Ann Rehabil Med.
2024 Feb;48(1):42-49. 10.5535/arm.23064.
Insole Pressure Sensors to Assess Post-Stroke Gait
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Sheikh Khalifa Specialty Hospital, Ras al Khaimah, United Arab Emirates
- 2Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 3Wearable Health Lab, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Stanford University, Redwood City, CA, United States
- 4Stanford Stroke Center, Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA, United States
- KMID: 2553160
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.23064
Abstract
Objective
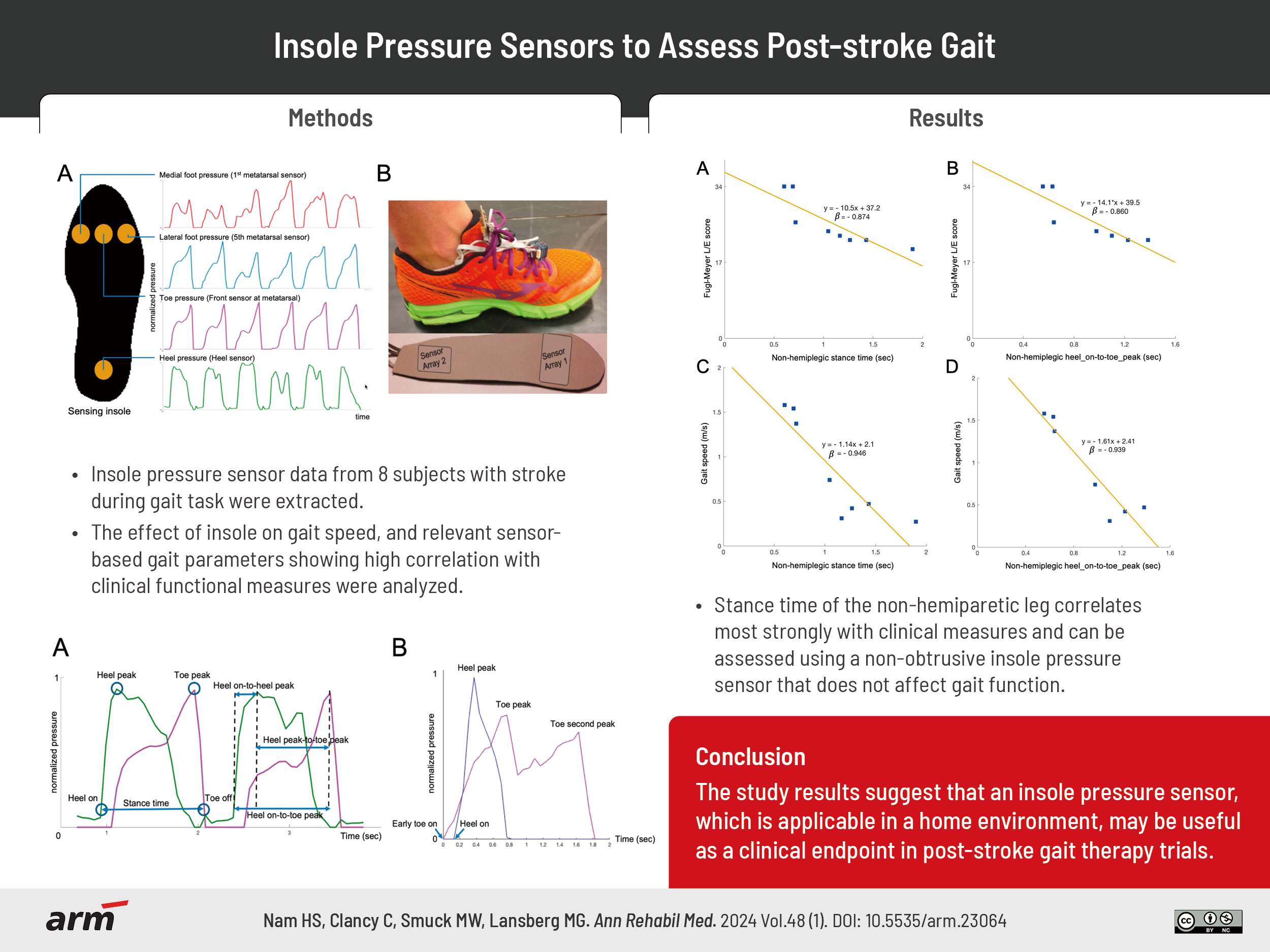
To confirm that the simplified insole does not affect the gait speed and to identify objective sensor-based gait parameters that correlate strongly with existing clinical gait assessment scales.
