived (p = 0.001). NAC significantly reduced the hazard of death (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.20; 95% confidence interval, 0.07−0.54; p = 0.001). CA19-9 > 100 µ/mL showed poor discrimination in predicting mortality, but was a moderate predictor of resectability.
Conclusions
We found a survival benefit of NAC with FOLFIRINOX for BRPC. Greater pre-treatment of CA19-9 and multivessel involvement on initial imaging were associated with progression of the disease following NAC.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. McGuigan A, Kelly P, Turkington RC, Jones C, Coleman HG, McCain RS. 2018; Pancreatic cancer: a review of clinical diagnosis, epidemiology, treatment and outcomes. World J Gastroenterol. 24:4846–4861. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i43.4846. PMID: 30487695. PMCID: PMC6250924.
Article2. Lopez NE, Prendergast C, Lowy AM. 2014; Borderline resectable pancreatic cancer: definitions and management. World J Gastroenterol. 20:10740–10751. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i31.10740. PMID: 25152577. PMCID: PMC4138454.
Article3. Raufi AG, Manji GA, Chabot JA, Bates SE. 2019; Neoadjuvant treatment for pancreatic cancer. Semin Oncol. 46:19–27. DOI: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2018.12.002. PMID: 30630600.
Article4. Tang K, Lu W, Qin W, Wu Y. 2016; Neoadjuvant therapy for patients with borderline resectable pancreatic cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of response and resection percentages. Pancreatology. 16:28–37. DOI: 10.1016/j.pan.2015.11.007. PMID: 26687001.
Article5. Müller PC, Frey MC, Ruzza CM, Nickel F, Jost C, Gwerder C, et al. 2021; Neoadjuvant chemotherapy in pancreatic cancer: an appraisal of the current high-level evidence. Pharmacology. 106:143–153. DOI: 10.1159/000510343. PMID: 32966993.
Article6. He J, Schulick RD, Del Chiaro M. 2021; Landmark series: neoadjuvant treatment in borderline resectable pancreatic cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 28:1514–1520. DOI: 10.1245/s10434-020-09535-x. PMID: 33415556.
Article7. Versteijne E, Suker M, Groothuis K, Akkermans-Vogelaar JM, Besselink MG, Bonsing BA, et al. 2020; Preoperative chemoradiotherapy versus immediate surgery for resectable and borderline resectable pancreatic cancer: results of the Dutch randomized phase III PREOPANC trial. J Clin Oncol. 38:1763–1773. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.19.02274. PMID: 32105518. PMCID: PMC8265386.
Article8. Scheufele F, Hartmann D, Friess H. 2019; Treatment of pancreatic cancer-neoadjuvant treatment in borderline resectable/locally advanced pancreatic cancer. Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol. 4:32. DOI: 10.21037/tgh.2019.04.09. PMID: 31231699. PMCID: PMC6556697.
Article9. Janssen QP, Buettner S, Suker M, Beumer BR, Addeo P, Bachellier P, et al. 2019; Neoadjuvant FOLFIRINOX in patients with borderline resectable pancreatic cancer: a systematic review and patient-level meta-analysis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 111:782–794. DOI: 10.1093/jnci/djz073. PMID: 31086963. PMCID: PMC6695305.
Article10. Isaji S, Mizuno S, Windsor JA, Bassi C, Fernández-del Castillo C, Hackert T, et al. 2018; International consensus on definition and criteria of borderline resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma 2017. Pancreatology. 18:2–11. DOI: 10.1016/j.pan.2017.11.011. PMID: 29191513.
Article11. Varadhachary GR. Neoptolemos JP, Urrutia R, Abbruzzese JL, Büchler MW, editors. 2018. Borderline resectable pancreatic cancer. Pancreatic cancer. Springer New York;p. 1001–1020. DOI: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7193-0_46.
Article12. Sabater L, Muñoz E, Roselló S, Dorcaratto D, Garcés-Albir M, Huerta M, et al. 2018; Borderline resectable pancreatic cancer. Challenges and controversies. Cancer Treat Rev. 68:124–135. DOI: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2018.06.006. PMID: 29957372.
