Korean J Gastroenterol.
2024 Feb;83(2):45-53. 10.4166/kjg.2023.107.
Diagnosis and Management of Hepatic Hydrothorax
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gastroentero-Hepatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Universitas Airlangga - Dr.Soetomo Teaching Hospital, Surabaya, Indonesia
- 2Helicobacter pylori and Mycrobiota Study Group, Institute Tropical Disease, Universitas Airlangga, Surabaya, Indonesia
- KMID: 2553434
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2023.107
Abstract
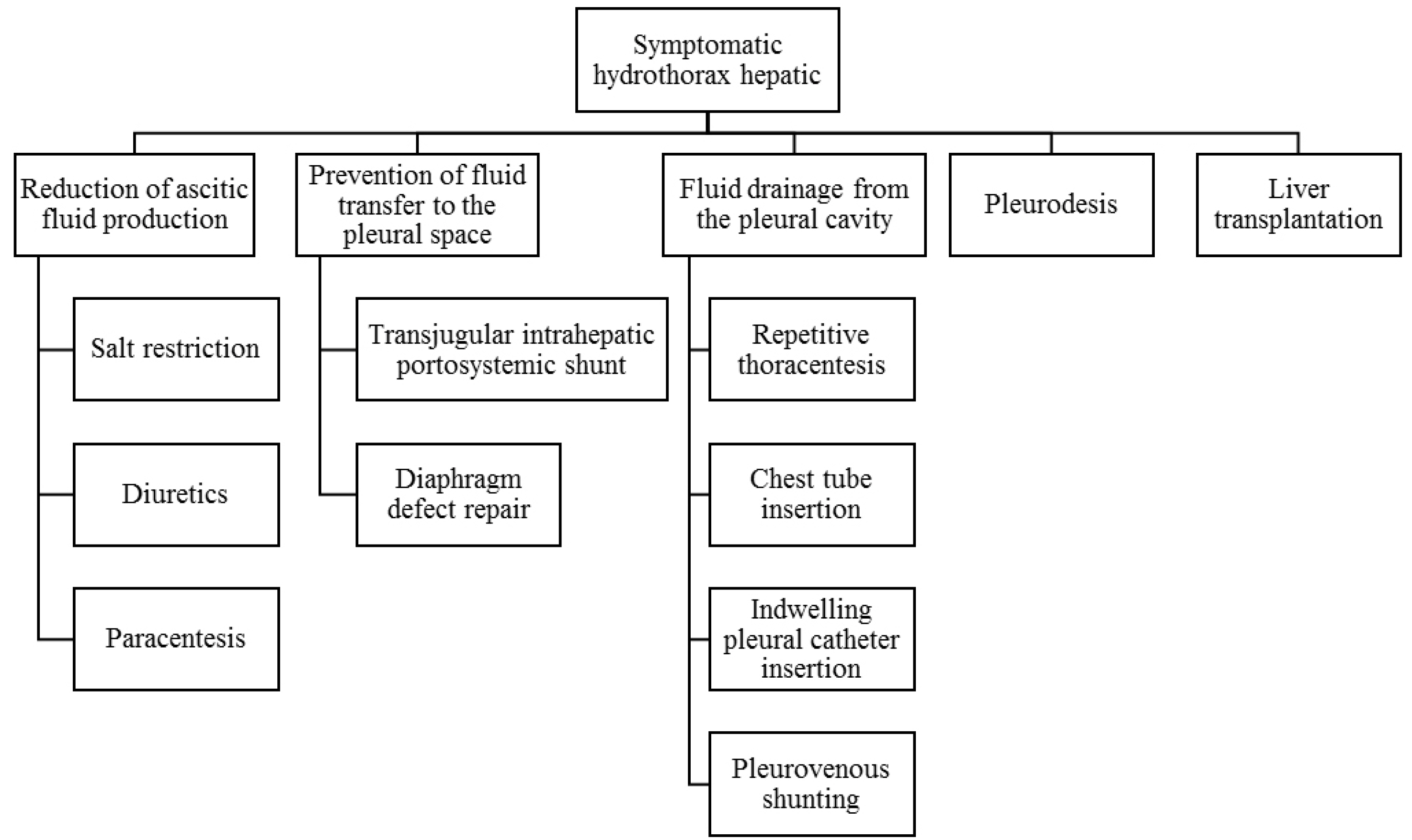
- Hepatic hydrothorax is a pleural effusion (typically ≥500 mL) that develops in patients with cirrhosis and/or portal hypertension in the absence of other causes. In most cases, hepatic hydrothorax is seen in patients with ascites. However, ascites is not always found at diagnosis and is not clinically detected in 20% of patients with hepatic hydrothorax. Some patients have no symptoms and incidental findings on radiologic examination lead to the diagnosis of the condition. In the majority of cases, the patients present with symptoms such as dyspnea at rest, cough, nausea, and pleuritic chest pain. The diagnosis of hepatic hydrothorax is based on clinical manifestations, radiological features, and thoracocentesis to exclude other etiologies such as infection (parapneumonic effusion, tuberculosis), malignancy (lymphoma, adenocarcinoma) and chylothorax. The management strategy involves a stepwise approach of one or more of the following: Reducing ascitic fluid production, preventing fluid transfer to the pleural space, fluid drainage from the pleural cavity, pleurodesis (obliteration of the pleural cavity), and liver transplantation. The complications of hepatic hydrothorax are associated with significant morbidity and mortality. The complication that causes the highest morbidity and mortality is spontaneous bacterial empyema (also called spontaneous bacterial pleuritis).
