Clin Endosc.
2024 May;57(3):309-316. 10.5946/ce.2023.217.
Role of endoscopic duodenojejunal bypass liner in obesity management and glycemic control
- Affiliations
-
- 1Endoscopy Unit, Hospital de Amor da Amazônia, Rondonia, Brazil
- 2Serviço de Endoscopia Gastrointestinal, Departamento de Gastroenterologia, Hospital das Clínicas da Faculdade de Medicina da Universidade de São Paulo, São Paulo, Brazil
- 3American University of Beirut Faculty of Medicine, American University of Beirut Medical Center, Beirut, Lebanon
- 4Gastrointestinal Endoscopy Division, Instituto D’Or de Pesquisa e Ensino, Hospital Vila Nova Star, São Paulo, Brazil
- KMID: 2555891
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2023.217
Abstract
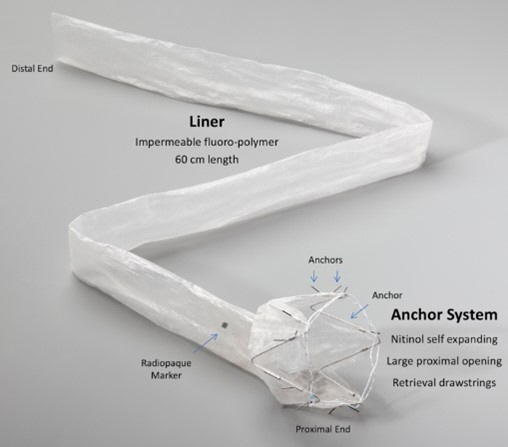
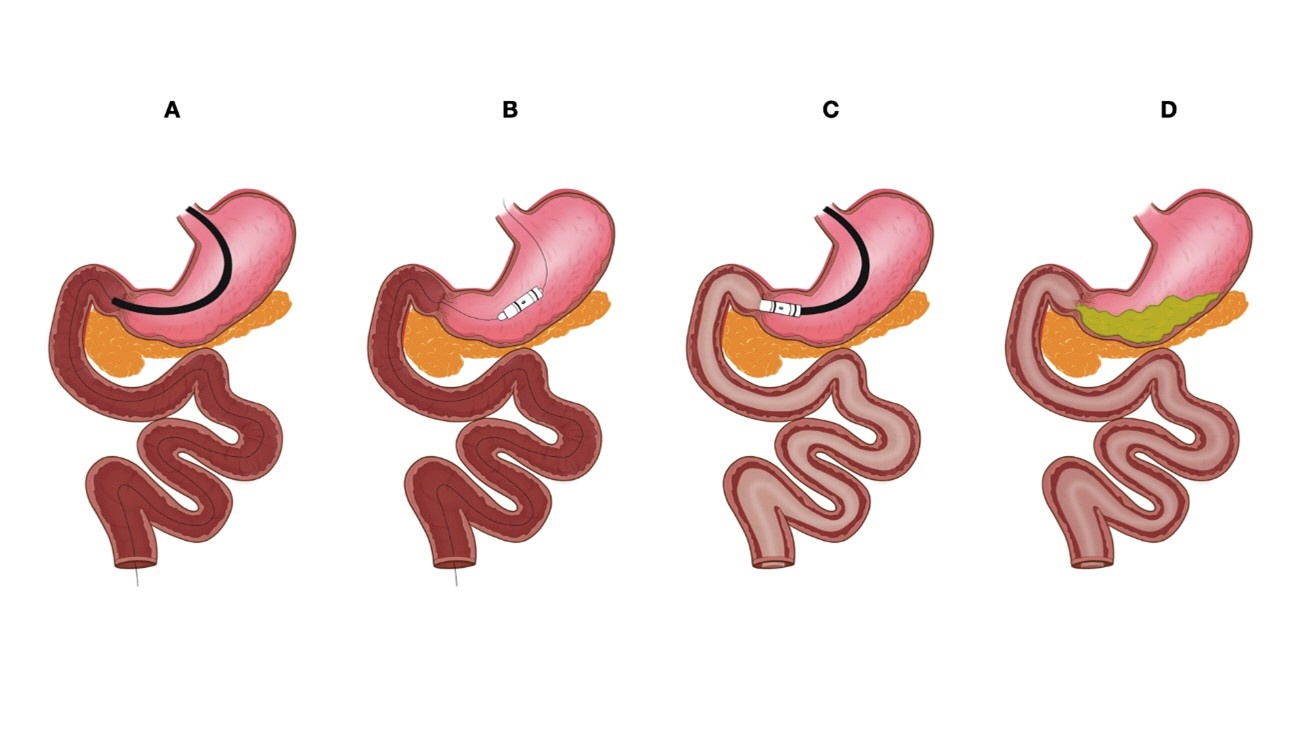
- The treatment of obesity and its comorbidities ranges from clinical management involving lifestyle changes and medications to bariatric and metabolic surgery. Various endoscopic bariatric and metabolic therapies recently emerged to address an important therapeutic gap by offering a less invasive alternative to surgery that is more effective than conservative therapies. This article comprehensively reviews the technical aspects, mechanism of action, outcomes, and future perspectives of one of the most promising endoscopic bariatric and metabolic therapies, named duodenojejunal bypass liner. The duodenojejunal bypass liner mimics the mechanism of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass by preventing food contact with the duodenum and proximal jejunum, thereby initiating a series of hormonal changes that lead to delayed gastric emptying and malabsorptive effects. These physiological changes result in significant weight loss and improved metabolic control, leading to better glycemic levels, preventing dyslipidemia and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and mitigating cardiovascular risk. However, concern exists regarding the safety profile of this device due to the reported high rates of severe adverse events, particularly liver abscesses. Ongoing technical changes aiming to reduce adverse events are being evaluated in clinical trials and may provide more reliable data to support its routine use in clinical practice.