Methods
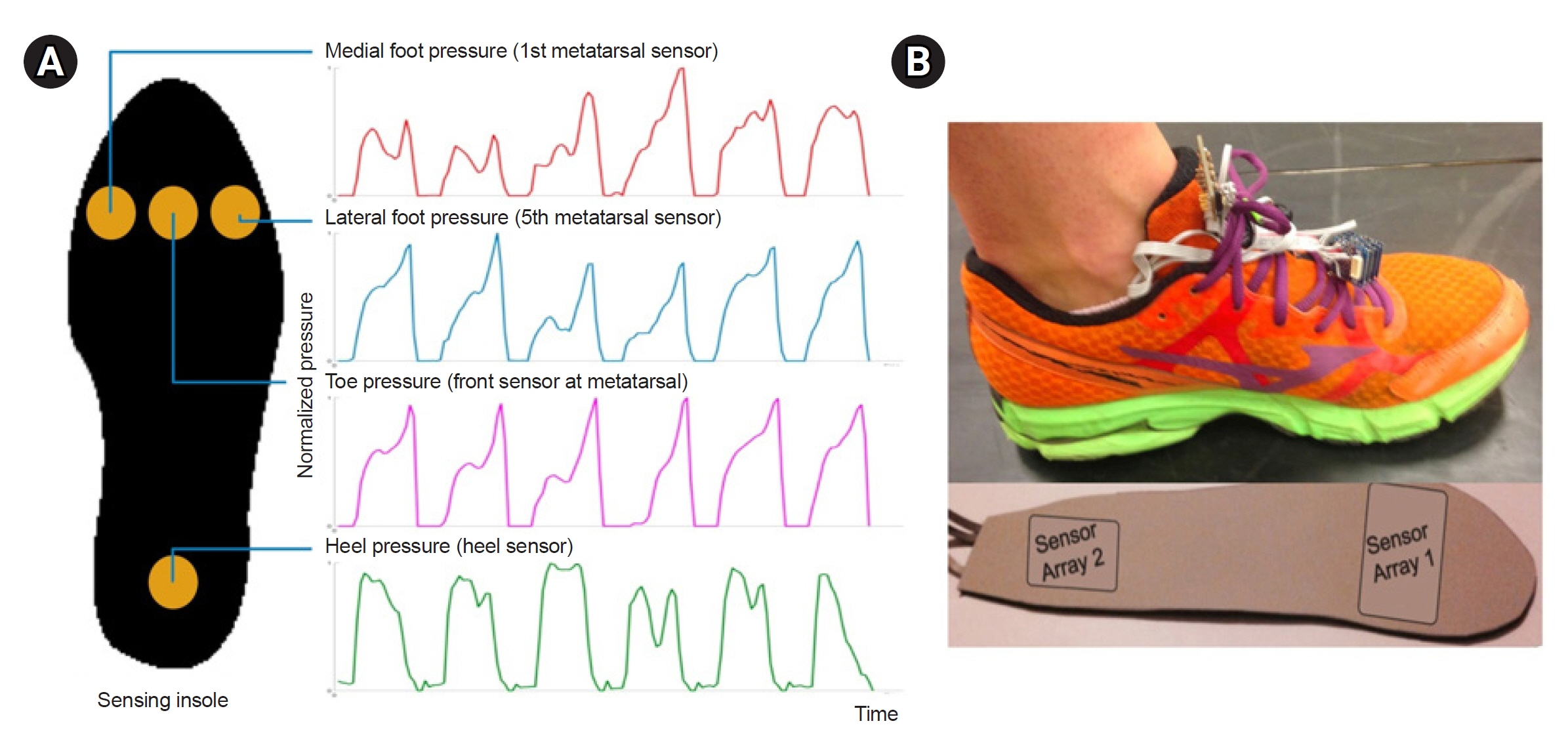
Ten participants with gait impairment due to hemiplegic stroke were enrolled in this study. Pairs of insoles with four pressure sensors on each side were manufactured and placed in each shoe. Data were extracted during the 10-Meter Walk Test. Several sensor-derived parameters (for example stance time, heel_on-to-toe_peak time, and toe_peak pressure) were calculated and correlated with gait speed and lower extremity Fugl-Meyer (F-M) score.
