Ann Lab Med.
2023 May;43(3):263-272. 10.3343/alm.2023.43.3.263.
Virulence-associated Genome Sequences of Pasteurella canis and Unique Toxin Gene Prevalence of P. canis and Pasteurella multocida Isolated from Humans and Companion Animals
- Affiliations
-
- 1Laboratory of Infectious Diseases, Graduate School of Infection Control Sciences & Ōmura Satoshi Memorial Institute, Kitasato University, Tokyo, Japan
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Division of Clinical Laboratory, Sanritsu Zelkova Veterinary Laboratory, Tokyo, Japan
- 4Division of Clinical Laboratory, Sanritsu Laboratory, Chiba, Japan
- 5Department of Clinical Laboratory, Chiba Kaihin Municipal Hospital, Chiba, Japan
- KMID: 2551710
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2023.43.3.263
Abstract
- Background
Comparative analysis of virulence factors (VFs) between Pasteurella canis and Pasteurella multocida are lacking, although both cause zoonotic infections. We determined the virulence-associated genome sequence characteristics of P. canis and assessed the toxin gene prevalence unique to P. canis among clinical isolates of P. canis and P. multocida.
Methods
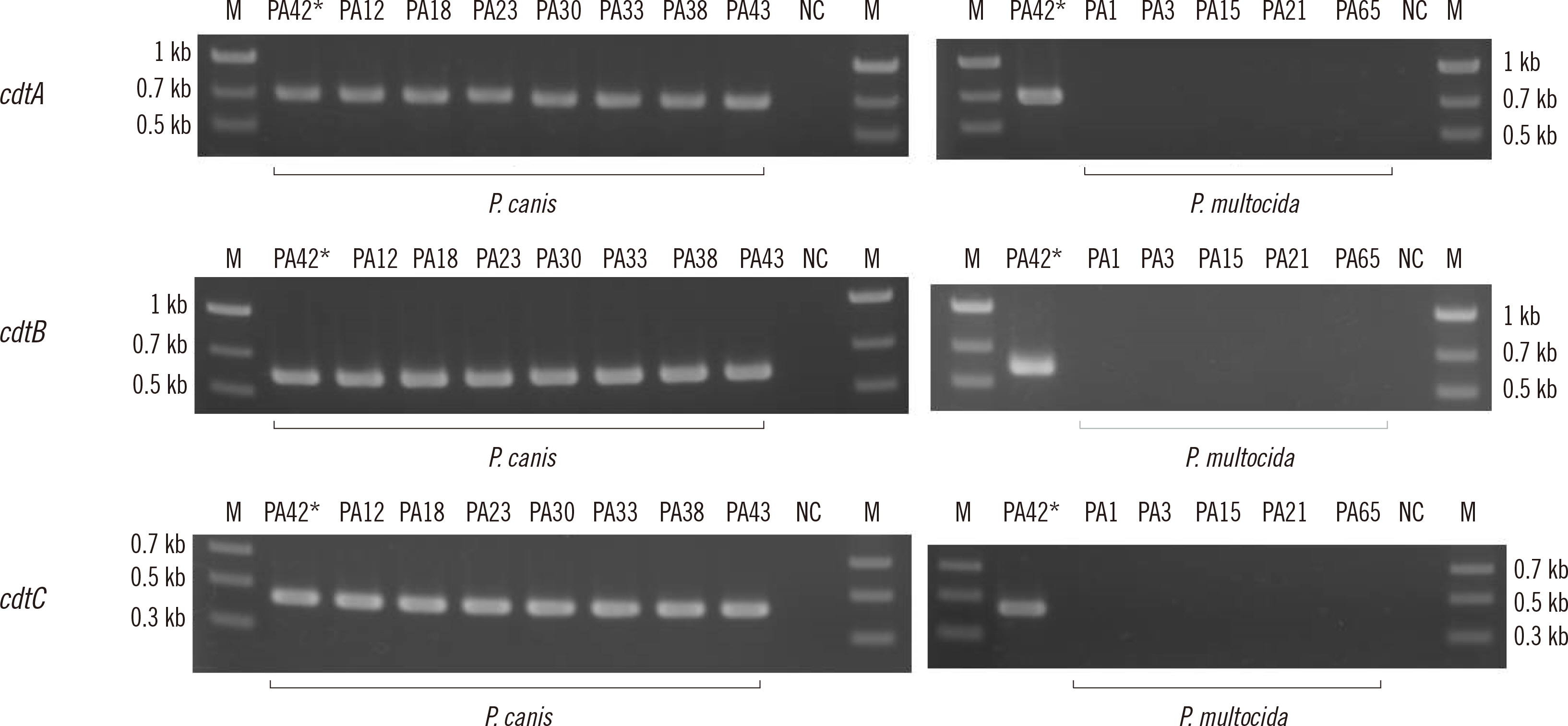
