Brain Tumor Res Treat.
2024 Jan;12(1):50-57. 10.14791/btrt.2023.0050.
Temporal Analysis of Postoperative Outcomes With or Without Intraoperative Motor Evoked Potentials and Somatosensory Evoked Potentials Monitoring for Intracranial Meningioma Surgery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, St. Vincent’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2552338
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14791/btrt.2023.0050
Abstract
- Background
This study aimed to retrospectively assess results of intracranial meningioma surgery with or without intraoperative neuromonitoring (IONM) in a single institution.
Methods
Two cohorts (a historical cohort and a monitoring cohort) were collected for the analy- sis. Before IONM was introduced, a total of 107 patients underwent intracranial meningioma operation without IONM from January 2000 to December 2008 by one neurosurgeon (historical cohort). After IONM was introduced, a total of 99 patients with intracranial meningioma were operated under IONM between November 2018 and February 2023 by two neurosurgeons (monitoring cohort). A retrospective comparison was made on the complications from meningioma surgery between the two groups.
Results
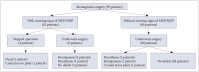
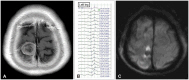
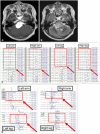
In the monitoring cohort, warning signals of motor evoked potential (MEPs) or so- matosensory evoked potential (SSEPs) were alarmed in 10 patients. Two of these 10 patients aborted the operation and eight of these 10 patients with warning signals underwent tumor resection. Of these eight patients, five showed postoperative morbidity. Five of 89 patients without warning signals developed neurological deficits. In the historical cohort, 14 of 107 patients showed postoperative morbidity or mortality.
Conclusion
Even after successful resection of intracranial meningiomas prior to the advent of IONM, integration of MEPs and SSEPs monitoring yielded valuable insights for surgical teams during operative procedures.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jung KW, Ha J, Lee SH, Won YJ, Yoo H. An updated nationwide epidemiology of primary brain tumors in Republic of Korea. Brain Tumor Res Treat. 2013; 1:16–23. PMID: 24904884.
Article2. Wiedemayer H, Fauser B, Sandalcioglu IE, Schäfer H, Stolke D. The impact of neurophysiological intraoperative monitoring on surgical decisions: a critical analysis of 423 cases. J Neurosurg. 2002; 96:255–262. PMID: 11838799.
Article3. Bello L, Comi A, Riva M, Pessina F, Alfiero T, Raneri F, et al. Glioma surgery: tailoring intraoperative neurophysiological strategies to clinical conditions enhances resection, extends indications, and keeps patient functional integrity. Neuro Oncol. 2014; 16(suppl 3):iii47.
Article4. Nossek E, Korn A, Shahar T, Kanner AA, Yaffe H, Marcovici D, et al. Intraoperative mapping and monitoring of the corticospinal tracts with neurophysiological assessment and 3-dimensional ultrasonography-based navigation: clinical article. J Neurosurg. 2011; 114:738–746. PMID: 20799862.
Article5. You H, Qiao H. Intraoperative neuromonitoring during resection of gliomas involving eloquent areas. Front Neurol. 2021; 12:658680. PMID: 34248818.
Article6. Kothbauer K, Deletis V, Epstein FJ. Intraoperative spinal cord monitoring for intramedullary surgery: an essential adjunct. Pediatr Neurosurg. 1997; 26:247–254. PMID: 9440494.7. Lall RR, Lall RR, Hauptman JS, Munoz C, Cybulski GR, Koski T, et al. Intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring in spine surgery: indications, efficacy, and role of the preoperative checklist. Neurosurg Focus. 2012; 33:E10.
