Ann Lab Med.
2023 Jan;43(1):120-123. 10.3343/alm.2023.43.1.120.
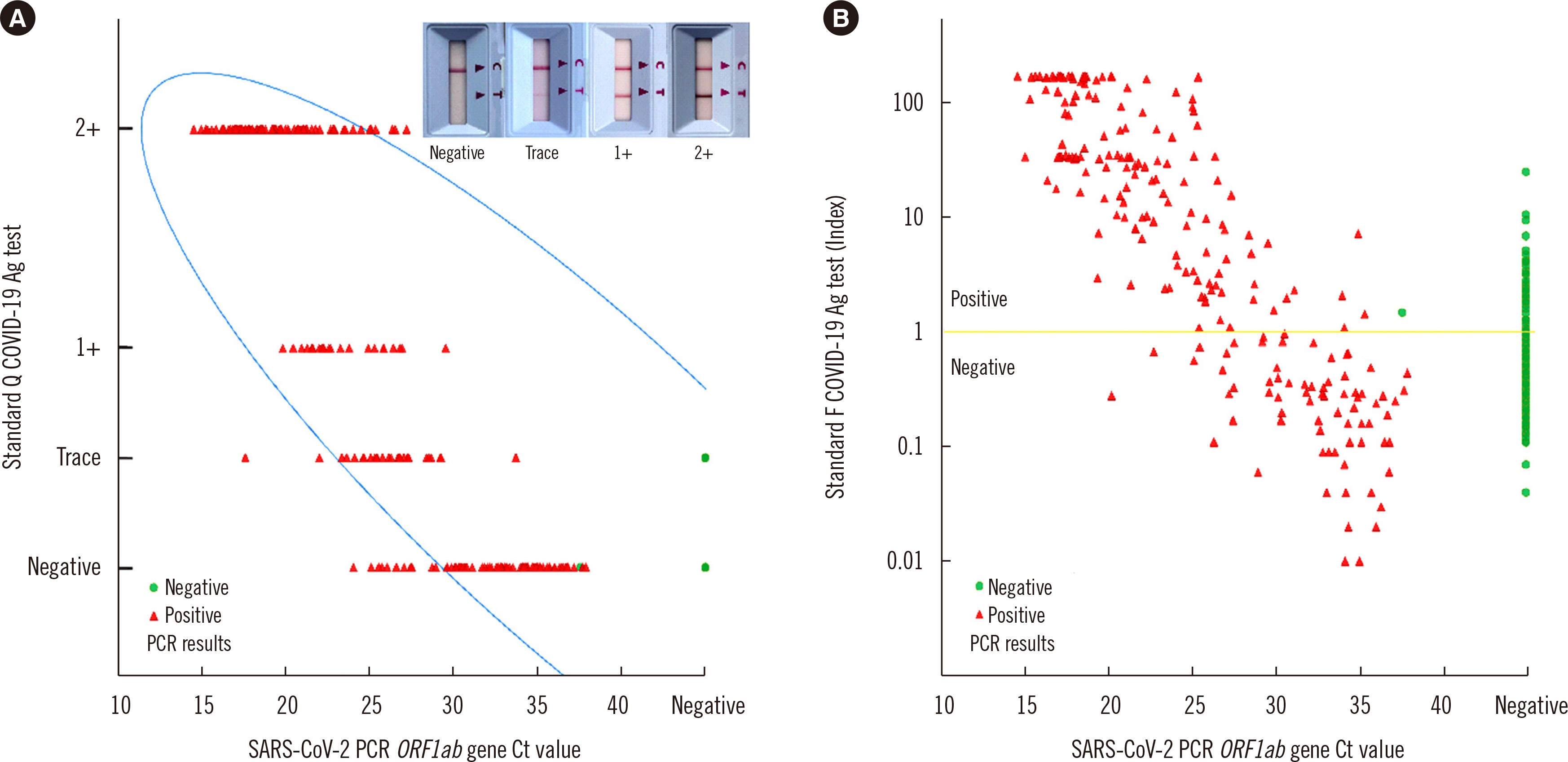
Clinical Evaluation of Two Rapid Antigen Tests for Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Detection
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2551616
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2023.43.1.120
Figure
Reference
-
1. Dinnes J, Deeks JJ, Adriano A, Berhane S, Davenport C, Dittrich S, et al. 2020; Rapid, point-of-care antigen and molecular-based tests for diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 8:CD013705. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD013705. PMID: 32845525. PMCID: PMC8078202.
Article2. World Health Organization. Diagnostic testing for SARS-CoV-2: interim guidance. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/334254. Update on September, 2020.3. Hong KH, Kim GJ, Roh KH, Sung H, Lee J, Kim SY, et al. 2022; Update of guidelines for laboratory diagnosis of COVID-19 in Korea. Ann Lab Med. 42:391–7. DOI: 10.3343/alm.2022.42.4.391. PMID: 35177559. PMCID: PMC8859556.
Article4. Kim HW, Park M, Lee JH. 2022; Clinical evaluation of the Rapid STANDARD Q COVID-19 Ag test for the screening of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. Ann Lab Med. 42:100–4. DOI: 10.3343/alm.2022.42.1.100. PMID: 34374355. PMCID: PMC8368224.
Article5. World Health Organization. Antigen-detection in the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection using rapid immunoassays. https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/antigen-detection-in-the-diagnosis-of-sars-cov-2infection-using-rapid-immunoassays. Update on October, 2021.6. Jaaskelainen AE, Ahava MJ, Jokela P, Szirovicza L, Pohjala S, Vapalahti O, et al. 2021; Evaluation of three rapid lateral flow antigen detection tests for the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 infection. J Clin Virol. 137:104785. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcv.2021.104785. PMID: 33711694. PMCID: PMC7934791.7. Porte L, Legarraga P, Iruretagoyena M, Vollrath V, Pizarro G, Munita J, et al. 2021; Evaluation of two fluorescence immunoassays for the rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 antigen-new tool to detect infective COVID-19 patients. PeerJ. 9:e10801. DOI: 10.7717/peerj.10801. PMID: 33552746. PMCID: PMC7827970.
Article8. Corman VM, Haage VC, Bleicker T, Schmidt ML, Mühlemann B, Zuchowski M, et al. 2021; Comparison of seven commercial SARS-CoV-2 rapid point-of-care antigen tests: a single-centre laboratory evaluation study. The Lancet Microbe. 2:e311–9. DOI: 10.1016/S2666-5247(21)00056-2.
Article9. Pena-Rodriguez M, Viera-Segura O, Garcia-Chagollan M, Zepeda-Nuno JS, Munoz-Valle JF, Mora-Mora J, et al. 2021; Performance evaluation of a lateral flow assay for nasopharyngeal antigen detection for SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis. J Clin Lab Anal. 35:e23745. DOI: 10.1002/jcla.23745. PMID: 33675086. PMCID: PMC8128319.
Article10. Ferre VM, Peiffer-Smadja N, Visseaux B, Descamps D, Ghosn J, Charpentier C. 2022; Omicron SARS-CoV-2 variant: What we know and what we don't. Anaesth Crit Care Pain Med. 41:100998. DOI: 10.1016/j.accpm.2021.100998. PMID: 34902630. PMCID: PMC8660660.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Challenges of Scaling Up SARS-CoV-2 Rapid Antigen Tests
- Acute-onset respiratory signs in a Labrador Retriever with a positive SARS-CoV-2 rapid antigen test and infection confirmed by RT-PCR analysis: a case report
- Response to positive patients with COVID-19 self-test visiting the emergency department
- Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome, SARS
- Epidemiology, virology, and clinical features of severe acute respiratory syndrome -coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2; Coronavirus Disease-19)