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Badillo R, Rockey DC. 2014; Hepatic hydrothorax: clinical features, management, and outcomes in 77 patients and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 93:135–142. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000000025. PMID: 24797168. PMCID: PMC4632908.2. Chaaban T, Kanj N, Bou Akl I. 2019; Hepatic hydrothorax: an updated review on a challenging disease. Lung. 197:399–405. DOI: 10.1007/s00408-019-00231-6. PMID: 31129701.
Article3. GBD 2017 Cirrhosis Collaborators. The global, regional, and national burden of cirrhosis by cause in 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020; 5:245–266. DOI: 10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30349-8. PMID: 31981519.4. Al-Zoubi RK, Abu Ghanimeh M, Gohar A, Salzman GA, Yousef O. 2016; Hepatic hydrothorax: clinical review and update on consensus guidelines. Hosp Pract (1995). 44:213–223. DOI: 10.1080/21548331.2016.1227685. PMID: 27580053.
Article5. Morrow CS, Kantor M, Armen RN. 1958; Hepatic hydrothorax. Ann Intern Med. 49:193–203. DOI: 10.7326/0003-4819-49-1-193. PMID: 13545745.
Article6. Singh A, Bajwa A, Shujaat A. 2013; Evidence-based review of the management of hepatic hydrothorax. Respiration. 86:155–173. DOI: 10.1159/000346996. PMID: 23571767.
Article7. Lechner AJ, Matuschak GM, Brink DS. 2012. Respiratory: an integrated approach to disease. McGraw Hill;New York:8. Jameson J, Fauci AS, Kasper DL, Hauser SL, Longo DL, Loscalzo J. 2018. Principles of Internal Medicine. 20th ed. McGraw Hill;New York:9. Banini BA, Alwatari Y, Stovall M, et al. Multidisciplinary management of hepatic hydrothorax in 2020: an evidence-based review and guidance. Hepatology. 2020; 72:1851–1863. DOI: 10.1002/hep.31434. PMID: 32585037.
Article10. Lv Y, Han G, Fan D. 2018; Hepatic Hydrothorax. Ann Hepatol. 17:33–46. DOI: 10.5604/01.3001.0010.7533. PMID: 29311408.
Article11. Tsao GG. Dooley JS, Lok AS, Garcia-Tsao G, Pinzani M, editors. 2018. Chapter 9 Ascites Mechanisms of ascites formation. Sherlock's Diseases of the Liver and Biliary System. 13th ed. Wiley-Blackwell;New York: p. 127–150. DOI: 10.1002/9781119237662.ch9.12. Feldmen M, Friedman LS, Brandt LJ. 2010. Sleisenger and Fordtran's Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease- 2 Volume Set: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, Management. 11th ed. Elsevier;New York:13. Pippard B, Bhatnagar M, McNeill L, Donnelly M, Frew K, Aujayeb A. 2022; Hepatic hydrothorax: a narrative review. Pulm Ther. 8:241–254. DOI: 10.1007/s41030-022-00195-8. PMID: 35751800. PMCID: PMC9458779.
Article14. Bielsa S, Porcel JM, Castellote J, Mas E, Esquerda A, Light RW. 2012; Solving the Light's criteria misclassification rate of cardiac and hepatic transudates. Respirology. 17:721–726. DOI: 10.1111/j.1440-1843.2012.02155.x. PMID: 22372660.
Article15. Yoon JH, Kim HJ, Jun CH, Cho SB, Jung Y, Choi SK. 2019; Various treatment modalities in hepatic hydrothorax: what is safe and effective? Yonsei Med J. 60:944–951. DOI: 10.3349/ymj.2019.60.10.944. PMID: 31538429. PMCID: PMC6753336.