Results
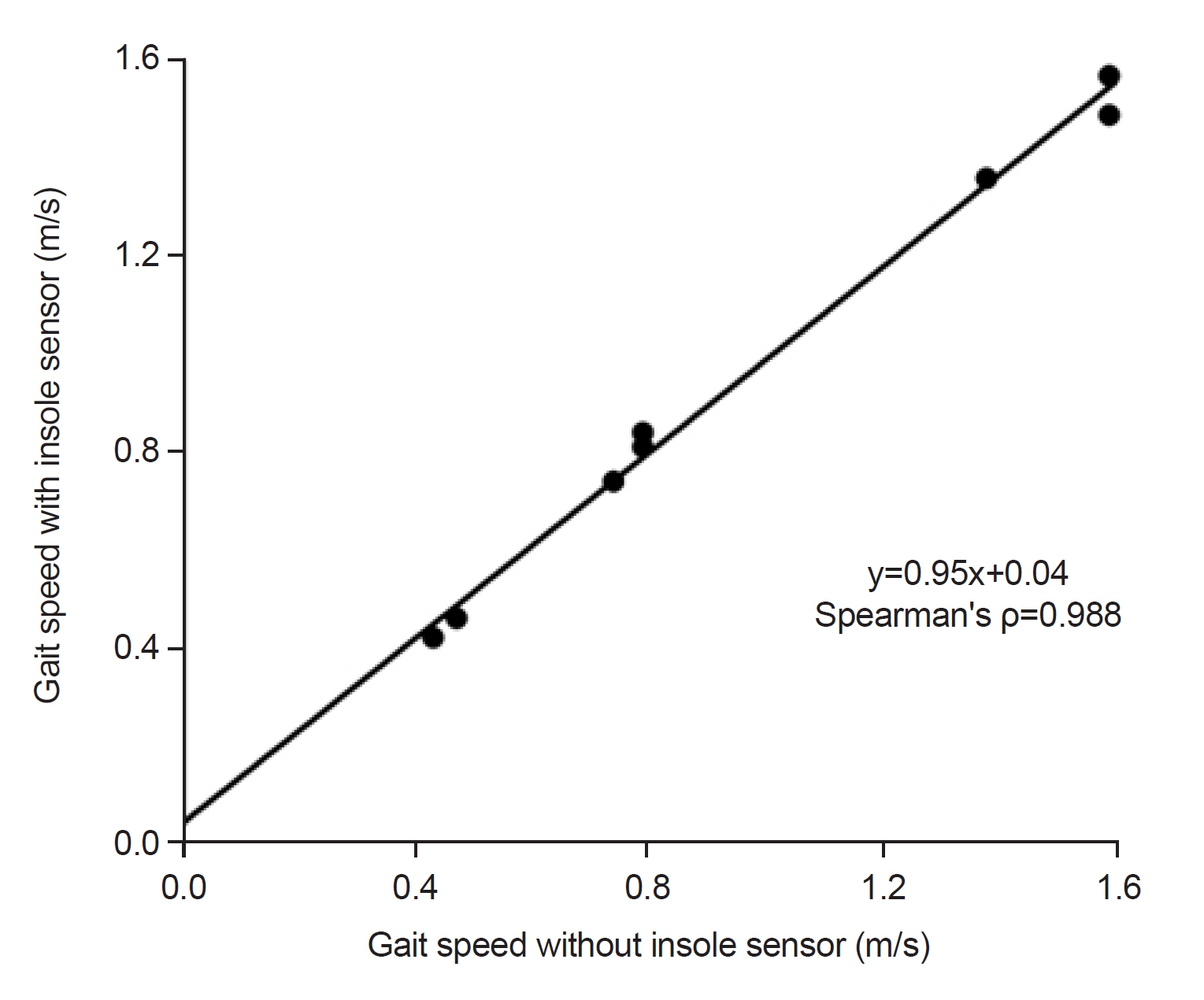
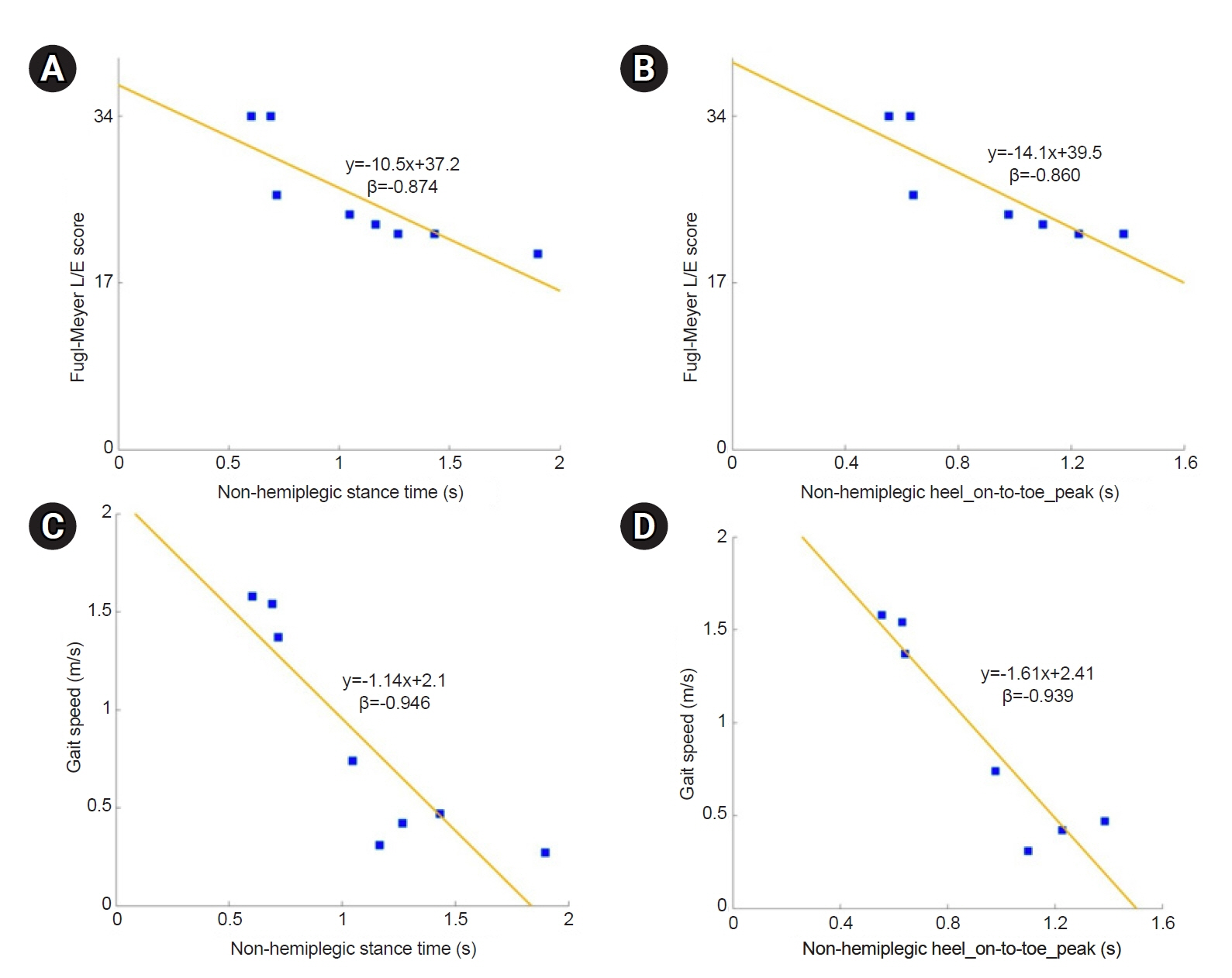
The insole pressure sensor did not affect gait, as indicated by a strong correlation (ρ=0.988) and high agreement (ICC=0.924) between the gait speeds with and without the insole. The parameters that correlated most strongly with highest β coefficients against the clinical measures were stance time of the non-hemiplegic leg (β=-0.87 with F-M and β=-0.95 with gait speed) and heel_on-to-toe_peak time of the non-hemiplegic leg (β=-0.86 with F-M and -0.94 with gait speed).
Conclusion
Stance time of the non-hemiparetic leg correlates most strongly with clinical measures and can be assessed using a non-obtrusive insole pressure sensor that does not affect gait function. These results suggest that an insole pressure sensor, which is applicable in a home environment, may be useful as a clinical endpoint in post-stroke gait therapy trials.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Benjamin EJ, Blaha MJ, Chiuve SE, Cushman M, Das SR, Deo R, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2017 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2017; 135:e146–603. Erratum in: Circulation 2017;135:e646. Erratum in: Circulation 2017;136:e196.2. Duncan PW, Zorowitz R, Bates B, Choi JY, Glasberg JJ, Graham GD, et al. Management of Adult Stroke Rehabilitation Care: a clinical practice guideline. Stroke. 2005; 36:e100–43.3. Geiger M, Supiot A, Pradon D, Do MC, Zory R, Roche N. Minimal detectable change of kinematic and spatiotemporal parameters in patients with chronic stroke across three sessions of gait analysis. Hum Mov Sci. 2019; 64:101–7.4. Graham JE, Ostir GV, Fisher SR, Ottenbacher KJ. Assessing walking speed in clinical research: a systematic review. J Eval Clin Pract. 2008; 14:552–62.5. Nagano K, Hori H, Muramatsu K. A comparison of at-home walking and 10-meter walking test parameters of individuals with post-stroke hemiparesis. J Phys Ther Sci. 2015; 27:357–9.6. Bergamini E, Iosa M, Belluscio V, Morone G, Tramontano M, Vannozzi G. Multi-sensor assessment of dynamic balance during gait in patients with subacute stroke. J Biomech. 2017; 61:208–15.7. David V, Forjan M, Martinek J, Kotzian S, Jagos H, Rafolt D. Evaluating wearable multimodal sensor insoles for motion-pattern measurements in stroke rehabilitation - a pilot study. IEEE Int Conf Rehabil Robot. 2017; 2017:1543–8.8. Munoz-Organero M, Parker J, Powell L, Mawson S. Assessing walking strategies using insole pressure sensors for stroke survivors. Sensors (Basel). 2016; 16:1631.9. Howell AM, Kobayashi T, Chou TR, Daly W, Orendurff M, Bamberg SJ. A laboratory insole for analysis of sensor placement to determine ground reaction force and ankle moment in patients with stroke. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2012; 2012:6394–7.10. Sungkarat S, Fisher BE, Kovindha A. Efficacy of an insole shoe wedge and augmented pressure sensor for gait training in individuals with stroke: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Rehabil. 2011; 25:360–9.11. Zhang W, Smuck M, Legault C, Ith MA, Muaremi A, Aminian K. Simple gait symmetry measures based on foot angular velocity: analysis in post stroke patients. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2018; 2018:5442–5.12. Sullivan KJ, Tilson JK, Cen SY, Rose DK, Hershberg J, Correa A, et al. Fugl-Meyer assessment of sensorimotor function after stroke: standardized training procedure for clinical practice and clinical trials. Stroke. 2011; 42:427–32.13. Watson MJ. Refining the ten-metre walking test for use with neurologically impaired people. Physiotherapy. 2002; 88:386–97.14. Lindemann U. Spatiotemporal gait analysis of older persons in clinical practice and research: which parameters are relevant? Z Gerontol Geriatr. 2020; 53:171–8.15. Balaban B, Tok F. Gait disturbances in patients with stroke. PM R. 2014; 6:635–42.16. Lopez-Meyer P, Fulk GD, Sazonov ES. Automatic detection of temporal gait parameters in poststroke individuals. IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed. 2011; 15:594–601.17. Guzik A, Drużbicki M, Przysada G, Kwolek A, Brzozowska-Magoń A, Wolan-Nieroda A. Analysis of consistency between temporospatial gait parameters and gait assessment with the use of Wisconsin Gait Scale in post-stroke patients. Neurol Neurochir Pol. 2017; 51:60–65.18. van Meulen FB, Weenk D, Buurke JH, van Beijnum BJ, Veltink PH. Ambulatory assessment of walking balance after stroke using instrumented shoes. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2016; 13:48.19. Błażkiewicz M, Wiszomirska I, Wit A. Comparison of four methods of calculating the symmetry of spatial-temporal parameters of gait. Acta Bioeng Biomech. 2014; 16:29–35.20. Nigg S, Vienneau J, Maurer C, Nigg BM. Development of a symmetry index using discrete variables. Gait Posture. 2013; 38:115–9.21. Rozanski GM, Wong JS, Inness EL, Patterson KK, Mansfield A. Longitudinal change in spatiotemporal gait symmetry after discharge from inpatient stroke rehabilitation. Disabil Rehabil. 2020; 42:705–11.22. Zhang W, Smuck M, Legault C, Ith MA, Muaremi A, Aminian K. Gait symmetry assessment with a low back 3D accelerometer in post-stroke patients. Sensors (Basel). 2018; 18:3322.23. McGinley JL, Morris ME, Greenwood KM, Goldie PA, Olney SJ. Accuracy of clinical observations of push-off during gait after stroke. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2006; 87:779–85.24. Nam HS, Lee WH, Seo HG, Smuck MW, Kim S. Evaluation of motion segment size as a new sensor-based functional outcome measure in stroke rehabilitation. J Int Med Res. 2022; 50:3000605221122750.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Effect of Metatarsal Pad for Foot Pressure
- Gait Training Strategy Focusing on Perceptual Learning for Improved Gait Capacity in Stroke Survivors
- The Comparison of the Peak Plantar Pressure according to Wedge Type in Osteoarthritis Patients
- Comparison of the Forefoot Pressure-Relieving Effects of Foot Orthoses
- Effect of Ankle Foot Orthosis on Hemiplegic Gait