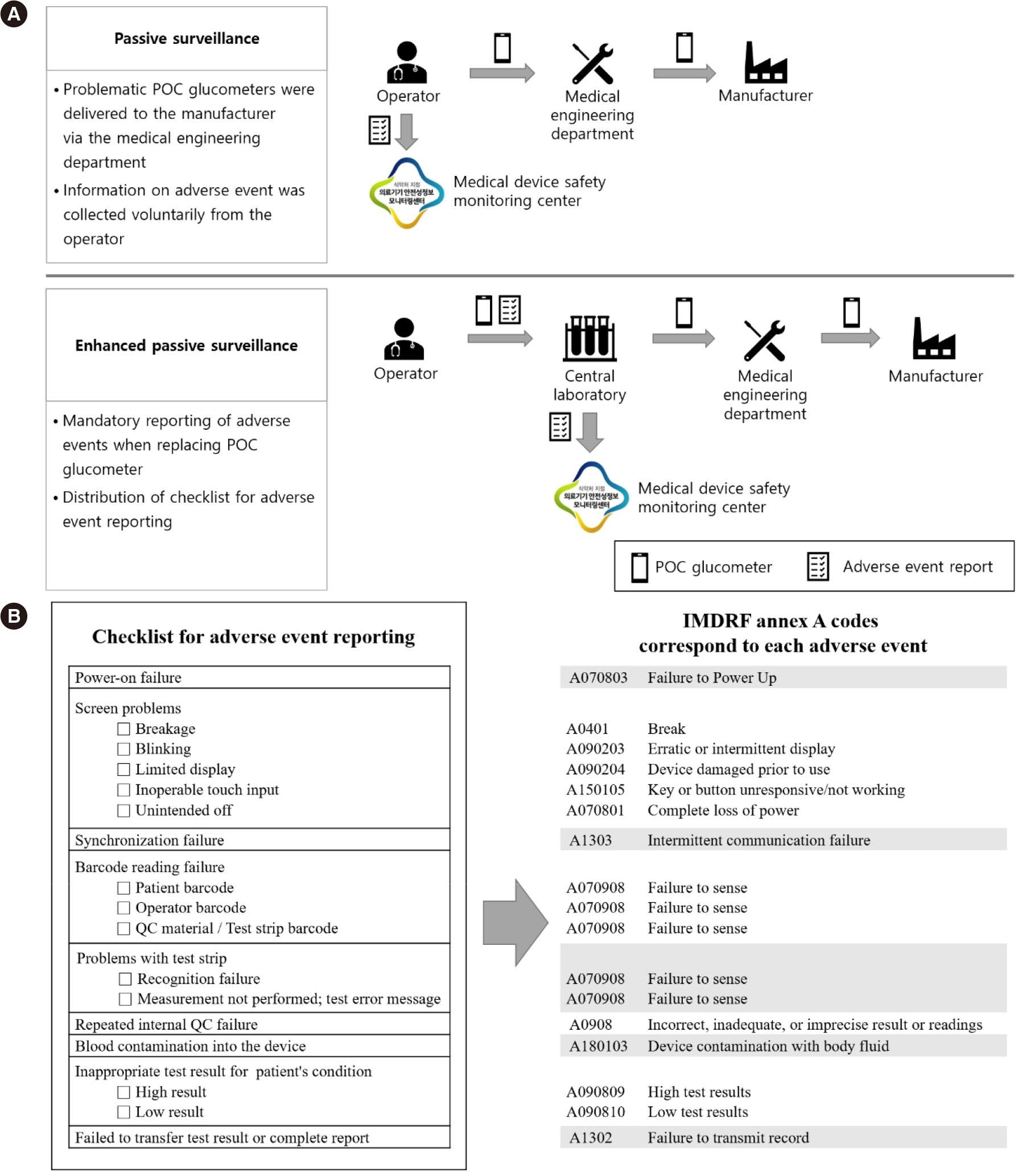
Ann Lab Med.
