Korean J Gastroenterol.
2024 Mar;83(3):111-118. 10.4166/kjg.2023.141.
Comparison of Glecaprevir/Pibrentasvir and Sofosbuvir/Ledipasvir in Patients with Hepatitis C Virus Genotype 1 and 2 in South Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Gastroenterology, Dankook University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea
- 2Department of Gastroenterology, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea
- 3Department of Gastroenterology, Konyang University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea
- 4Department of Gastroenterology, Chungnam University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea
- 5Department of Gastroenterology, Chungbuk University College of Medicine, Cheongju, Korea
- 6Department of Gastroenterology, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Daejeon, Korea
- 7Department of Gastroenterology, Konkuk University College of Medicine, Chungju, Korea
- KMID: 2554264
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2023.141
Abstract
- Background/Aims
This study compared the effectiveness and safety of glecaprevir/pibrentasvir (GLE/PIB) and sofosbuvir/ledipasvir (SOF/LDV) in real-life clinical practice.
Methods
The data from genotype 1 or 2 chronic hepatitis C patients treated with GLE/PIB or sofosbuvir + ribavirin or SOF/LDV in South Korea were collected retrospectively. The analysis included the treatment completion rate, sustained virologic response at 12 weeks (SVR12) test rate, treatment effectiveness, and adverse events.
Results
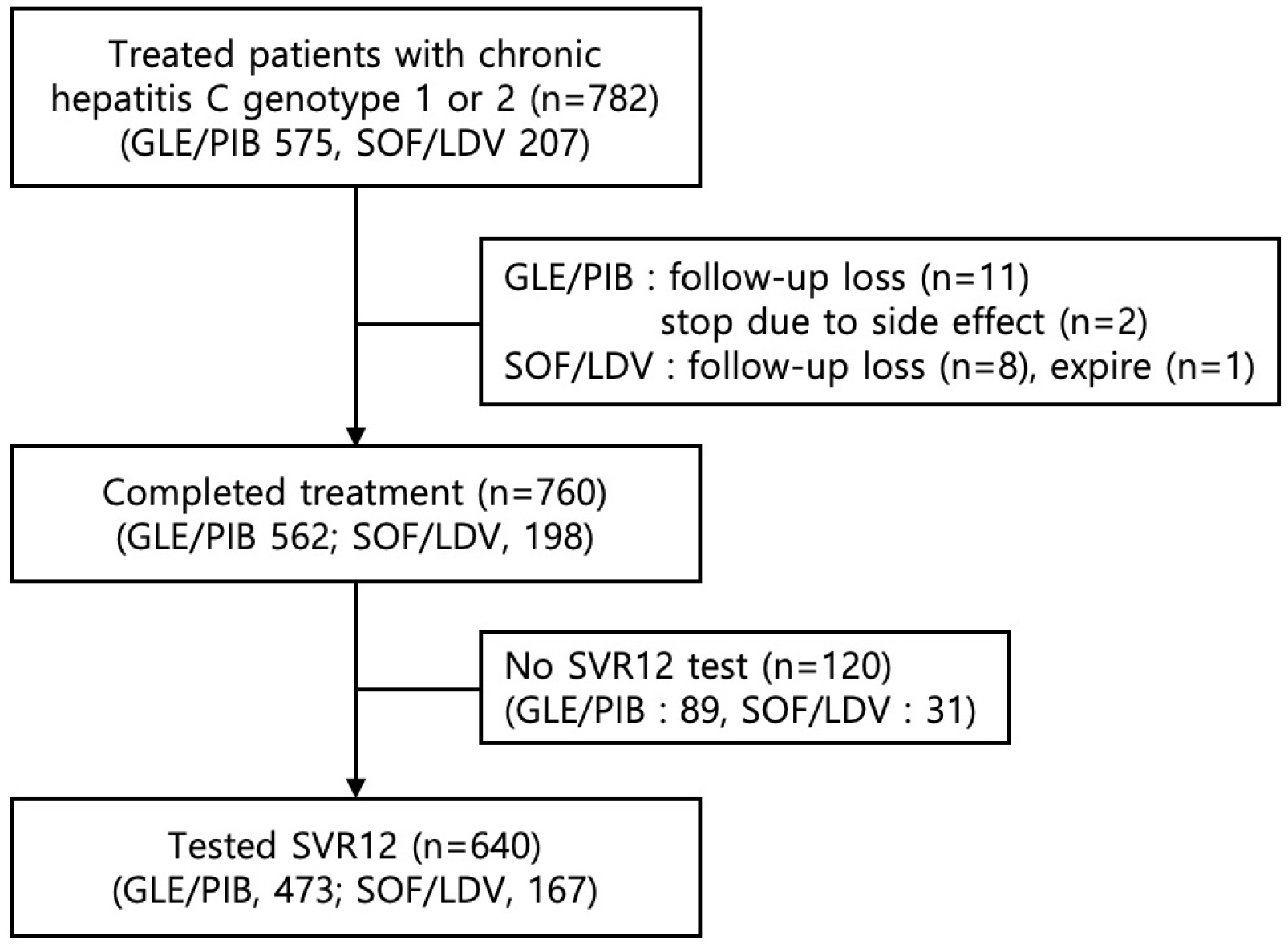
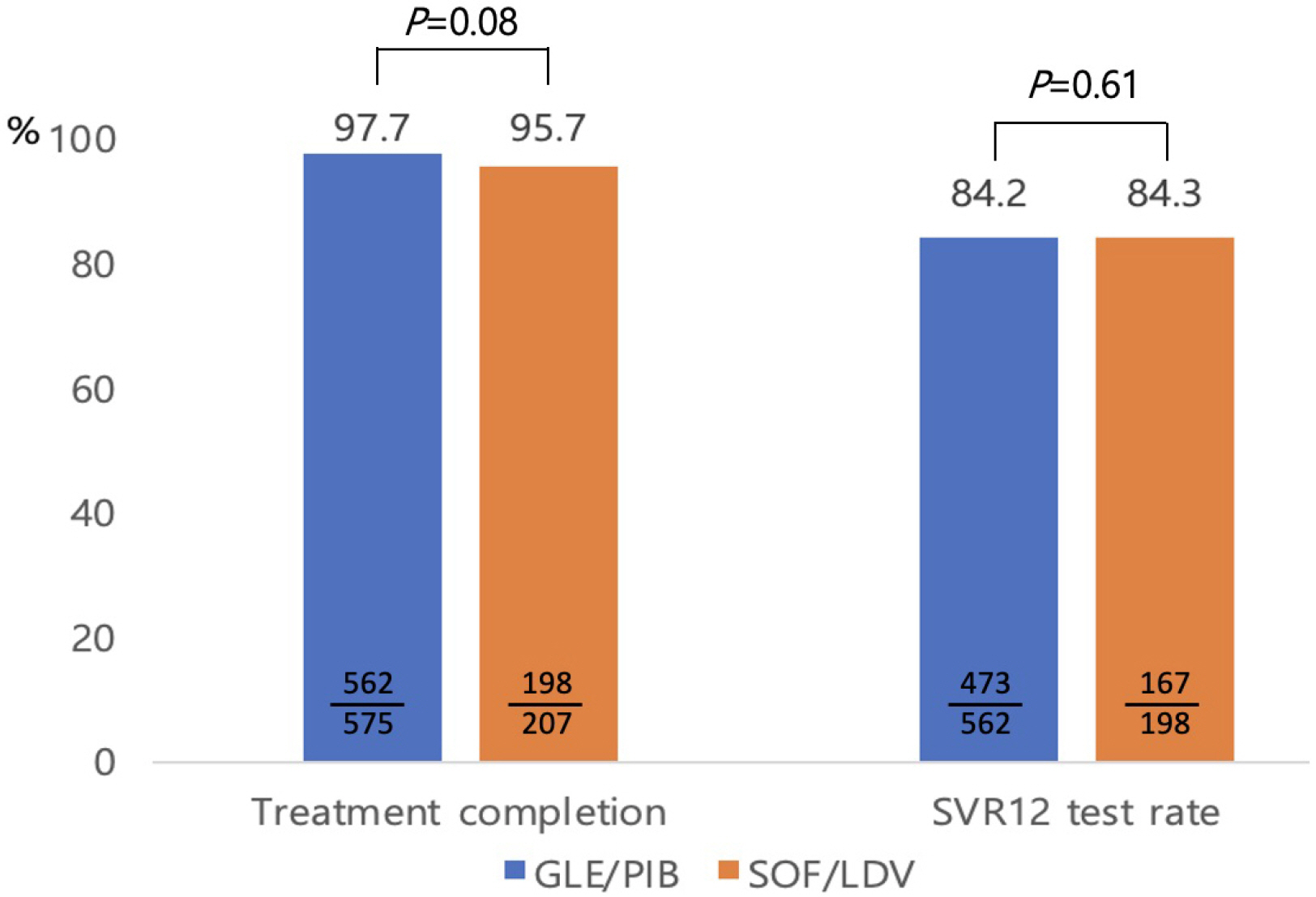
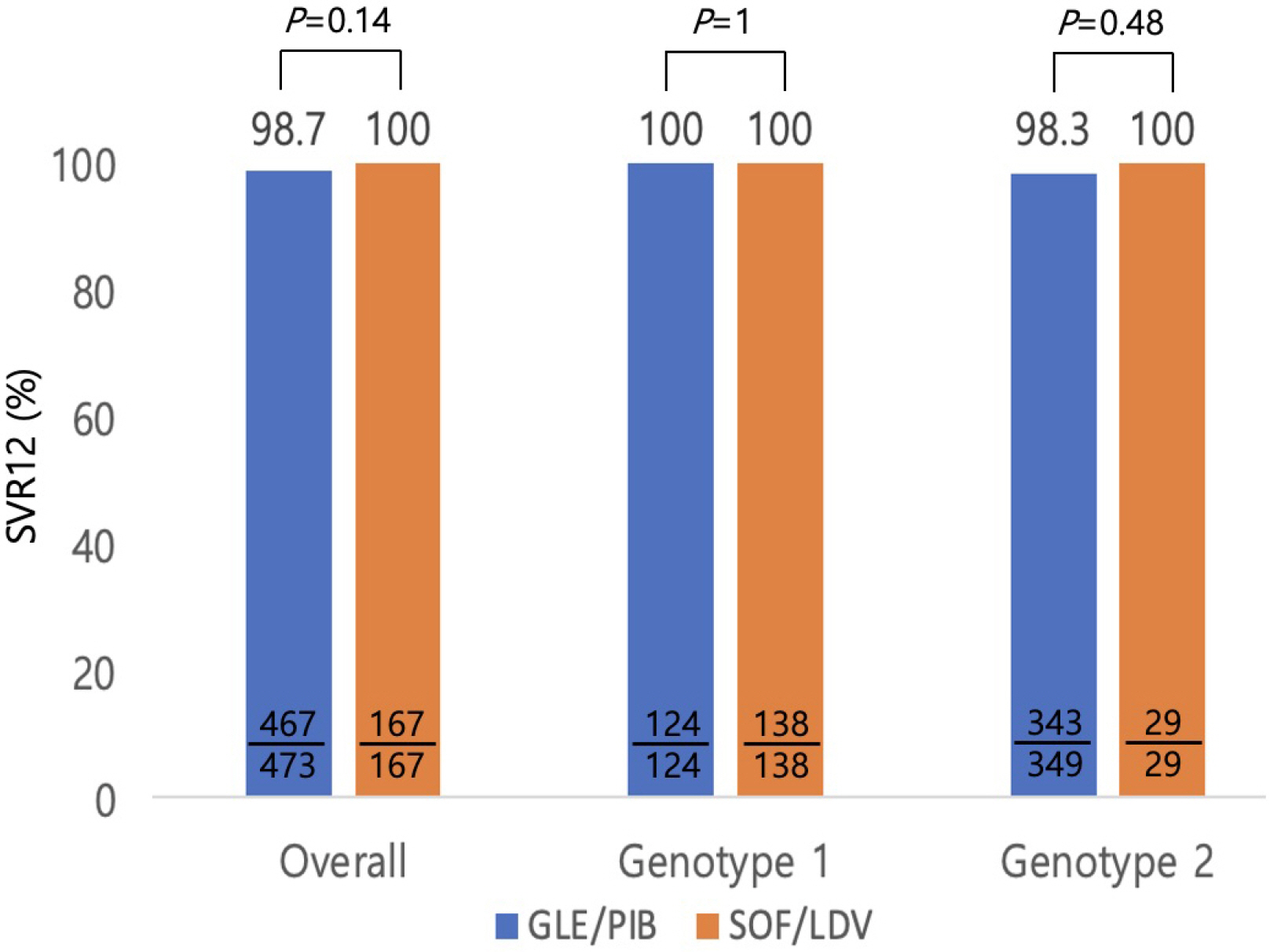
Seven hundred and eighty-two patients with genotype 1 or 2 chronic hepatitis C who were treated with GLE/PIB (n=575) or SOF/LDV (n=207) were included in this retrospective study. The baseline demographic and clinical characteristics revealed significant statistical differences in age, genotype, ascites, liver cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma between the GLE/PIB and SOF/LDV groups. Twenty-two patients did not complete the treatment protocol. The treatment completion rate was high for both regimens without statistical significance (97.7% vs. 95.7%, p=0.08). The overall SVR12 of intention-to-treat analysis was 81.2% vs. 80.7% without statistical significance (p=0.87). The overall SVR12 of per protocol analysis was 98.7% vs. 100% without statistical significance (p=0.14). Six patients treated with GLE/PIB experienced treatment failure. They were all male, genotype 2, and showed a negative hepatitis C virus RNA level at the end of treatment. Two patients treated with GLE/PIB stopped medication because of fever and abdominal discomfort.