Article16. Adams SR. Hepatic hydrothorax. Proceedings of UCLA Health. 2020; 4.17. Maghfirah DM, Abubakar A, Yusuf F. 2018; Management of ascites in hepatic cirrhosis. Nangroe Med J. 1:47–58.18. Runyon BA. AASLD Practice Guidelines Committee. 2009; Management of adult patients with ascites due to cirrhosis: an update. Hepatology. 49:2087–2106. DOI: 10.1002/hep.22853. PMID: 19475696.
Article19. European Association for the Study of the Liver. 2010; EASL clinical practice guidelines on the management of ascites, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, and hepatorenal syndrome in cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 53:397–417. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhep.2010.05.004. PMID: 20633946.20. Kandarini Y. 2015. Nutritional management in prialysis and dialysis CKD patients. USDI;Available from: https://simdos.unud.ac.id/uploads/file_penelitian_dir/c79f978ea9cf8074706ebd6237fae79d.pdf.21. Garbuzenko DV, Arefyev NO. 2017; Hepatic hydrothorax: an update and review of the literature. World J Hepatol. 9:1197–1204. DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v9.i31.1197. PMID: 29152039. PMCID: PMC5680207.
Article22. Krok KL. 2014; Hepatic hydrothorax: Current concepts. Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken). 4:35–37. DOI: 10.1002/cld.375. PMID: 30992917. PMCID: PMC6448729.
Article23. Koul A, Sood J. Vohra V, Gupta N, Jolly AS, Bhalotra S, editors. 2023. Preoperative Assessment and Optimization of Liver Transplant Patient: Ascites and Hydrothorax. Peri-operative Anesthetic Management in Liver Transplantation. Springer Nature Singapore;Singapore: p. 115–126. DOI: 10.1007/978-981-19-6045-1_9.
Article24. Gilbert CR, Shojaee S, Maldonado F, et al. 2022; Pleural interventions in the management of hepatic hydrothorax. Chest. 161:276–283. DOI: 10.1016/j.chest.2021.08.043. PMID: 34390708.
Article25. Jung Y, Song SY, Na KJ, Chon SH, Jun CH, Choi SK. 2020; Minimally invasive surgical strategy for refractory hepatic hydrothorax. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 57:881–887. DOI: 10.1093/ejcts/ezz342. PMID: 31958113.
Article26. Osman KT, Abdelfattah AM, Mahmood SK, et al. 2022; Refractory hepatic hydrothorax is an independent predictor of mortality when compared to refractory ascites. Dig Dis Sci. 67:4929–4938. DOI: 10.1007/s10620-022-07522-8. PMID: 35534742.
Article27. Ma B, Shang T, Huang J, et al. 2022; Analysis of clinical features and prognostic factors in patients with hepatic hydrothorax: a single-center study from China. BMC Gastroenterol. 22:333. DOI: 10.1186/s12876-022-02412-9. PMID: 35799114. PMCID: PMC9264701.
Article28. Mirza M, Ahmed R, Ayaz A, Manzoor K. 2023; Spontaneous bacterial empyema (SPEM) with concurrent spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP) in liver cirrhosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 207:A5023. DOI: 10.1164/ajrccm-conference.2023.207.1_MeetingAbstracts.A5023.
Article29. Lazaridis KN, Frank JW, Krowka MJ, Kamath PS. 2004; Hepatic hydrothorax: pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management. Am J Med. 107:262–267. DOI: 10.1016/S0002-9343(99)00217-X. PMID: 10492320.
Article30. Uddin MM, Regmi N, Usama M, et al. 2020; Spontaneous bacterial empyema-an underdiagnosed complication of hepatic hydrothorax. Arch Clin Med Case Rep. 5:64–69. DOI: 10.26502/acmcr.96550327.31. Tharappel KJ, Bolanthakodi N, Vidyasagar S, Varma M. 2019; Acute tension hydrothorax in chronic liver disease secondary to spontaneous diaphragmatic rupture. BMJ Case Rep. 12:e231604. DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2019-231604. PMID: 31678925. PMCID: PMC6827727.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Refractory Hepatic Hydrothorax That Was Not Treated by Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt
- A Case of the Hepatic Hydrothorax in the Absence of Ascites Confirmed by Tc-99m Macroaggregated Serum Albumin Scan
- Complete Remission of Refractory Hepatic Hydrothorax in Patient with Advanced Liver Cirrhosis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma Using Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt
- A case of hepatic hydrothorax
- Early Diagnosis of Hepatic Hydrothorax with Associated Occlusion of a Peritoneo-Venous Shunt with Tc-99m MAA