We selected 10 P. canis and 16 P. multocida whole-genome sequences (WGSs) from the National Center for Biotechnology database. The VFanalyzer tool was used to estimate P. canis-characteristic VFs. Amino acid sequences of VFs were compared with multiple-aligned sequences. The genome structure containing P. canis-characteristic and adjacent loci was compared to the corresponding P. multocida genome structure. After designing primer sequences and assessing their accuracy, we examined the gene prevalence of the P. canis-characteristic VFs using PCR among clinical isolates of P. multocida and P. canis.
Results
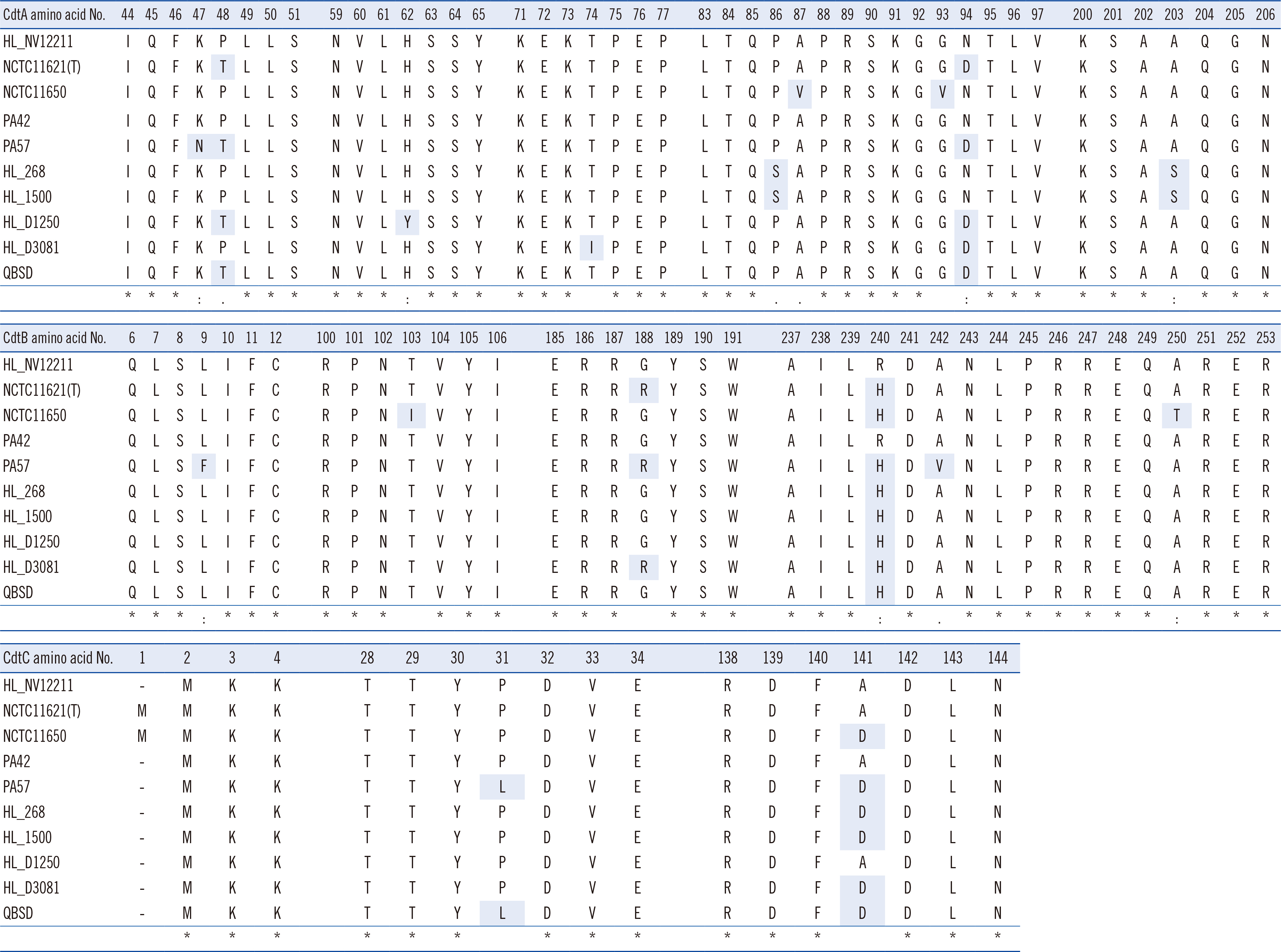
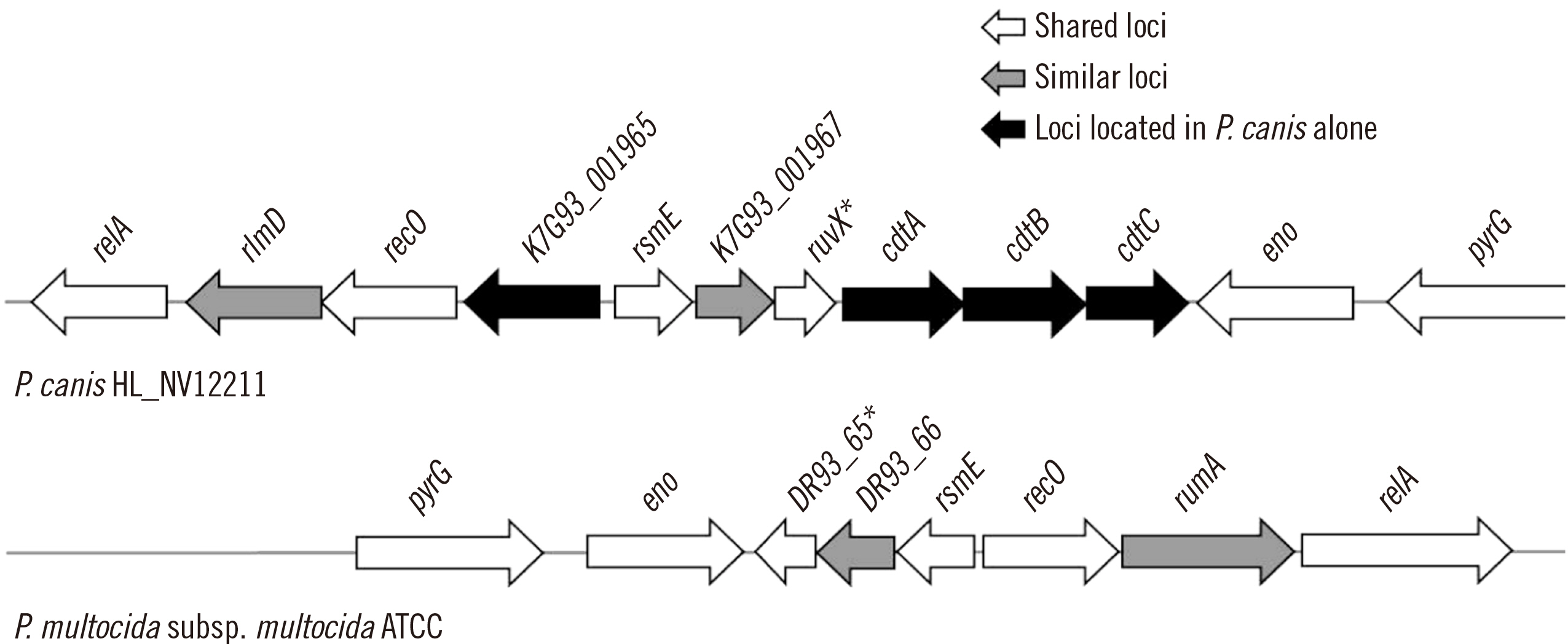
Using VFanalyzer, we found virulence-associated cytolethal distending toxin (cdt)A–cdtB–cdtC loci common to all P. canis WGSs that were not found in P. multocida WGSs. Similarities in the multiple alignments of CdtA–CdtB–CdtC amino acid sequences were found among the 10 P. canis WGSs. Shared or similar loci around cdtA–cdtB–cdtC were identified between the P. canis and P. multocida genome structures. The PCR-based cdtA–cdtB–cdtC prevalence differed for P. canis and P. multocida clinical isolates.
