J Korean Med Sci.
2024 Apr;39(14):e137. 10.3346/jkms.2024.39.e137.
Comparison of the Clinical Outcomes Between Early and Delayed Transplantation After SARS-CoV-2 Infection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Infectious Diseases, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Infectious Diseases, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Yangsan, Korea
- KMID: 2554588
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2024.39.e137
Abstract
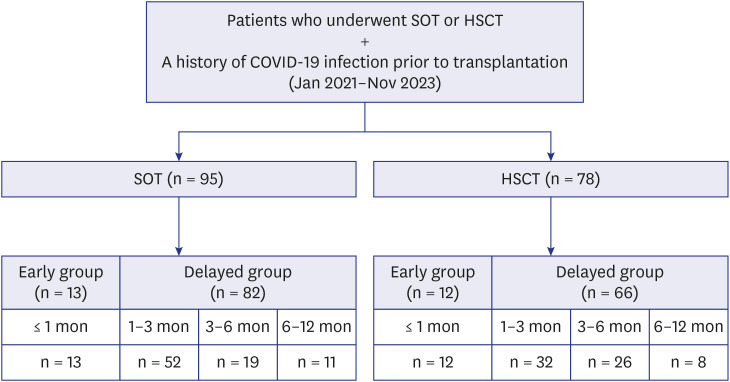
- Our study analyzed 95 solid organ transplant (SOT) and 78 hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) recipients with prior coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Patients who underwent transplantation within 30 days of COVID-19 infection comprised the early group, and those who underwent transplantation post-30 days of COVID-19 infection comprised the delayed group. In the early transplantation group, no patient, whether undergoing SOT and HSCT, experienced COVID-19-associated complications. In the delayed transplantation group, one patient each from SOT and HSCT experienced COVID-19-associated complications. Additionally, among early SOT and HSCT recipients, two and six patients underwent transplantation within seven days of COVID-19 diagnosis, respectively. However, no significant differences were observed in the clinical outcomes of these patients compared to those in other patients. Early transplantation following severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection can be performed without increased risk of COVID-19-associated complications. Therefore, transplantation needs not be delayed by COVID-19 infection.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Guan WJ, Ni ZY, Hu Y, Liang WH, Ou CQ, He JX, et al. Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China. N Engl J Med. 2020; 382(18):1708–1720. PMID: 32109013.2. Turkkan S, Beyoglu MA, Sahin MF, Yazicioglu A, Tezer Tekce Y, Yekeler E. COVID-19 in lung transplant recipients: a single-center experience. Transpl Infect Dis. 2021; 23(5):e13700. PMID: 34323353.3. Permpalung N, Bazemore K, Chiang TP, Mathew J, Barker L, Nematollahi S, et al. Impact of COVID-19 on lung allograft and clinical outcomes in lung transplant recipients: a case-control study. Transplantation. 2021; 105(9):2072–2079. PMID: 34075005.4. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Guidance for antigen testing for SARS-CoV-2 for healthcare providers testing individuals in the community. Updated 2023. Accessed February 15, 2023. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/lab/resources/antigen-tests-guidelines.html .5. Bartelt L, van Duin D. An overview of COVID-19 in solid organ transplantation. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2022; 28(6):779–784. PMID: 35189336.6. Waghmare A, Abidi MZ, Boeckh M, Chemaly RF, Dadwal S, El Boghdadly Z, et al. Guidelines for COVID-19 management in hematopoietic cell transplantation and cellular therapy recipients. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2020; 26(11):1983–1994. PMID: 32736007.7. Kulkarni AV, Parthasarathy K, Kumar P, Sharma M, Reddy R, Chaitanya Akkaraju Venkata K, et al. Early liver transplantation after COVID-19 infection: the first report. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21(6):2279–2284. PMID: 33508881.8. Yahav D, Yelin D, Eckerle I, Eberhardt CS, Wang J, Cao B, et al. Definitions for coronavirus disease 2019 reinfection, relapse and PCR re-positivity. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2021; 27(3):315–318. PMID: 33285276.9. World Health Organization. COVID-19 weekly epidemiological update. Updated 2024. Accessed December 31, 2023. https://data.who.int/dashboards/covid19/cases?n=c .10. Loupy A, Aubert O, Reese PP, Bastien O, Bayer F, Jacquelinet C. Organ procurement and transplantation during the COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet. 2020; 395(10237):e95–e96. PMID: 32407668.11. American Society of Transplantation. COVID-19: FAQs for Organ Transplantation. Updated 2023. Accessed December 31, 2023. https://www.myast.org/sites/default/files/COVID%20FAQ%20for%20Tx%20professionals%202-2023%20FINAL.pdf .12. Kute VB, Guleria S, Bhalla AK, Sharma A, Agarwal SK, Sahay M, et al. ISOT consensus statement for the kidney transplant recipient and living donor with a previous diagnosis of COVID-19. Indian J Nephrol. 