2023 Sep;43(5):515-519. 10.3343/alm.2023.43.5.515.
Real-World Evidence of Point-of-Care Glucometers: Enhanced Passive Surveillance and Adverse Event Reporting Status in Korea and the United States
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine and Genetics, Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Bucheon, Korea
- 2Soonchunhyang Medical Devices Clinical Research Center, Soonchunhyang University, Asan, Korea
- 3Division of Nephrology, Department of Internal Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Bucheon, Korea
- KMID: 2552002
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2023.43.5.515
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Effectiveness of Unified Computerized Reporting of Point-of-Care Glucose Meter Test
Sooin Choi, Dughyun Choi, Soo Jeong Choi, Jin Kuk Kim, You Kyoung Lee, Yong-Wha Lee
Ann Lab Med. 2024;44(1):103-106. doi: 10.3343/alm.2024.44.1.103.
Reference
-
1. Choi S, Choi SJ, Jeon BR, Lee YW, Oh J, Lee YK. 2021; What we should consider in point of care blood glucose test; current quality management status of a single institution. Medicina (Kaunas). 57:238. DOI: 10.3390/medicina57030238. PMID: 33806620. PMCID: PMC8001912.
Article2. Klonoff DC. 2014; Point-of-care blood glucose meter accuracy in the hospital setting. Diabetes Spectr. 27:174–9. DOI: 10.2337/diaspect.27.3.174. PMID: 26246776. PMCID: PMC4523734.
Article3. Klonoff DC, Parkes JL, Kovatchev BP, Kerr D, Bevier WC, Brazg RL, et al. 2018; Investigation of the accuracy of 18 marketed blood glucose monitors. Diabetes Care. 41:1681–8. DOI: 10.2337/dc17-1960. PMID: 29898901.
Article4. Pfützner A, Demircik F, Kirsch V, Pfützner J, Strobl S, Hanna M, et al. 2019; System accuracy assessment of a blood glucose meter with wireless internet access associated with unusual hypoglycemia patterns in clinical trials. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 13:507–13. DOI: 10.1177/1932296819841353. PMID: 30974985. PMCID: PMC6501533.
Article5. Tau N, Shepshelovich D. 2020; Assessment of data sources that support US Food and Drug Administration medical devices safety communications. JAMA Intern Med. 180:1420–6. DOI: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.3514. PMID: 32986074. PMCID: PMC7522775.
Article6. de Lusignan S, Ferreira F, Damaso S, Byford R, Pathirannehelage S, Yeakey A, et al. 2019; Enhanced passive surveillance of influenza vaccination in England, 2016-2017- an observational study using an adverse events reporting card. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 15:1048–59. DOI: 10.1080/21645515.2019.1565258. PMID: 30648923. PMCID: PMC6605873.
Article7. Schroeder LF, Giacherio D, Gianchandani R, Engoren M, Shah NH. 2016; Postmarket surveillance of point-of-care glucose meters through analysis of electronic medical records. Clin Chem. 62:716–24. DOI: 10.1373/clinchem.2015.251827. PMID: 26988586.
Article8. Resnic FS, Normand SL. 2012; Postmarketing surveillance of medical devices--filling in the gaps. N Engl J Med. 366:875–7. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMp1114865. PMID: 22332950.
Article9. International Medical Device Regulators Forum. Terminologies for categorized adverse event reporting (AER): terms, terminology structure and codes. https://www.imdrf.org/documents/terminologies-categorized-adverse-event-reporting-aer-terms-terminology-and-codes. Updated on Apr 2020.10. Choi S, Choi SJ, Kim JK, Lee J, Lee YK. 2022; Adverse events associated with the use of leukocyte reduction filters and blood transfusion sets: experience of a single institute in Korea and status of adverse event reporting in Korea and the United States. Korean J Blood Transfus. 33:161–70. DOI: 10.17945/kjbt.2022.33.3.161.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Identifying the Patterns of Adverse Drug Responses of Cetuximab
- Reactogenicity to COVID-19 vaccination in the United States of America
- Recent Trends in Real-World Data Access, Linkage and Validation of the United States, Europe, and South Korea and Further Recommendations for South Korea
- An evaluation of the Manufacturer And User Facility Device Experience database that inspired the United States Food and Drug Administration's Reclassification of transvaginal mesh
- Current Status and Future Directions of Digital Therapeutics for Insomnia