J Korean Foot Ankle Soc.
2023 Dec;27(4):144-147. 10.14193/jkfas.2023.27.4.144.
May-Thurner Syndrome Appearing as Recurrent Swelling and Cellulitis in the Left Leg and Foot
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Daejeon St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Daejeon, Korea
- KMID: 2553007
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14193/jkfas.2023.27.4.144
Abstract
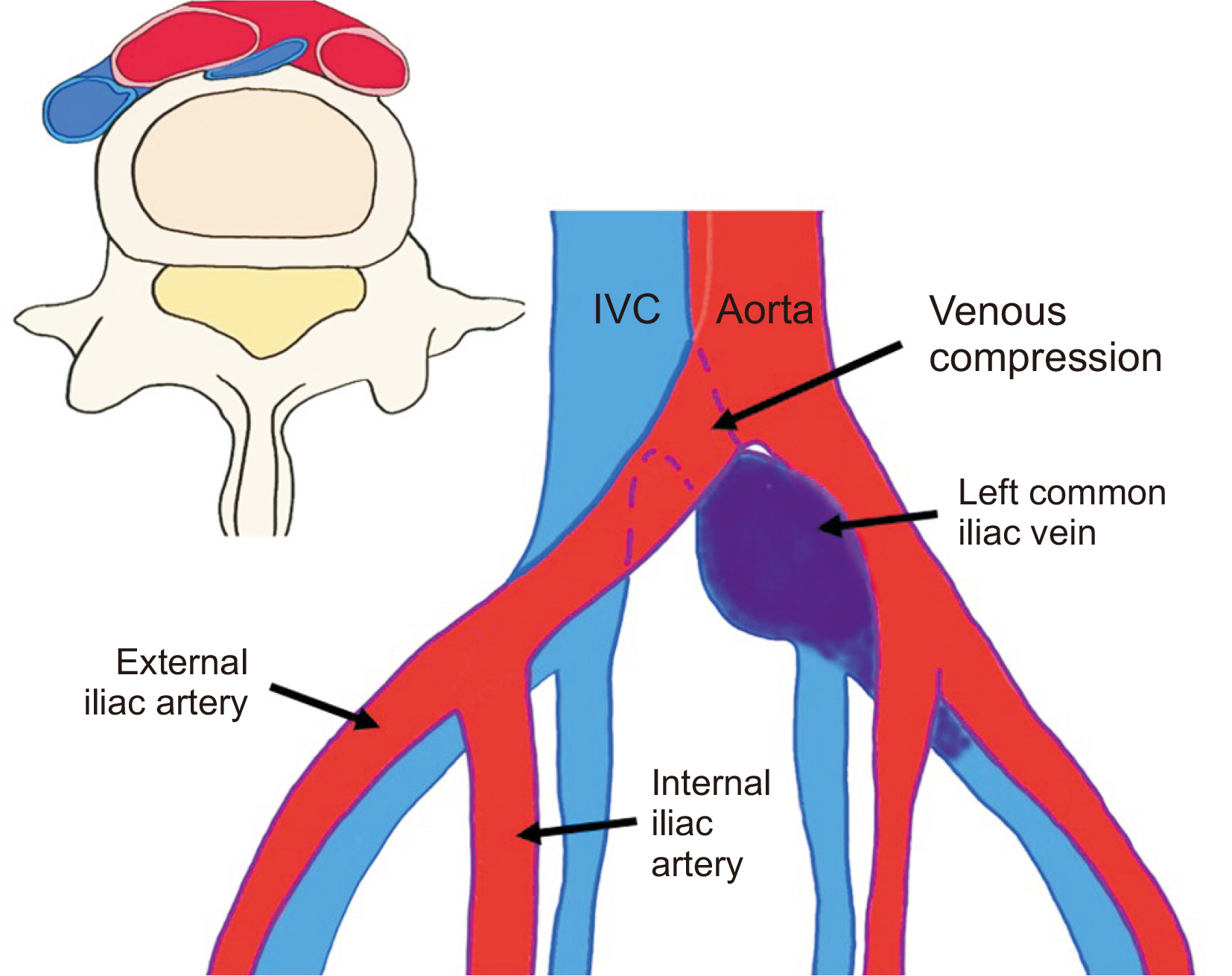
- The authors have diagnosed and treated patients with May-Thurner syndrome who presented with recurrent edema and redness in the left lower leg and foot. Although May–Thurner syndrome is a rare vascular disease, its primary symptoms manifest as edema and redness in the left lower leg and foot, leading the patients to seek foot and ankle surgery. Suspicion should be directed towards May-Thurner syndrome if an obese individual who spends prolonged periods sitting repeatedly complains of edema and redness in the left lower leg and foot area, in which a blood clot forms due to compression of the left common iliac vein within the pelvis.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. May R, Thurner J. 1957; The cause of the predominantly sinistral occurrence of thrombosis of the pelvic veins. Angiology. 8:419–27. doi: 10.1177/000331975700800505. DOI: 10.1177/000331975700800505. PMID: 13478912.