Conclusions
P. canis-specific cdtA–cdtB–cdtC prevalence was identified among clinical isolates. These three loci may be unique toxin genes and promising targets for the rapid identification of P. canis in clinical settings.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Comparative Genomic Analysis of Staphylococcal Cassette Chromosome
mec Type VStaphylococcus aureus Strains and Estimation of the Emergence of SCCmec V Clinical Isolates in Korea
Takashi Takahashi, Hyaekang Kim, Han-Sung Kim, Hyun Soo Kim, Wonkeun Song, Jae-Seok Kim
Ann Lab Med. 2024;44(1):47-55. doi: 10.3343/alm.2024.44.1.47.Establishment of a Multilocus Sequence Typing Scheme for
Pasteurella canis Using Isolates from Infected Humans and Diseased Companion Animals
Haruno Yoshida, Jae-Seok Kim, Takahiro Maeda, Mieko Goto, Yuzo Tsuyuki, Kenichi Shizuno, Takashi Takahashi
Ann Lab Med. 2025;45(3):300-311. doi: 10.3343/alm.2024.0501.
Reference
-
1. Mutters R, Ihm P, Pohl S, Frederiksen W, Mannheim W. 1985; Reclassification of the genus Pasteurella Trevisan 1887 on the basis of deoxyribonucleic acid homology, with proposals for the new species Pasteurella dagmatis, Pasteurella canis, Pasteurella stomatis, Pasteurella anatis, and Pasteurella langaa. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 35:309–22. DOI: 10.1099/00207713-35-3-309.2. Maeda T, Yoshida H, Kim JM, Tsuyuki Y, Kurita G, Kim JS, et al. 2022; Draft genome sequence of blood-origin Pasteurella canis strain PA42, isolated from a dog in Japan. Microbiol Resour Announc. 11:e0026022. DOI: 10.1128/mra.00260-22. PMID: 35638811. PMCID: PMC9302189.
Article3. Gautier AL, Dubois D, Escande F, Avril JL, Trieu-Cuot P, Gaillot O. 2005; Rapid and accurate identification of human isolates of Pasteurella and related species by sequencing the sodA gene. J Clin Microbiol. 43:2307–14. DOI: 10.1128/JCM.43.5.2307-2314.2005. PMID: 15872260. PMCID: PMC1153776.
Article4. Albert TJ, Stevens DL. 2010; The first case of Pasteurella canis bacteremia: a cirrhotic patient with an open leg wound. Infection. 38:483–5. DOI: 10.1007/s15010-010-0040-1. PMID: 20623245.
Article5. Kim B, Pai H, Lee KH, Lee Y. 2016; Identification of Pasteurella canis in a soft tissue infection caused by a dog bite: the first report in Korea. Ann Lab Med. 36:617–9. DOI: 10.3343/alm.2016.36.6.617. PMID: 27578520. PMCID: PMC5011120.