Conclusions
Both regimens had similar treatment completion rates, effectiveness, and safety profiles. Therefore, the SOF/LDV regimen can also be considered a viable DAA for the treatment of patients with genotype 1 or 2 chronic hepatitis C.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. AASLD-IDSA HCV Guidance Panel. Hepatitis C guidance 2018 update: AASLD-IDSA recommendations for testing, managing, and treating hepatitis C virus infection. Clin Infect Dis. 2018; 67:1477–1492. DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciy585. PMID: 30215672. PMCID: PMC7190892.2. European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Recommendations on treatment of hepatitis C 2018. J Hepatol. 2018; 69:461–511. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.03.026. PMID: 29650333.3. Gower E, Estes C, Blach S, Razavi-Shearer K, Razavi H. 2014; Global epidemiology and genotype distribution of the hepatitis C virus infection. J Hepatol. 61(1 Suppl):S45–57. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.07.027. PMID: 25086286.
Article4. Asahina Y, Izumi N, Hiromitsu K, et al. 2016; JSH guidelines for the management of hepatitis C virus infection: A 2016 update for genotype 1 and 2. Hepatol Res. 46:129–165. DOI: 10.1111/hepr.12645. PMID: 26876581.
Article5. Korean Association for the Study of the Liver. 2016; KASL clinical practice guidelines: management of chronic hepatitis B. Clin Mol Hepatol. 22:18–75. DOI: 10.3350/cmh.2016.22.1.18. PMID: 27044762. PMCID: PMC4825166.6. Afdhal N, Zeuzem S, Kwo P, et al. 2014; Ledipasvir and sofosbuvir for untreated HCV genotype 1 infection. N Engl J Med. 370:1889–1898. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1402454. PMID: 24725239.
Article7. Mizokami M, Yokosuka O, Takehara T, et al. 2015; Ledipasvir and sofosbuvir fixed-dose combination with and without ribavirin for 12 weeks in treatment-naive and previously treated Japanese patients with genotype 1 hepatitis C: an open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Infect Dis. 15:645–653. DOI: 10.1016/S1473-3099(15)70099-X. PMID: 25863559.8. Lim YS, Ahn SH, Lee KS, et al. 2016; A phase IIIb study of ledipasvir/sofosbuvir fixed-dose combination tablet in treatment-naïve and treatment-experienced Korean patients chronically infected with genotype 1 hepatitis C virus. Hepatol Int. 10:947–955. DOI: 10.1007/s12072-016-9726-5. PMID: 27198664.
Article9. Chuang WL, Chien RN, Peng CY, et al. 2016; Ledipasvir/sofosbuvir fixed-dose combination tablet in Taiwanese patients with chronic genotype 1 hepatitis C virus. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 31:1323–1329. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.13305. PMID: 26841930.
Article10. Kwo PY, Poordad F, Asatryan A, et al. 2017; Glecaprevir and pibrentasvir yield high response rates in patients with HCV genotype 1-6 without cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 67:263–271. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.03.039. PMID: 28412293.