Article13. Santucci N, Facy O, Ortega-Deballon P, Lequeu J-B, Rat P, Rat P. 2018; CA 19-9 predicts resectability of pancreatic cancer even in jaundiced patients. Pancreatology. 18:666–670. DOI: 10.1016/j.pan.2018.07.001. PMID: 30153902.
Article14. Hartwig W, Strobel O, Hinz U, Fritz S, Hackert T, Roth C, et al. 2013; CA19-9 in potentially resectable pancreatic cancer: perspective to adjust surgical and perioperative therapy. Ann Surg Oncol. 20:2188–2196. DOI: 10.1245/s10434-012-2809-1. PMID: 23247983.
Article15. La Greca G, Sofia M, Lombardo R, Latteri S, Ricotta A, Puleo S, et al. 2012; Adjusting CA19-9 values to predict malignancy in obstructive jaundice: influence of bilirubin and C-reactive protein. World J Gastroenterol. 18:4150–4155. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i31.4150. PMID: 22919247. PMCID: PMC3422795.
Article16. Versteijne E, Vogel JA, Besselink MG, Busch ORC, Wilmink JW, Daams JG, et al. 2018; Meta-analysis comparing upfront surgery with neoadjuvant treatment in patients with resectable or borderline resectable pancreatic cancer. Br J Surg. 105:946–958. DOI: 10.1002/bjs.10870. PMID: 29708592. PMCID: PMC6033157.
Article17. Dhir M, Malhotra GK, Sohal DPS, Hein NA, Smith LM, O'Reilly EM, et al. 2017; Neoadjuvant treatment of pancreatic adenocarcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 5520 patients. World J Surg Oncol. 15:183. DOI: 10.1186/s12957-017-1240-2. PMID: 29017581. PMCID: PMC5634869.
Article18. Barnes CA, Chavez MI, Tsai S, Aldakkak M, George B, Ritch PS, et al. 2019; Survival of patients with borderline resectable pancreatic cancer who received neoadjuvant therapy and surgery. Surgery. 166:277–285. DOI: 10.1016/j.surg.2019.05.010. PMID: 31272811.
Article19. Tran NH, Sahai V, Griffith KA, Nathan H, Kaza R, Cuneo KC, et al. 2020; Phase 2 trial of neoadjuvant FOLFIRINOX and intensity modulated radiation therapy concurrent with fixed-dose rate-gemcitabine in patients with borderline resectable pancreatic cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 106:124–133. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2019.08.057. PMID: 31494181. PMCID: PMC7245020.
Article20. Murphy JE, Wo JY, Ryan DP, Jiang W, Yeap BY, Drapek LC, et al. 2018; Total neoadjuvant therapy with FOLFIRINOX followed by individualized chemoradiotherapy for borderline resectable pancreatic adenocarcinoma: a phase 2 clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. 4:963–969. DOI: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.0329. PMID: 29800971. PMCID: PMC6145728.
Article21. Truty MJ, Kendrick ML, Nagorney DM, Smoot RL, Cleary SP, Graham RP, et al. 2021; Factors predicting response, perioperative outcomes, and survival following total neoadjuvant therapy for borderline/locally advanced pancreatic cancer. Ann Surg. 273:341–349. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000003284. PMID: 30946090.
Article22. Anger F, Döring A, van Dam J, Lock JF, Klein I, Bittrich M, et al. 2021; Impact of borderline resectability in pancreatic head cancer on patient survival: biology matters according to the new international consensus criteria. Ann Surg Oncol. 28:2325–2336. DOI: 10.1245/s10434-020-09100-6. PMID: 32920720. PMCID: PMC7940298.
Article23. Ushida Y, Inoue Y, Ito H, Oba A, Mise Y, Ono Y, et al. 2021; High CA19-9 level in resectable pancreatic cancer is a potential indication of neoadjuvant treatment. Pancreatology. 21:130–137. DOI: 10.1016/j.pan.2020.11.026. PMID: 33303373.