Article6. Shah A, Talati M, Mauger T. 2017; Medical and surgical management of Pasteurella canis infectious keratitis. IDCases. 9:42–4. DOI: 10.1016/j.idcr.2017.05.012. PMID: 28660128. PMCID: PMC5479940.
Article7. Bhat S, Acharya PR, Biranthabail D, Rangnekar A, Shiragavi S. 2015; A case of lower respiratory tract infection with canine-associated Pasteurella canis in a patient with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Clin Diagn Res. 9:DD03–4. DOI: 10.7860/JCDR/2015/13900.6351. PMID: 26435948. PMCID: PMC4576539.8. Hazelton BJ, Axt MW, Jones CA. 2013; Pasteurella canis osteoarticular infections in childhood: review of bone and joint infections due to pasteurella species over 10 years at a tertiary pediatric hospital and in the literature. J Pediatr Orthop. 33:e34–8. DOI: 10.1097/BPO.0b013e318287ffe6. PMID: 23482278.9. Hara H, Ochiai T, Morishima T, Arashima Y, Kumasaka K, Kawano KY. 2002; Pasteurella canis osteomyelitis and cutaneous abscess after a domestic dog bite. J Am Acad Dermatol. 46(S5):S151–2. DOI: 10.1067/mjd.2002.106350. PMID: 12004298.10. Mensah-Glanowska P, Fornagiel S, Chrzan R, Ulatowska-Białas M, Piątkowska-Jakubas B. 2020; Of horses and zebras: a gastrointestinal infection with Pasteurella canis in a patient with acute myeloid leukemia. Pol Arch Intern Med. 130:335–7. DOI: 10.20452/pamw.15142. PMID: 31933489.11. Hannouille J, Belgrado JP, Vankerchove S, Vandermeeren L. 2019; Breast implant infection with Pasteurella canis: first case-report. JPRAS Open. 21:86–8. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpra.2019.07.006. PMID: 32158890. PMCID: PMC7061584.
Article12. Castellano I, Marín JP, Gallego S, Mora M, Rangel G, Suarez MA, et al. 2011; Pasteurella canis peritonitis in a peritoneal dialysis patient. Perit Dial Int. 31:503–4. DOI: 10.3747/pdi.2011.00007. PMID: 21799062.
Article13. Talan DA, Citron DM, Abrahamian FM, Moran GJ, Goldstein EJ. 1999; Bacteriologic analysis of infected dog and cat bites. Emergency Medicine Animal Bite Infection Study Group. N Engl J Med. 340:85–92. DOI: 10.1056/NEJM199901143400202. PMID: 9887159.
Article14. Liu B, Zheng D, Jin Q, Chen L, Yang J. VFDB 2019: a comparative pathogenomic platform with an interactive web interface. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019; 47:D687–92. DOI: 10.1093/nar/gky1080. PMID: 30395255. PMCID: PMC6324032.
Article15. Liu B, Zheng D, Zhou S, Chen L, Yang J. VFDB 2022: a general classification scheme for bacterial virulence factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022; 50:D912–7. DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkab1107. PMID: 34850947. PMCID: PMC8728188.
Article16. Takahashi T, Maeda T, Lee S, Lee DH, Kim S. 2020; Clonal distribution of clindamycin-resistant erythromycin-susceptible (CRES) Streptococcus agalactiae in Korea based on whole genome sequences. Ann Lab Med. 40:370–81. DOI: 10.3343/alm.2020.40.5.370. PMID: 32311850. PMCID: PMC7169627.
Article17. Shin H, Takahashi T, Lee S, Choi EH, Maeda T, Fukushima Y, et al. 2022; Comparing genomic characteristics of Streptococcus pyogenes associated with invasiveness over a 20-year period in Korea. Ann Lab Med. 42:438–46. DOI: 10.3343/alm.2022.42.4.438. PMID: 35177564. PMCID: PMC8859563.