Article11. Zeuzem S, Feld JJ, Wang S, et al. 2016; ENDURANCE-1: Efficacy and safety of 8-versus 12-week treatment with ABT-493/ABT-530 in patients with chronic HCV genotype 1 infection [Abstract]. Hepatology. 64:132A–133A.12. Puoti M, Foster G, Wang S, et al. 2017; SAT-233-High SVR rates with eight and twelve weeks of pangenotypic glecaprevir/pibrentasvir: integrated efficacy and safety analysis of genotype 1-6 patients without cirrhosis [Abstract]. J Hepatol. 66:S721. DOI: 10.1016/S0168-8278(17)31927-X.13. Gane E, Poordad F, Wang S, et al. 2016; High Efficacy of ABT-493 and ABT-530 treatment in patients with HCV genotype 1 or 3 infection and compensated cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 151:651–659. e1DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.07.020. PMID: 27456384.
Article14. Forns X, Lee SS, Valdes J, et al. 2017; Glecaprevir plus pibrentasvir for chronic hepatitis C virus genotype 1, 2, 4, 5, or 6 infection in adults with compensated cirrhosis (EXPEDITION-1): a single-arm, open-label, multicentre phase 3 trial. Lancet Infect Dis. 17:1062–1068. DOI: 10.1016/S1473-3099(17)30496-6. PMID: 28818546.
Article15. Park YJ, Woo HY, Heo J, et al. 2021; Real-life effectiveness and safety of glecaprevir/pibrentasvir for Korean patients with chronic hepatitis C at a single institution. Gut Liver. 15:440–450. DOI: 10.5009/gnl19393. PMID: 32839365. PMCID: PMC8129668.
Article16. Heo J, Kim YJ, Lee JW, et al. 2021; Efficacy and safety of glecaprevir/pibrentasvir in Korean patients with chronic hepatitis C: A pooled analysis of five phase II/III trials. Gut Liver. 15:895–903. DOI: 10.5009/gnl20321. PMID: 34053916. PMCID: PMC8593501.
Article17. Ogawa E, Nomura H, Nakamuta M, et al. 2020; Ledipasvir and sofosbuvir for 12 weeks for hepatitis C virus genotype 2 infection: A propensity score matched analysis. Hepatol Res. 50:174–181. DOI: 10.1111/hepr.13437. PMID: 31634412.
Article18. Gane EJ, Hyland RH, Yang Y, et al. 2017; Efficacy of ledipasvir plus sofosbuvir for 8 or 12 weeks in patients with hepatitis C virus genotype 2 infection. Gastroenterology. 152:1366–1371. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.01.017. PMID: 28137593.
Article19. Liu CJ, Chuang WL, Sheen IS, et al. 2018; Efficacy of ledipasvir and sofosbuvir treatment of HCV infection in patients coinfected with HBV. Gastroenterology. 154:989–997. DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.11.011. PMID: 29174546.
Article20. Asahina Y, Itoh Y, Ueno Y, et al. 2018; Ledipasvir-sofosbuvir for treating Japanese patients with chronic hepatitis C virus genotype 2 infection. Liver Int. 38:1552–1561. DOI: 10.1111/liv.13685. PMID: 29297980.
Article21. Welzel TM, Bhardwaj N, Hedskog C, et al. 2017; Global epidemiology of HCV subtypes and resistance-associated substitutions evaluated by sequencing-based subtype analyses. J Hepatol. 67:224–236. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.03.014. PMID: 28343981.
Article22. German P, Mathias A, Brainard D, Kearney BP. 2016; Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of ledipasvir/sofosbuvir, a fixed-dose combination tablet for the treatment of hepatitis C. Clin Pharmacokinet. 55:1337–1351. DOI: 10.1007/s40262-016-0397-0. PMID: 27193156.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Does the old-fashioned sofosbuvir plus ribavirin treatment in genotype 2 chronic hepatitis C patients still works for Koreans?
- Next-generation sequencing analysis of hepatitis C virus resistance–associated substitutions in direct-acting antiviral failure in South Korea
- Outcomes of Hepatitis C Virus Treatment with Ledipasvir/Sofosbuvir in Mongolian Population: Successes and Challenges Facing Scale-up of Care
- Direct Acting Antiviral Agents in Korean Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C and Hemophilia Who Are Treatment-Naïve or Treatment-Experienced
- Upcoming direct acting antivirals for hepatitis C patients with a prior treatment failure