2022; 32(4):288–290. PMID: 35967531.13. The International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation. Guidance from the International Society of Heart and Lung Transplantation regarding the SARS CoV-2 pandemic 2020. Updated 2020. Accessed December 31, 2023. https://ishlt.org/ishlt/media/documents/SARS-CoV-2_-Guidance-for-Cardiothoracic-Transplant-and-VAD-centers.pdf .14. The Transplantation Society. Guidance on coronavirus disease 2019 (covid-19) for transplant clinicians. Updated 2020. Accessed December 31, 2023. https://tts.org/23-tid/tid-news/657-tid-update-and-guidance-on-2019-novel-coronavirus-2019-ncov-for-transplant-id-clinicians.html .15. Ljungman P, Mikulska M, de la Camara R, Basak GW, Chabannon C, Corbacioglu S, et al. The challenge of COVID-19 and hematopoietic cell transplantation; EBMT recommendations for management of hematopoietic cell transplant recipients, their donors, and patients undergoing CAR T-cell therapy. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2020; 55(11):2071–2076. PMID: 32404975.16. Algwaiz G, Aljurf M, Koh M, Horowitz MM, Ljungman P, Weisdorf D, et al. Real-world issues and potential solutions in hematopoietic cell transplantation during the COVID-19 pandemic: perspectives from the Worldwide Network for Blood and Marrow Transplantation and Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research Health Services and International Studies Committee. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2020; 26(12):2181–2189. PMID: 32717432.17. Danziger-Isakov L, Blumberg EA, Manuel O, Sester M. Impact of COVID-19 in solid organ transplant recipients. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21(3):925–937. PMID: 33319449.18. Kang SW, Kim JW, Kim JY, Lim SY, Jang CY, Chang E, et al. Virological characteristics and the rapid antigen test as deisolation criteria in immunocompromised patients with COVID-19: a prospective cohort study. J Med Virol. 2023; 95(11):e29228. PMID: 38009999.19. Craig-Schapiro R, Salinas T, Lubetzky M, Abel BT, Sultan S, Lee JR, et al. COVID-19 outcomes in patients waitlisted for kidney transplantation and kidney transplant recipients. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21(4):1576–1585. PMID: 33043597.20. Mohan M, Kothari A, Verhagen N, Shreenivas A, Radhakrishnan SV, Dhakal B, et al. Blood and marrow transplant within 4 weeks of SARS-CoV-2 infection is associated with increased risk of mortality: a National COVID Cohort Collaborative (N3C) Study. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2024; 59(1):121–124. PMID: 37803198.21. Natori Y, Anjan S, Martin EF, Selvagi G, Villavicencio A, Coro A, et al. When is it safe to perform abdominal transplantation in patients with prior SARS-CoV-2 infection: a case series. Clin Transplant. 2021; 35(12):e14370. PMID: 34032328.22. Knaus HA, Rabitsch W, Buchtele N, Cserna J, Wohlfarth P. Autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation with concomitant SARS-CoV-2 infection. Ann Hematol. 2022; 101(5):1107–1110. PMID: 34643768.23. Shah N, Dahi PB, Ponce DM, Sauter CS, Shaffer BC, Chung DJ, et al. Hematopoietic cell transplantation is feasible in patients with prior COVID-19 INFECTION. Transplant Cell Ther. 2022; 28(1):55.e1–55.e5.24. Johnstad CM, Murray D, Dhingra R, Smith JW, Fiedler AG. Successful heart transplantation in a patient who recovered from COVID-19. J Card Surg. 2021; 36(3):1148–1149. PMID: 33448478.25. Kute V, Meshram HS, Fleetwood VA, Chauhan S, Lentine KL. Solid organ transplantation in SARS-CoV-2 recovered transplant candidates: a comprehensive review of recent literature. Curr Transplant Rep. 2022; 9(2):95–107. PMID: 35284204.26. Dhand A, Bodin R, Wolf DC, Schluger A, Nabors C, Nog R, et al. Successful liver transplantation in a patient recovered from COVID-19. Transpl Infect Dis. 2021; 23(2):e13492. PMID: 33040430.27. Eichenberger EM, Aslam S. Changing paradigm: Transplanting candidates with coronavirus disease 2019. Transpl Infect Dis. 2023; 25(5):e14156. PMID: 37724753.28. Zavala S, DeLaurentis C, Aaron JG, Miko BA, Fox AN, Bergelson M, et al. When you need to dive in the deep end-Transplanting SARS-CoV-2 PCR+ recipients. Transpl Infect Dis. 2023; 25(5):e14110. PMID: 37527176.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- New Insights Into SARS-CoV-2-specific Antibody Levels in Kidney Transplantation Recipients After Three Vaccination Doses
- Gastrointestinal AA Amyloidosis following Recurrent SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Case Report
- Changes in SARS-CoV-2 antibody titers 6 months after the booster dose of BNT162b2 COVID-19 vaccine among health care workers
- SARS-CoV-2 in the Prostate: Immunohistochemical and Ultrastructural Studies
- SARS-CoV-2-Specific T Cell Responses in Patients with COVID-19 and Unexposed Individuals