Article18. Stackebrandt E, Ebers J. 2006; Taxonomic parameters revisited: tarnished gold standards. Microbiol Today. 33:152–5.19. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. One Health. https://www.cdc.gov/onehealth/index.html. Updated on Oct 2022.20. Fukushima M, Hinenoya A, Asakura M, Nishimura K, Hasegawa T, Honda Y, et al. Cell toxic activity of cytolethal distending toxin (cdt) gene-positive Pasteurella canis isolated from oral cavities of dogs. Abstract at the 59th Annual Meeting of the Japanese Society of Bacteriology, Kansai Branch in 2006 (in Japanese).21. Johnson WM, Lior H. 1987; Production of Shiga toxin and a cytolethal distending toxin (CLDT) by serogroups of Shigella spp. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 48:235–8. DOI: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1987.tb02548.x.22. Johnson WM, Lior H. 1988; A new heat-labile cytolethal distending toxin (CLDT) produced by Campylobacter spp. Microb Pathog. 4:115–26. DOI: 10.1016/0882-4010(88)90053-8. PMID: 2849028.23. Guerra L, Guidi R, Frisan T. 2011; Do bacterial genotoxins contribute to chronic inflammation, genomic instability and tumor progression? FEBS J. 278:4577–88. DOI: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08125.x. PMID: 21585655.
Article24. Scott DA, Kaper JB. 1994; Cloning and sequencing of the genes encoding Escherichia coli cytolethal distending toxin. Infect Immun. 62:244–51. DOI: 10.1128/iai.62.1.244-251.1994. PMID: 8262635. PMCID: PMC186093.
Article25. Elwell CA, Dreyfus LA. 2000; DNase I homologous residues in CdtB are critical for cytolethal distending toxin-mediated cell cycle arrest. Mol Microbiol. 37:952–63. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2000.02070.x. PMID: 10972814.
Article26. Cortes-Bratti X, Chaves-Olarte E, Lagergård T, Thelestam M. 2000; Cellular internalization of cytolethal distending toxin from Haemophilus ducreyi. Infect Immun. 68:6903–11. DOI: 10.1128/IAI.68.12.6903-6911.2000. PMID: 11083812. PMCID: PMC97797.
Article27. Guidi R, Guerra L, Levi L, Stenerlöw B, Fox JG, Josenhans C, et al. 2013; Chronic exposure to the cytolethal distending toxins of Gram-negative bacteria promotes genomic instability and altered DNA damage response. Cell Microbiol. 15:98–113. DOI: 10.1111/cmi.12034. PMID: 22998585. PMCID: PMC4136655.
Article28. Belibasakis GN, Maula T, Bao K, Lindholm M, Bostanci N, Oscarsson J, et al. 2019; Virulence and pathogenicity properties of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans. Pathogens. 8:222. DOI: 10.3390/pathogens8040222. PMID: 31698835. PMCID: PMC6963787.
Article29. Pons BJ, Loiseau N, Hashim S, Tadrist S, Mirey G, Vignard J. 2020; Functional study of Haemophilus ducreyi cytolethal distending toxin subunit B. Toxins. 12:530. DOI: 10.3390/toxins12090530. PMID: 32825080. PMCID: PMC7551728.
Article30. Robb Huhn G 3rd, Torres-Mangual N, Clore J, Cilenti L, Frisan T, Teter K. 2021; Endocytosis of the CdtA subunit from the Haemophilus ducreyi cytolethal distending toxin. Cell Microbiol. 23:e13380. DOI: 10.1111/cmi.13380. PMID: 34292647.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of pasteurella multocida pleural empyema
- Pasteurella multocida isolation from pigs with respiratory disease in Korea
- A case of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis and sepsis due to Pasteurella multocida in a patient with liver cirrhosis
- Meningoencephalitis and pneumonia caused by Pasteurella multocida in rabbits
- Cat-induced Pasteurella multocida peritonitis in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis