Ann Lab Med.
2023 May;43(3):273-279. 10.3343/alm.2023.43.3.273.
Collaborative Study to Establish National Reference Standards for Anti-HIV-1 Antibody
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Ewha Womans University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, Sanggye Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 4Department of Laboratory Medicine, National Health Insurance Service Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea
- 5Laboratory Medicine, Biobank Team, Institut Pasteur Korea, Seongnam, Korea
- KMID: 2551711
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2023.43.3.273
Abstract
- Background
National reference standards for anti-HIV-1 antibody are needed to evaluate the performance and maintain the quality control of anti-HIV-1 antibody assays. The aim of this study was to prepare a mixed-titer performance panel and assess its suitability as a national reference standard for anti-HIV-1 antibody according to stability, collaboration, and other studies.
Methods
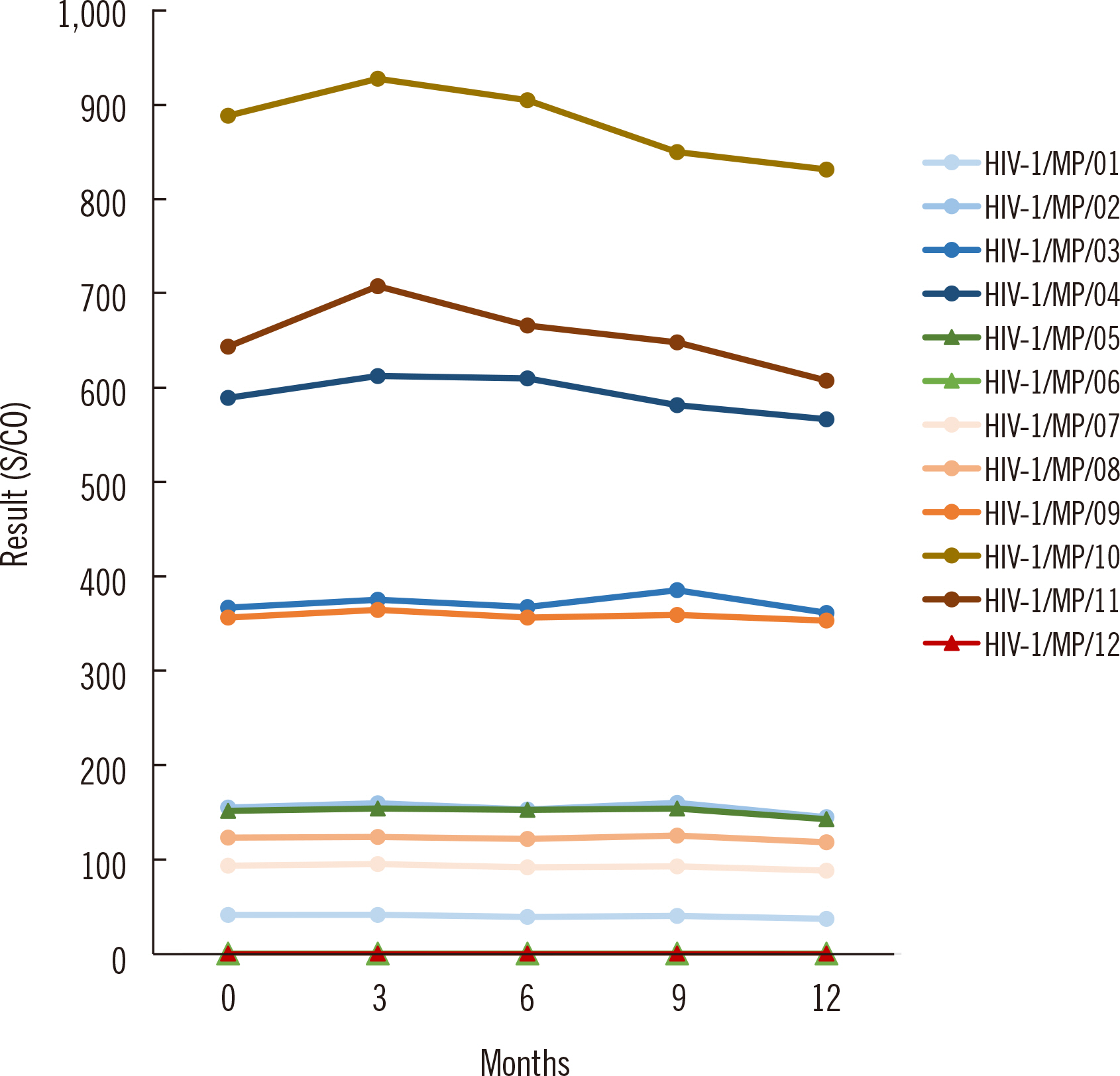
Nineteen serum samples from different HIV patients were obtained, along with 15 units of fresh frozen plasma samples with negative anti-HIV-1 antibody results. Ten anti-HIV-1 antibody-positive candidate standards and two negative candidate standards were prepared based on the reactivity in the Alinity i HIV Ag/Ab combo assay (Abbott Laboratories, Wiesbaden, Germany). A collaborative study was conducted across eight laboratories using five anti-HIV-1 antibody assays. Real-time and accelerated stability were evaluated to assess the long-term stability.
Results
In the collaborative study, results of all five anti-HIV-1 antibody assays were positive for all 10 candidate standards prepared using HIV patient samples. The CV of each assay for every candidate standard was within 10%, except for one assay result. No real-time and accelerated stability change trend was observed at −70°C or −20°C, supporting that the reference standards were maintained in a stable state at −70°C for long-term storage.
Conclusions
The overall results suggest that the 12 candidate standards could serve as national reference standards for anti-HIV-1 antibody.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. WHO. Latest HIV estimates and updates on HIV policies uptake 2021. https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/hq-hiv-hepatitis-and-stis-library/2021_global_summary_web_v32.pdf?sfvrsn=4b8815ad_30. Updated on Mar 2022.2. Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency. Annual report on the notified HIV/AIDS in Korea 2020. http://www.kdca.go.kr/filepath/boardDownload.es?bid=0031&list_no=717120&seq=1. Updated on Mar 2022.3. Korean Association of External Quality Assessment Service. Annual report on external quality assessment 2021. https://keqas.org/. Updated on Mar 2022.4. List of Ministry of Food and Drug Safety Reference Standards. http://www.nifds.go.kr/brd/m_212/view.do?seq=18700&srchFr=&srchTo=&srchWord=&srchTp=&itm_seq_1=0&itm_seq_2=0&multi_itm_seq=0& company_cd=&company_nm=&page=6. Updated on Sep 2022.5. ISO. 2017. ISO Guide 35:2017. Reference materials-Guidance for characterization and assessment of homogeneity and stability. International Organization for Standardization;Switzerland: https://www.iso.org/standard/60281.html. Updated on Sep 2022.6. WHO. 2006. Recommendations for the preparation, characterization and establishment of international and other biological reference standards (revised 2004). Technical Report Series; No. 932, Annex 2. World Health Organization;Switzerland: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/annex2-trs932. Updated on Sep 2022.7. Castro AR, Kikkert SE, Fears MB, Pope V. 2002; Defibrination of blood plasma for use in serological tests for syphilis. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 9:1376–8. DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.9.6.1376-1378.2002. PMID: 12414778. PMCID: PMC130115.
Article8. CLSI. 2009. Evaluation of stability of in vitro diagnostic reagents; approved guideline. CLSI EP25-A. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;Wayne, PA:9. Korean Ministry of Food and Drug Safety. Guidebook on Ministry of Food and Drug Safety reference standards, 2022. https://www.nifds.go.kr/brd/m_212/view.do?seq=33133&srchFr=&srchTo=&srchWord=&srchTp=&itm_seq_1=0&itm_seq_2=0&multi_itm_seq=0&company_cd=&company_nm=&page=4. Updated on Sep 2022.10. Stone M, Bainbridge J, Sanchez AM, Keating SM, Pappas A, Rountree W, et al. 2018; Comparison of detection limits of fourth- and fifth-generation combination HIV antigen-antibody, p24 antigen, and viral load assays on diverse HIV isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 56:e02045–17. DOI: 10.1128/JCM.02045-17. PMID: 29793968. PMCID: PMC6062817.
Article11. Park YH, Roh JH, Kim SY. 2022; Performance evaluation of the Aptima assays in comparison with the cobas 6800 assays for the detection of HIV-1, HBV, and HCV in clinical samples. Ann Lab Med. 42:447–56. DOI: 10.3343/alm.2022.42.4.447. PMID: 35177565. PMCID: PMC8859551.
Article12. Yang YC, Yang-Chih Shih D, Tsai MH, Cheng CH, Cheng HF, Lo CF, et al. 2013; A collaborative study to establish the first National Standard for HIV-1 RNA nucleic acid amplification techniques (NAT) in Taiwan. J Virol Methods. 191:122–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2013.04.002. PMID: 23608407.
Article13. World Health Organization & WHO Expert Committee on Biological Standardization. 2016. Collaborative study to evaluate the proposed WHO 4th international standard for hepatitis B virus (HBV) DNA for nucleic acid amplification technique (NAT) based assays. World Health Organization;Geneva, Switzerland: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/253052/WHO-BS-2016.2291-eng.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y. Updated on Sep 2022.14. World Health Organization & WHO Expert Committee on Biological Standardization. WHO/BS.2020.2403. Establishment of the WHO International Standard and Reference Panel for anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody. https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/WHO-BS-2020.2403. Updated on Nov 2022.15. Park TJ, Choi CW, Oh HK, Kim JO, Kim BK, Kang HK, et al. 2017; Stability evaluation of national reference standards for blood products in Korea. Toxicol Res. 33:225–31. DOI: 10.5487/TR.2017.33.3.225. PMID: 28744354. PMCID: PMC5523560.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evaluation of a simultaneous HIV antigen and antibody detection test in Korean population
- Long-Term Stability of HBV, HCV, and HIV-1 National Reference Standards for in vitro Diagnostic Medical Devices Intended to Be Used for the Nucleic Acid Amplification Test
- Experience of the Use of Three Screening Kits, Enzygnost Anti-HIV1/2 Plus, ABBOTT TESTPACK HIV- 1/HIV-2 & SERODIA. HIV- 1/2 for the Detection of Antibodies to HIV
- New Development of Anti-HIV Drugs
- Establishment and Multicenter Evaluation of a National Reference Panel for Syphilis Antibodies in Korea