Article8. Policicchio D, Ticca S, Dipellegrini G, Doda A, Muggianu G, Boccaletti R. Multimodal surgical management of cerebral lesions in motor-eloquent areas combining intraoperative 3D ultrasound with neurophysiological mapping. J Neurol Surg A Cent Eur Neurosurg. 2021; 82:344–356. PMID: 33352612.9. Bakhshi SK, Jawed N, Shafiq F, Enam SA. Awake craniotomy for resection of intracranial meningioma: first case series from a low- and middle-income country. Cureus. 2021; 13:e18716. PMID: 34790471.10. Tanaka S, Tashiro T, Gomi A, Takanashi J, Ujiie H. Sensitivity and specificity in transcranial motor-evoked potential monitoring during neurosurgical operations. Surg Neurol Int. 2011; 2:111. PMID: 21886884.
Article11. Kang D, Yao P, Wu Z, Yu L. Ischemia changes and tolerance ratio of evoked potential monitoring in intracranial aneurysm surgery. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2013; 115:552–556. PMID: 22795547.
Article12. Lee JJ, Kim YI, Hong JT, Sung JH, Lee SW, Yang SH. Intraoperative monitoring of motor-evoked potentials for supratentorial tumor surgery. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2014; 56:98–102. PMID: 25328645.
Article13. Cai Q, Wang S, Zheng M, Wang X, Liu R, Liu L, et al. Risk factors influencing cerebral venous infarction after meningioma resection. BMC Neurol. 2022; 22:259. PMID: 35831795.
Article14. Ottenhausen M, Rumalla K, Younus I, Minkowitz S, Tsiouris AJ, Schwartz TH. Predictors of postoperative motor function in rolandic meningiomas. J Neurosurg. 2018; 130:1283–1288. PMID: 29799346.
Article15. Strand PS, Sagberg LM, Gulati S, Solheim O. Brain infarction following meningioma surgery-incidence, risk factors, and impact on function, seizure risk, and patient-reported quality of life. Neurosurg Rev. 2022; 45:3237–3244. PMID: 35902426.
Article16. Magill ST, Nguyen MP, Aghi MK, Theodosopoulos PV, Villanueva-Meyer JE, McDermott MW. Postoperative diffusion-weighted imaging and neurological outcome after convexity meningioma resection. J Neurosurg. 2021; 135:1008–1015. PMID: 33513570.
Article17. Nakase H, Shin Y, Nakagawa I, Kimura R, Sakaki T. Clinical features of postoperative cerebral venous infarction. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2005; 147:621–626. PMID: 15770350.
Article18. Dützmann S, Geßler F, Bink A, Quick J, Franz K, Seifert V, et al. Risk of ischemia in glioma surgery: comparison of first and repeat procedures. J Neurooncol. 2012; 107:599–607. PMID: 22249690.
Article19. Umemura T, Nishizawa S, Nakano Y, Saito T, Kitagawa T, Miyaoka R, et al. Intraoperative monitoring of motor-evoked potential for parenchymal brain tumor removal: an analysis of false-negative cases. J Clin Neurosci. 2018; 57:105–110. PMID: 30145081.
Article20. Cabraja M, Stockhammer F, Mularski S, Suess O, Kombos T, Vajkoczy P. Neurophysiological intraoperative monitoring in neurosurgery: aid or handicap? An international survey. Neurosurg Focus. 2009; 27:E2.21. Ostrý S, Netuka D, Beneš V. Rolandic area meningioma resection controlled and guided by intraoperative cortical mapping. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2012; 154:843–853. PMID: 22426820.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Intraoperative Neurophysiological Monitoring for Spinal Cord Tumor Surgery: Comparison of Motor and Somatosensory Evoked Potentials According to Tumor Types
- Monitoring of Motor and Somatosensory Evoked Potentials During Spine Surgery: Intraoperative Changes and Postoperative Outcomes
- Intraoperative Neurophysiologic Monitoring: Basic Principles and Recent Update
- Intraoperative Monitoring for Tethered Cord Syndrome Using Somatosensory Evoked Potential and Motor Evoked Potential: Report of three cases
- Intraoperative monitoring of somatosensory and visual evoked potentials for detecting posterior cerebral artery infarction during anteromesial temporal resection