Article24. Nurmi AM, Mustonen H, Haglund C, Seppänen H. 2021; Changes in CRP and CA19-9 during preoperative oncological therapy predict postoperative survival in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncology. 99:686–698. DOI: 10.1159/000517835. PMID: 34412062.
Article25. Tzeng CWD, Balachandran A, Ahmad M, Lee JE, Krishnan S, Wang H, et al. 2014; Serum carbohydrate antigen 19-9 represents a marker of response to neoadjuvant therapy in patients with borderline resectable pancreatic cancer. HPB (Oxford). 16:430–438. DOI: 10.1111/hpb.12154. PMID: 23991810. PMCID: PMC4008161.
Article26. Takahashi H, Yamada D, Asukai K, Wada H, Hasegawa S, Hara H, et al. 2020; Clinical implications of the serum CA19-9 level in "biological borderline resectability" and "biological downstaging" in the setting of preoperative chemoradiation therapy for pancreatic cancer. Pancreatology. 20:919–928. DOI: 10.1016/j.pan.2020.05.020. PMID: 32563596.
Article27. Zhang S, Wang YM, Sun CD, Lu Y, Wu LQ. 2008; Clinical value of serum CA19-9 levels in evaluating resectability of pancreatic carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 14:3750–3753. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.14.3750. PMID: 18595144. PMCID: PMC2719240.
Article28. Sugiura T, Uesaka K, Kanemoto H, Mizuno T, Sasaki K, Furukawa H, et al. 2012; Serum CA19-9 is a significant predictor among preoperative parameters for early recurrence after resection of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J Gastrointest Surg. 16:977–985. DOI: 10.1007/s11605-012-1859-9. PMID: 22411488.
Article29. Bergquist JR, Puig CA, Shubert CR, Groeschl RT, Habermann EB, Kendrick ML, et al. 2016; Carbohydrate antigen 19-9 elevation in anatomically resectable, early stage pancreatic cancer is independently associated with decreased overall survival and an indication for neoadjuvant therapy: a national cancer database study. J Am Coll Surg. 223:52–65. DOI: 10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2016.02.009. PMID: 27049786.
Article30. Kato Y, Yamada S, Tashiro M, Sonohara F, Takami H, Hayashi M, et al. 2019; Biological and conditional factors should be included when defining criteria for resectability for patients with pancreatic cancer. HPB (Oxford). 21:1211–1218. DOI: 10.1016/j.hpb.2019.01.012. PMID: 30773450.
Article31. Schlieman MG, Ho HS, Bold RJ. 2003; Utility of tumor markers in determining resectability of pancreatic cancer. Arch Surg. 138:951–955. DOI: 10.1001/archsurg.138.9.951. PMID: 12963650.
Article32. Rose JB, Edwards AM, Rocha FG, Clark C, Alseidi AA, Biehl TR, et al. 2020; Sustained carbohydrate antigen 19-9 response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in borderline resectable pancreatic cancer predicts progression and survival. Oncologist. 25:859–866. DOI: 10.1634/theoncologist.2019-0878. PMID: 32277842. PMCID: PMC7543354.
Article33. He Z, Lu H, Du X, Hu W, Zhaoda BT. 2013; CA19-9 as a predictor of resectability in patients with borderline resectable pancreatic cancer. Hepatogastroenterology. 60:900–903.34. Michelakos T, Pergolini I, Castillo CF Del, Honselmann KC, Cai L, Deshpande V, et al. 2019; Predictors of resectability and survival in patients with borderline and locally advanced pancreatic cancer who underwent neoadjuvant treatment with FOLFIRINOX. Ann Surg. 269:733–740. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000002600. PMID: 29227344.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Neoadjuvant Therapy for Resectable or Borderline Resectable Pancreatic Cancer
- Neoadjuvant and Adjuvant Treatments for Resectable and Borderline Resectable Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma: The Current Status of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Treatment in Japan
- Updates of Chemotherapy for Pancreatic Cancer
- Updates of Chemotherapy and Radiotherapy for Pancreatic Cancer
- Comparison of Clinical Outcomes of Borderline Resectable Pancreatic Cancer According to the Neoadjuvant Chemo-Regimens: Gemcitabine versus FOLFIRINOX