Article2. Harbin MM, Lutsey PL. 2020; May-Thurner syndrome: history of understanding and need for defining population prevalence. J Thromb Haemost. 18:534–42. doi: 10.1111/jth.14707. DOI: 10.1111/jth.14707. PMID: 31821707.
Article3. Cockett FB, Thomas ML. 1965; The iliac compression syndrome. Br J Surg. 52:816–21. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800521028. DOI: 10.1002/bjs.1800521028. PMID: 5828716.
Article4. Liddell RP, Evans NS. 2018; May-Thurner syndrome. Vasc Med. 23:493–6. doi: 10.1177/1358863X18794276. DOI: 10.1177/1358863X18794276. PMID: 30187833.
Article5. Ibrahim W, Al Safran Z, Hasan H, Zeid WA. 2012; Endovascular management of May-Thurner syndrome. Ann Vasc Dis. 5:217–21. doi: 10.3400/avd.cr.12.00007. DOI: 10.3400/avd.cr.12.00007. PMID: 23555515. PMCID: PMC3595863.
Article6. Wu WL, Tzeng WS, Wu RH, Tsai WL, Chen MC, Lin PC, et al. 2012; Comprehensive MDCT evaluation of patients with suspected May-Thurner syndrome. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 199:W638–45. doi: 10.2214/AJR.11.8040. DOI: 10.2214/AJR.11.8040. PMID: 23096209.
Article7. Berger A, Jaffe JW, York TN. 1995; Iliac compression syndrome treated with stent placement. J Vasc Surg. 21:510–4. doi: 10.1016/s0741-5214(95)70295-4. DOI: 10.1016/S0741-5214(95)70295-4. PMID: 7877235.
Article8. Park JY, Ahn JH, Jeon YS, Cho SG, Kim JY, Hong KC. 2014; Iliac vein stenting as a durable option for residual stenosis after catheter-directed thrombolysis and angioplasty of iliofemoral deep vein thrombosis secondary to May-Thurner syndrome. Phlebology. 29:461–70. doi: 10.1177/0268355513491724. DOI: 10.1177/0268355513491724. PMID: 23761876.
Article9. Vedantham S, Millward SF, Cardella JF, Hofmann LV, Razavi MK, Grassi CJ, et al. 2006; Society of Interventional Radiology. Society of Interventional Radiology position statement: treatment of acute iliofemoral deep vein thrombosis with use of adjunctive catheter-directed intrathrombus thrombolysis. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 17:613–6. doi: 10.1097/01.RVI.0000203802.35689.66. DOI: 10.1097/01.RVI.0000203802.35689.66. PMID: 16614142.
Article10. Tsai CJ, Lee CY. 2019; Comparative outcomes of catheter-directed thrombolysis plus rivaroxaban vs rivaroxaban alone in patients with acute iliofemoral deep vein thrombosis. J Chin Med Assoc. 82:902–8. doi: 10.1097/JCMA.0000000000000206. DOI: 10.1097/JCMA.0000000000000206. PMID: 31567881.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Atypical May-Thurner Syndrome Caused by Bone Spur of the L4∼5 Lumbar Vertebrae
- May–Thurner Syndrome after Total Knee Arthroplasty
- May-Thurner Syndrome with Coexisting Arteriovenous Fistula Treated Using an Endovascular Procedure
- Unilateral Left Lower Extremity Swelling after Femur Neck Fracture Surgery Related to Undiagnosed May-Thurner Syndrome
- May-Thurner Syndrome Treated with Endovascular Wall Stent