Figure
Reference
-
1. World Obesity Federation. World Obesity Atlas 2023 [Internet]. World Obesity Federation;2023. [cited 2023 Apr 8]. Available from: https://data.worldobesity.org/publications/?cat=19.2. Michaelidou M, Pappachan JM, Jeeyavudeen MS. Management of diabesity: current concepts. World J Diabetes. 2023; 14:396–411.
Article3. Na HK, De Moura DT; Study Group for Endoscopic Bariatric and Metabolic Therapies of the Korean Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. Various novel and emerging technologies in endoscopic bariatric and metabolic treatments. Clin Endosc. 2021; 54:25–31.
Article4. Cambi MP, Baretta GA, Magro DO, et al. Multidisciplinary approach for weight regain-how to manage this challenging condition: an expert review. Obes Surg. 2021; 31:1290–1303.
Article5. Colquitt JL, Pickett K, Loveman E, et al. Surgery for weight loss in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014; 2014:CD003641.
Article6. Nguyen NT, Masoomi H, Magno CP, et al. Trends in use of bariatric surgery, 2003-2008. J Am Coll Surg. 2011; 213:261–266.
Article7. Tatarian T, Rona KA, Shin DH, et al. Evolving procedural options for the treatment of obesity. Curr Probl Surg. 2020; 57:100742.
Article8. Günthert SJ, Aksan A, Schröder O, et al. Glycemic control and BMI changes after endoscopic implantation of a duodenojejunal bypass liner compared with laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery: a propensity score matching analysis. Surg Endosc. 2022; 36:5979–5985.
Article9. Betzel B, Cooiman MI, Aarts EO, et al. Clinical follow-up on weight loss, glycemic control, and safety aspects of 24 months of duodenal-jejunal bypass liner implantation. Surg Endosc. 2020; 34:209–215.
Article10. Simons M, Sharaiha RZ. Updates in metabolic bariatric endoscopy. Dig Endosc. 2023; 36:107–115.
Article11. Shenoy A, Schulman AR. Advances in endobariatrics: past, present, and future. Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf). 2023; 11:goad043.
Article12. Dave N, Dawod E, Simmons OL. Endobariatrics: a still underutilized weight loss tool. Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol. 2023; 21:172–184.
Article13. McCarty TR, Thompson CC. The current state of bariatric endoscopy. Dig Endosc. 2021; 33:321–334.
Article14. Campbell JE, Drucker DJ. Pharmacology, physiology, and mechanisms of incretin hormone action. Cell Metab. 2013; 17:819–837.
Article15. Chen JH, Yu ZH, Liu QF, et al. Research progress of duodenal-jejunal bypass liner in the treatment of obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2022; 15:3319–3327.
Article16. Jirapinyo P, Haas AV, Thompson CC. Effect of the duodenal-jejunal bypass liner on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes with obesity: a meta-analysis with secondary analysis on weight loss and hormonal changes. Diabetes Care. 2018; 41:1106–1115.
Article17. de Moura EG, Lopes GS, Martins BC, et al. Effects of duodenal-jejunal bypass liner (EndoBarrier®) on gastric emptying in obese and type 2 diabetic patients. Obes Surg. 2015; 25:1618–1625.
Article18. Yvamoto EY, de Moura DT, Proença IM, et al. The effectiveness and safety of the duodenal-jejunal bypass liner (DJBL) for the management of obesity and glycaemic control: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Obes Surg. 2023; 33:585–599.
Article19. Jirapinyo P, de Moura DT, Horton LC, et al. Effect of aspiration therapy on obesity-related comorbidities: systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Endosc. 2020; 53:686–697.
Article20. Cho JH, Bilal M, Kim MC, et al. The clinical and metabolic effects of intragastric balloon on morbid obesity and its related comorbidities. Clin Endosc. 2021; 54:9–16.
