Ann Clin Neurophysiol.
2024 Apr;26(1):34-35. 10.14253/acn.23003.
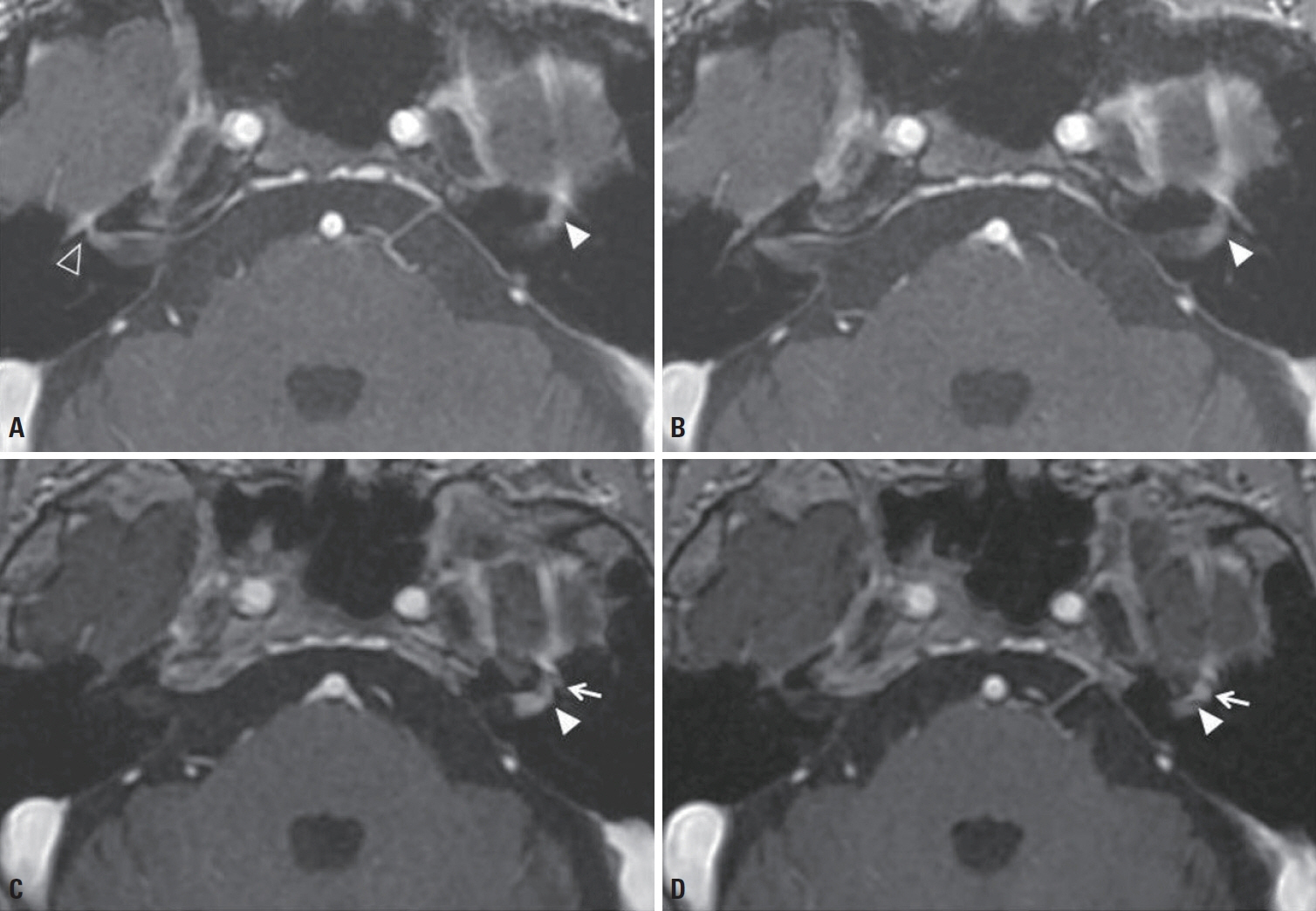
A case of Bell’s palsy with an incidental finding of facial nerve schwannoma: comparison of magnetic resonance imaging findings
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Daegu Catholic University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
- KMID: 2554853
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14253/acn.23003
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. McMonagle B, Al-Sanosi A, Croxson G, Fagan P. Facial schwannoma: results of a large case series and review. J Laryngol Otol. 2008; 122:1139–1150.
Article2. Thompson AL, Aviv RI, Chen JM, Nedzelski JM, Yuen HW, Fox AJ, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of facial nerve schwannoma. Laryngoscope. 2009; 119:2428–2436.
Article3. Tien R, Dillon WP, Jackler RK. Contrast-enhanced MR imaging of the facial nerve in 11 patients with Bell’s palsy. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1990; 155:573–579.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Serious Neurological Disorders That Mimic Bell’s Palsy: A 10-Year Experience
- How Long Could the Enhancement of Facial Nerve Last in Bell’s Palsy?
- Association of the Prognosis and the Facial Nerve Enhancement in Gadolinium Enhanced MRI in Patients with Bell's Palsy
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Facial Nerve Palsy: Comparison between Bell's Palsy and Herpes Zoster Oticus
- Correlation between MRI and Operative Findings in Bell's Palsy and Ramsay Hunt Syndrome