Article21. Boonchaya-Anant P, Bueter M, Gubler C, et al. Sustained weight loss after duodenal-jejunal bypass liner treatment in patients with body mass index below, but not above 35 kg/m2: a retrospective cohort study. Clin Obes. 2023; 13:e12561.22. van Rijn S, Roebroek YG, de Jonge C, et al. Effect of the EndoBarrier device: a 4-year follow-up of a multicenter randomized clinical trial. Obes Surg. 2019; 29:1117–1121.
Article23. Ryder RE, Laubner K, Benes M, et al. Endoscopic duodenal-jejunal bypass liner treatment for type 2 diabetes and obesity: glycemic and cardiovascular disease risk factor improvements in 1,022 patients treated worldwide. Diabetes Care. 2023; 46:e89–e91.
Article24. Karlas T, Petroff D, Feisthammel J, et al. Endoscopic bariatric treatment with duodenal-jejunal bypass liner improves non-invasive markers of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Obes Surg. 2022; 32:2495–2503.
Article25. Roehlen N, Laubner K, Nicolaus L, et al. Impact of duodenal-jejunal bypass liner (DJBL) on NAFLD in patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nutrition. 2022; 103-104:111806.
Article26. Vilarrasa N, Fabregat A, Toro S, et al. Nutritional deficiencies and bone metabolism after endobarrier in obese type 2 patients with diabetes. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2018; 72:1447–1450.
Article27. Roehlen N, Laubner K, Bettinger D, et al. Duodenal-jejunal bypass liner (DJBL) improves cardiovascular risk biomarkers and predicted 4-year risk of major CV events in patients with type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome. Obes Surg. 2020; 30:1200–1210.
Article28. Betzel B, Drenth JP, Siersema PD. Adverse events of the duodenal-jejunal bypass liner: a systematic review. Obes Surg. 2018; 28:3669–3677.
Article29. Cotton PB, Eisen GM, Aabakken L, et al. A lexicon for endoscopic adverse events: report of an ASGE workshop. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 71:446–454.
Article30. Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien PA. Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann Surg. 2004; 240:205–213.31. Nass KJ, Zwager LW, van der Vlugt M, et al. Novel classification for adverse events in GI endoscopy: the AGREE classification. Gastrointest Endosc. 2022; 95:1078–1085.
Article32. De Moura EG, de Moura DT, Galvão-Neto M, et al. Endoscopic management of anchor erosion adjacent to the pylorus following duodenal-jejunal bypass sleeve. Obes Surg. 2019; 29:2003–2004.
Article33. Laubner K, Riedel N, Fink K, et al. Comparative efficacy and safety of the duodenal-jejunal bypass liner in obese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a case control study. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018; 20:1868–1877.
Article34. ASGE/ASMBS Task Force on Endoscopic Bariatric Therapy. A pathway to endoscopic bariatric therapies. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2011; 7:672–682.35. ASGE Bariatric Endoscopy Task Force and ASGE Technology Committee, Abu Dayyeh BK, Kumar N, et al. ASGE Bariatric Endoscopy Task Force systematic review and meta-analysis assessing the ASGE PIVI thresholds for adopting endoscopic bariatric therapies. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015; 82:425–438.
Article36. Mauro A, Lusetti F, Scalvini D, et al. A comprehensive review on bariatric endoscopy: where we are now and where we are going. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023; 59:636.
Article37. Singh S, Bazarbashi AN, Khan A, et al. Primary obesity surgery endoluminal (POSE) for the treatment of obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg Endosc. 2022; 36:252–266.
Article38. de Oliveira GH, de Moura DT, Funari MP, et al. Metabolic effects of endoscopic duodenal mucosal resurfacing: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes Surg. 2021; 31:1304–1312.
Article39. Kotinda AP, de Moura DT, Ribeiro IB, et al. Efficacy of intragastric balloons for weight loss in overweight and obese adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Obes Surg. 2020; 30:2743–2753.
Article40. de Miranda Neto AA, de Moura DT, Ribeiro IB, et al. Efficacy and safety of endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty at mid term in the management of overweight and obese patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes Surg. 2020; 30:1971–1987.
Article41. Huberty V, Boskoski I, Bove V, et al. Endoscopic sutured gastroplasty in addition to lifestyle modification: short-term efficacy in a controlled randomised trial. Gut. 2021; 70:1479–1485.
Article42. Ren M, Ji F. Small intestine-targeted endoscopic bariatrics: current status and future perspectives. Dig Endosc. 2023; 35:684–697.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Metabolic Efficacy and Diabetes Remission Predictors Following‘Sleeve Gastrectomy with Loop Duodenojejunal Bypass' Surgery
- Role of Gastroenterologists in Management of Obesity
- Initial Experience with Laparoscopic Loop Duodenojejunal Bypass with Sleeve Gastrectomy in Korean Obese Patients
- Letter: Factors Predicting Weight Loss after “Sleeve Gastrectomy with Loop Duodenojejunal Bypass” Surgery for Obesity (J Obes Metab Syndr 2020;29:208-14)
- Role of Restrictive Endoscopic Procedures in Obesity Treatment